"Network topology is the arrangement of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer network. Essentially, it is the topological structure of a network, and may be depicted physically or logically. Physical topology refers to the placement of the network's various components, including device location and cable installation, while logical topology shows how data flows within a network, regardless of its physical design. Distances between nodes, physical interconnections, transmission rates, and/ or signal types may differ between two networks, yet their topologies may be identical. The study of network topology recognizes eight basic topologies: Point-to-point, Bus, Star, Ring or circular, Mesh, Tree, Hybrid, Daisy chain." [Network topology. Wikipedia]
The computer network topologies diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The computer network topologies diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Logical topology, or signal topology, is the arrangement of devices on a computer network and how they communicate with one another. How devices are connected to the network through the actual cables that transmit data, or the physical structure of the network, is called the physical topology. Physical topology defines how the systems are physically connected. It represents the physical layout of the devices on the network. The logical topology defines how the systems communicate across the physical topologies.
Logical topologies are bound to network protocols and describe how data is moved across the network. ...
EXAMPLE : twisted pair Ethernet is a logical bus topology in a physical star topology layout. while IBM's token ring is a logical ring topology, it is physically set up in star topology." [Logical topology. Wikipedia]
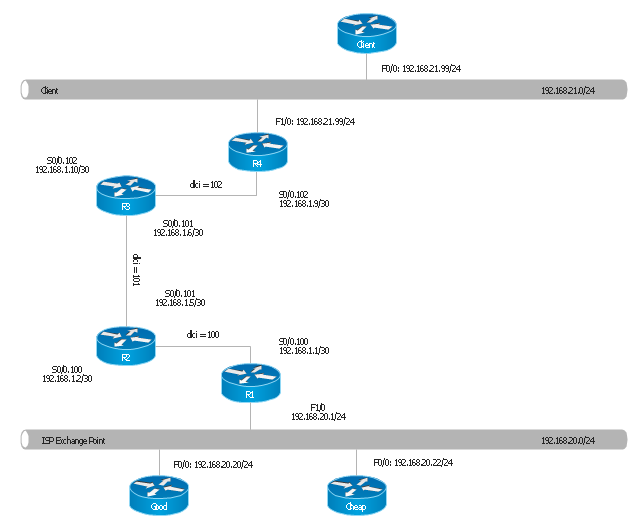
This Cisco logical computer network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Logical topologies are bound to network protocols and describe how data is moved across the network. ...
EXAMPLE : twisted pair Ethernet is a logical bus topology in a physical star topology layout. while IBM's token ring is a logical ring topology, it is physically set up in star topology." [Logical topology. Wikipedia]
This Cisco logical computer network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Differences Between Star And Mesh Network Topologies
- Differentiate Between Star And Bus Topology
- Difference Between Star Topology And Extended Star Topology
- Difference Between Bus Ring And Star Topology
- Different Between Bustopology And Star In Computer
- Deference Between Bus Topology And Star Topology
- Difference Between Star Andbus Topology
- What Is The Difference Between Star Topology And Bus Topology Of
- Using A Diagram Differentiate Between Star Topology And Tree
- Comparison Between Bus Star And Tree Topology
- Difference Between Star Topology And Mesh Topology
- State One Different Between Star And Bus Topology
- Differences Between Star And Bus Topology
- State The Difference Between Bus And Mesh Topology
- Difference Between Star And Bus Topologies Of Connection
- Fully Connected Network Topology Diagram | Star Network ...
- Diffrence Between Bus Topology And Tree Topology
- What Is The Difference Between Star N Bus Topology
- Differentiate Between Mesh Topology And Hybrid Topology
- Diagram Physical Topologies | Network Diagram Software Physical ...