Ring Network Topology
Ring Network Topology Diagram
A network topology in which each of the nodes connects to two other nodes, resulting in forming a continuous pathway for the signals through each of the nodes known to be called the “rings”, is known to be called as a “ring network”. Data within such networks is known to be traveling from one node to another node, through all the nodes one by one along its way handling every single packet. The mentioned “rings” can be “unidirectional”, having all its traffic travelling clockwise or anticlockwise all the way around the ring. Also, it can be the so called “bidirectional”, providing only one single pathway between two nodes out of many other nodes. A unidirectional ring network is known to be very likely disrupted by the failure of some link appearing to be nearby.
A node failure as well as any cable break may lead to isolation of every single node, which is attached to the “ring”. Some of the ring networks are known to be adding a so called "counter-rotating ring", also known to be called a “C-Ring”. Adding the mentioned ring can be done for forming a redundant topology. Thus, once break happens, a data may get wrapped back on the ring before it reaches the end of the cable. Such data is known to be maintaining a path to every single node all the way along the resulting counter-rotating ring.
The "dual ring" networks are known to be including the so called “Spatial Reuse Protocol”, as well as the “Fiber Distributed Data Interface”, or “FDDI”, and the “Resilient Packet Ring”. The well-known “IBM token ring networks” are also sometimes called as the “802.5 networks”. They are commonly used for avoiding all the possible and existing weakness of a ring topology by using another topology — a “star” one. Such mentioned topology is usually used at the physical layer for imitating a ring at the so called “data link layer”.
Some of the previously mentioned “SONET/SDH rings” have two sets of the bidirectional links, which can be found between the nodes, allowing the failures or maintenance at the multiple points of the same ring resulting in no loss of the primary traffic on the outer ring in a way of switching the traffic on the inner ring after the so called “failure points”.
One of the advantages of using such network topology can be mentioned the convenience of using it for performing in a better way than a bus topology does, especially in the cases of the need of loading under the so called “heavy network”. The mentioned network topology is known to be used within a very orderly network having every device accessing to the “token” having the opportunity to transmit. Such ring network topologies do not require any central nodes for managing the connectivity between different computers. Because of such point to point line configuration of devices with a device on another side, it is quite simple to install as well as to re-configure whatever is needed by removing or adding any device.
Another special feature of the ring network topologies is its “point to point” line configuration, which makes it much simpler to isolate all the previously identified faults. Also, the reconfiguration for line faults of bidirectional rings in ring network topology can be very fast, having all the switching happening at the highest level, leading to the traffic not requiring any individual re-routing.
The disadvantages of the ring network topology: first of all, it is always more difficult to configure using it to compare to using a “star” one as any node adjunction equals to the ring reconfiguration and shutdown. One of the malfunctioning workstations within the ring network topology can create lots of problems for all the network. This can be solved by using a switch or a dual ring used for closing off the break. Every time there’s some moving, changing and adding the devices can affect the entire ring network and the communication delay is known to be directly proportional to the number of all the existing nodes in the ring network.
It is important to remember that any ring network may afford the so called “fault tolerance” to the telecommunication network having two paths between any two nodes on the network. Ring protection is known to be a system commonly used for assuring any needed communications, continuing in the event of failure of only one path. The most widely used protection architectures are “1+1” as well as “1:1”.
In 1+1 architecture, every single protection path is known to be used for protecting the signal having the bridge at the head of the path on a permanent basis, while the switching occurs at its tail end. There are more than two parallel routes are sent in this architecture traffic and the receiving end is known to be selecting the better of the mentioned two signals. Once some failure occurs, the destination switches into one of the alternative paths. The mentioned architecture is quite a widely used for as it is simple for implementing, resulting quite fast restoration. Although, there’s still a drawback, which is the wastage of the bandwidth, occurring for a reason of no traffic traveling through the redundant path.
Pic. 1. Ring Network Topology
Drawing the ring network topology diagrams taking into consideration any of the mentioned architectures can be always much simpler using a professional software for completing such tasks. One of the best applications nowadays is ConceptDraw DIAGRAM one, enabling all its users to create a great looking diagram, such as a ring network topology one, especially having the Computer and Networks solution downloaded from ConceptDraw STORE application.

Pic. 2. Ring Network Topology Diagram
Having the ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software means having all the needed tools for making smart looking drawings, at the same time having the ConceptDraw STORE which is meant to be used while working in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM means simplifying your work with creating such diagrams by using the previously developed solutions full of the stencil libraries with the design symbols depending on the subject of your drawing.
See Also Network Topologies:
- Bus Network Topology
- Star Network Topology
- Mesh Network Topology
- Tree Network Topology
- Fully Connected Network Topology
TEN RELATED HOW TO's:There are several basic topologies including bus, star, point-to-point, ring and a hybrid. Two computers can form a fully connected network topology, and as the number of network nodes increases, the network diagram gets more complicated. This type of topology is also called a full mesh. This is a visual example of a computer network built using a mesh topology. This diagram presents the schematic structure of the full mesh network topology. A common mesh network topology means that each network device is connected with several points in the network, so if the one node of the network goes down, it does not cause an issue with an operability of the entire computer network. In a full mesh network topology, every computer or device in the network is interconnected with each of the other devices in the network. Picture: Fully Connected Network Topology DiagramRelated Solution:Closed-circuit television (CCTV) uses cameras and monitors to carry out video surveillance. Unlike broadcast television this system has only local signal. It is a feature of almost every video camera, yet CCTV is mainly a system for visual control of certain areas such as banks, airports, supermarkets, and other places for security reasons. Developing and installing CCTV system is a time-consuming process. It also requires certain knowledge and skills. ConceptDraw is a solution of setting video cameras rationally. You can achieve two aims at once: CCTV Design Tool saves your time and your money and helps you make professional video surveillance system.
Picture: Fully Connected Network Topology DiagramRelated Solution:Closed-circuit television (CCTV) uses cameras and monitors to carry out video surveillance. Unlike broadcast television this system has only local signal. It is a feature of almost every video camera, yet CCTV is mainly a system for visual control of certain areas such as banks, airports, supermarkets, and other places for security reasons. Developing and installing CCTV system is a time-consuming process. It also requires certain knowledge and skills. ConceptDraw is a solution of setting video cameras rationally. You can achieve two aims at once: CCTV Design Tool saves your time and your money and helps you make professional video surveillance system.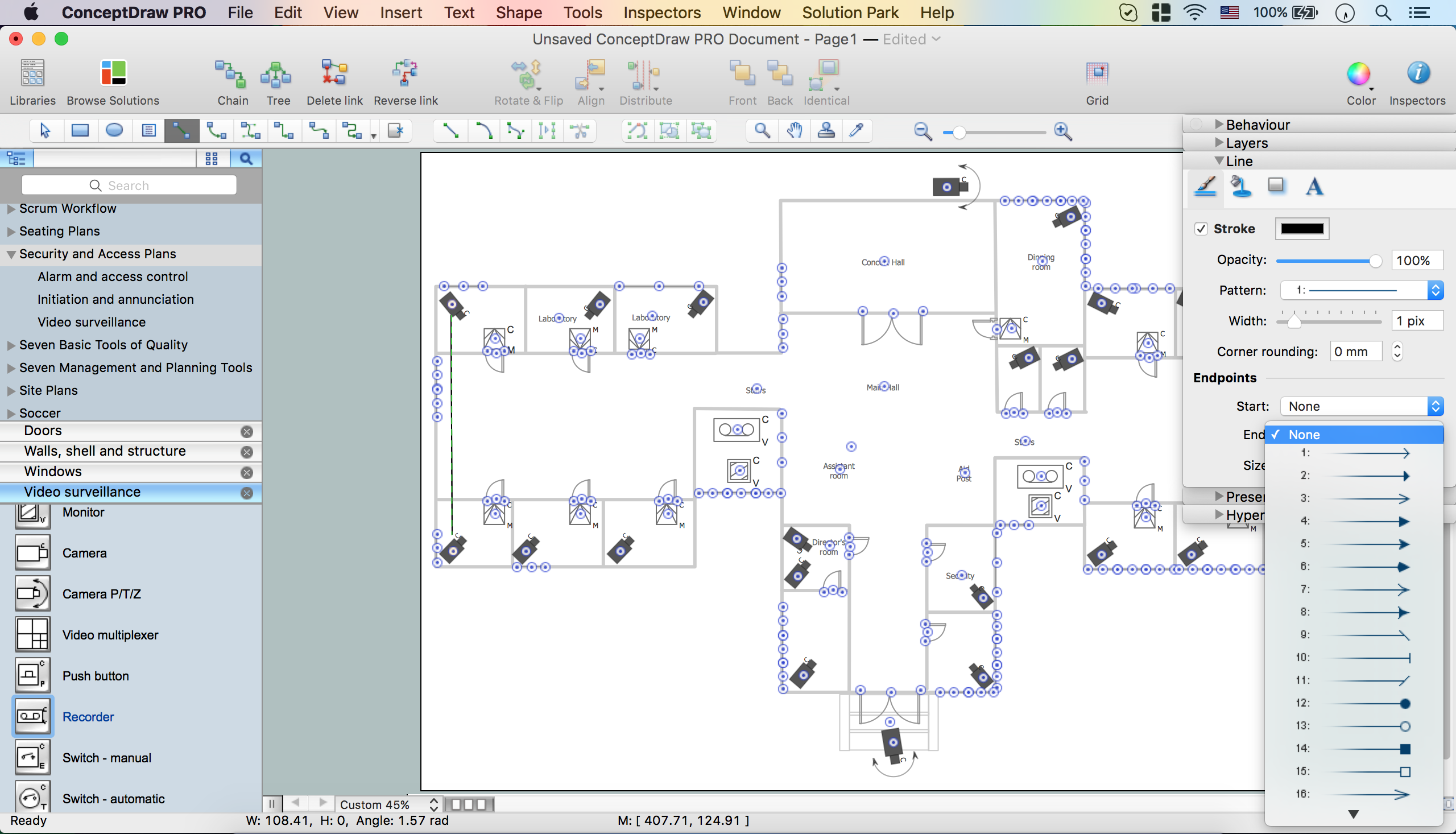 Picture: How To Create CCTV Network DiagramRelated Solutions:The ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is a best Network Diagramming software.
Picture: How To Create CCTV Network DiagramRelated Solutions:The ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is a best Network Diagramming software. Picture: Building NetworksRelated Solution:A flowchart is a simple but very functional tool when it comes to understanding a workflow or to removing unnecessary stages from a process. When drawing flowcharts, keep in mind that there are four common types of flowcharts, like document flowcharts and data flowcharts that show control over a data or document flow over a system. To show controls on a physical level, use system flowcharts. In addition, to show controls in a program, you can draw a program flowchart. This flowchart diagram represents the piece of an article editing process, that involves the author and editor. It was created using the Basic Flowchart notation that consists from the basic flowchart symbols. The start and the end of the process are indicated with "Terminator" symbols. The "Process" symbols show the action steps consisting from making edits and searching for a compromise, when the author does not agree with the suggestions of the editor. The "Process" symbol is the general symbol in process flowcharts. The "Decision" symbol indicates a branching in the process flow. There are two branches indicated by a Decision shape in the current flowchart (Yes/No, Disagree/Agree). This basic flowchart can be used as a repeating unit in the workflow diagram describing the working process of some editorial office.
Picture: Building NetworksRelated Solution:A flowchart is a simple but very functional tool when it comes to understanding a workflow or to removing unnecessary stages from a process. When drawing flowcharts, keep in mind that there are four common types of flowcharts, like document flowcharts and data flowcharts that show control over a data or document flow over a system. To show controls on a physical level, use system flowcharts. In addition, to show controls in a program, you can draw a program flowchart. This flowchart diagram represents the piece of an article editing process, that involves the author and editor. It was created using the Basic Flowchart notation that consists from the basic flowchart symbols. The start and the end of the process are indicated with "Terminator" symbols. The "Process" symbols show the action steps consisting from making edits and searching for a compromise, when the author does not agree with the suggestions of the editor. The "Process" symbol is the general symbol in process flowcharts. The "Decision" symbol indicates a branching in the process flow. There are two branches indicated by a Decision shape in the current flowchart (Yes/No, Disagree/Agree). This basic flowchart can be used as a repeating unit in the workflow diagram describing the working process of some editorial office. Picture: Types of FlowchartsRelated Solution:Aside from decorating inner spaces, which is a realm of interior design, the art of exterior design is about home facades, playgrounds and yards. To start a project, first of all, you need a site plan of the place, and a list of customers’ requirements. With special software you can do a plan of any place like parking, interchange or driveway easily. There is one of the three libraries supplied with ConceptDraw Site Plans solution. It is designed to draw planning areas adjacent to buildings. For example parking, exit road or house territory for rest. This kind of building plans can be used for providing parking control that helps to organize traffic near residential areas. The well considered road planning will improve safety and will help to manage the number of vehicles near buildings. The ConceptDraw library "Parking and Roads" includes vector graphic images of parking spaces, lots and strips as well as street junctions, driveways and interchanges.
Picture: Types of FlowchartsRelated Solution:Aside from decorating inner spaces, which is a realm of interior design, the art of exterior design is about home facades, playgrounds and yards. To start a project, first of all, you need a site plan of the place, and a list of customers’ requirements. With special software you can do a plan of any place like parking, interchange or driveway easily. There is one of the three libraries supplied with ConceptDraw Site Plans solution. It is designed to draw planning areas adjacent to buildings. For example parking, exit road or house territory for rest. This kind of building plans can be used for providing parking control that helps to organize traffic near residential areas. The well considered road planning will improve safety and will help to manage the number of vehicles near buildings. The ConceptDraw library "Parking and Roads" includes vector graphic images of parking spaces, lots and strips as well as street junctions, driveways and interchanges. Picture: Interior Design. Site Plan — Design ElementsRelated Solution:Netflow is a network protocol used for accounting the IP network traffic. It was developed by Cisco Systems. Now it is actually the industrial standard, it is supported by many devices. There are several versions of the protocol, but the most common are the versions 5 and 9. This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the Computer and Networks Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park and shows the Netflow architecture.
Picture: Interior Design. Site Plan — Design ElementsRelated Solution:Netflow is a network protocol used for accounting the IP network traffic. It was developed by Cisco Systems. Now it is actually the industrial standard, it is supported by many devices. There are several versions of the protocol, but the most common are the versions 5 and 9. This diagram was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the Computer and Networks Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park and shows the Netflow architecture. Picture: Netflow architecture. Computer and Network ExamplesRelated Solution:OSPF is an interior gateway protocol (IGP), it is widely used in large enterprise networks. OSPF routes the IP packets within a single routing domain. It gathers the information about the link state from the routers and makes the network topology map. This example was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the Computer and Networks Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park and shows the OSPF diagram.
Picture: Netflow architecture. Computer and Network ExamplesRelated Solution:OSPF is an interior gateway protocol (IGP), it is widely used in large enterprise networks. OSPF routes the IP packets within a single routing domain. It gathers the information about the link state from the routers and makes the network topology map. This example was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM using the Computer and Networks Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park and shows the OSPF diagram. Picture: OSPF Network. Computer and Network ExamplesRelated Solution:It's no secret that there is a list of skills that every average system administrator should have. And it's important to be able to manage domains via active directory technologies. The best way to keep all the details in mind is to draw a diagram representing users, groups and domains. This diagram represents an Active Directory Services (Active Directory Domain Services). It can be helpful for system and network administrators to organize a network physical and logical elements (domains, data bases, servers, network equipment, end-user computers etc.) into a secure and logical structure. The logical structure of Active Directory is a hierarchical organization of all network components. The data that is stored in Active Directory comes from some diverse sources. The Active Directory diagram created using ConceptDraw Active Directory Diagram solution. It shows allocating group policies and functions assigned to end users. It helps to plan, manage and maintain the certain user access scenario.
Picture: OSPF Network. Computer and Network ExamplesRelated Solution:It's no secret that there is a list of skills that every average system administrator should have. And it's important to be able to manage domains via active directory technologies. The best way to keep all the details in mind is to draw a diagram representing users, groups and domains. This diagram represents an Active Directory Services (Active Directory Domain Services). It can be helpful for system and network administrators to organize a network physical and logical elements (domains, data bases, servers, network equipment, end-user computers etc.) into a secure and logical structure. The logical structure of Active Directory is a hierarchical organization of all network components. The data that is stored in Active Directory comes from some diverse sources. The Active Directory diagram created using ConceptDraw Active Directory Diagram solution. It shows allocating group policies and functions assigned to end users. It helps to plan, manage and maintain the certain user access scenario.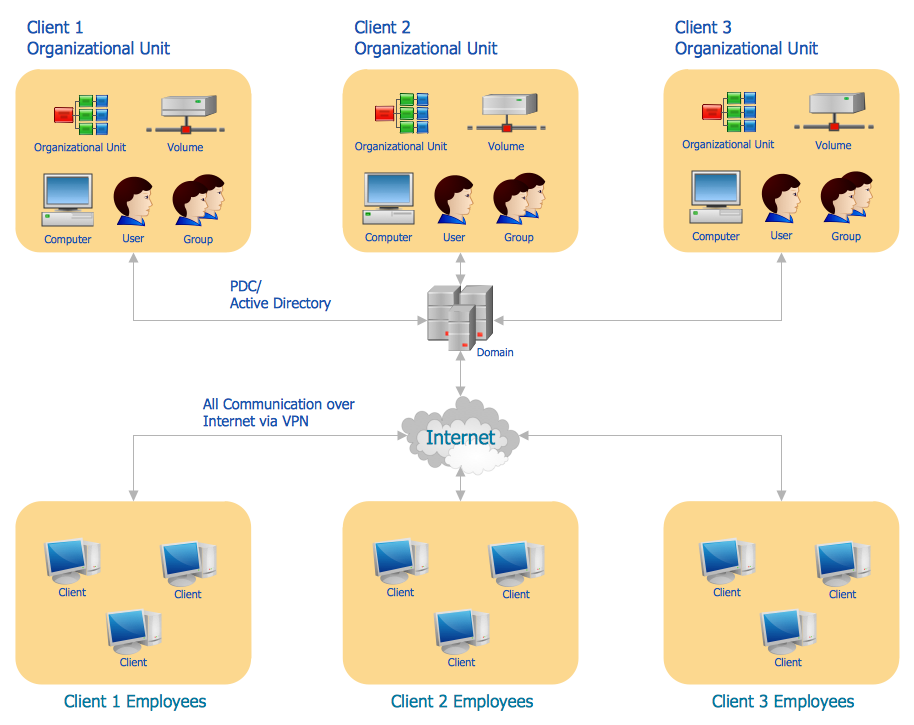 Picture: Active Directory DiagramRelated Solution:Local area network connects computers and other network appliances within an area, such as office building or a campus. It can be difficult to provide such network without a predesigned plan. For these purposes you can use network diagram software, which helps you to create LAN network diagrams and office network diagrams quickly and effortless. This will speed up your work and you can save the diagram for the future network improvements. The following diagram illustrates a network topology of the small office. LAN configuration has a star topology. The local network joins 8 computers among which are several desktop PCs, laptop, two iMacs and iBook. The end-point devices are divided into three groups. Each group is connected to its hub. There is a network printer and a modem, which are interconnected with other devices through a network server. Each computer on the LAN can access the server through a corresponding hub.
Picture: Active Directory DiagramRelated Solution:Local area network connects computers and other network appliances within an area, such as office building or a campus. It can be difficult to provide such network without a predesigned plan. For these purposes you can use network diagram software, which helps you to create LAN network diagrams and office network diagrams quickly and effortless. This will speed up your work and you can save the diagram for the future network improvements. The following diagram illustrates a network topology of the small office. LAN configuration has a star topology. The local network joins 8 computers among which are several desktop PCs, laptop, two iMacs and iBook. The end-point devices are divided into three groups. Each group is connected to its hub. There is a network printer and a modem, which are interconnected with other devices through a network server. Each computer on the LAN can access the server through a corresponding hub. Picture: Network Diagram Software. LAN Network Diagrams. Physical Office Network DiagramsRelated Solution:ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Security and Access Plans Solution from the Building Plans Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is a powerful software for fast and easy drawing professional looking Physical Security Plan.
Picture: Network Diagram Software. LAN Network Diagrams. Physical Office Network DiagramsRelated Solution:ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Security and Access Plans Solution from the Building Plans Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is a powerful software for fast and easy drawing professional looking Physical Security Plan.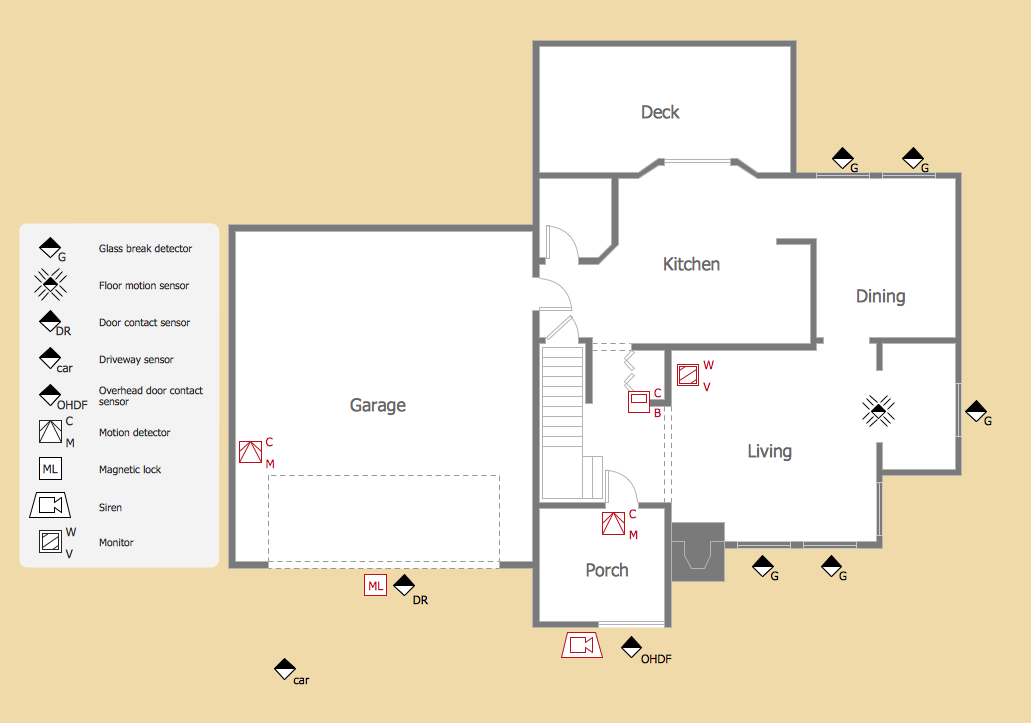 Picture: Physical Security PlanRelated Solution:ConceptDrawDIAGRAM 18
Picture: Physical Security PlanRelated Solution:ConceptDrawDIAGRAM 18
