"Carbohydrate catabolism is the breakdown of carbohydrates into smaller units. Carbohydrates literally undergo combustion to retrieve the large amounts of energy in their bonds. Energy is secured by mitochondria in the form of ATP.
There are several different types of carbohydrates: polysaccharides (e.g., starch, amylopectin, glycogen, cellulose), monosaccharides (e.g., glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose) and the disaccharides (e.g., maltose, lactose).
Glucose reacts with oxygen in the following redox reaction, C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O, the carbon dioxide and water is a waste product and the chemical reaction is exothermic.
The breakdown of glucose into energy in the form of molecules of ATP is therefore one of the most important biochemical pathways found in living organisms." [Carbohydrate catabolism. Wikipedia]
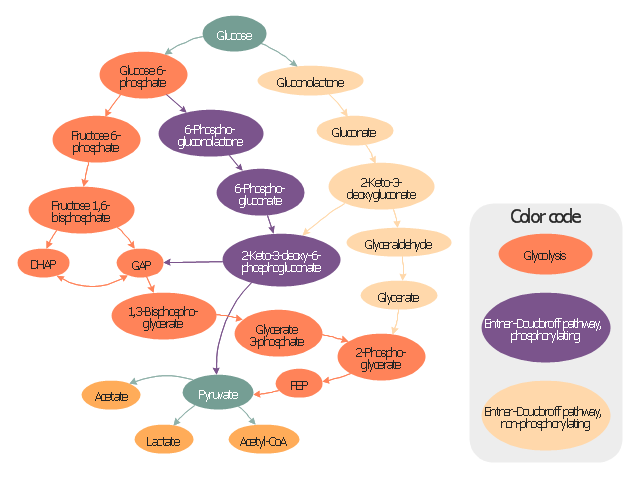
This glucose catabolism pathways map shows glycolysis by orange color, Entner-Doudoroff phosphorylating pathway by green color, Entner-Doudoroff non-phosphorylating pathway by Yellow color.
This methabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikimedia file: Glucose catabolism pathways.svg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Glucose_ catabolism_ pathways.svg]
The biochemical diagram example "Glucose catabolism pathways map" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-biology
There are several different types of carbohydrates: polysaccharides (e.g., starch, amylopectin, glycogen, cellulose), monosaccharides (e.g., glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose) and the disaccharides (e.g., maltose, lactose).
Glucose reacts with oxygen in the following redox reaction, C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O, the carbon dioxide and water is a waste product and the chemical reaction is exothermic.
The breakdown of glucose into energy in the form of molecules of ATP is therefore one of the most important biochemical pathways found in living organisms." [Carbohydrate catabolism. Wikipedia]
This glucose catabolism pathways map shows glycolysis by orange color, Entner-Doudoroff phosphorylating pathway by green color, Entner-Doudoroff non-phosphorylating pathway by Yellow color.
This methabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikimedia file: Glucose catabolism pathways.svg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Glucose_ catabolism_ pathways.svg]
The biochemical diagram example "Glucose catabolism pathways map" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-biology
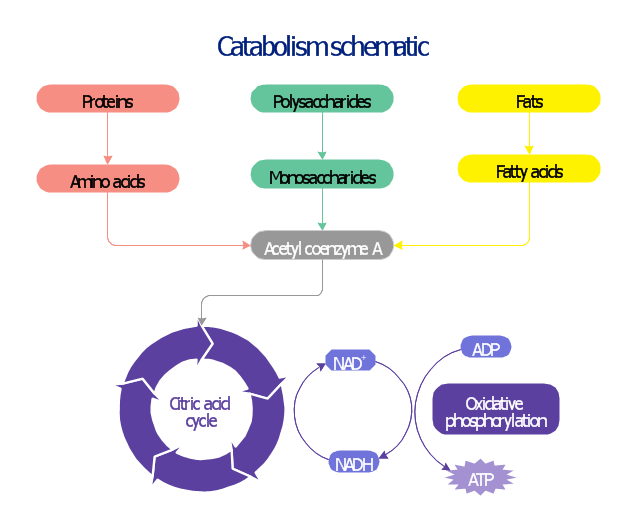
This biochemical chart display how proteins, polysaccharides and fats from food are digested into gastrointestinal tract into aminoacids, monosaccharides and fatty acids, and then broken down and oxidized to carbon dioxide and water in cellular processes of energy generation.
This metabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikipedia file: Catabolism schematic.svg. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Catabolism_ schematic.svg]
The biochemical diagram example "Catabolism schematic" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-biology
This metabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikipedia file: Catabolism schematic.svg. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Catabolism_ schematic.svg]
The biochemical diagram example "Catabolism schematic" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-biology
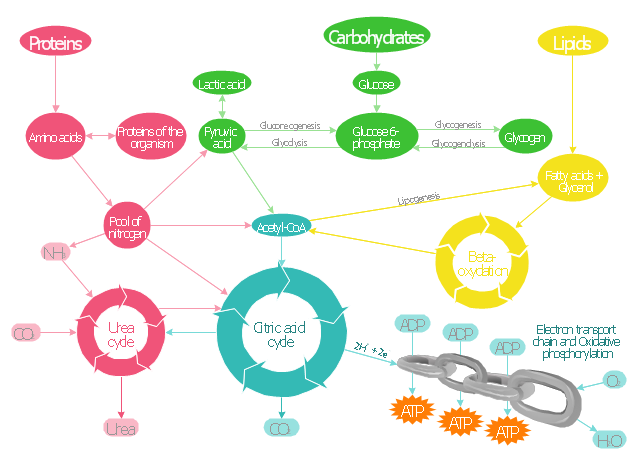
"Metabolism is refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells. Metabolism is usually divided into catabolism, that breaks down organic matter and harvests energy by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism that uses energy to construct components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids.
The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes." [Metabolism. Wikipedia]
The biochemical pathway map example "Key metabolic processes" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-biology
The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes." [Metabolism. Wikipedia]
The biochemical pathway map example "Key metabolic processes" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-biology
- Catabolism schematic | Glucose catabolism pathways map ...
- Glucose catabolism pathways map - Conceptdraw.com
- Catabolism schematic | - Conceptdraw.com
- Glucose catabolism pathways map | Catabolism schematic ...
- Catabolism schematic | Biochemical metabolic pathway map diagram |
- Biology | Bio Flowchart Lite | Glucose catabolism pathways map |
- Citric acid cycle (TCA cycle) | Biochemical metabolic pathway map ...
- Catabolism schematic | Design elements - Biochemistry of ...
- Glucose catabolism pathways map |
- Metabolic pathway map - Biochemical diagram | Catabolism ...
- Business Diagram Software | Glucose catabolism pathways map ...
- Glycolysis overview diagram | Catabolism schematic | Glucose ...
- Biology | Glucose catabolism pathways map | ConceptDraw Solution ...
- Biology | Catabolism schematic - Biochemical diagram |
- Catabolism schematic | Biochemical metabolic pathway map diagram |
- Glycolysis overview diagram
- Catabolism schematic - Biochemical diagram | Citric acid cycle (TCA ...
- Biochemical pathway map - Key metabolic processes | Glucose ...
- Business Diagram Software | Catabolism schematic |
- Biochemical pathway map - Key metabolic processes | Catabolism ...