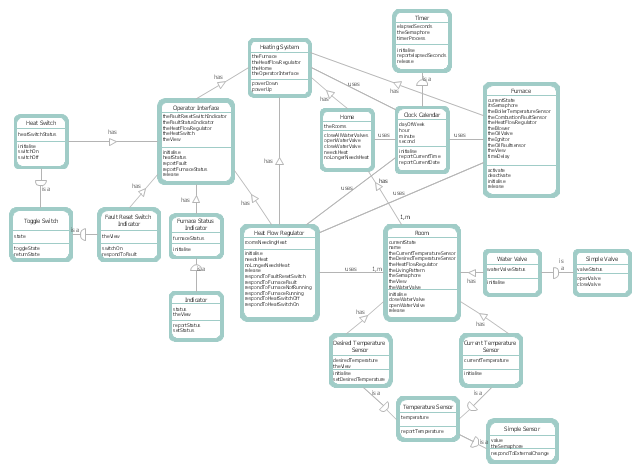
This DFD sample was created on the base of the figure illustrating "A Survey of Object-Oriented Methods" by Peter Biggs from University of Durham.
[students.cs.byu.edu/ ~pbiggs/ images/ coadsys.gif]
"Object-oriented analysis and design (OOAD) is a popular technical approach to analyzing, designing an application, system, or business by applying the object-oriented paradigm and visual modeling throughout the development life cycles to foster better stakeholder communication and product quality.
According to the popular guide Unified Process, OOAD in modern software engineering is best conducted in an iterative and incremental way. Iteration by iteration, the outputs of OOAD activities, analysis models for OOA and design models for OOD respectively, will be refined and evolve continuously driven by key factors like risks and business values." [Object-oriented analysis and design. Wikipedia]
The DFD example "Coad/ Yourdon's Object-Oriented Analysis model" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Data Flow Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[students.cs.byu.edu/ ~pbiggs/ images/ coadsys.gif]
"Object-oriented analysis and design (OOAD) is a popular technical approach to analyzing, designing an application, system, or business by applying the object-oriented paradigm and visual modeling throughout the development life cycles to foster better stakeholder communication and product quality.
According to the popular guide Unified Process, OOAD in modern software engineering is best conducted in an iterative and incremental way. Iteration by iteration, the outputs of OOAD activities, analysis models for OOA and design models for OOD respectively, will be refined and evolve continuously driven by key factors like risks and business values." [Object-oriented analysis and design. Wikipedia]
The DFD example "Coad/ Yourdon's Object-Oriented Analysis model" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Data Flow Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
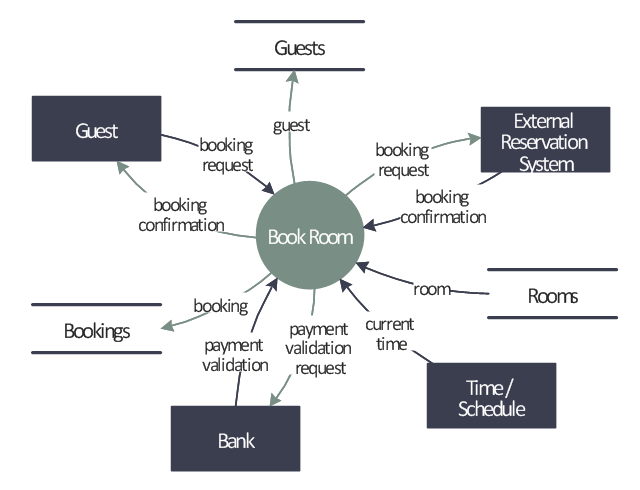
This example was redesigned from the Wikipedia file: LastResortHotel BookRoom Process.png. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:LastResortHotel_ BookRoom_ Process.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ ]
"Event partitioning is an easy-to-apply systems analysis technique that helps the analyst organize requirements for large systems into a collection of smaller, simpler, minimally-connected, easier-to-understand ‘mini systems’ / use cases. ...
Defining requirements.
Single process in a fictitious hotel using data flow diagram notation.
Single use case in a fictitious hotel using use case diagram notation.
This approach helps the analyst to decompose the system into ‘mentally bite-sized’ mini-systems using events that require a planned response. The level of detail of each response is at the level of ‘primary use cases’. Each planned response may be modelled using DFD notation or as a single use case using use case diagram notation.
The basic flow within a process or use case can usually be described in a relatively small number of steps, often fewer than twenty or thirty, possibly using something like ‘structured English’. Ideally, all of the steps would be visible all at once (often a page or less). The intention is to reduce one of the risks associated with short-term memory, namely, forgetting what is not immediately visible (‘out of sight, out of mind’). ...
Single process in a fictitious hotel using data flow diagram notation." [Event partitioning. Wikipedia]
The DFD example "Last resort hotel book room process" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Data Flow Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ ]
"Event partitioning is an easy-to-apply systems analysis technique that helps the analyst organize requirements for large systems into a collection of smaller, simpler, minimally-connected, easier-to-understand ‘mini systems’ / use cases. ...
Defining requirements.
Single process in a fictitious hotel using data flow diagram notation.
Single use case in a fictitious hotel using use case diagram notation.
This approach helps the analyst to decompose the system into ‘mentally bite-sized’ mini-systems using events that require a planned response. The level of detail of each response is at the level of ‘primary use cases’. Each planned response may be modelled using DFD notation or as a single use case using use case diagram notation.
The basic flow within a process or use case can usually be described in a relatively small number of steps, often fewer than twenty or thirty, possibly using something like ‘structured English’. Ideally, all of the steps would be visible all at once (often a page or less). The intention is to reduce one of the risks associated with short-term memory, namely, forgetting what is not immediately visible (‘out of sight, out of mind’). ...
Single process in a fictitious hotel using data flow diagram notation." [Event partitioning. Wikipedia]
The DFD example "Last resort hotel book room process" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Data Flow Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Data Flow Diagram For Job Application
- Data Flow Diagram For Online Job Application System
- Sample Application Data Flow Diagram
- Application Context Diagram
- Data Flow Diagram For Web Application
- Data Flow Diagram With Easy Business Example
- Data Flow Diagrams ( DFD ) | Types of Flowchart - Overview ...
- DFD Library System | Process Flowchart | Functional Block Diagram ...
- Data Flow Diagram Examples For Android Application
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Data Flow Diagram ...
- Data flow Model Diagram | Data Flow Diagram Model | Structured ...
- Mail Server Dfd Diagram Context Level
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Data Flow Diagram ...
- Described The Flow Chart Job Application
- Data Flow Diagram For Health Care System
- Example of DFD for Online Store
- Data Flow Diagram Of Medical Store Management System
- Gane Sarson Diagram | DFD , Gane-Sarson notation - Vector stencils ...
- DFD Library System | Data Flow Diagram Symbols. DFD Library ...
- Dfd For Barcode System