Data Flow Diagram Free
A Data Flow Diagram (DFD) is a type of flowchart, which shows graphically the flow of data through a business process or information system. It is a convenient way to document the process or system, design its architecture, and realize an initial top-down analysis of a system. Because DFD gives a clear understanding of process and system operations, the interactions and data exchanges between the processes, shows how data is transferred from the inputs to the file storage with generating the reports.
Data Flow Diagram focuses on data and information and helps discover potential problems and improve efficiency when developing systems. It shows the boundaries of a system, the sequence of processes that are done in a particular order to achieve a particular goal, how data enter a system, how are processed, and where they go. The arrows describe the flow of data and information.
Data Flow Diagrams are equally beneficial for simple and complex processes or systems and are designed both as simple overviews and detailed ones. One differs two types of DFDs: logical and physical, which provide different perspectives of the same data flow and give together a complete understanding of an entire process. Logical DFD describes the system focusing on the information required for its operation. Physical DFD gives information about the involved entities and how the system is or will be implemented.
Logical DFD is useful to show business information, the flow of business actions. It clarifies business activities, types of functionalities in a particular business and is a powerful tool for business analysis and improvement of business processes. Physical DFD shows how the system is organized and operates, and how data move through it. It includes hardware, software, files, and ensures that the processes described in the logical DFD will be implemented correctly. Usually, a logical DFD is less complex than a physical DFD, but the physical is created on its basis and is more detailed.
Data Flow Diagrams are used for analysis and modeling of systems in different areas. These include technical areas, software engineering, business management, database development, business analysis, system structure analysis, business process re-engineering, agile development, and others. Visualization using DFD is useful to explain processes and make them memorable. DFDs are used to analyze the systems and improve them, troubleshoot, find and eliminate inefficiencies, steps that might be missed or not fully understood. They are also a powerful tool for communication and collaboration.
A clear understanding of processes in a company helps to streamline them, improve the company's operation, and make your business successful. DFDs help to improve customer service, design more agile processes, increase competitiveness in the market, cut operational costs, measure progress, encourage system improvement and development. Being used in software development, Data flow diagrams help to design the application and show its architecture before its coding. They help engineers and developers understand the needs and wants of customers. DFDs easier the work with complex databases by clarifying the movement and storing of data, support ensuring cyber security and data protection.
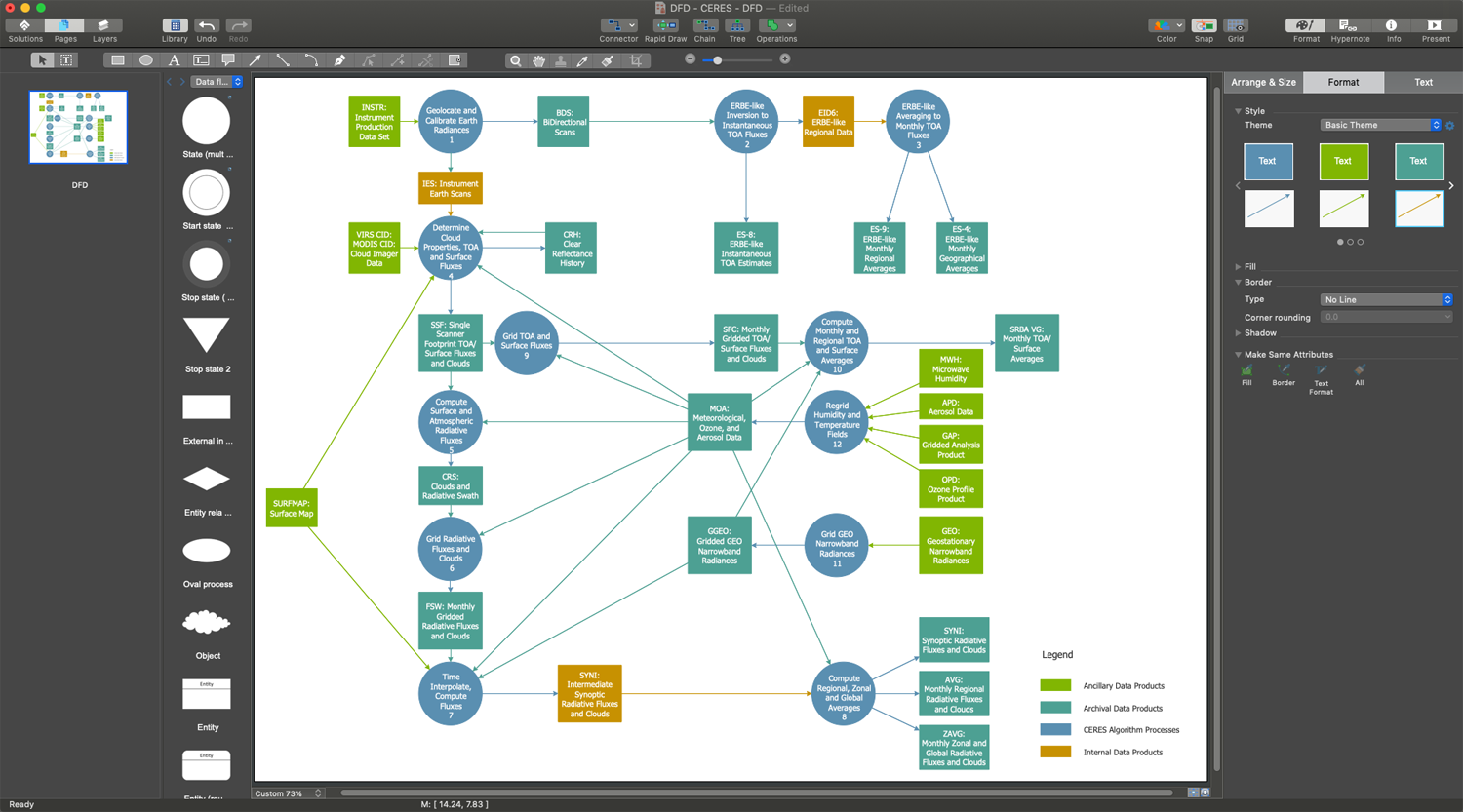
Example 1. Data Flow Diagram Free in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM
Data Flow Diagrams can range from simple, which give a process overview to complex multi-layered diagrams including a lot of details about the system. The complexity of DFD also depends on the complexity of the system it represents. As a rule, Data Flow Diagram includes 3-4 levels numbered as 0, 1, 2, 3, and rarely beyond. The level of detail determines how deep the diagram shows a system, its processes and subprocesses.
DFD Level 0 is a basic level called a Context diagram, it shows the overall system or high-level process overview and its relationships to external entities. DFD Level 1 is a more detailed breakout of the processes of Level 0 and shows the main functions and subprocesses within the system. DFD Level 2 provides more deeper description than shown at Level 1. More levels are also added if needed.
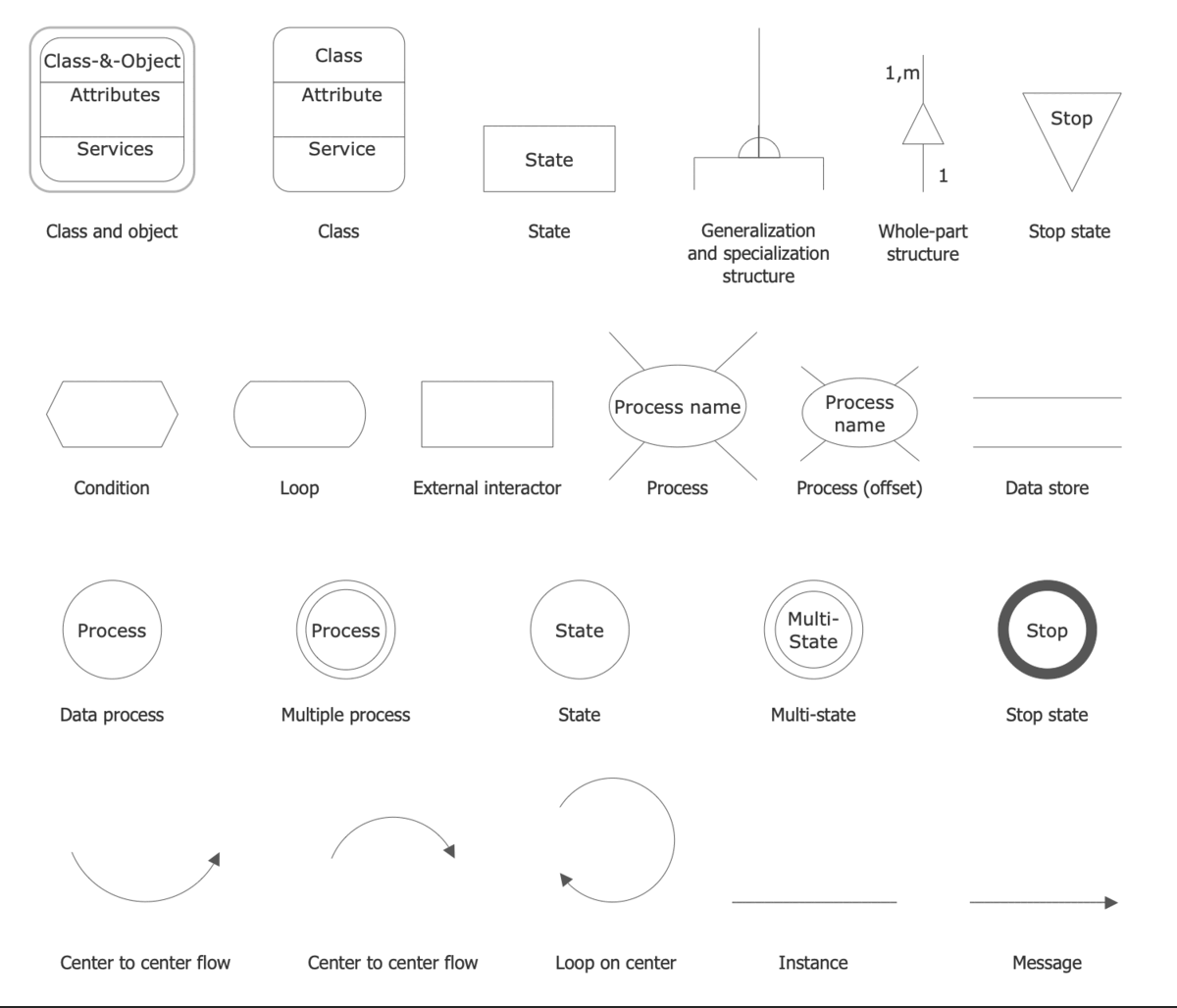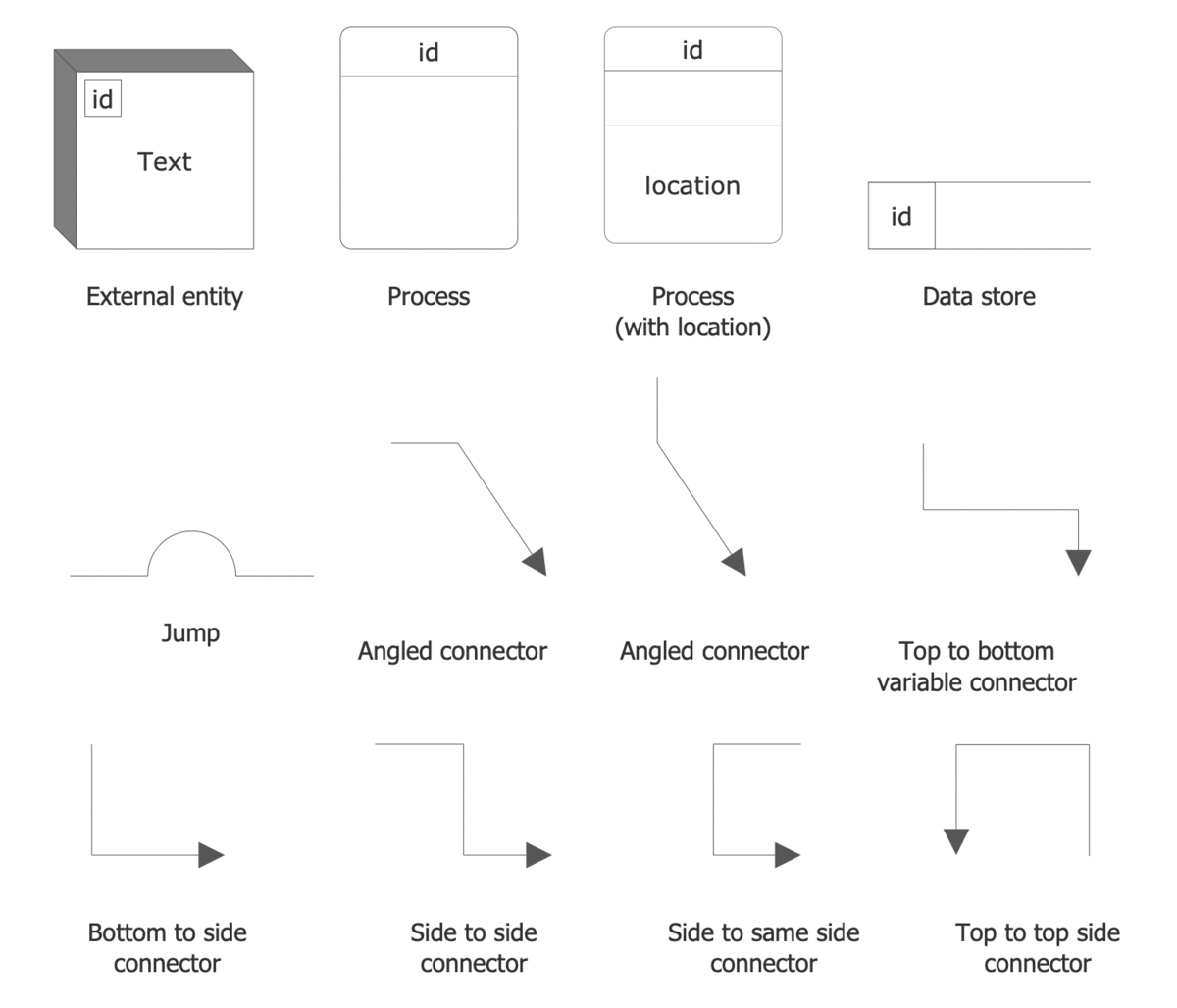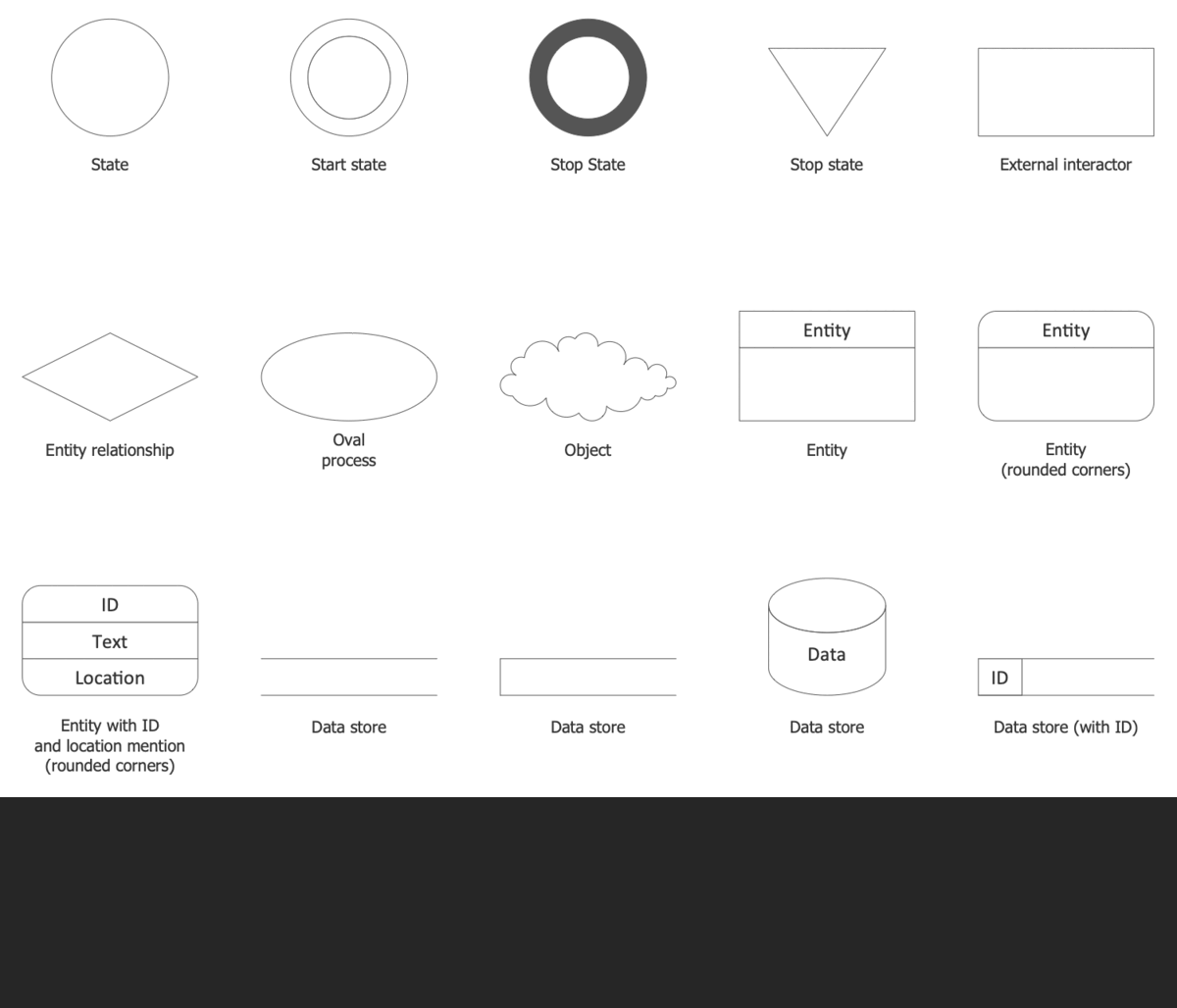
The basic symbols used to create a Data Flow Diagram are standardized by Yourdon & Coad and Gane & Sarson notations and include rectangles, circles, triangles, cylinders, arrows, text labels, and other symbols to show entities, data stores, and other components. Being standardized, these symbols make your diagram comprehensive for all team members and easy to implement. The main difference in these notations is that Yourdon-Coad notation uses circles to show processes, while Gane-Sarson notation uses rectangles with rounded corners.
Example 2. Data Flow Diagrams Solution- Libraries Design Elements
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM extended with Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) solution is a powerful software for designing a Data Flow Diagram free and easily. Use the specialized design elements — Yourdon and Coad notation and Gane-Sarson notation, and pre-made templates to show the flow of data through your system as a Data Flow Diagram in minutes. The included DFD examples are also helpful for designing your own diagrams. You can customize any of them relative to your needs, your processes, external entities, data stores, data flow, etc.
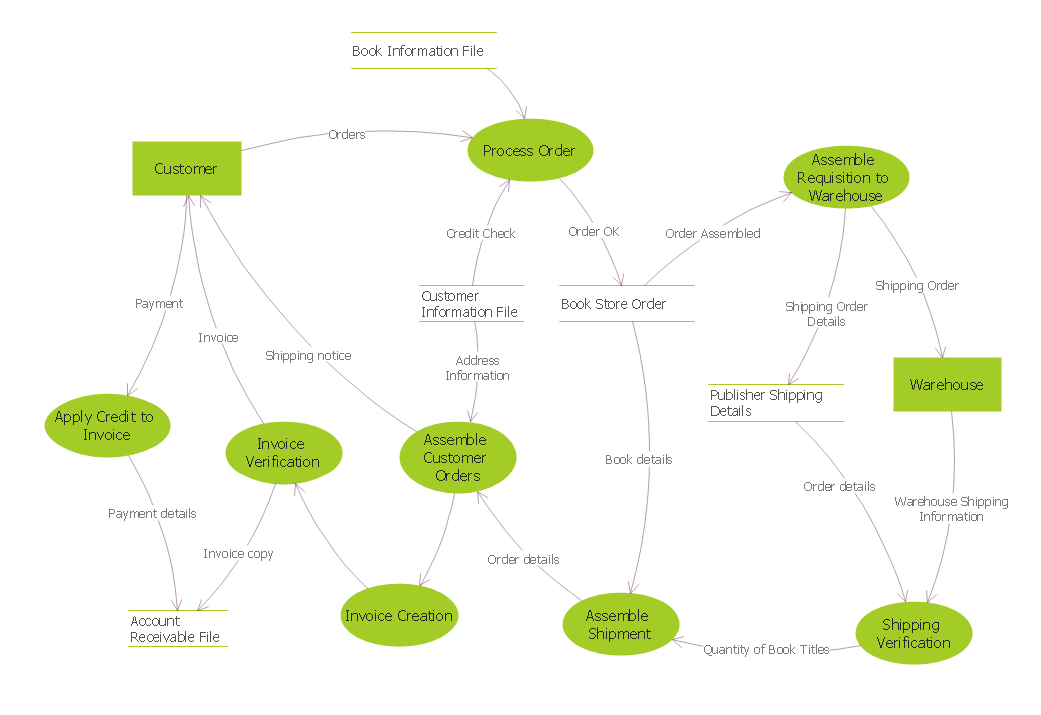
Example 3. DFD — Process of Account Receivable
The Data Flow Diagram examples you see on this page were created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the objects from the libraries of Data Flow Diagrams solution. These samples demonstrate the solution's capabilities and the professional results you can achieve. An experienced user spent 15 minutes creating each of these samples.
Use the Data Flow Diagrams solution for designing your own Data Flow Diagrams quick, simply, and effectively.
All source documents are vector graphic documents. They are available for reviewing, modifying, or converting to a variety of formats (PDF file, MS PowerPoint, MS Visio, and many graphic formats) from the ConceptDraw STORE. The Data Flow Diagrams Solution is available for all ConceptDraw DIAGRAM users.