"There are two competing notions of the predicate in theories of grammar. The first concerns traditional grammar, which tends to view a predicate as one of two main parts of a sentence, the other part being the subject; the purpose of the predicate is to modify the subject. The second derives from work in predicate calculus (predicate logic, first order logic) and is prominent in modern theories of syntax and grammar. In this approach, the predicate of a sentence corresponds mainly to the main verb and any auxiliaries that accompany the main verb, whereas the arguments of that predicate (e.g. the subject and object noun phrases) are outside the predicate." [Predicate (grammar). Wikipedia]
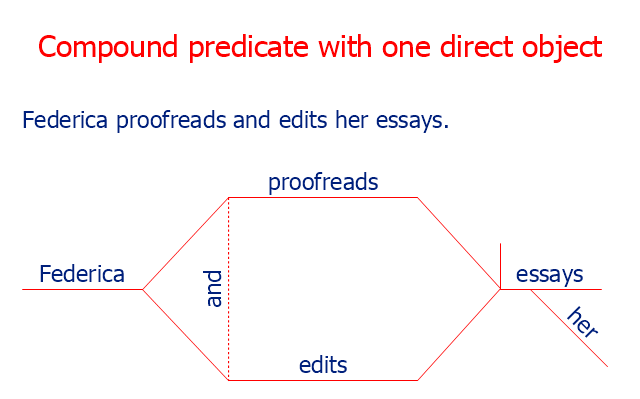
The sentence diagram example "Compound predicate with one direct object" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Language Learning solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The sentence diagram example "Compound predicate with one direct object" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Language Learning solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This sentence diagram sample was createb on the base of the webpage "Diagramming Sentences" from the website of the Capital Community College, Hartford CT. [grammar.ccc.commnet.edu/ grammar/ diagrams2/ one_ pager2.htm]
"In grammar, clause structure refers to the classification of sentences based on the number and kind of clauses in their syntactic structure. Such division is an element of traditional grammar.
A simple sentence consists of only one clause. A compound sentence consists of two or more independent clauses. A complex sentence has at least one independent clause plus at least one dependent clause.
A sentence consisting of one or more dependent clauses plus two or more independent clauses may be called a complex-compound sentence or compound-complex sentence. ...
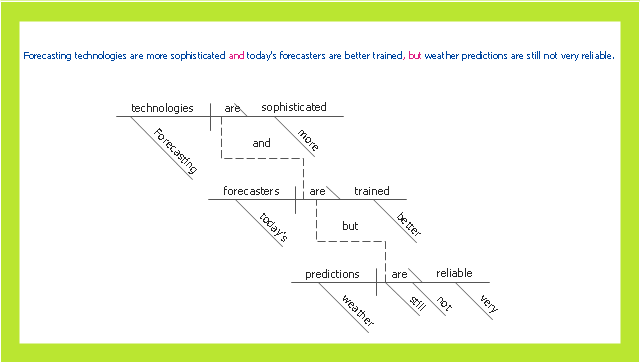
A compound sentence is composed of at least two independent clauses. It does not require a dependent clause. The clauses are joined by a coordinating conjunction (with or without a comma), a semicolon that functions as a conjunction, a colon instead of a semicolon between two sentences when the second sentence explains or illustrates the first sentence and no coordinating conjunction is being used to connect the sentences, or a conjunctive adverb preceded by a semicolon. A conjunction can be used to make a compound sentence. Conjunctions are words such as for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (the first letters of which spell "fanboys"). The use of a comma to separate two independent clauses without the addition of an appropriate conjunction is called a comma splice and is generally considered an error (when used in the English language)." [Sentence clause structure. Wikipedia]
The example "Compound sentence" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Language Learning solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In grammar, clause structure refers to the classification of sentences based on the number and kind of clauses in their syntactic structure. Such division is an element of traditional grammar.
A simple sentence consists of only one clause. A compound sentence consists of two or more independent clauses. A complex sentence has at least one independent clause plus at least one dependent clause.
A sentence consisting of one or more dependent clauses plus two or more independent clauses may be called a complex-compound sentence or compound-complex sentence. ...
A compound sentence is composed of at least two independent clauses. It does not require a dependent clause. The clauses are joined by a coordinating conjunction (with or without a comma), a semicolon that functions as a conjunction, a colon instead of a semicolon between two sentences when the second sentence explains or illustrates the first sentence and no coordinating conjunction is being used to connect the sentences, or a conjunctive adverb preceded by a semicolon. A conjunction can be used to make a compound sentence. Conjunctions are words such as for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (the first letters of which spell "fanboys"). The use of a comma to separate two independent clauses without the addition of an appropriate conjunction is called a comma splice and is generally considered an error (when used in the English language)." [Sentence clause structure. Wikipedia]
The example "Compound sentence" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Language Learning solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
A Sentence Diagram is a pictorial representation of the grammatical structure of a natural-language sentence.
Diagramming sentences is a way to visualize how the different parts of a sentence fit together: the subject of a clause goes in one slot, the verb in another, and so on. Words that modify another word are attached to the word they modify. Understanding the functions of parts of the speech in a sentence and their relationship to one another can be very helpful in learning to construct good sentences.
The diagram of a sentence begins with a horizontal line called the base. The subject is written on the left, the predicate on the right, separated by a vertical bar which extends through the base. The predicate must contain a verb, and the verb either requires other sentence elements to complete the predicate, permits them to do so, or precludes them from doing so. The verb and its object, when present, are separated by a line that ends at the baseline.
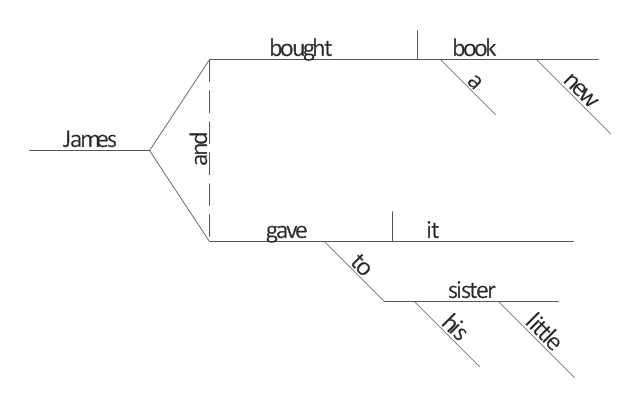
For example, let's consider the following sentence: James bought a new book and gave it to his little sister. So, we see such parts of a sentence:
- James is the subject;
- bought a book and gave it are the compound predicate with direct objects (book, it);
- his sister is the indirect object;
- new, little are adjectives.
[Sentence diagram. Wikipedia]
This sentence diagram template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Language Learning solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Diagramming sentences is a way to visualize how the different parts of a sentence fit together: the subject of a clause goes in one slot, the verb in another, and so on. Words that modify another word are attached to the word they modify. Understanding the functions of parts of the speech in a sentence and their relationship to one another can be very helpful in learning to construct good sentences.
The diagram of a sentence begins with a horizontal line called the base. The subject is written on the left, the predicate on the right, separated by a vertical bar which extends through the base. The predicate must contain a verb, and the verb either requires other sentence elements to complete the predicate, permits them to do so, or precludes them from doing so. The verb and its object, when present, are separated by a line that ends at the baseline.
For example, let's consider the following sentence: James bought a new book and gave it to his little sister. So, we see such parts of a sentence:
- James is the subject;
- bought a book and gave it are the compound predicate with direct objects (book, it);
- his sister is the indirect object;
- new, little are adjectives.
[Sentence diagram. Wikipedia]
This sentence diagram template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Language Learning solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Sentence diagram - Compound predicate with one direct object ...
- Sentence diagram - Compound predicate with one direct object ...
- Sentence diagram - Compound predicate with one direct object ...
- Compound sentence | Sentence diagram - Compound predicate ...
- Sentence diagram - Compound predicate with one direct object ...
- How to Diagram Sentences in ConceptDraw PRO | Sentence ...
- Free Sentence Diagrammer | Sentence diagram - Compound ...
- Examples of Reed-Kellogg diagrams | Sentence diagram ...
- Compound sentence | Sentence diagram - Compound predicate ...
- UML sequence diagram - GET request | Sentence diagram ...
- Design elements - Sentence diagrams | Sentence diagram ...
- How To Diagram A Simple Sentence
- Sentence Diagram | How to Diagram Sentences in ConceptDraw ...
- Free Sentence Diagrammer | Examples of Reed-Kellogg diagrams ...
- Education | Sentence diagram sample | Sentence diagram ...
- How To Diagram A Sentence With An Indirect Object And Direct Object
- Examples of Reed-Kellogg diagrams | Compound sentence ...
- Sentence diagram - Template | Blank Compound Sentence Diagram
- Compound sentence | How to Diagram Sentences in ConceptDraw ...
- English Diagramming Sentences