What Is a Wireless Network? Professional Network Drawing
A wireless network refers to any computer network that uses a wireless connection, often radio waves or infrared signals, instead of a physical cable to connect devices and transmit data. Currently, wireless networks are incredibly popular. They enable users to access the internet and connect numerous wireless devices such as laptops, smartphones, tablets, routers, adapters, access points (APs) broadcasting a wireless signal, etc. Wireless computer network diagrams help system administrators and network engineers determine the amount and type of equipment needed for each office WLAN.
Wireless networks are convenient and used everywhere, from our homes to large enterprises and public spaces, and perform numerous functions from connecting personal devices to enabling communication across regions. Data transmission occurs in packets, which travel over specific frequency bands, with 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies. Different wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, LTE, and 5G are used. These technologies are constantly being improved to provide higher data rates and ranges.
Wireless networks offer significant advantages over other network types, including ease of installation, mobility, flexibility, security, and more. Security and protecting against unauthorized access and data breaches are crucial aspects of wireless networks and are provided by encryption using WEP, WPA, WPA2, and WPA3 protocols. However, wireless networks can face interference, which degrades signal strength and connection quality. Physical obstacles like microwaves, Bluetooth, electronic devices, walls, and furniture can cause these interferences.
Example 1. Mobile Data Offloading
Types of Wireless Networks
Wireless networks are classified into several types, each of which is unique based on its range, speed, and connectivity requirements, and is intended for specific purposes, applications, and environments. These include:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) | Are used for short-range communication, typically up to 100 meters, to connect personal devices like smartphones, tablets, laptops, headphones, and other peripherals. Bluetooth and Zigbee are key technologies in this category. |
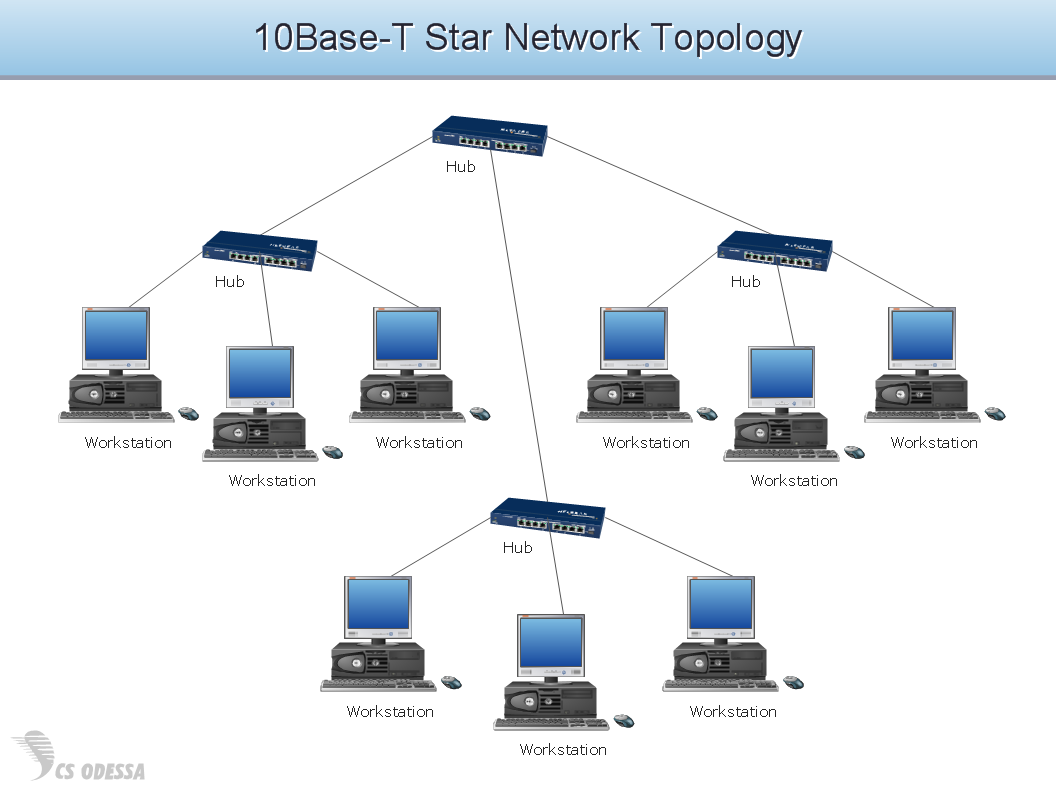
| Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) | Connect devices within a small limited geographic area, such as a home, office, school, university, campus, etc., and provide communication and shared access to different devices and resources, like printers, computers, etc. Typically, Ethernet cables and Wi-Fi are used for wireless network connection to provide high data transfer speeds and low latency. A modem is connected to the cable, a wireless router in turn is connected to it and serves as a wireless access point to transmit a signal. |
| Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks (WMANs) | Cover large areas, larger than WLANs but smaller than WWANs, typically covering distances of up to 100 kilometers, such as campus or city. The key technology used in WMANs is fiber optic technology providing high speed. Access points are connected to the internet via a wired network and broadcast a wireless signal throughout the area. |
| Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs) | Connect multiple LANs over a broad geographic area of a city, country, or continent and enable communication and data transfer across large distances. Typically, they use transmission technologies such as leased lines, satellite links, internet, cellular technology, MPLS, VPNs, SD-WAN, and towers to provide coverage across vast regions. |
Connect multiple LANs over a broad geographic area of a city, country, or continent and enable communication and data transfer across large distances. Typically, they use transmission technologies such as leased lines, satellite links, internet, cellular technology, MPLS, VPNs, SD-WAN, and towers to provide coverage across vast regions.
Components of a Wireless Network
Typically, a wireless network consists of several essential components, which work together to enable seamless communication without physical connections. The main components include:
| Main Components | Description |
|---|---|
| Access point (AP) | A network device that allows wireless devices to connect to and communicate with wired networks. |
| Router | A device that connects two or more packet-switched networks or subnetworks, manages traffic between the networks, receives and sends data on computer networks, and allows multiple devices to use the same wireless Internet connection. |
| Wireless devices | Electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, game consoles, and other gadgets equipped with wireless adapters that allow them to connect to the network without wires. |
| Modem | A device that connects the network to the Internet Service Provider (ISP) and converts digital signals for transmission. |
| Antennas | Devices that enhance signal strength and coverage, either built into electronic devices or attached externally. |
| Switch | An electrical component used to control multiple devices remotely without physical wiring. |
| Repeater | An electronic device that receives a wireless signal and amplifies it, extending the network's coverage area. |
| Extender | A device that boosts the wireless signal range and retransmits it to farther distances, helping to bridge gaps in coverage. |
| Bridge | A device used to improve and extend Wi-Fi network coverage, connecting the segments of the same network. |
| Firewall | A network security device that monitors incoming and outgoing traffic and blocks unauthorized access. |
| Gateway | A device that connects different networks, allowing communication between different protocols, or wired and wireless networks. |
| Load balancer | A device that distributes network traffic across multiple connections to optimize performance and reduce overloading. |
Additional components may include hardware components, such as a proxy server, Network Interface Card (NIC), firmware that manages the hardware components, network management software for monitoring and managing network performance, security, and configuration, and security protocols.
Applications of Wireless Networks
Wireless networks have a wide range of applications across multiple fields, enhancing communication and connectivity. They significantly impact and improve various aspects of daily life and work, industry operations, etc. The main applications of wireless networks include:
- internet access in premises of various purposes such as homes, offices, and public spaces through wireless technologies like Wi-Fi;
- mobile communication, data transfer, voice calls, text messaging, and internet services using 3G, 4G, and 5G technologies;
- remote work and collaboration in different fields;
- smart homes and Internet of Things (IoT), where wireless networks help to connect devices and provide automation work and remote monitoring;
- navigation in the transportation sector, real-time traffic updates, sharing information about road conditions and potential hazards;
- optimizing the work of traffic management, waste disposal, and public safety systems;
- functioning of smart cities;
- ensuring public safety through effective communication and coordination during emergencies, and improved response times using wireless networks;
- environmental monitoring through real-time data collection from various sensors that track environmental conditions;
- automation of processes in agriculture, such as automated irrigation, precision agriculture, etc.;
- ensuring the convenient operation of mobile banking, payment solutions, and other financial services;
- advertising and social networking, content sharing, and global communication;
- operation of e-learning platforms, research and development portals supporting remote data collection, fostering innovation, and collaboration across geographical boundaries;
- logistics, commerce, and supply chain management.
Example 2. Wi-Fi Repeater
Advantages of Wireless Networks
Wireless networks are a popular choice for both personal and business use due to the numerous advantages they provide. Here are some key benefits of wireless networks:
- ease of installation and setting up in spaces of different purposes, locations, and areas, both in homes, offices, large enterprises, and public spaces;
- ease and user-friendly connection for the network due to the automatic detection of available networks;
- accessibility for all users;
- increased coverage relative to the traditional wired networks;
- mobility and flexibility, allowing users to connect to the internet and access network resources from anywhere within the coverage area;
- support for multiple devices and scalability, allowing the addition of new devices to the network and their repositioning without any efforts or infrastructure changes;
- improved aesthetics and organization of the environment due to reduced cabling in spaces;
- remote access to network resources that helps to improve business productivity, making it easier to work renotely from any point outside the office;
- enhanced collaboration and fast sharing of information among team members;
- cost-effectiveness through reduced cabling and installation expenses;
- integration with various technologies, cloud services, security systems, smart home devices, smart cities technologies;
- automatic updates;
- support for VoIP and video conferencing, and many others.
Security in Wireless Networks
Security and stability of wireless networks are the most essential issues because of their vulnerability to unauthorized access, interception of data, and other attacks. Without a corresponding defense, they are as endangered as wired networks, and are exposed to a range of cyber risks, being susceptible to interference from other wireless devices, environmental factors, and physical obstacles. Latent threats like unsecured Wi-Fi networks or weak passwords and phishing attacks via Wi-Fi can endanger online privacy and security. As a result, serious consequences, such as hijacking of online accounts, loss of personal data, banking disclosure, and others can occur.
Most wireless network vulnerabilities refer to weaknesses and security gaps that can be exploited by hackers or unauthorized users. However, the careful and correct network configuration, wireless network design, implementation, and setup ensure reliable security and sustainability against cyber attacks. Therefore, the key task is to make our Wi-Fi networks as secure and stable as possible, eliminating vulnerabilities and factors that can reduce the signal strength or cause disruptions.
A comprehensive and multi-layered security strategy is vital and helps to protect wireless networks from various threats efficiently. Key measures include encryption protocols like WPA2 and WPA3, which protect data during transmission. Using complex passwords, biometric verification, multi-factor authentication, and other strong authentication methods, as well as employing firewalls and other protective software and regular updating them, help to protect networks from unauthorized access.
Additional methods are also efficient in enhancing security. These include intrusion detection systems (IDS) used to monitor traffic for suspicious activity on the network, network segmentation that limits access to sensitive data and isolates devices from general access, MAC address filtering, VPNs, and access control lists.
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM Software for Wireless Network Design
Wireless Networks solution from the ConceptDraw Solution Park extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM vector diagramming software to help network engineers and designers efficiently design, create, and illustrate wireless networks of various complexity, purposes, and types. The solution contains a comprehensive library of objects for drawing different types of Wireless network diagrams and professionally designed wireless network diagram examples.
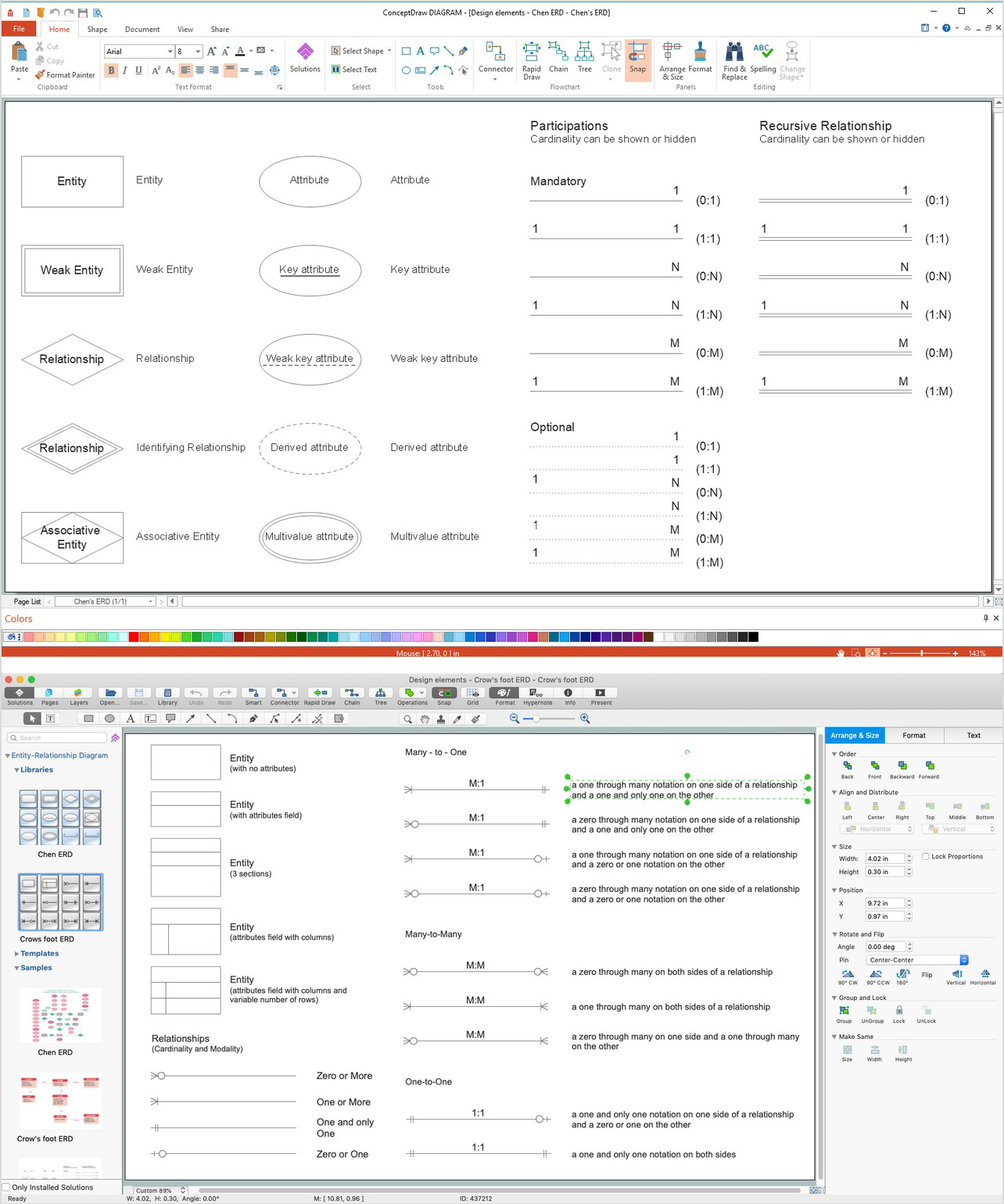
Example 3. Wireless Communications Library Design Elements
When planning a WLAN for a complex office environment, it is important to be able to display clearly the interactions between all devices. In ConceptDraw DIAGRAM wireless design software it is simple to show all devices of your network, connect them with the relationships, and indicate technical capabilities.

Example 4. Wireless Router Network Diagram
Conclusion
Currently, wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular, and others, have become an essential part of our lives due to their ease of use, flexibility, and ability to support a large number of connected devices. They enable us to stay in touch at all times and in any location, whether at home, in the workplace, or in a public space, etc. A well-thought-out design and protective measures against hidden dangers help to make wireless networks reliable and secure.
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM wireless network design software is ideal for both personal use and businesses, to project and implement wireless networks for home and enterprise networking, incorporate them into daily operations, explore their vulnerabilities, and take measures to address them.