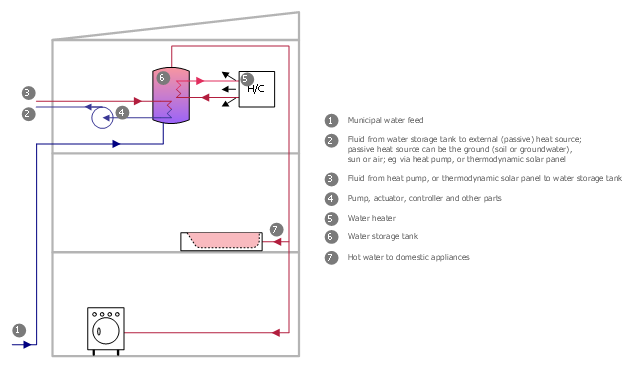
This plumbing plan example was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Active Indirect Water Heater Diagram.svg.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Active_ Indirect_ Water_ Heater_ Diagram.svg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Water heating is a thermodynamic process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated to steam have many uses.
Domestically, water is traditionally heated in vessels known as water heaters, kettles, cauldrons, pots, or coppers. These metal vessels that heat a batch of water do not produce a continual supply of heated water at a preset temperature. Rarely, hot water occurs naturally, usually from natural hot springs. The temperature varies based on the consumption rate, becoming cooler as flow increases.
Appliances that provide a continual supply of hot water are called water heaters, hot water heaters, hot water tanks, boilers, heat exchangers, geysers, or calorifiers. These names depend on region, and whether they heat potable or non-potable water, are in domestic or industrial use, and their energy source. In domestic installations, potable water heated for uses other than space heating is also called domestic hot water (DHW).
Fossil fuels (natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, oil), or solid fuels are commonly used for heating water. These may be consumed directly or may produce electricity that, in turn, heats water. Electricity to heat water may also come from any other electrical source, such as nuclear power or renewable energy. Alternative energy such as solar energy, heat pumps, hot water heat recycling, and geothermal heating can also heat water, often in combination with backup systems powered by fossil fuels or electricity." [Water heating. Wikipedia]
The plumbing plan example "Active indirect water heater diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Plumbing and Piping Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Active_ Indirect_ Water_ Heater_ Diagram.svg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Water heating is a thermodynamic process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated to steam have many uses.
Domestically, water is traditionally heated in vessels known as water heaters, kettles, cauldrons, pots, or coppers. These metal vessels that heat a batch of water do not produce a continual supply of heated water at a preset temperature. Rarely, hot water occurs naturally, usually from natural hot springs. The temperature varies based on the consumption rate, becoming cooler as flow increases.
Appliances that provide a continual supply of hot water are called water heaters, hot water heaters, hot water tanks, boilers, heat exchangers, geysers, or calorifiers. These names depend on region, and whether they heat potable or non-potable water, are in domestic or industrial use, and their energy source. In domestic installations, potable water heated for uses other than space heating is also called domestic hot water (DHW).
Fossil fuels (natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, oil), or solid fuels are commonly used for heating water. These may be consumed directly or may produce electricity that, in turn, heats water. Electricity to heat water may also come from any other electrical source, such as nuclear power or renewable energy. Alternative energy such as solar energy, heat pumps, hot water heat recycling, and geothermal heating can also heat water, often in combination with backup systems powered by fossil fuels or electricity." [Water heating. Wikipedia]
The plumbing plan example "Active indirect water heater diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Plumbing and Piping Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This plumbing plan example was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Active Indirect Water Heater Diagram.svg.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Active_ Indirect_ Water_ Heater_ Diagram.svg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Water heating is a thermodynamic process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated to steam have many uses.
Domestically, water is traditionally heated in vessels known as water heaters, kettles, cauldrons, pots, or coppers. These metal vessels that heat a batch of water do not produce a continual supply of heated water at a preset temperature. Rarely, hot water occurs naturally, usually from natural hot springs. The temperature varies based on the consumption rate, becoming cooler as flow increases.
Appliances that provide a continual supply of hot water are called water heaters, hot water heaters, hot water tanks, boilers, heat exchangers, geysers, or calorifiers. These names depend on region, and whether they heat potable or non-potable water, are in domestic or industrial use, and their energy source. In domestic installations, potable water heated for uses other than space heating is also called domestic hot water (DHW).
Fossil fuels (natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, oil), or solid fuels are commonly used for heating water. These may be consumed directly or may produce electricity that, in turn, heats water. Electricity to heat water may also come from any other electrical source, such as nuclear power or renewable energy. Alternative energy such as solar energy, heat pumps, hot water heat recycling, and geothermal heating can also heat water, often in combination with backup systems powered by fossil fuels or electricity." [Water heating. Wikipedia]
The plumbing plan example "Active indirect water heater diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Plumbing and Piping Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Active_ Indirect_ Water_ Heater_ Diagram.svg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Water heating is a thermodynamic process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated to steam have many uses.
Domestically, water is traditionally heated in vessels known as water heaters, kettles, cauldrons, pots, or coppers. These metal vessels that heat a batch of water do not produce a continual supply of heated water at a preset temperature. Rarely, hot water occurs naturally, usually from natural hot springs. The temperature varies based on the consumption rate, becoming cooler as flow increases.
Appliances that provide a continual supply of hot water are called water heaters, hot water heaters, hot water tanks, boilers, heat exchangers, geysers, or calorifiers. These names depend on region, and whether they heat potable or non-potable water, are in domestic or industrial use, and their energy source. In domestic installations, potable water heated for uses other than space heating is also called domestic hot water (DHW).
Fossil fuels (natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, oil), or solid fuels are commonly used for heating water. These may be consumed directly or may produce electricity that, in turn, heats water. Electricity to heat water may also come from any other electrical source, such as nuclear power or renewable energy. Alternative energy such as solar energy, heat pumps, hot water heat recycling, and geothermal heating can also heat water, often in combination with backup systems powered by fossil fuels or electricity." [Water heating. Wikipedia]
The plumbing plan example "Active indirect water heater diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Plumbing and Piping Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Manufacturing and Maintenance | Energy resources diagram | Active ...
- Water cycle diagram | Active indirect water heater diagram | Double ...
- Manufacturing and Maintenance | Energy resources diagram | Active ...
- Active indirect water heater diagram | Design elements - Appliances ...
- Recreation signs - Vector stencils library | Active indirect water ...
- Energy resources diagram | U.S. energy consumption by source ...
- Piping and instrumentation diagram template ... - Conceptdraw.com
- Design elements - Nuclear physics | Proton-proton chain reaction ...
- Road signs - Vector stencils library | Network Glossary Definition ...
- Design elements - Vessels | Vessels - Vector stencils library | Design ...
- Natural gas condensate - PFD | Divided bar graph - Global natural ...
- ConceptDraw Solution Park | Reflected Ceiling Plans | Flowcharts ...
- Air temperature correlations - Cafe dashboard | Cafe performance ...
- Manufacturing and Maintenance | Renewable And Nonrenewable ...
- Manufacturing and Maintenance | An Example Of A Renewable ...
- Divided bar diagram - London election results | Relative Value Chart ...
- Laboratory equipment - Vector stencils library | Gravity filtration of ...
- Computer peripheral devices - Vector stencils library | Mains Supply ...
- Manufacturing and Maintenance | Divided bar graph - Global natural ...
- Bathroom - Vector stencils library | Laboratory equipment - Vector ...