Hydropower
Hydropower is energy derived from flowing, falling, or fast-running water to produce electricity by driving turbines. Hydroelectric power plants are usually located near a water source or on it. Water flows through a pipe, pushes and turns blades in a turbine, a generator is spun and produces electricity. The volume of the water flow and elevation change, called a head, determines the amount of electricity produced by a hydropower plant.
Hydropower is one of the oldest and the largest sources of energy used for electricity generation. In ancient times waterpower was used in watermills and was helping the ancient Greeks to turn paddle wheels on rivers for grinding grain. Lumber mills were also powered by hydropower. Hydropower from watermills was used for irrigation and operation of gristmills, ore mills, sawmills, trip hammers, dock cranes and lifts, and other mechanical devices. Currently, it is the second largest renewable electricity source.
The generation of hydropower requires a sufficiently energetic source of water. Therefore, hydropower plants of various sizes are constructed on rivers or elevated lakes. Currently, there are used configurations of hydropower plants with dams, reservoirs, and without them. The first ones are more powerful, allow storing water over short or long periods, provide the ability to produce energy at a larger scale and meet peak demand. Hydropower is generated using the elevation difference, created by a dam or diversion structure, water flows in on one side and out on the other below. Sometimes in river systems, several power stations are installed in a cascade, one after the other, and the water’s energy is exploited several times.
Hydroelectric facilities include:
- Storage systems created by dams and reservoirs on streams and rivers. The water is accumulated in reservoirs and then is released through hydro turbines. The small dams are applied for separate purposes like night or day use, seasonal storage, pumping electricity.
- Run-of-the-river systems, which don't include reservoirs and the force of the river current apply pressure on a turbine.
- Pumped-storage hydropower systems, where water is pumped from a water source to a storage reservoir located at a higher elevation and then is released from it to power hydro turbines located below.
Hydropower has a lot of benefits, it is a renewable, sustainable, reliable, affordable, flexible, versatile and low-cost source of clean electricity. Hydropower does not produce atmospheric pollutants and shows the lowest greenhouse gas emissions of all power generation technologies. The generation of hydropower also provides responsible water management and is used in energy storage systems. It helps to speed up the transition to clean, renewable and sustainable energy, stop the pollution of the environment and prevent climate change.

Example 1. Hydropower
Hydropower is one of the most cost-effective ways to generate electricity. It requires relatively low costs for maintenance during the operation lifetime, which is also a significant advantage. In addition, hydropower technology delivers storage of power, which is important to maintain the stability of the electricity system and compensate variable energy production from solar and wind. It can serve as a flexible and reliable form of backup power because can immediately provide power to the grid and helps to handle electricity outages or disruptions.
Hydropower is a relatively consistent source of power and low-carbon economic development mean. However, hydropower generation is highly affected by changes and seasonal variations in precipitation. In addition, significant upfront costs for the construction of hydropower facilities are required. They include large costs for constructing hydroelectric dam, tunnel, and other infrastructure, for buying electromechanical equipment and installing it. However, the correct selection of location and design helps to reduce these costs. In addition, the low exploitation costs and long term of using equipment help to save money during the exploitation term.
Currently, hydropower accounts for approximately one sixth of the total world's electricity supply, around 17% of the total EU's electricity and 6.3% in the USA, and around 31.5% of the USA's and 33% of the EU's renewable electricity production. In Norway, 90% of all power generation comes from hydropower. Most hydroelectricity is produced at dams on major rivers.
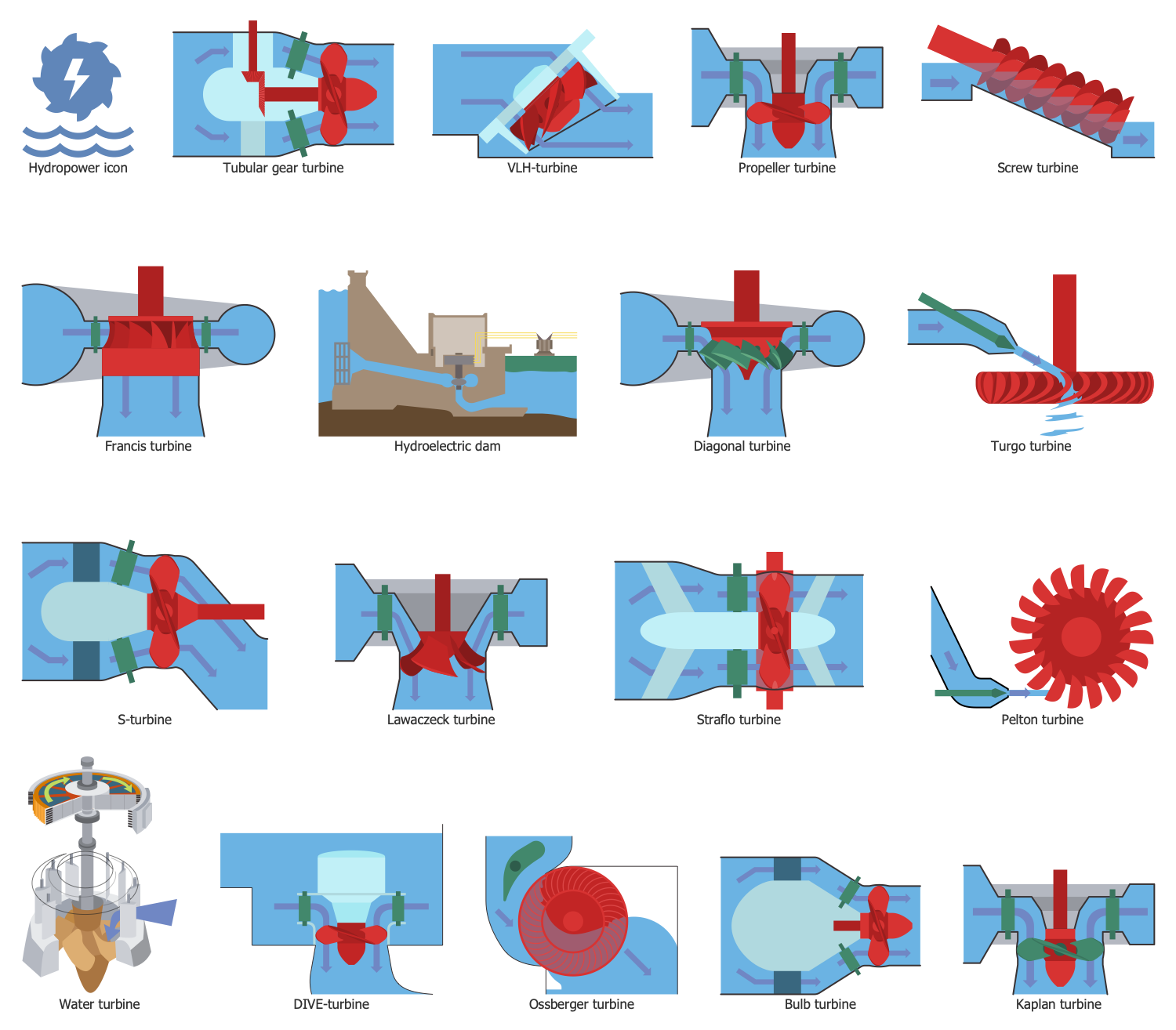
Example 2. Hydropower Library Design Elements
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM vector design software provides the Green Energy solution with Hydropower library including a set of thematic vector design elements. It is the best assistant to design diagrams and infographics about hydropower. Illustrate the advantages of using this kind of power in minutes.
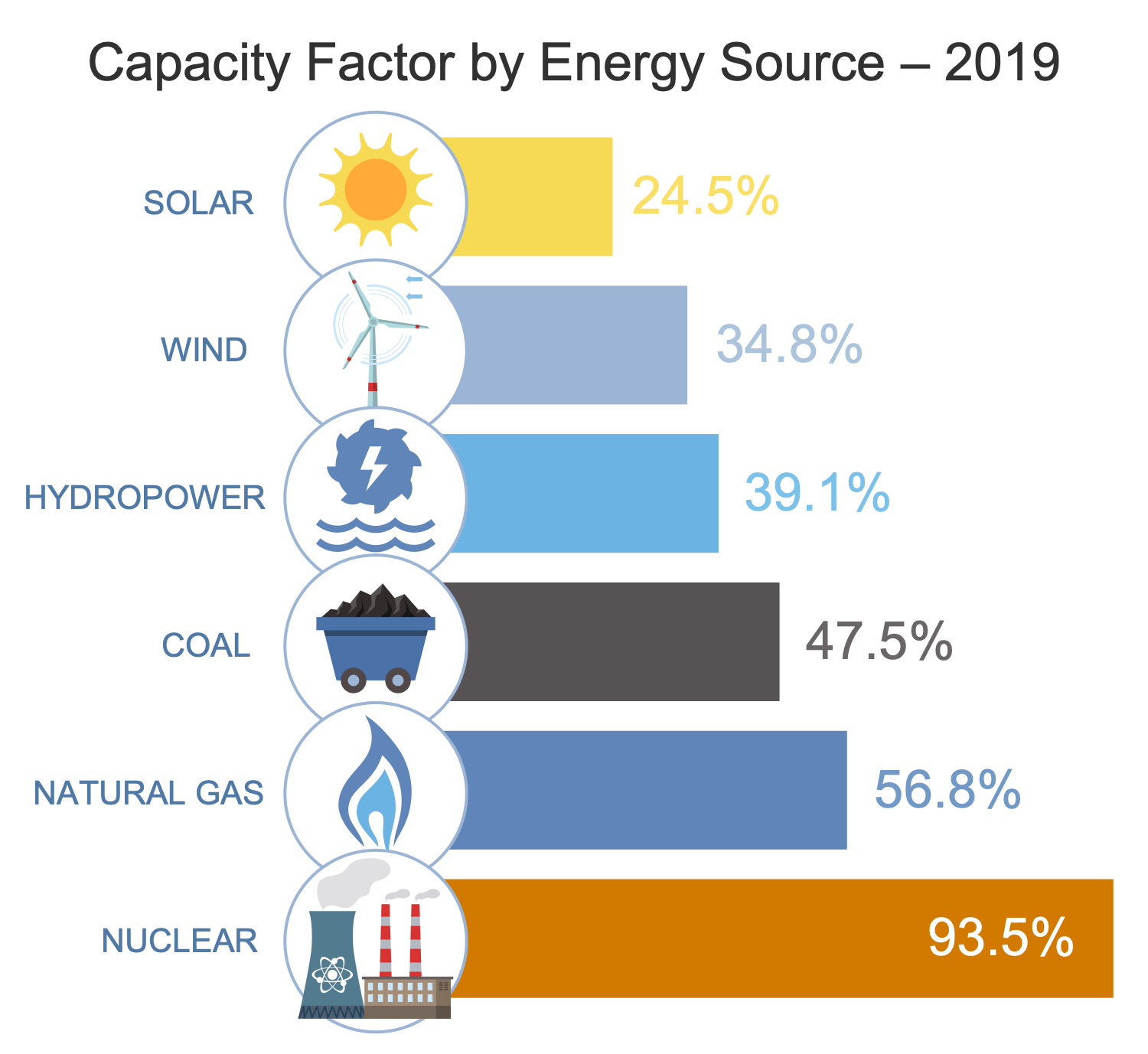
Example 3. Green Energy Infographics - Generation Capacity Factor
The Hydropower Infographics samples you see on this page were created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software using the drawing tools of the Green Energy Solution. These examples successfully demonstrate solution's capabilities and the professional results you can achieve using it. An experienced user spent 10-15 minutes creating each of these samples.
Use the powerful tools of the Green Energy solution to design your own Green Energy Infographics quick, easy and effective.
All source documents are vector graphic documents. They are available for reviewing, modifying, or converting to a variety of formats (PDF file, MS PowerPoint, MS Visio, and many other graphic formats) from the ConceptDraw STORE. The Green Energy Solution is available for ConceptDraw DIAGRAM users.