The vector stencils library "Winter Olympics pictograms" contains 29 pictograms and silhouettes.
Use it for drawing Winter Olympics diagrams, infographics and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Winter Sports solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for drawing Winter Olympics diagrams, infographics and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Winter Sports solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In ice hockey, a play is offside if a player on the attacking team enters the offensive zone before the puck, unless the puck is sent or carried there by a defending player. When an offside violation occurs, a linesman will stop play. A faceoff is then held at a neutral ice spot closest to the infraction to restart play. ...
The National Hockey League (NHL) and International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF) apply similar rules for determining offside. A player is judged to be offside if their skates completely cross the blue line dividing their offensive zone from the neutral zone before the puck completely crosses the same line. In both organizations, it is the position of a player's skates that are important. They cannot use their stick or other part of their body to remain onside. The lone caveat to this rule is that an attacking player's skates may precede the puck into the attacking zone when they are skating backwards and if they are in control of the puck." [Offside (ice hockey). Wikipedia]
The ice hockey tactic diagram example "Offside (ice hockey)" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Hockey solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The National Hockey League (NHL) and International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF) apply similar rules for determining offside. A player is judged to be offside if their skates completely cross the blue line dividing their offensive zone from the neutral zone before the puck completely crosses the same line. In both organizations, it is the position of a player's skates that are important. They cannot use their stick or other part of their body to remain onside. The lone caveat to this rule is that an attacking player's skates may precede the puck into the attacking zone when they are skating backwards and if they are in control of the puck." [Offside (ice hockey). Wikipedia]
The ice hockey tactic diagram example "Offside (ice hockey)" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Hockey solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A deke is an ice hockey technique which a player uses to get past an opponent or "fake out" an opposing player. The term is a Canadianism formed by abbreviating decoy.
The deke may originally have referred to quickly pushing the puck forward or laterally with the forehand and catching it on the backhand (or vice-versa), but as hockey has evolved so has the deke and it is now used to refer to a wide variety of feints, fakes or skillful maneuvers to beat defenders or goaltenders. The position of the player performing the deke and the opponent determines where the puck will be moved and the speed. The deke can be used to move the puck out of reach of an opposing player, move the puck past the opposing player, or quickly change direction of the puck so the opposing player is caught out of position. Dekes are usually used in combination with either a change of direction or speed, or both; the deke may refer to the entire sequence of actions as well as the maneuver(s) made with the stick. Often a change in direction or a change in speed is enough to get past an opposing player, but dekes are used in combination with these to better protect the puck and get by a defender." [Deke (ice hockey). Wikipedia]
The ice hockey tactic diagram example "Deke (ice hockey)" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Hockey solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The deke may originally have referred to quickly pushing the puck forward or laterally with the forehand and catching it on the backhand (or vice-versa), but as hockey has evolved so has the deke and it is now used to refer to a wide variety of feints, fakes or skillful maneuvers to beat defenders or goaltenders. The position of the player performing the deke and the opponent determines where the puck will be moved and the speed. The deke can be used to move the puck out of reach of an opposing player, move the puck past the opposing player, or quickly change direction of the puck so the opposing player is caught out of position. Dekes are usually used in combination with either a change of direction or speed, or both; the deke may refer to the entire sequence of actions as well as the maneuver(s) made with the stick. Often a change in direction or a change in speed is enough to get past an opposing player, but dekes are used in combination with these to better protect the puck and get by a defender." [Deke (ice hockey). Wikipedia]
The ice hockey tactic diagram example "Deke (ice hockey)" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Hockey solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
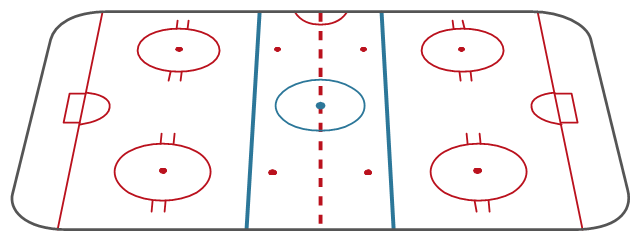
"Markings.
Lines.
The centre line divides the ice in half crosswise. It is used to judge icing, meaning that if a team sends the puck across the centre line (red line), blue line and then across the goal line (that is to say, shoots or dumps the puck past the goal line from behind their own side of the centre line) it is said to be icing. ...
Faceoff spots and circles.
There are 9 faceoff spots on a hockey rink. Most faceoffs take place at these spots. There are two spots in each end zone, two at each end of the neutral zone, and one in the centre of the rink.
There are faceoff circles around the centre ice and end zone faceoff spots. There are hash marks painted on the ice near the end zone faceoff spots. The circles and hash marks show where players may legally position themselves during a faceoff or in game play. ...
Spot and circle dimensions.
Both the center faceoff spot and center faceoff circle are blue. The spot is a solid blue circle 12 inches (30 cm) in diameter. Within the spot is a center, a circle 30 feet (9.1 m) in diameter, painted with a blue line 2 inches (5.1 cm) in width.
All of the other faceoff spots have outlines 2 inches (5.1 cm) thick, forming a circle 2 feet (0.61 m) in diameter measured from the outsides of the outlines, and are filled in with red in all areas except for the 3 inches (7.6 cm) space from the tops and bottoms of the circles, measured from the insides of the outline. ...
Goal posts and nets.
At each end of the ice, there is a goal consisting of a metal goal frame and cloth net in which each team must place the puck to earn points. According to NHL and IIHF rules, the entire puck must cross the entire goal line in order to be counted as a goal. ...
Goal area.
The crease is a special area of the ice designed to allow the goaltender to perform without interference. In most leagues, goals are disallowed if an attacking player enters the goal crease with a stick, skate, or any body part before the puck. For the purposes of this rule, the crease extends vertically from the painted lines to the top of the goal frame. ...
Goaltender trapezoid.
During the 2004-05 American Hockey League (AHL) season, an experimental rule was implemented for the first seven weeks of the season, instituting a goaltender trap zone, more commonly called the trapezoid in reference to its shape. Under the rule, it is prohibited for the goaltender to handle the puck anywhere behind the goal line that is not within the trapezoidal area. If they do so they are assessed a minor penalty for delay of game. ...
Referee's crease.
The referee's crease is a semicircle ten feet in radius in front of the scorekeepers bench." [Ice hockey rink. Wikipedia]
The diagram template "Ice hockey rink view from long side" for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Hockey solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Lines.
The centre line divides the ice in half crosswise. It is used to judge icing, meaning that if a team sends the puck across the centre line (red line), blue line and then across the goal line (that is to say, shoots or dumps the puck past the goal line from behind their own side of the centre line) it is said to be icing. ...
Faceoff spots and circles.
There are 9 faceoff spots on a hockey rink. Most faceoffs take place at these spots. There are two spots in each end zone, two at each end of the neutral zone, and one in the centre of the rink.
There are faceoff circles around the centre ice and end zone faceoff spots. There are hash marks painted on the ice near the end zone faceoff spots. The circles and hash marks show where players may legally position themselves during a faceoff or in game play. ...
Spot and circle dimensions.
Both the center faceoff spot and center faceoff circle are blue. The spot is a solid blue circle 12 inches (30 cm) in diameter. Within the spot is a center, a circle 30 feet (9.1 m) in diameter, painted with a blue line 2 inches (5.1 cm) in width.
All of the other faceoff spots have outlines 2 inches (5.1 cm) thick, forming a circle 2 feet (0.61 m) in diameter measured from the outsides of the outlines, and are filled in with red in all areas except for the 3 inches (7.6 cm) space from the tops and bottoms of the circles, measured from the insides of the outline. ...
Goal posts and nets.
At each end of the ice, there is a goal consisting of a metal goal frame and cloth net in which each team must place the puck to earn points. According to NHL and IIHF rules, the entire puck must cross the entire goal line in order to be counted as a goal. ...
Goal area.
The crease is a special area of the ice designed to allow the goaltender to perform without interference. In most leagues, goals are disallowed if an attacking player enters the goal crease with a stick, skate, or any body part before the puck. For the purposes of this rule, the crease extends vertically from the painted lines to the top of the goal frame. ...
Goaltender trapezoid.
During the 2004-05 American Hockey League (AHL) season, an experimental rule was implemented for the first seven weeks of the season, instituting a goaltender trap zone, more commonly called the trapezoid in reference to its shape. Under the rule, it is prohibited for the goaltender to handle the puck anywhere behind the goal line that is not within the trapezoidal area. If they do so they are assessed a minor penalty for delay of game. ...
Referee's crease.
The referee's crease is a semicircle ten feet in radius in front of the scorekeepers bench." [Ice hockey rink. Wikipedia]
The diagram template "Ice hockey rink view from long side" for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Hockey solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Winter Sports
Winter Sports
The Winter Sports solution from Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park contains winter sports illustration examples, templates and vector clipart libraries.
- Draw A Hockey Stick And Lebel It
- Draw And Label The Hockey Stick And Pitch
- Drawing And Labelling Of Hockey Sticks
- Hockey Stick Drawing And Labelling
- Draw And Label A Hockey Pitch
- Draw And Label Hockey Stick
- Draw And Label A Hockey Pitch The Stick And The Ball
- Soccer (Football) Positions | Hockey Stick And Label
- Draw The Hockey Stick And Label
- Soccer (Football) Positions | Word Exchange | Hockey Stick Diagram ...

























.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)