"Porter five forces analysis is a framework for industry analysis and business strategy development. It draws upon industrial organization (IO) economics to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and therefore attractiveness of a market. Attractiveness in this context refers to the overall industry profitability. An "unattractive" industry is one in which the combination of these five forces acts to drive down overall profitability. A very unattractive industry would be one approaching "pure competition", in which available profits for all firms are driven to normal profit.
Three of Porter's five forces refer to competition from external sources. The remainder are internal threats.
Porter referred to these forces as the micro environment, to contrast it with the more general term macro environment. They consist of those forces close to a company that affect its ability to serve its customers and make a profit. A change in any of the forces normally requires a business unit to re-assess the marketplace given the overall change in industry information. The overall industry attractiveness does not imply that every firm in the industry will return the same profitability. Firms are able to apply their core competencies, business model or network to achieve a profit above the industry average. A clear example of this is the airline industry. As an industry, profitability is low and yet individual companies, by applying unique business models, have been able to make a return in excess of the industry average.
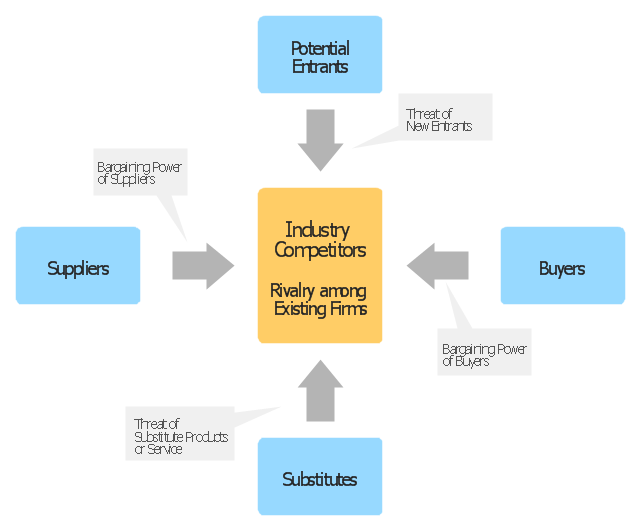
Porter's five forces include - three forces from 'horizontal' competition: the threat of substitute products or services, the threat of established rivals, and the threat of new entrants; and two forces from 'vertical' competition: the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of customers.
This five forces analysis, is just one part of the complete Porter strategic models. The other elements are the value chain and the generic strategies." [Porter five forces analysis. Wikipedia]
The block diagram example "Porter's five forces model" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Block Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Three of Porter's five forces refer to competition from external sources. The remainder are internal threats.
Porter referred to these forces as the micro environment, to contrast it with the more general term macro environment. They consist of those forces close to a company that affect its ability to serve its customers and make a profit. A change in any of the forces normally requires a business unit to re-assess the marketplace given the overall change in industry information. The overall industry attractiveness does not imply that every firm in the industry will return the same profitability. Firms are able to apply their core competencies, business model or network to achieve a profit above the industry average. A clear example of this is the airline industry. As an industry, profitability is low and yet individual companies, by applying unique business models, have been able to make a return in excess of the industry average.
Porter's five forces include - three forces from 'horizontal' competition: the threat of substitute products or services, the threat of established rivals, and the threat of new entrants; and two forces from 'vertical' competition: the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of customers.
This five forces analysis, is just one part of the complete Porter strategic models. The other elements are the value chain and the generic strategies." [Porter five forces analysis. Wikipedia]
The block diagram example "Porter's five forces model" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Block Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
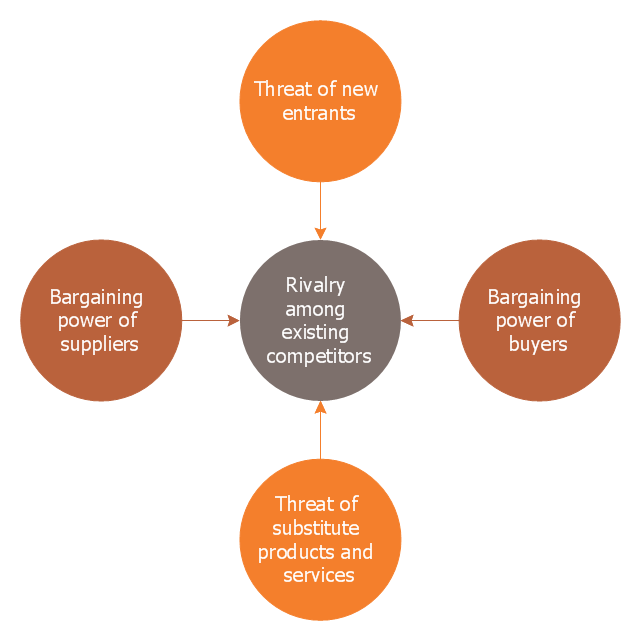
This circle-spoke diagram sample shows the Porter five forces model. It was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Modelo Porter.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Modelo_ Porter.png]
"Porter's five forces analysis is a framework that attempts to analyze the level of competition within an industry and business strategy development. It draws upon industrial organization (IO) economics to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and therefore attractiveness of an Industry. Attractiveness in this context refers to the overall industry profitability. An "unattractive" industry is one in which the combination of these five forces acts to drive down overall profitability. A very unattractive industry would be one approaching "pure competition", in which available profits for all firms are driven to normal profit. This analysis is associated with its principal innovator Michael E. Porter of Harvard University. ...
Porter's five forces include – three forces from 'horizontal' competition: the threat of substitute products or services, the threat of established rivals, and the threat of new entrants; and two forces from 'vertical' competition: the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of customers." [Porter's five forces analysis. Wikipedia]
The hub-and-spoke diagram example "Porter five forces model" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Circle-Spoke Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Porter's five forces analysis is a framework that attempts to analyze the level of competition within an industry and business strategy development. It draws upon industrial organization (IO) economics to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and therefore attractiveness of an Industry. Attractiveness in this context refers to the overall industry profitability. An "unattractive" industry is one in which the combination of these five forces acts to drive down overall profitability. A very unattractive industry would be one approaching "pure competition", in which available profits for all firms are driven to normal profit. This analysis is associated with its principal innovator Michael E. Porter of Harvard University. ...
Porter's five forces include – three forces from 'horizontal' competition: the threat of substitute products or services, the threat of established rivals, and the threat of new entrants; and two forces from 'vertical' competition: the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of customers." [Porter's five forces analysis. Wikipedia]
The hub-and-spoke diagram example "Porter five forces model" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Circle-Spoke Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Competitor Analysis
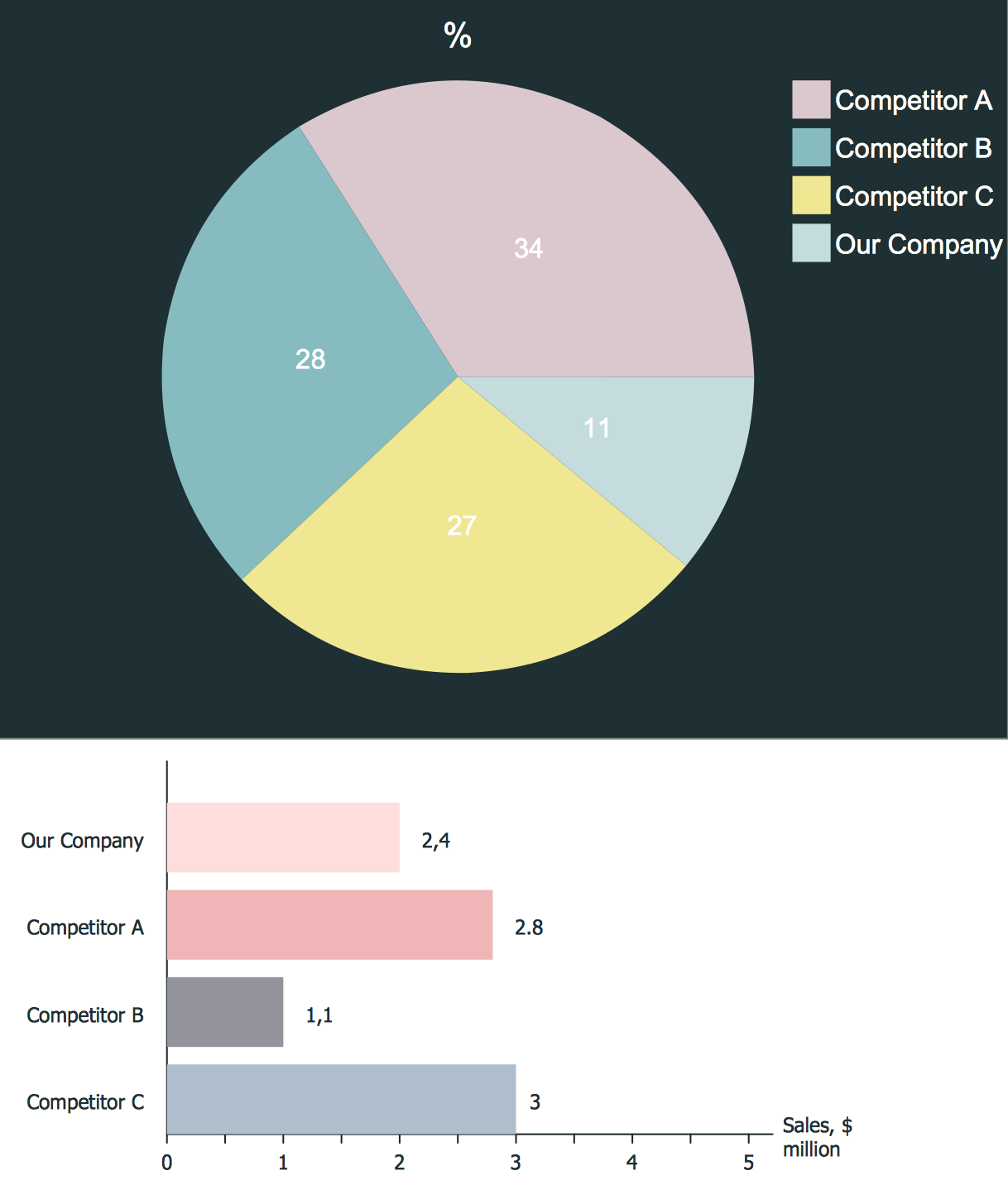
Competitor analysis is a first and obligatory step in elaboration the proper corporate marketing strategy and creating sustainable competitive advantage. Use powerful opportunities of numerous solutions from ConceptDraw Solution Park for designing illustrative diagrams, charts, matrices which are necessary for effective competitor analysis.
 Basic Circle-Spoke Diagrams
Basic Circle-Spoke Diagrams
Basic circle-spoke diagrams are well suited for marketing, management documents, and presentations.
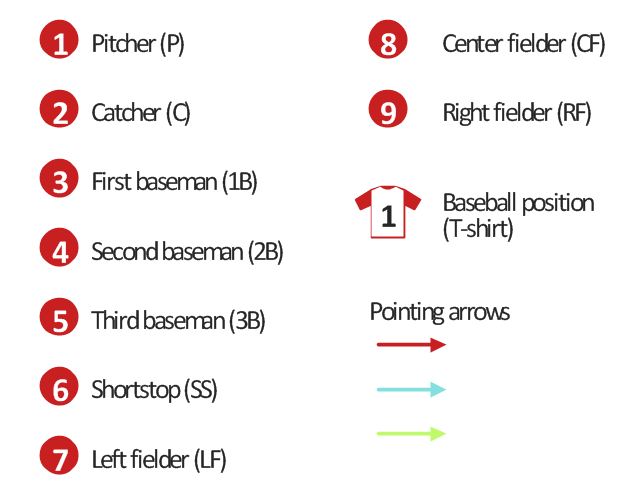
The vector stencils library "Baseball positions" contains 13 symbols: pitcher, catcher, first baseman, second baseman, third baseman, shortstop, left fielder, center fielder, right fielder, baseball position, pointing arrows.
"Baseball is unlike most other competitive sports in that the defense is given control of the ball. Additionally, the number of players on the field at any given time is lopsided in favor of the defense which always has nine players on the field; the offense has between one and four. ...
Each play starts with the ball in the hands of the pitcher, whose job as a member of the defense is to use his skills to somehow prevent the batter from reaching base. The pitcher throws the ball toward the catcher, whose must catch the pitched ball if it is not hit by the batter. In each half-inning, the defense attempts to force three outs.
There are three basic ways in which an out can occur: 1.) If three strikes are recorded against the batter, 2.) if a ball hit by a batter is caught by a defensive player before it hits the ground, or 3.) if a runner who is between bases or has not reached a base to which he is forced is put out by a defensive player in possession of the ball.
If the batter manages to hit the ball, all nine defensive players become active and use the ball in attempting to prevent the batter from reaching base and runners already on base from advancing or scoring. while the offense is busy attempting to move runners around the baseball diamond toward home plate, the defense uses the ball in various ways to achieve outs.
If the defense forces three outs, their team is moved into the offensive role. The exception is if it is the ninth or an extra inning and they are ahead, in which case, the game ends and the defensive team wins." [Defense (sports). Wikipedia]
The symbols example "Design elements - Baseball positions" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Baseball solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Baseball is unlike most other competitive sports in that the defense is given control of the ball. Additionally, the number of players on the field at any given time is lopsided in favor of the defense which always has nine players on the field; the offense has between one and four. ...
Each play starts with the ball in the hands of the pitcher, whose job as a member of the defense is to use his skills to somehow prevent the batter from reaching base. The pitcher throws the ball toward the catcher, whose must catch the pitched ball if it is not hit by the batter. In each half-inning, the defense attempts to force three outs.
There are three basic ways in which an out can occur: 1.) If three strikes are recorded against the batter, 2.) if a ball hit by a batter is caught by a defensive player before it hits the ground, or 3.) if a runner who is between bases or has not reached a base to which he is forced is put out by a defensive player in possession of the ball.
If the batter manages to hit the ball, all nine defensive players become active and use the ball in attempting to prevent the batter from reaching base and runners already on base from advancing or scoring. while the offense is busy attempting to move runners around the baseball diamond toward home plate, the defense uses the ball in various ways to achieve outs.
If the defense forces three outs, their team is moved into the offensive role. The exception is if it is the ninth or an extra inning and they are ahead, in which case, the game ends and the defensive team wins." [Defense (sports). Wikipedia]
The symbols example "Design elements - Baseball positions" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Baseball solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Marketing Area
Marketing Area
The solutions from Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park collect templates, samples and libraries of vector stencils for drawing the marketing diagrams and mind maps.
Target Diagram
Target Diagram is a convenient and visual way of presentation information which is popular and widely used in marketing, business and economics. ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is ideal for fast and easy drawing a Target Diagram.- Competitive Forces Examples
- Porters Competitive Forces
- Michael Porters Competitive Forces Model
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy
- The Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy Pdf
- International Business Competitive Forces
- Competitive Forces Analysis
- Porter's Value Chain | Block diagram - Porter's five forces model ...
- Block diagram - Porter's five forces model | Porter's Value Chain ...
- Draw Porter Generic Competitive Strategy
- Porter's generic strategies matrix diagram | Block diagram - Porter's ...
- Competitor Analysis | Block diagram - Porter's five forces model ...
- Concept Draw Competition
- Block diagram - Porter's five forces model
- Block diagram - Porter's five forces model | Competitor Analysis ...
- Block diagram - Porter's five forces model | Process Flowchart ...
- Block diagram - Porter's five forces model | Marketing Diagrams ...
- Five forces model - Template
- Block diagram - Porter's five forces model | Target diagrams - Vector ...
- Five forces model