Electrical Symbols — Switches and Relays
Both switches and relays are fundamental components in electrical engineering. They are used to manage and direct electrical power, provide control, safety, and automation in systems of various sizes and purposes, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
A switch is an electrical component used to control the flow of electricity. It can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or redirecting it from one conductor to another. Opening and closing the circuit can be done manually or automatically. Switches allow users to turn electrical devices on and off and have various applications, from simple household lighting to complex industrial systems. The mechanism of a switch may be operated directly by a human, a moving object, or some sensing element. Examples include a light switch, a button on an electrical device, door-operated switch, sensors for pressure, temperature, flow, etc.
A relay is a switch operated by electricity and enables the control and automation of electrical processes. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switch mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used in cases when it is necessary to control a circuit by a separate low-power signal, or when several circuits must be controlled by one signal. Relays protect the electrical system or equipment and provide their safe operation by opening and closing contacts, switching from too high to low voltage or current, and vice versa.
Purpose of Switches and Relays
Switches and relays have similar functions and the main purpose of both is control. Switches enable the control of electrical flow through the manual or automatic opening and closing of an electrical circuit. They are used to operate electrical devices and appliances by controlling the flow of electricity to them. Switches help to configure circuit operations, change the path of electrical flow in complex systems, and turn lights on and off. They also provide safety functions and help to prevent electrical hazards by disconnecting power to circuits during emergencies and maintenance.
At the same time, relays allow the control of high-power circuits using a low-power signal, also on the distance. Relays are an integral part of automating processes ensuring the safe operation of equipment and preventing failures. They play a protective role, helping to protect the electrical system from overloading by disconnecting it when excessive current or high voltage is detected. Relays enable to provide isolation between different parts of a circuit and their use includes industrial control panels. Remote switching is used in remote control systems and telecommunications.
Applications of Switches and Relays
Switches and relays play critical roles in both everyday consumer applications and complex industrial systems. They are used to provide control, automation, protection, and safety across a wide range of electrical and electronic systems.
A relay is an essential component for managing the operation of various electrical systems. Its primary purpose is to protect the electrical system from excessively high voltage or current ensuring the safe operation of equipment it connects to. Relays allow the control of high-power circuits using low-power signals. They isolate wiring and electronic components from high voltages or current surges. This explains their high protection, control, and automation role.
Relays have commercial, industrial, and residential uses. With advancing requests, different types of relays have been developed to satisfy wide-ranging needs. A variety of relays' applications includes industrial automated control systems, protective devices against overloads and short circuits, safety and alarm systems, telecommunications, power management systems, automotive systems to control starter motors, lighting, fuel pumps, remote control systems, etc.
Switches find their applications in diverse areas including industrial automation, automotive systems, electronics, home automation, telecommunication, military, aerospace, etc. They have a wide application in residential and commercial premises to turn on and off different items, such as lighting, household appliances, electrical outlets, thermostats in HVAC systems, automotive components, industrial machines and equipment by making or breaking the electrical circuit. Many electrical appliances and electronic devices we use every day have switches built into them.
Example 1. Electrical Relay Schematic Design in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM
Types of Switches and Relays
There are different types of switches and relays, which meet various needs and perform different functions, ranging from simple switching tasks and light control in homes to complex control, automation, and protection functions in industrial systems with many electrical components or control points.
One differs the following switches:
- Single-pole, double-pole, three-way, and four-way switches — are used to control a single or two separate circuits from one, two, three, or more different locations respectively.
- Push button, toggle, and rotary switches — are operated by pressing a button, flipping a lever up or down to toggle, or rotating a knob to select a required position respectively.
- Momentary switches — close and open the circuit by pressing and releasing the button.
- Limit switches — are activated by the actuator when an object contacts it.
- Selector switches — permit selection between different operating modes by rotating or sliding.
- Dimmer switches — adjust the light intensity.
- Combination switches — unify multiple functions into a single device.
There are also various types of relays classified into different categories according to their properties, configuration, operation principles, purpose, numbers of poles, and throw inside it. One differs:
- Electromechanical relays (EMRs) — use an electromagnet.
- Solid-state relays (SSRs) — use the semiconductor components.
- Hybrid relays — use both SSR and EMR relays.
- Reed relays — use the magnetic field that influences a pair of reed switches included.
- Time-delay relays — help to delay switching operations.
- Overload relays — disconnect the load automatically when an overload or excessive current is detected.
- Latching relays — keep up their position after being activated.
- Safety relays — are used to ensure safety and reliability in critical systems.
- Pulse relays — respond to short electrical pulses.
- Thermal relays — detect and respond to temperature changes using the thermal expansion of materials.
- Polarized and non-polarized relays — use the magnetic flux of the built-in permanent magnet or operation indicators or surge-absorbing diodes respectively.
- Multi-function relays — combine multiple functions.
Installation and Wiring Practices
Installation of switches and relays requires compliance with established rules, safety standards, and local electrical codes in order to ensure reliable and safe operation of the electrical system. Well-organized electrical systems are installed clearly according to the specific circuit design or electrical wiring diagram. They include switches mounted properly within electrical boxes and wiring connected to the switch terminals according to the specifications. Wires should be routed clearly, carefully, and labeled to be easily identified during maintenance and repair.
The installation of relays requires a reliable mounting on a stable base or panel to prevent vibrations and overheating. It is moreover vital to guarantee the correct wiring of relays to the control circuit and load circuit. The connectors and wire gauge should be chosen correctly according to the requirements, all connections should be tight and well-insulated.
Once the switches or relays are connected, the system should be tested to verify it functions properly, responds to control signals correctly, and meets safety regulations, and then you can adjust the settings, if required.
Testing and Troubleshooting
Testing and troubleshooting are essential actions for the reliable, efficient, and safe operation of switches, relays, and overall electrical system. The circuit should be checked for continuity and any signs of damage or wear, such as loose connections, frayed wires, switch or relay failures, or tripped circuit breakers. It is fundamental to make sure that switches or relays are wired correctly, that they open and close the circuit properly, connections are secure, and contacts are not damaged or stuck.
Measuring of the relay's coil resistance helps to confirm that it matches the specifications. If any intermittent operation or damage of the switch or relay is detected, it should be fixed to ensure secure and correct operation of the circuit. Potential issues like voltage fluctuations, inadequate coil voltage, or interference also can cause failures in the operation of relays and switches.
Example 2. Switches and Relays Library
Benefits of ConceptDraw DIAGRAM for Electrical Engineering
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is a powerful software for creating professional-looking electrical diagrams quickly and easily. For this purpose, it is convenient to use the Electrical Engineering solution from the Industrial Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Electrical Engineering solution provides 926 predesigned and ready-to-use vector electrical signs and symbols in 26 libraries, including relays and switches symbols, as well as templates and samples. The included libraries of the Electrical Engineering solution make your electrical diagramming quick, simple, and efficient. You can drop the ready-to-use electrical diagram symbols from libraries into your document to create an electrical diagram of any complexity fast and simply.
Example 3. Electrical Engineering symbols
Electrical diagram software will assist you in drawing your electrical diagrams and schematics with minimal effort and makes it very easy for beginners. Electrical symbols and smart connectors help present your electrical drawings, electrical schematics, wiring diagrams, and electrical blueprints.
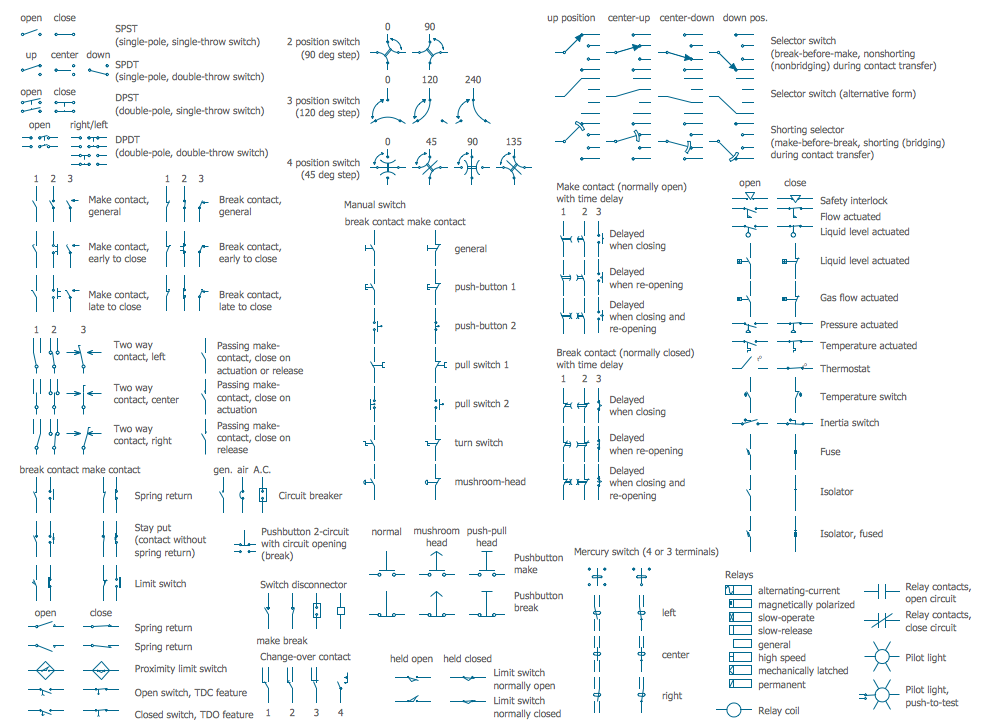
Example 4. Electrical Symbols — Switches and Relays
Most of the electrical symbols can be changed in their appearance, styles, and colors according to users' requirements. Electrical symbols are used to represent various electrical and electronic devices in a schematic diagram of an electrical or electronic circuit.
The following table lists some switch symbols and relay symbols in our electrical diagram ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software. This table of electrical symbols and meanings is incredibly useful when creating and reading electrical schematics.
| Symbol | Meaning | |
| Electrical Symbols — Switches and Relays | ||
 | SPST | |
 | SPDT | |
 | DPST | |
 | DPDT | |
 | Make contact | |
 | Break contact | |
 | Two way contact | |
 | Passing make-contact | |
 | Spring return | |
 | Stay put | |
 | Limit switch | |
 | Circuit breaker | |
 | Spring return 2 | |
 | Spring return 3 | |
 | Limit switch n/o | |
 | Limit switch n/c | |
 | 2 position switch | |
 | 3 position switch | |
 | 4 position switch | |
 | Manual switch | |
 | Pushbutton make | |
 | Pushbutton break | |
 | Pushbutton 2-circuit | |
 | Selector switch | |
 | Shorting selector | |
 | Proximity limit switch | |
 | Time delay make | |
 | Time delay break | |
 | Time delay make 2 | |
 | Time delay break 2 | |
 | Safety interlock | |
 | Flow actuated | |
 | Liquid level actuated | |
 | Liquid level actuated 2 | |
 | Gas flow actuated | |
 | Pressure actuated | |
 | Temperature actuated | |
 | Thermostat | |
 | Temperature switch | |
 | Inertia switch | |
 | Mercury switch | |
 | Mercury switch 2 | |
 | Fuse | |
 | Switch disconnector | |
 | Isolator | |
 | Change-over contact | |
 | Relay, alternating-current | |
 | Relay, magnetically polarized | |
 | Relay, slow-operate | |
 | Relay, slow-release | |
 | Relay | |
 | Relay, high speed | |
 | Relay, mechanically latched | |
 | Relay, permanent | |
 | Relay coil | |
 | Relay contacts | |
 | Pilot light | |
 | Pilot light, push-to-test | |
How to Create an Electrical Diagram Using Switches and Relays Library
- Open ConceptDraw DIAGRAM new document page.
- Select libraries with standard electrical symbols from the Electrical Engineering section.

- Switches and relays library contains objects, identified by a blue tile in the library pane. Such objects can be edited by using the Action button menu. To open the menu, select an object and click the
 button in the upper right corner of the object.
button in the upper right corner of the object.

- Select the Smart Connector tool
 . To connect schematic symbols using this tool, drag the connector from one connect dot to another. You can use Layers to place connections on different layers.
. To connect schematic symbols using this tool, drag the connector from one connect dot to another. You can use Layers to place connections on different layers.
- Result: Circuit Diagram.