Active Directory Domain Services
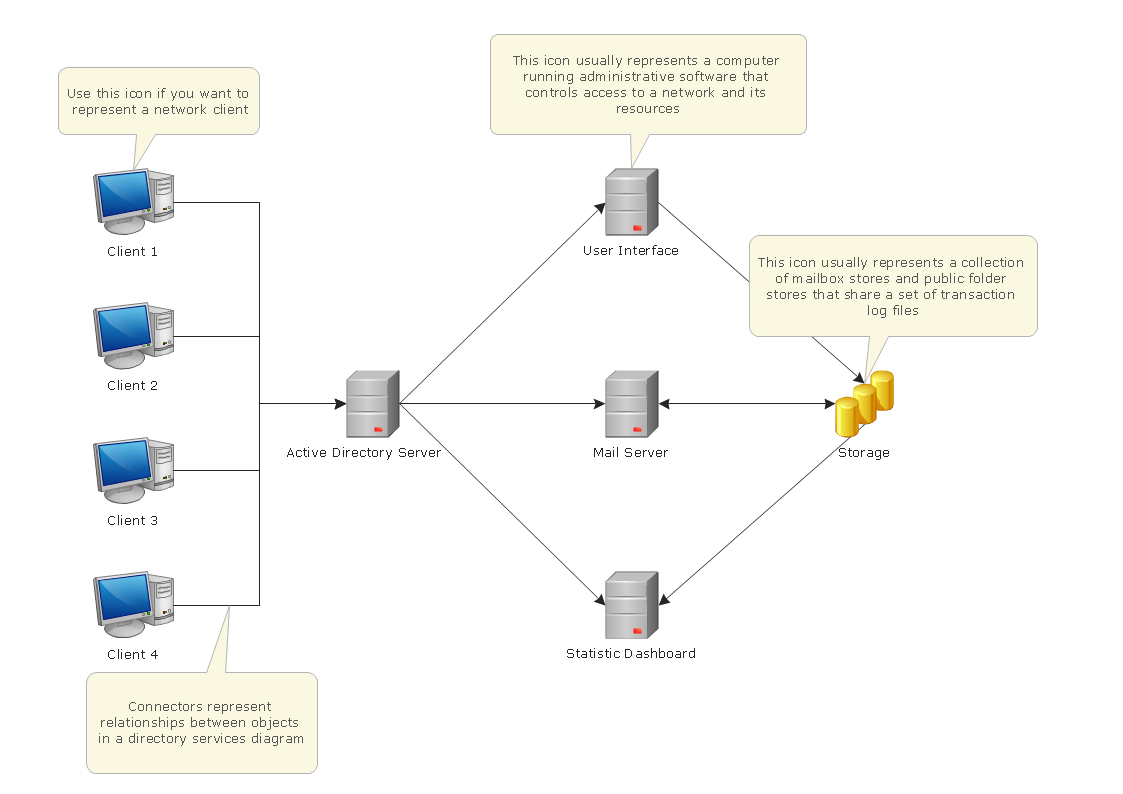
Active Directory Diagrams visualize the detailed structures of the Microsoft Windows networks, Active Directory Domain topology, the Active Directory Site topology, the Organizational Units (OU), and the Exchange Server Organization.This example was drawn on the base of the Figure 2 illustrating the "Active Directory FAQ" from the website "Information Management Systems & Services" (IMSS) of the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) campus. [imss.caltech.edu/ node/ 412]
"By using the Active Directory® Domain Services (AD DS) server role, you can create a scalable, secure, and manageable infrastructure for user and resource management, and you can provide support for directory-enabled applications, such as Microsoft® Exchange Server. ...
AD DS provides a distributed database that stores and manages information about network resources and application-specific data from directory-enabled applications. Administrators can use AD DS to organize elements of a network, such as users, computers, and other devices, into a hierarchical containment structure. The hierarchical containment structure includes the Active Directory forest, domains in the forest, and organizational units (OUs) in each domain. A server that is running AD DS is called a domain controller." [technet.microsoft.com/ en-us/ library/ 9a5cba91-7153-4265-adda-c70df2321982]
The Active Directory Domain Services diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Active Directory Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"By using the Active Directory® Domain Services (AD DS) server role, you can create a scalable, secure, and manageable infrastructure for user and resource management, and you can provide support for directory-enabled applications, such as Microsoft® Exchange Server. ...
AD DS provides a distributed database that stores and manages information about network resources and application-specific data from directory-enabled applications. Administrators can use AD DS to organize elements of a network, such as users, computers, and other devices, into a hierarchical containment structure. The hierarchical containment structure includes the Active Directory forest, domains in the forest, and organizational units (OUs) in each domain. A server that is running AD DS is called a domain controller." [technet.microsoft.com/ en-us/ library/ 9a5cba91-7153-4265-adda-c70df2321982]
The Active Directory Domain Services diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Active Directory Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Active Directory Diagrams
Active Directory Diagrams
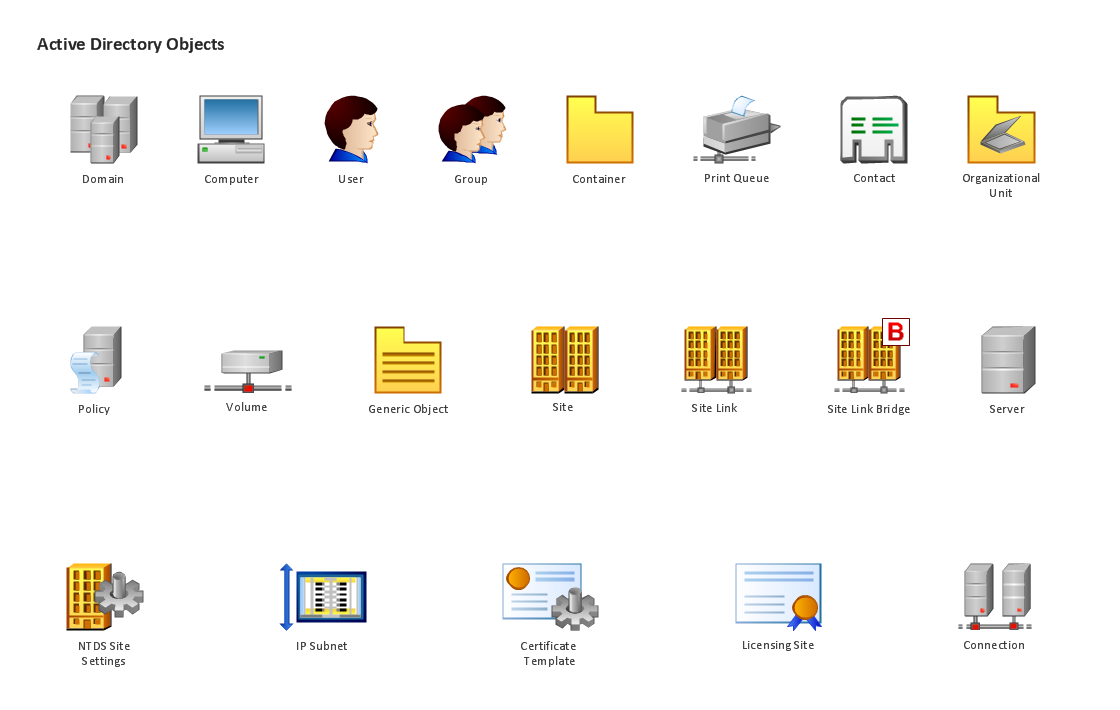
Active Directory Diagrams solution significantly extends the capabilities of ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software with special Active Directory samples, convenient template and libraries of Active Directory vector stencils, common icons of sites and services, icons of LDPA elements, which were developed to help you in planning and modelling network structures and network topologies, in designing excellently looking Active Directory diagrams, Active Directory Structure diagrams, and Active Directory Services diagram, which are perfect way to visualize detailed structures of Microsoft Windows networks, Active Directory Domain topology, Active Directory Site topology, Organizational Units (OU), and Exchange Server organization.
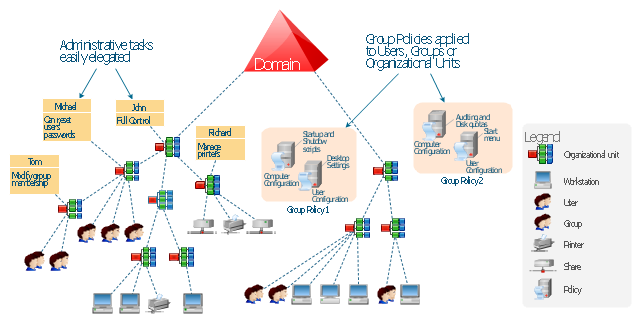
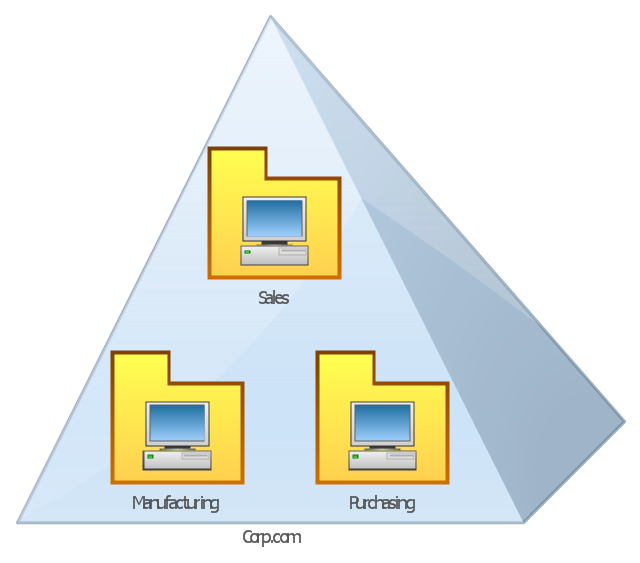
This AD diagram example was redesigned from the picture "Single root domain with a structured OU model" from the book "Active Directory for Dummies".
"A domain is the cornerstone that you lay whenever you create trees and forests. Regardless of whether you design a tree or a forest, the starting point is always the root domain. The root domain is the first domain that you create in your AD structure, and it sits at the top of your diagram.
The root domain of your tree, similar to any other domain, is a grouping of
resources built on the following components:
(1) Domain controllers.
(2) Security policies. ...
For many small and medium-sized companies, a single root domain with a
structured OU (organizational unit) model... provides sufficient flexibility for an AD tree. ...
However, larger companies, companies with complex organization charts, and
companies with multiple sites often find that a single domain isn’t suitable." [Steve Clines and Marcia Loughry, Active Directory® For Dummies®, 2nd Edition. 2008]
The Active Directory diagram example "Single root domain with a structured OU model" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Active Directory Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A domain is the cornerstone that you lay whenever you create trees and forests. Regardless of whether you design a tree or a forest, the starting point is always the root domain. The root domain is the first domain that you create in your AD structure, and it sits at the top of your diagram.
The root domain of your tree, similar to any other domain, is a grouping of
resources built on the following components:
(1) Domain controllers.
(2) Security policies. ...
For many small and medium-sized companies, a single root domain with a
structured OU (organizational unit) model... provides sufficient flexibility for an AD tree. ...
However, larger companies, companies with complex organization charts, and
companies with multiple sites often find that a single domain isn’t suitable." [Steve Clines and Marcia Loughry, Active Directory® For Dummies®, 2nd Edition. 2008]
The Active Directory diagram example "Single root domain with a structured OU model" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Active Directory Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Enterprise Architecture Diagrams
Enterprise Architecture Diagrams
Enterprise Architecture Diagrams solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software with templates, samples and library of vector stencils for drawing the diagrams of enterprise architecture models.
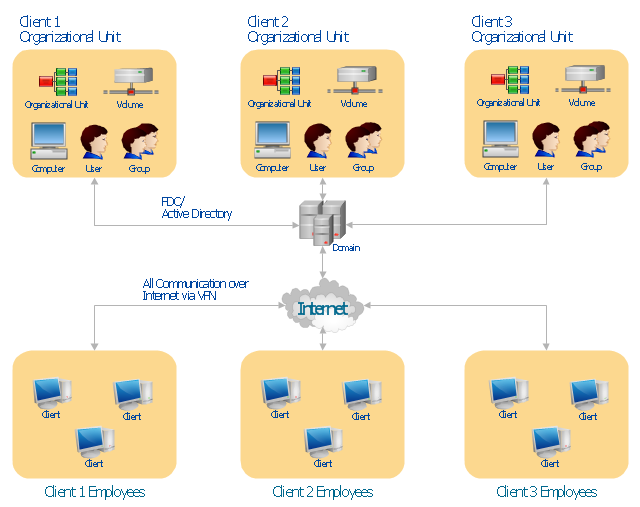
"Microsoft Windows 2000 Server introduces Active Directory to replace domain functionality. Active Directory will continue to get the job done, but in a much more efficient way. Active Directory can be replicated between multiple domain controllers, so no single system is critical. In this way, the crucial data stored within Active Directory is both redundant and load-balanced.
A directory, in the most generic sense, is a comprehensive listing of objects. A phone book is a type of directory that stores information about people, businesses, and government organizations. Phone books typically record names, addresses, and phone numbers. Active Directory is similar to a phone book in several ways, and it is far more flexible. Active Directory will store information about organizations, sites, systems, users, shares, and just about any other network object that you can imagine. Not all objects are as similar to each other as those stored in the phone book, so Active Directory includes the ability to record different types of information about different objects." [technet.microsoft.com/ en-us/ library/ bb742424.aspx]
The AD diagram example "Active Directory structure diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Active Directory Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
A directory, in the most generic sense, is a comprehensive listing of objects. A phone book is a type of directory that stores information about people, businesses, and government organizations. Phone books typically record names, addresses, and phone numbers. Active Directory is similar to a phone book in several ways, and it is far more flexible. Active Directory will store information about organizations, sites, systems, users, shares, and just about any other network object that you can imagine. Not all objects are as similar to each other as those stored in the phone book, so Active Directory includes the ability to record different types of information about different objects." [technet.microsoft.com/ en-us/ library/ bb742424.aspx]
The AD diagram example "Active Directory structure diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Active Directory Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Network Diagram Examples
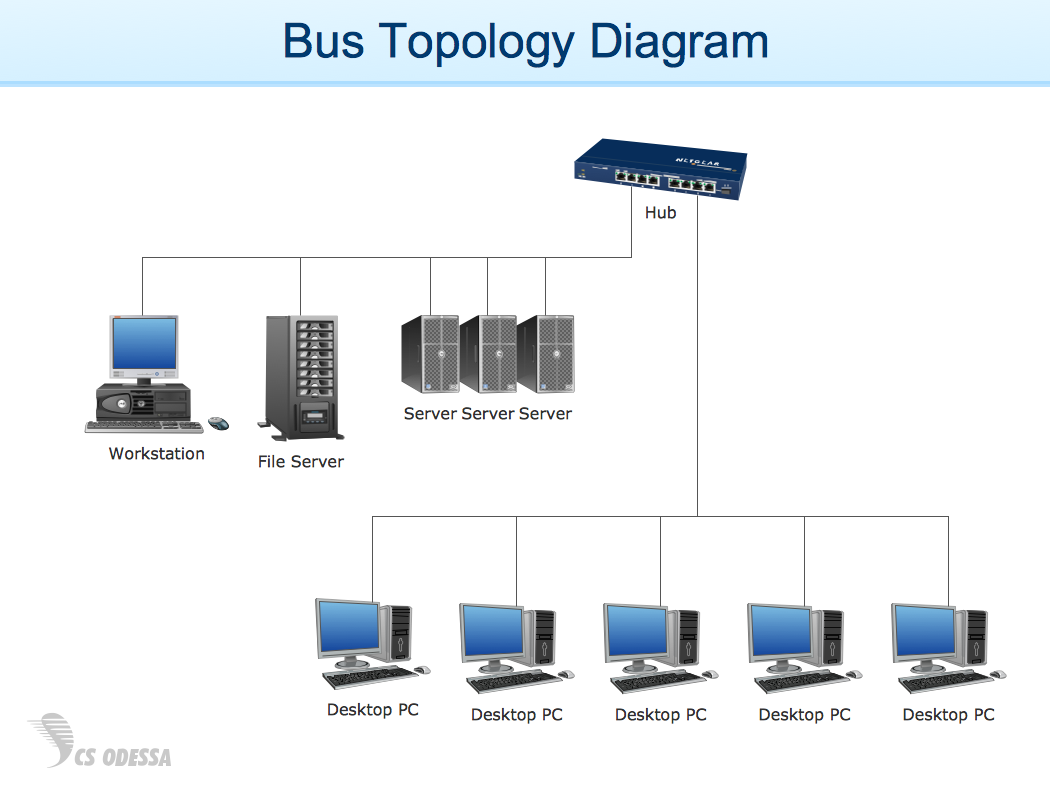
Network diagram is a chart which represents nodes and connections between them in computer network or any telecommunication network, it is a visual depiction of network architecture, physical or logical network topology. There are used common icons for the Network diagrams design, such as icons of various network appliances, computer devices, routers, clouds, peripheral devices, digital devices, etc. Network diagrams can represent networks of different scales (LAN level, WAN level) and detailization. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming software enhanced with Computer Network Diagrams solution from Computer and Networks area includes huge collection of computer and network templates, design objects and stencils, and numerous quantity of Network diagram examples and samples, among them: Basic Computer Network Diagrams, Communication Network Diagram, Wireless Router Network Diagram, LAN Topology Diagram, Computer Network System Design Diagram, Mobile Satellite Communication Network, Web-based Network Diagram, Hybrid Network Diagram, and many others.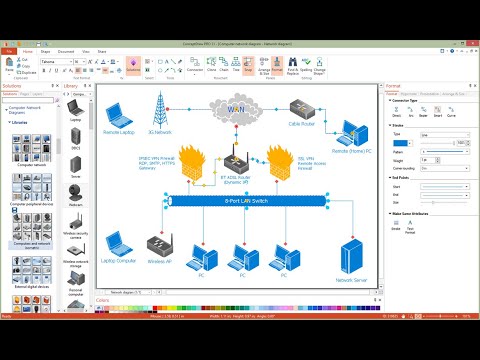
Design Element: Active Directory for Network Diagrams
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is perfect for software designers and software developers who need to draw Active Directory Network Diagrams.
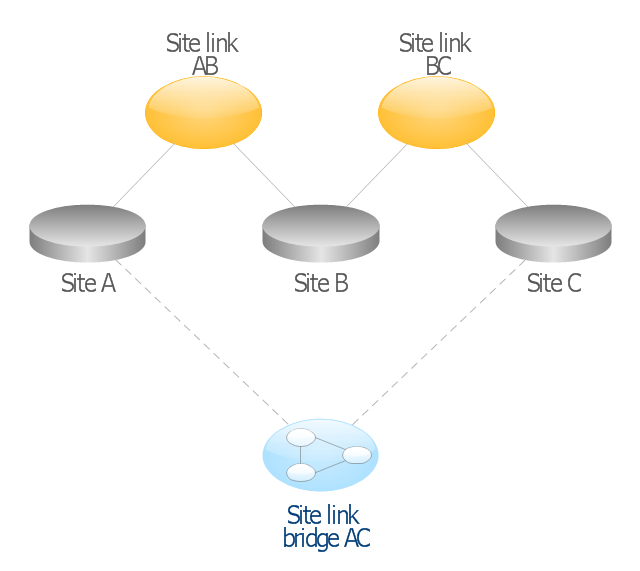
This AD diagram example was redesigned from the picture "Site links" from the book "Active Directory for Dummies".
"Site links represent the Active Directory replication paths between sites.
These paths are manually defined so that the designer has control over which network links the replication traffic occurs on. These site links also control how clients are directed to domain controllers when there’s no DC in the client’s local site. Each site link has the following attributes:
(1) Connected sites: A site link is defined by the sites to which it connects. A site link can connect two or more sites together.
(2) Network transport: Site links support replication communication over IP-based RPCs or with the Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP). You normally want to use RPC whenever possible, but you can use SMTP when the sites you’re linking don’t support RPC.
(3) Cost: Each site link has a cost associated with it. Costs are used to assign preferences to links that determine which link should be followed when multiple link paths are available between sites. The cost represents what it “costs” to use this site link relative to the other site links and affects replication traffic as well as how users are assigned a domain controller. Links with lower cost values have preference over links with higher cost values. Cost values range from 1–32,767; the default being 100.
(4) Frequency: The frequency value defines how often a replication occurs
when using this site link (the replication latency). You can configure the time between replications from a minimum of 15 minutes to a maximum of 10,080 minutes (one week). The default frequency is 180 minutes.
(5) Schedule: The schedule dictates when this link is active and available for replication between the sites. The schedule can also control which days of the week the link is available. Normally, the schedule is set so that the link is available 24 hours a day, but you can set up different schedules on a per-day-of-the-week basis.
By creating a site link, you enable two or more sites to be connected and to share the same site link attributes (transport, cost, frequency, and schedule). By default, site links create transitive connectivity between sites.
If you create a site link between sites A and B and another site link between
sites B and C, an automatic connection (known as a site link bridge) is created between sites A and C..." [Steve Clines and Marcia Loughry, Active Directory® For Dummies®, 2nd Edition. 2008]
The Active Directory diagram example "Site links" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Active Directory Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Site links represent the Active Directory replication paths between sites.
These paths are manually defined so that the designer has control over which network links the replication traffic occurs on. These site links also control how clients are directed to domain controllers when there’s no DC in the client’s local site. Each site link has the following attributes:
(1) Connected sites: A site link is defined by the sites to which it connects. A site link can connect two or more sites together.
(2) Network transport: Site links support replication communication over IP-based RPCs or with the Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP). You normally want to use RPC whenever possible, but you can use SMTP when the sites you’re linking don’t support RPC.
(3) Cost: Each site link has a cost associated with it. Costs are used to assign preferences to links that determine which link should be followed when multiple link paths are available between sites. The cost represents what it “costs” to use this site link relative to the other site links and affects replication traffic as well as how users are assigned a domain controller. Links with lower cost values have preference over links with higher cost values. Cost values range from 1–32,767; the default being 100.
(4) Frequency: The frequency value defines how often a replication occurs
when using this site link (the replication latency). You can configure the time between replications from a minimum of 15 minutes to a maximum of 10,080 minutes (one week). The default frequency is 180 minutes.
(5) Schedule: The schedule dictates when this link is active and available for replication between the sites. The schedule can also control which days of the week the link is available. Normally, the schedule is set so that the link is available 24 hours a day, but you can set up different schedules on a per-day-of-the-week basis.
By creating a site link, you enable two or more sites to be connected and to share the same site link attributes (transport, cost, frequency, and schedule). By default, site links create transitive connectivity between sites.
If you create a site link between sites A and B and another site link between
sites B and C, an automatic connection (known as a site link bridge) is created between sites A and C..." [Steve Clines and Marcia Loughry, Active Directory® For Dummies®, 2nd Edition. 2008]
The Active Directory diagram example "Site links" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Active Directory Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This enterprise architecture diagram sample was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Enterprise Architecture Domains Subdomains.jpg.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Enterprise_ Architecture_ Domains_ Subdomains.jpg]
An enterprise architecture’s landscape is usually divided into various domains based on the attributes of the environment and the logical grouping based on Industry EA Frameworks.
Enterprise Architecture consists of 5 domains: Business, Application, Information, and Technical (Infrastructure and Telecom).
The example "Enterprise architecture domains" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Enterprise Architecture Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Enterprise_ Architecture_ Domains_ Subdomains.jpg]
An enterprise architecture’s landscape is usually divided into various domains based on the attributes of the environment and the logical grouping based on Industry EA Frameworks.
Enterprise Architecture consists of 5 domains: Business, Application, Information, and Technical (Infrastructure and Telecom).
The example "Enterprise architecture domains" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Enterprise Architecture Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Domain Structure Example Diagram
- Active Directory Diagram | Active Directory Domain Services ...
- Domain Controller Diagram
- Active Directory Domain Services | Active Directory Diagram | Active ...
- Domain Server Diagram
- Active Directory Diagram | Active Directory Domain Services | Active ...
- Draw A Typical Window Diagram
- Www Diagram Of Typical Window Com
- Event Setup Diagram
- Physical LAN and WAN diagram - Template
- Organizational Structure | Active Directory Domain Services diagram ...
- Diagram Of Typical Window
- Logical network topology diagram | Network diagrams with ...
- Network diagrams with ConceptDraw PRO | Active Directory ...
- Domain Based Network Diagram
- Active Directory Domain Services | Design Element: Active Directory ...
- Organizational Structure | Active Directory Domain Services diagram ...
- Active Directory Diagram | Active Directory structure diagram | How ...
- Active Directory Domain Services | Active Directory Diagram | Active ...