Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning
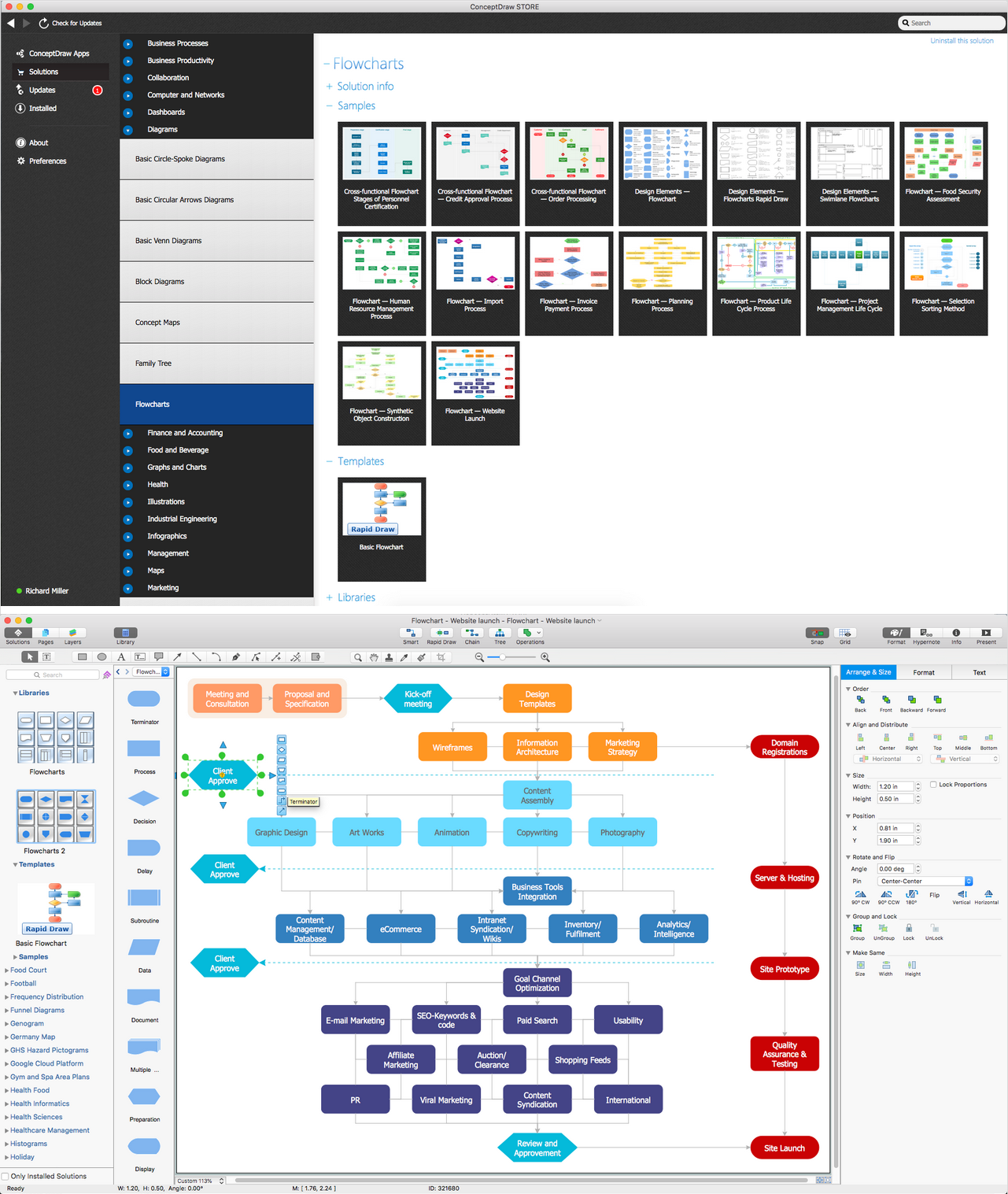
Flowcharts are the best for visually representation the business processes and the flow of a custom-order process through various departments within an organization. ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Flowcharts solution offers the full set of predesigned basic flowchart symbols which are gathered at two libraries: Flowchart and Flowcharts Rapid Draw. Among them are: process, terminator, decision, data, document, display, manual loop, and many other specific symbols. The meaning for each symbol offered by ConceptDraw gives the presentation about their proposed use in professional Flowcharts for business and technical processes, software algorithms, well-developed structures of web sites, Workflow diagrams, Process flow diagram and correlation in developing on-line instructional projects or business process system. Use of ready flow chart symbols in diagrams is incredibly useful - you need simply drag desired from the libraries to your document and arrange them in required order. There are a few serious alternatives to Visio for Mac, one of them is ConceptDraw PRO. It is one of the main contender with the most similar features and capabilities.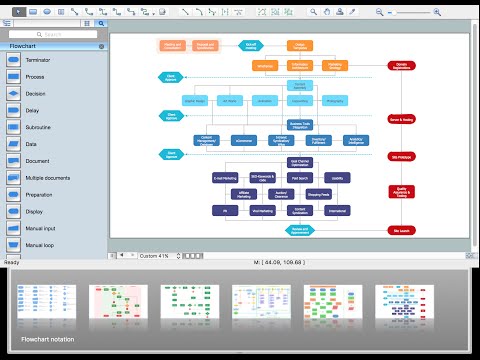
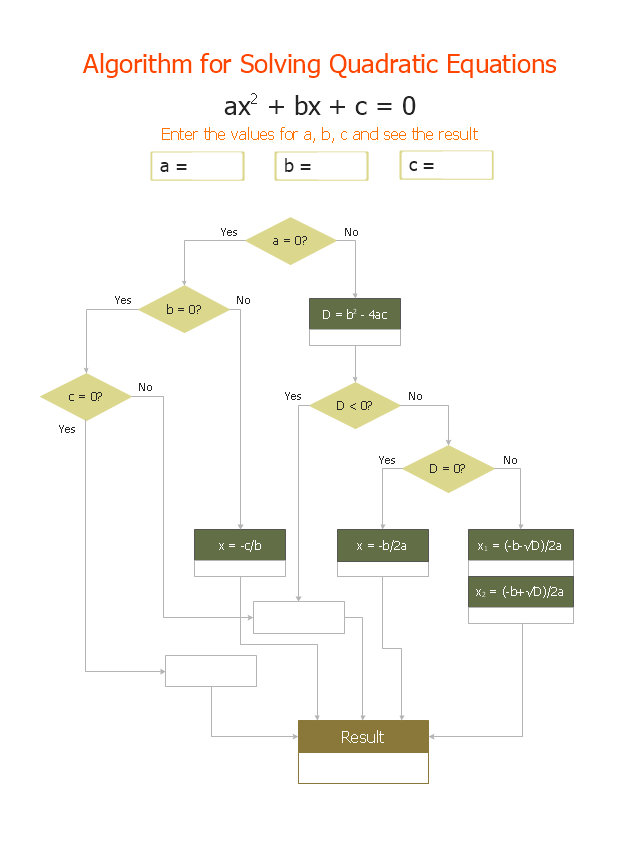
"In elementary algebra, a quadratic equation (from the Latin quadratus for "square") is any equation having the form
ax^2+bx+c=0
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c are constants with a not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The constants a, b, and c are called, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.
Because the quadratic equation involves only one unknown, it is called "univariate". The quadratic equation only contains powers of x that are non-negative integers, and therefore it is a polynomial equation, and in particular it is a second degree polynomial equation since the greatest power is two.
Quadratic equations can be solved by a process known in American English as factoring and in other varieties of English as factorising, by completing the square, by using the quadratic formula, or by graphing." [Quadratic equation. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Solving quadratic equation algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
ax^2+bx+c=0
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c are constants with a not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The constants a, b, and c are called, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.
Because the quadratic equation involves only one unknown, it is called "univariate". The quadratic equation only contains powers of x that are non-negative integers, and therefore it is a polynomial equation, and in particular it is a second degree polynomial equation since the greatest power is two.
Quadratic equations can be solved by a process known in American English as factoring and in other varieties of English as factorising, by completing the square, by using the quadratic formula, or by graphing." [Quadratic equation. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Solving quadratic equation algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 ConceptDraw Solution Park
ConceptDraw Solution Park
ConceptDraw Solution Park collects graphic extensions, examples and learning materials
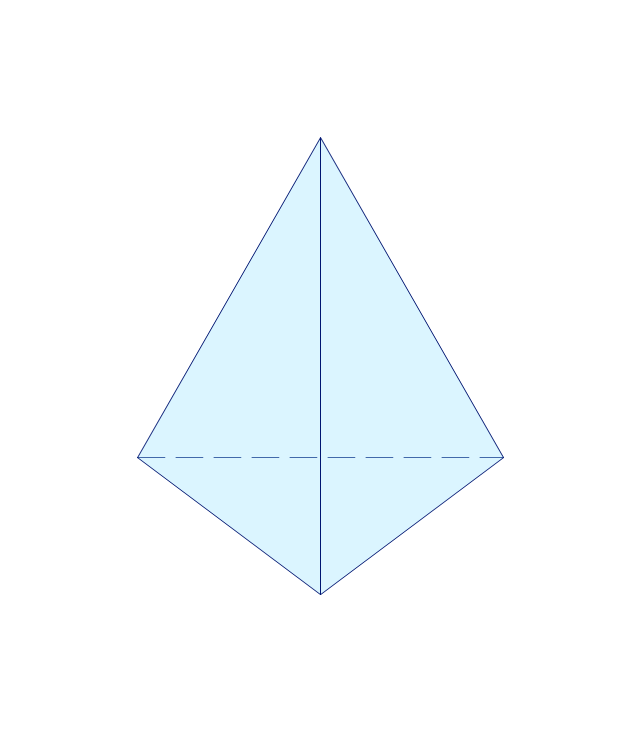
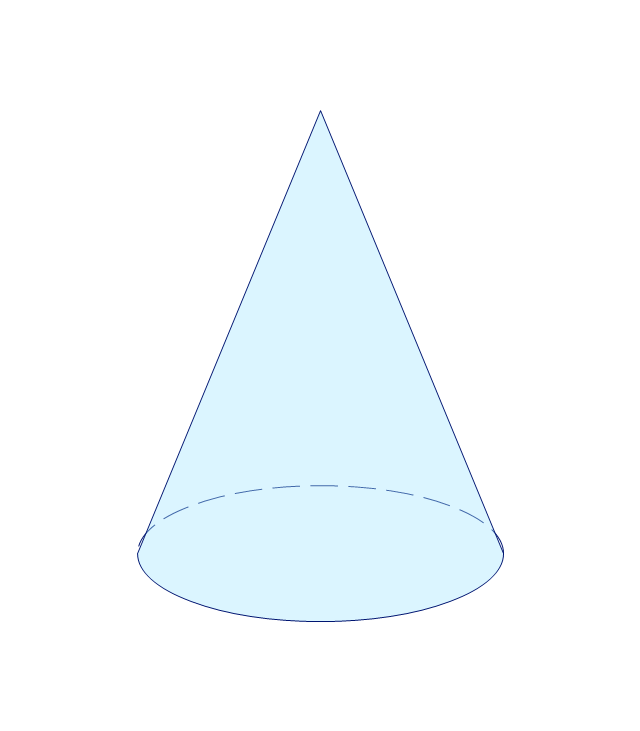
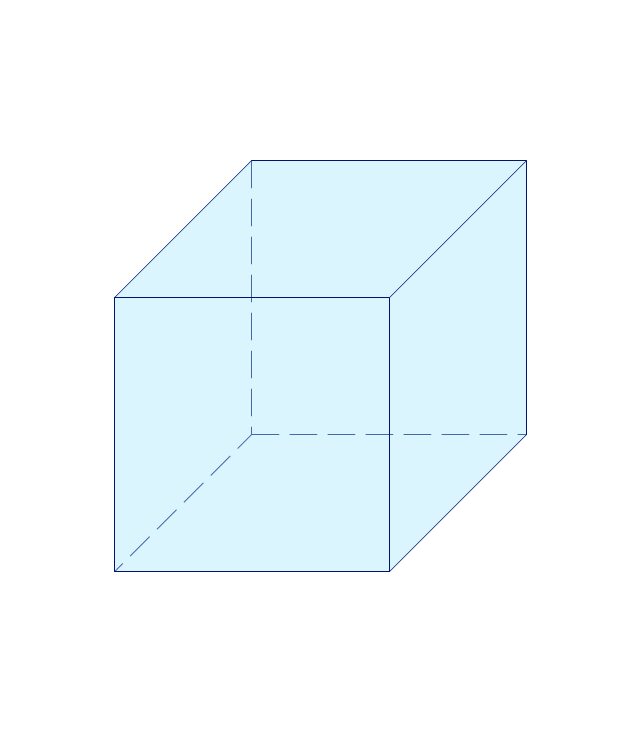
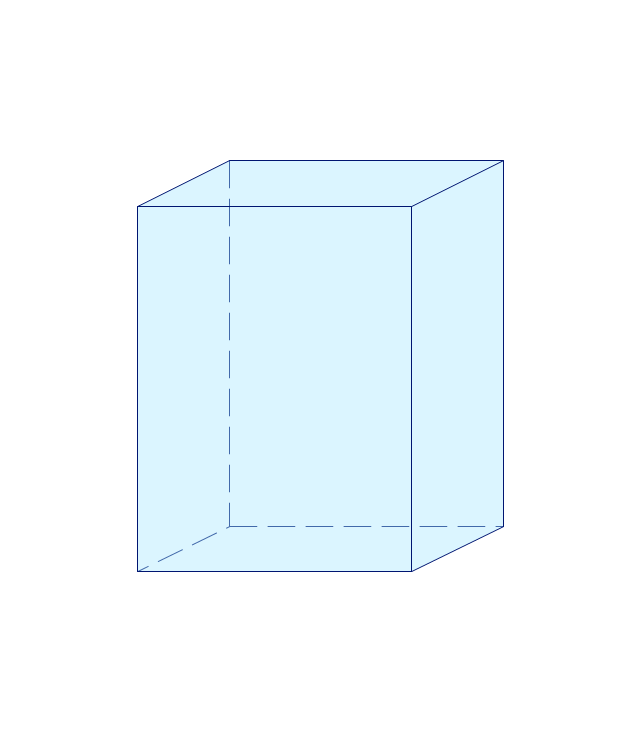
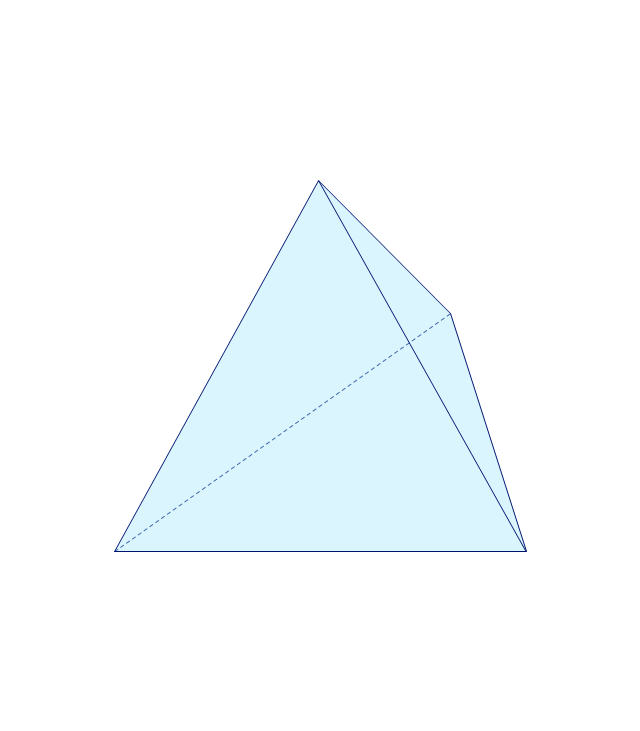
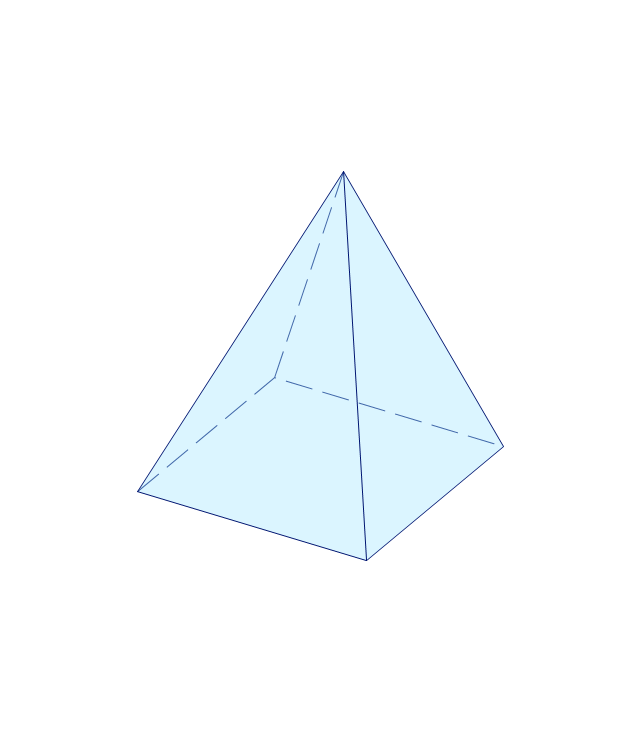
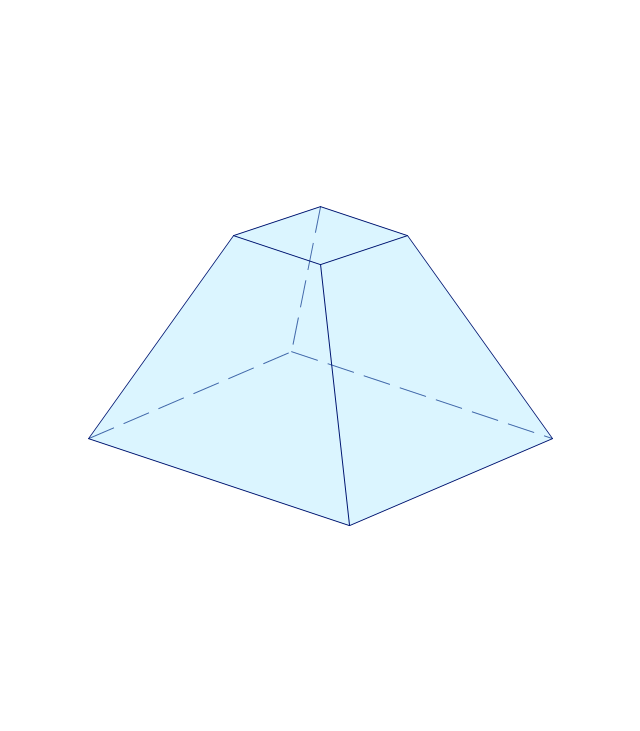
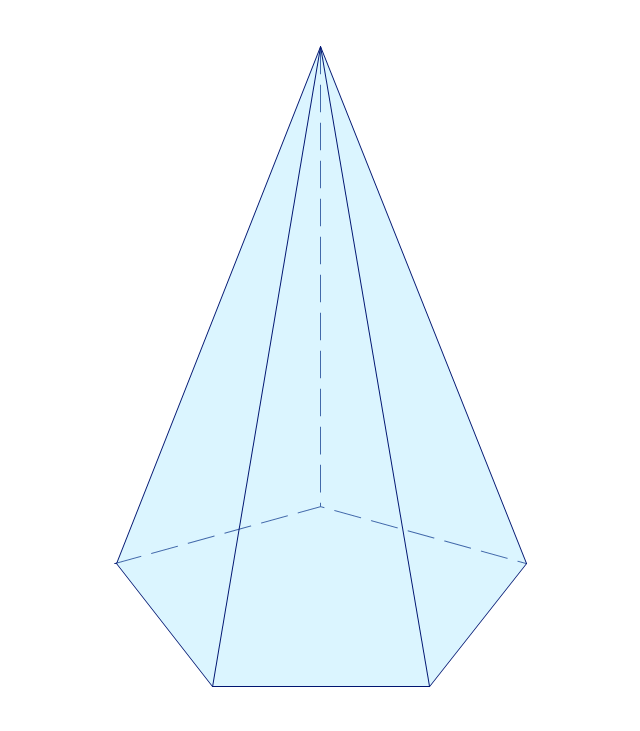
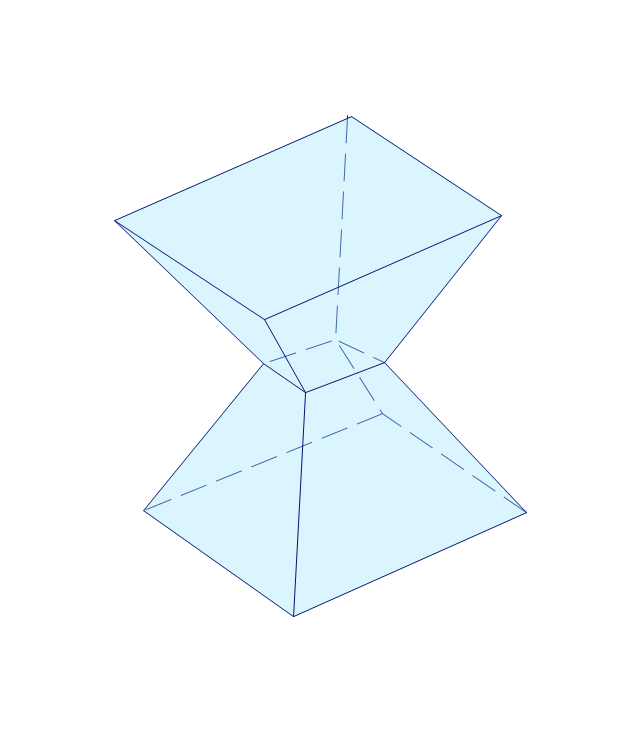
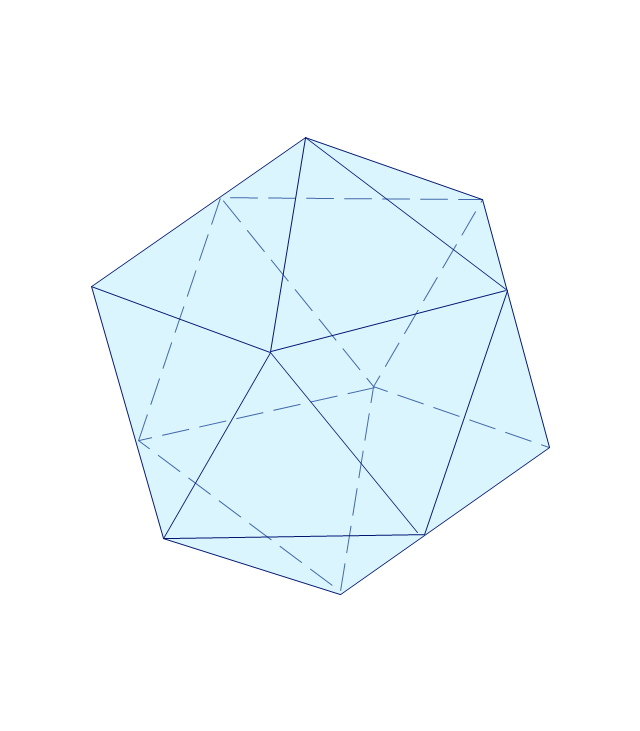
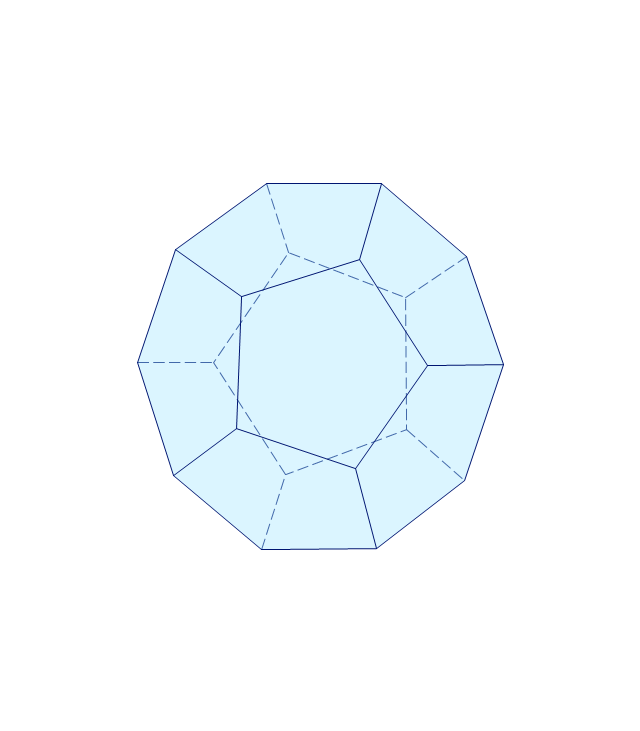
The vector stencils library "Solid geometry" contains 15 shapes of solid geometric figures.
Use these shapes to draw your geometrical diagrams and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these shapes to draw your geometrical diagrams and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
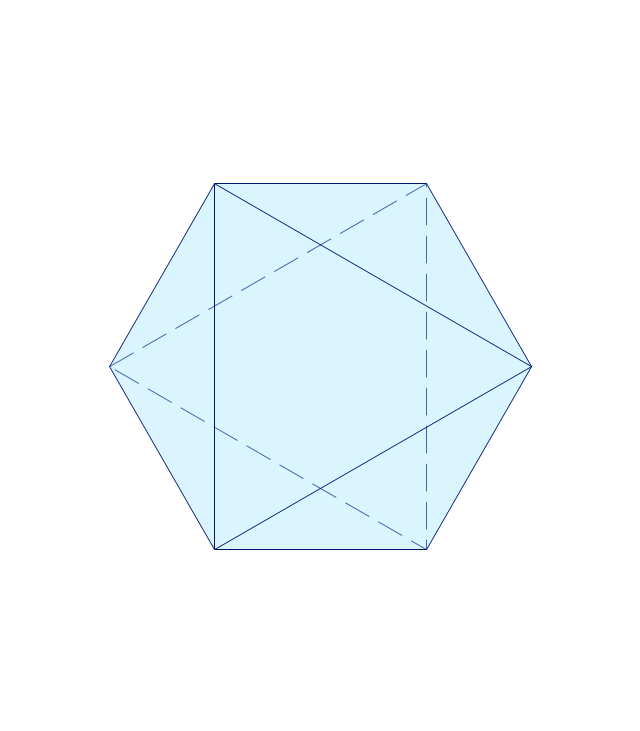
The vector stencils library "Plane geometry" contains 27 plane geometric figures.
Use these shapes to draw your geometrical diagrams and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these shapes to draw your geometrical diagrams and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In geometry a polygon is traditionally a plane figure that is bounded by a finite chain of straight line segments closing in a loop to form a closed chain or circuit. These segments are called its edges or sides, and the points where two edges meet are the polygon's vertices (singular: vertex) or corners. The interior of the polygon is sometimes called its body. An n-gon is a polygon with n sides. A polygon is a 2-dimensional example of the more general polytope in any number of dimensions. ...
The basic geometrical notion has been adapted in various ways to suit particular purposes. Mathematicians are often concerned only with the bounding closed polygonal chain and with simple polygons which do not self-intersect, and they often define a polygon accordingly. A polygonal boundary may be allowed to intersect itself, creating star polygons. Geometrically two edges meeting at a corner are required to form an angle that is not straight (180°); otherwise, the line segments may be considered parts of a single edge; however mathematically, such corners may sometimes be allowed. These and other generalizations of polygons are described below." [Polygon. Wikipedia]
The geometry diagram example "Polygon types" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The basic geometrical notion has been adapted in various ways to suit particular purposes. Mathematicians are often concerned only with the bounding closed polygonal chain and with simple polygons which do not self-intersect, and they often define a polygon accordingly. A polygonal boundary may be allowed to intersect itself, creating star polygons. Geometrically two edges meeting at a corner are required to form an angle that is not straight (180°); otherwise, the line segments may be considered parts of a single edge; however mathematically, such corners may sometimes be allowed. These and other generalizations of polygons are described below." [Polygon. Wikipedia]
The geometry diagram example "Polygon types" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Solving quadratic equation algorithm - Flowchart | Mathematics ...
- Math Topics Flow Chart Examples
- Geometry Diagrams
- Basic Diagramming | Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Accounting ...
- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Mathematics | Solving quadratic ...
- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Basic Flowchart Symbols and ...
- Basic Diagramming | Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Basic ...
- Solving quadratic equation algorithm - Flowchart | Basic ...
- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Solving quadratic equation ...
- Basic Diagramming | Solving quadratic equation algorithm ...
- All Kinds Of Solid Geometry
- Basic Diagramming | Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Basic ...
- Solving quadratic equation algorithm - Flowchart | Basic ...
- Basic Diagramming | Types of Flowchart - Overview | Mathematics ...
- Basic Diagramming | Solving quadratic equation algorithm ...
- Solid geometry - Vector stencils library | Design elements - Solid ...
- Basic Diagramming | Mathematics | Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart ...
- Mathematics | Mathematics Symbols | Mathematical Diagrams ...
- Solving quadratic equation algorithm - Flowchart | Contoh Flowchart ...
- Chemistry Equation Symbols | Basic Diagramming | Chemistry ...