"Consumption of energy resources, (e.g. turning on a light) requires resources and has an effect on the environment. Many electric power plants burn coal, oil or natural gas in order to generate electricity for energy needs. While burning these fossil fuels produces a readily available and instantaneous supply of electricity, it also generates air pollutants including carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur dioxide and trioxide (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). Carbon dioxide is an important greenhouse gas which is thought to be responsible for some fraction of the rapid increase in global warming seen especially in the temperature records in the 20th century, as compared with tens of thousands of years worth of temperature records which can be read from ice cores taken in Arctic regions. Burning fossil fuels for electricity generation also releases trace metals such as beryllium, cadmium, chromium, copper, manganese, mercury, nickel, and silver into the environment, which also act as pollutants.
The large-scale use of renewable energy technologies would "greatly mitigate or eliminate a wide range of environmental and human health impacts of energy use". Renewable energy technologies include biofuels, solar heating and cooling, hydroelectric power, solar power, and wind power. Energy conservation and the efficient use of energy would also help." [Energy industry. Environmental impact. Wikipedia]
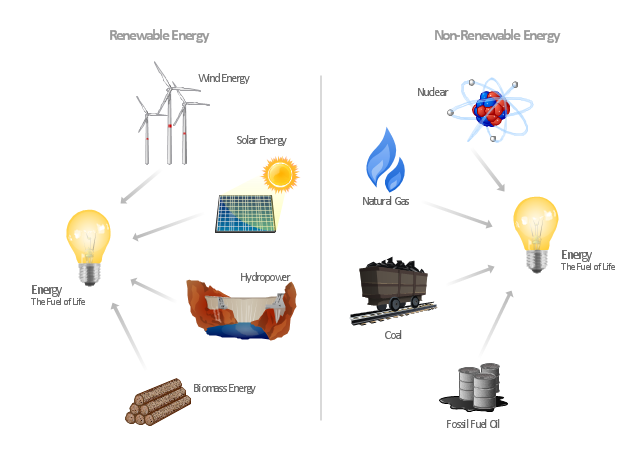
The Energy resources diagram example was created in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software using the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The large-scale use of renewable energy technologies would "greatly mitigate or eliminate a wide range of environmental and human health impacts of energy use". Renewable energy technologies include biofuels, solar heating and cooling, hydroelectric power, solar power, and wind power. Energy conservation and the efficient use of energy would also help." [Energy industry. Environmental impact. Wikipedia]
The Energy resources diagram example was created in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software using the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Resources and energy" contains 19 clipart images for drawing illustrations on resources and energy.
"Natural resources occur naturally within environments that exist relatively undisturbed by humanity, in a natural form. A natural resource is often characterized by amounts of biodiversity and geodiversity existent in various ecosystems.
Natural resources are derived from the environment. Some of them are essential for our survival while most are used for satisfying our wants. Natural resources may be further classified in different ways.
Natural resources are materials and components (something that can be used) that can be found within the environment. Every man-made product is composed of natural resources (at its fundamental level). A natural resource may exist as a separate entity such as fresh water, and air, as well as a living organism such as a fish, or it may exist in an alternate form which must be processed to obtain the resource such as metal ores, oil, and most forms of energy." [Natural resource. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Resources and energy - Vector stencils library" was created in ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software using the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Natural resources occur naturally within environments that exist relatively undisturbed by humanity, in a natural form. A natural resource is often characterized by amounts of biodiversity and geodiversity existent in various ecosystems.
Natural resources are derived from the environment. Some of them are essential for our survival while most are used for satisfying our wants. Natural resources may be further classified in different ways.
Natural resources are materials and components (something that can be used) that can be found within the environment. Every man-made product is composed of natural resources (at its fundamental level). A natural resource may exist as a separate entity such as fresh water, and air, as well as a living organism such as a fish, or it may exist in an alternate form which must be processed to obtain the resource such as metal ores, oil, and most forms of energy." [Natural resource. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Resources and energy - Vector stencils library" was created in ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software using the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
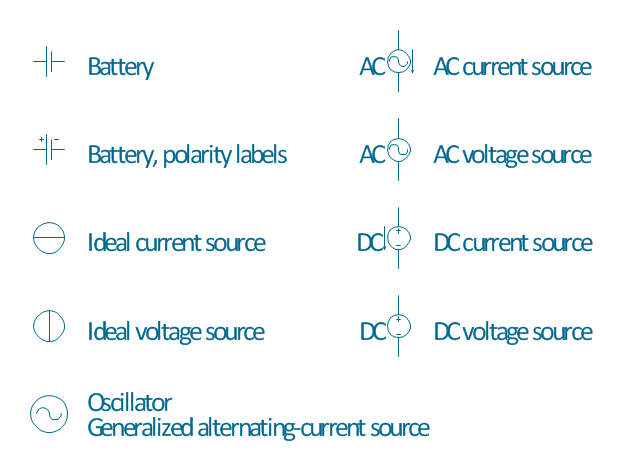
The vector stencils library "Power sources" contains 9 element symbols of power sources and batteries for drawing the electrical schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"A power supply is a device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The term is most commonly applied to electric power converters that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy (mechanical, chemical, solar) to electrical energy. A regulated power supply is one that controls the output voltage or current to a specific value; the controlled value is held nearly constant despite variations in either load current or the voltage supplied by the power supply's energy source.
Every power supply must obtain the energy it supplies to its load, as well as any energy it consumes while performing that task, from an energy source. Depending on its design, a power supply may obtain energy from:
(1) Electrical energy transmission systems. Common examples of this include power supplies that convert AC line voltage to DC voltage.
(2) Energy storage devices such as batteries and fuel cells.
(3) Electromechanical systems such as generators and alternators.
(4) Solar power." [Power supply. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Power sources" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A power supply is a device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The term is most commonly applied to electric power converters that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy (mechanical, chemical, solar) to electrical energy. A regulated power supply is one that controls the output voltage or current to a specific value; the controlled value is held nearly constant despite variations in either load current or the voltage supplied by the power supply's energy source.
Every power supply must obtain the energy it supplies to its load, as well as any energy it consumes while performing that task, from an energy source. Depending on its design, a power supply may obtain energy from:
(1) Electrical energy transmission systems. Common examples of this include power supplies that convert AC line voltage to DC voltage.
(2) Energy storage devices such as batteries and fuel cells.
(3) Electromechanical systems such as generators and alternators.
(4) Solar power." [Power supply. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Power sources" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Manufacturing and Maintenance
Manufacturing and Maintenance
Manufacturing and maintenance solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software with illustration samples, templates and vector stencils libraries with clip art of packaging systems, industrial vehicles, tools, resources and energy.
The vector stencils library "Resources and energy" for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software contains 19 clip art images of energy symbols and natural resources.
"A resource is a source or supply from which benefit is produced. Typically resources are materials, money, services, staff, or other assets that are transformed to produce benefit and in the process may be consumed or made unavailable. Benefits of resource utilization may include increased wealth, meeting needs or wants, proper functioning of a system, or enhanced well being. From a human perspective a natural resource is anything obtained from the environment to satisfy human needs and wants. From a broader biological or ecological perspective a resource satisfies the needs of a living organism.
The concept of resources has been applied in diverse realms, including with respect to economics, biology, computer science, land management, and human resources, and is linked to the concepts of competition, sustainability, conservation, and stewardship. In application within human society, commercial or non-commercial factors require resource allocation through resource management. " [Resource. Wikipedia]
The vector clipart library "Resources and energy" is included the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A resource is a source or supply from which benefit is produced. Typically resources are materials, money, services, staff, or other assets that are transformed to produce benefit and in the process may be consumed or made unavailable. Benefits of resource utilization may include increased wealth, meeting needs or wants, proper functioning of a system, or enhanced well being. From a human perspective a natural resource is anything obtained from the environment to satisfy human needs and wants. From a broader biological or ecological perspective a resource satisfies the needs of a living organism.
The concept of resources has been applied in diverse realms, including with respect to economics, biology, computer science, land management, and human resources, and is linked to the concepts of competition, sustainability, conservation, and stewardship. In application within human society, commercial or non-commercial factors require resource allocation through resource management. " [Resource. Wikipedia]
The vector clipart library "Resources and energy" is included the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This diagram sample illustrates the cooperative vehicular delay-tolerant network operation.
"Delay-tolerant networking (DTN) is an approach to computer network architecture that seeks to address the technical issues in heterogeneous networks that may lack continuous network connectivity. Examples of such networks are those operating in mobile or extreme terrestrial environments, or planned networks in space.
Recently, the term disruption-tolerant networking has gained currency in the United States due to support from DARPA, which has funded many DTN projects. Disruption may occur because of the limits of wireless radio range, sparsity of mobile nodes, energy resources, attack, and noise." [Delay-tolerant networking. Wikipedia]
"Routing in delay-tolerant networking concerns itself with the ability to transport, or route, data from a source to a destination, which is a fundamental ability all communication networks must have. Delay- and disruption-tolerant networks (DTNs) are characterized by their lack of connectivity, resulting in a lack of instantaneous end-to-end paths. In these challenging environments, popular ad hoc routing protocols such as AODV and DSR fail to establish routes. This is due to these protocols trying to first establish a complete route and then, after the route has been established, forward the actual data. However, when instantaneous end-to-end paths are difficult or impossible to establish, routing protocols must take to a "store and forward" approach, where data is incrementally moved and stored throughout the network in hopes that it will eventually reach its destination. A common technique used to maximize the probability of a message being successfully transferred is to replicate many copies of the message in hopes that one will succeed in reaching its destination." [Routing in delay-tolerant networking. Wikipedia]
The example "Cooperative vehicular delay-tolerant network diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Vehicular Networking solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Delay-tolerant networking (DTN) is an approach to computer network architecture that seeks to address the technical issues in heterogeneous networks that may lack continuous network connectivity. Examples of such networks are those operating in mobile or extreme terrestrial environments, or planned networks in space.
Recently, the term disruption-tolerant networking has gained currency in the United States due to support from DARPA, which has funded many DTN projects. Disruption may occur because of the limits of wireless radio range, sparsity of mobile nodes, energy resources, attack, and noise." [Delay-tolerant networking. Wikipedia]
"Routing in delay-tolerant networking concerns itself with the ability to transport, or route, data from a source to a destination, which is a fundamental ability all communication networks must have. Delay- and disruption-tolerant networks (DTNs) are characterized by their lack of connectivity, resulting in a lack of instantaneous end-to-end paths. In these challenging environments, popular ad hoc routing protocols such as AODV and DSR fail to establish routes. This is due to these protocols trying to first establish a complete route and then, after the route has been established, forward the actual data. However, when instantaneous end-to-end paths are difficult or impossible to establish, routing protocols must take to a "store and forward" approach, where data is incrementally moved and stored throughout the network in hopes that it will eventually reach its destination. A common technique used to maximize the probability of a message being successfully transferred is to replicate many copies of the message in hopes that one will succeed in reaching its destination." [Routing in delay-tolerant networking. Wikipedia]
The example "Cooperative vehicular delay-tolerant network diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Vehicular Networking solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
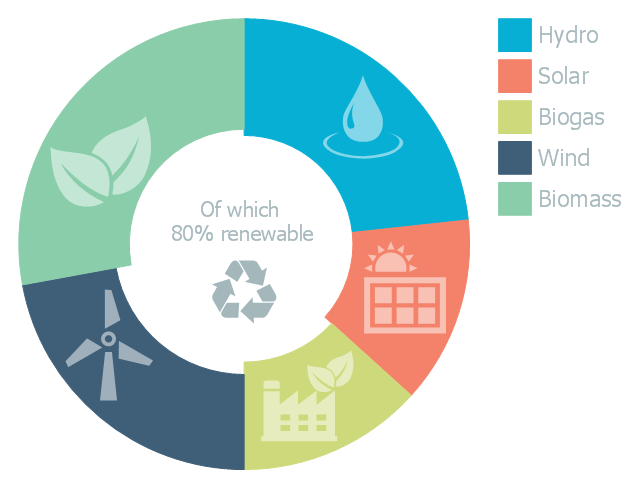
This doughnut chart sample illustrates the renewable energy sources. It was designed on the base of the Wikipedia file: Example of a doughnut chart.png.
[en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Example_ of_ a_ doughnut_ chart.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ ]
"Renewable energy is generally defined as energy that is collected from resources which are naturally replenished on a human timescale, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. Renewable energy often provides energy in four important areas: electricity generation, air and water heating/ cooling, transportation, and rural (off-grid) energy services." [Renewable energy. Wikipedia]
The donut chart example "Renewable energy" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Pie Charts solutiton of the Graphs and Charts area in ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Example_ of_ a_ doughnut_ chart.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ ]
"Renewable energy is generally defined as energy that is collected from resources which are naturally replenished on a human timescale, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. Renewable energy often provides energy in four important areas: electricity generation, air and water heating/ cooling, transportation, and rural (off-grid) energy services." [Renewable energy. Wikipedia]
The donut chart example "Renewable energy" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Pie Charts solutiton of the Graphs and Charts area in ConceptDraw Solution Park.
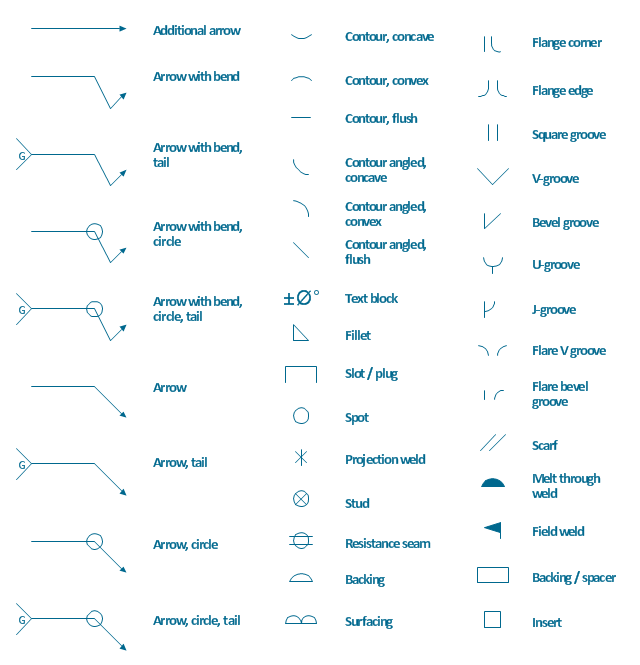
The vector stencils library "Welding" contains 38 welding joint symbols to identify fillets, contours, resistance seams, grooves, surfacing, and backing.
Use it to indicate welding operations on working drawings.
"Welding is a fabrication or sculptural process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. This is often done by melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material (the weld pool) that cools to become a strong joint, with pressure sometimes used in conjunction with heat, or by itself, to produce the weld. This is in contrast with soldering and brazing, which involve melting a lower-melting-point material between the workpieces to form a bond between them, without melting the workpieces.
Many different energy sources can be used for welding, including a gas flame, an electric arc, a laser, an electron beam, friction, and ultrasound.
Welds can be geometrically prepared in many different ways. The five basic types of weld joints are the butt joint, lap joint, corner joint, edge joint, and T-joint (a variant of this last is the cruciform joint). Other variations exist as well - for example, double-V preparation joints are characterized by the two pieces of material each tapering to a single center point at one-half their height. Single-U and double-U preparation joints are also fairly common - instead of having straight edges like the single-V and double-V preparation joints, they are curved, forming the shape of a U. Lap joints are also commonly more than two pieces thick - depending on the process used and the thickness of the material, many pieces can be welded together in a lap joint geometry." [Welding. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Welding" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mechanical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to indicate welding operations on working drawings.
"Welding is a fabrication or sculptural process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. This is often done by melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material (the weld pool) that cools to become a strong joint, with pressure sometimes used in conjunction with heat, or by itself, to produce the weld. This is in contrast with soldering and brazing, which involve melting a lower-melting-point material between the workpieces to form a bond between them, without melting the workpieces.
Many different energy sources can be used for welding, including a gas flame, an electric arc, a laser, an electron beam, friction, and ultrasound.
Welds can be geometrically prepared in many different ways. The five basic types of weld joints are the butt joint, lap joint, corner joint, edge joint, and T-joint (a variant of this last is the cruciform joint). Other variations exist as well - for example, double-V preparation joints are characterized by the two pieces of material each tapering to a single center point at one-half their height. Single-U and double-U preparation joints are also fairly common - instead of having straight edges like the single-V and double-V preparation joints, they are curved, forming the shape of a U. Lap joints are also commonly more than two pieces thick - depending on the process used and the thickness of the material, many pieces can be welded together in a lap joint geometry." [Welding. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Welding" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mechanical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Technical Drawing Software
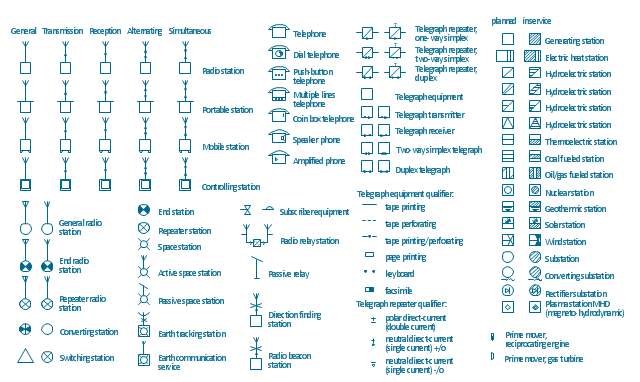
Technical drawing or draft is a form of specialized graphic communication, exchange of ideas in industry and engineering. It is a visual representation of object with indication of dimensions and used material, constructed with maintaining the proportions between its parts. Technical drawings are constructed by architects, technologists, engineers, designers, drafters, and other technical professionals according to defined rules, specifications, internationally accepted standards and standardized notations allowing to make unambiguous, clear and understandable technical drawings. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM extended with Electrical Engineering solution, Mechanical Engineering solution, Chemical and Process Engineering solution from Industrial Engineering Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is ideal technical drawing software. Its powerful drawing tools, predesigned vector objects, templates, samples are helpful for creation all kinds of Technical Drawings and Technical Diagrams, Electrical and Mechanical Schematics, Circuit and Wiring Diagrams, Structural Drawings, and many other.The vector stencils library "Stations" contains 110 symbols of communications equipment, generating, transmitting and receiving stations; substations; satellites; and power plants for power generation and distribution and radio relay systems.
"A power station (also referred to as a generating station, power plant, powerhouse or generating plant) is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. At the center of nearly all power stations is a generator, a rotating machine that converts mechanical power into electrical power by creating relative motion between a magnetic field and a conductor. The energy source harnessed to turn the generator varies widely. It depends chiefly on which fuels are easily available, cheap enough and on the types of technology that the power company has access to. Most power stations in the world burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity, and some use nuclear power, but there is an increasing use of cleaner renewable sources such as solar, wind, wave and hydroelectric." [Power station. Wikipedia]
"Radio broadcasting is a one-way wireless transmission over radio waves intended to reach a wide audience. Stations can be linked in radio networks to broadcast a common radio format, either in broadcast syndication or simulcast or both. Audio broadcasting also can be done via cable radio, local wire television networks, satellite radio, and internet radio via streaming media on the Internet.
The signal types can be either analog audio or digital audio." [Radio broadcasting. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Stations" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A power station (also referred to as a generating station, power plant, powerhouse or generating plant) is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. At the center of nearly all power stations is a generator, a rotating machine that converts mechanical power into electrical power by creating relative motion between a magnetic field and a conductor. The energy source harnessed to turn the generator varies widely. It depends chiefly on which fuels are easily available, cheap enough and on the types of technology that the power company has access to. Most power stations in the world burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity, and some use nuclear power, but there is an increasing use of cleaner renewable sources such as solar, wind, wave and hydroelectric." [Power station. Wikipedia]
"Radio broadcasting is a one-way wireless transmission over radio waves intended to reach a wide audience. Stations can be linked in radio networks to broadcast a common radio format, either in broadcast syndication or simulcast or both. Audio broadcasting also can be done via cable radio, local wire television networks, satellite radio, and internet radio via streaming media on the Internet.
The signal types can be either analog audio or digital audio." [Radio broadcasting. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Stations" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
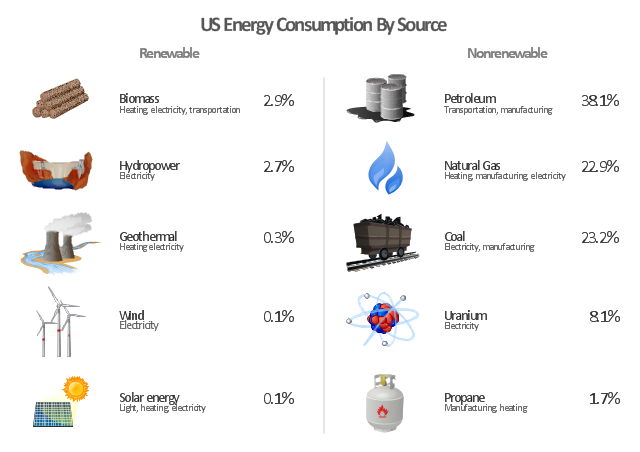
"The United States is the 800th largest energy consumer in terms of total use in 2010. ...
The majority of this energy is derived from fossil fuels: in 2010, data showed 25% of the nation's energy came from petroleum, 22% from coal, and 22% from natural gas. Nuclear power supplied 8.4% and renewable energy supplied 8%, which was mainly from hydroelectric dams although other renewables are included such as wind power, geothermal and solar energy." [Energy in the United States. Wikipedia]
The infographics example "U.S. energy consumption by source" was created in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software using the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The majority of this energy is derived from fossil fuels: in 2010, data showed 25% of the nation's energy came from petroleum, 22% from coal, and 22% from natural gas. Nuclear power supplied 8.4% and renewable energy supplied 8%, which was mainly from hydroelectric dams although other renewables are included such as wind power, geothermal and solar energy." [Energy in the United States. Wikipedia]
The infographics example "U.S. energy consumption by source" was created in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software using the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
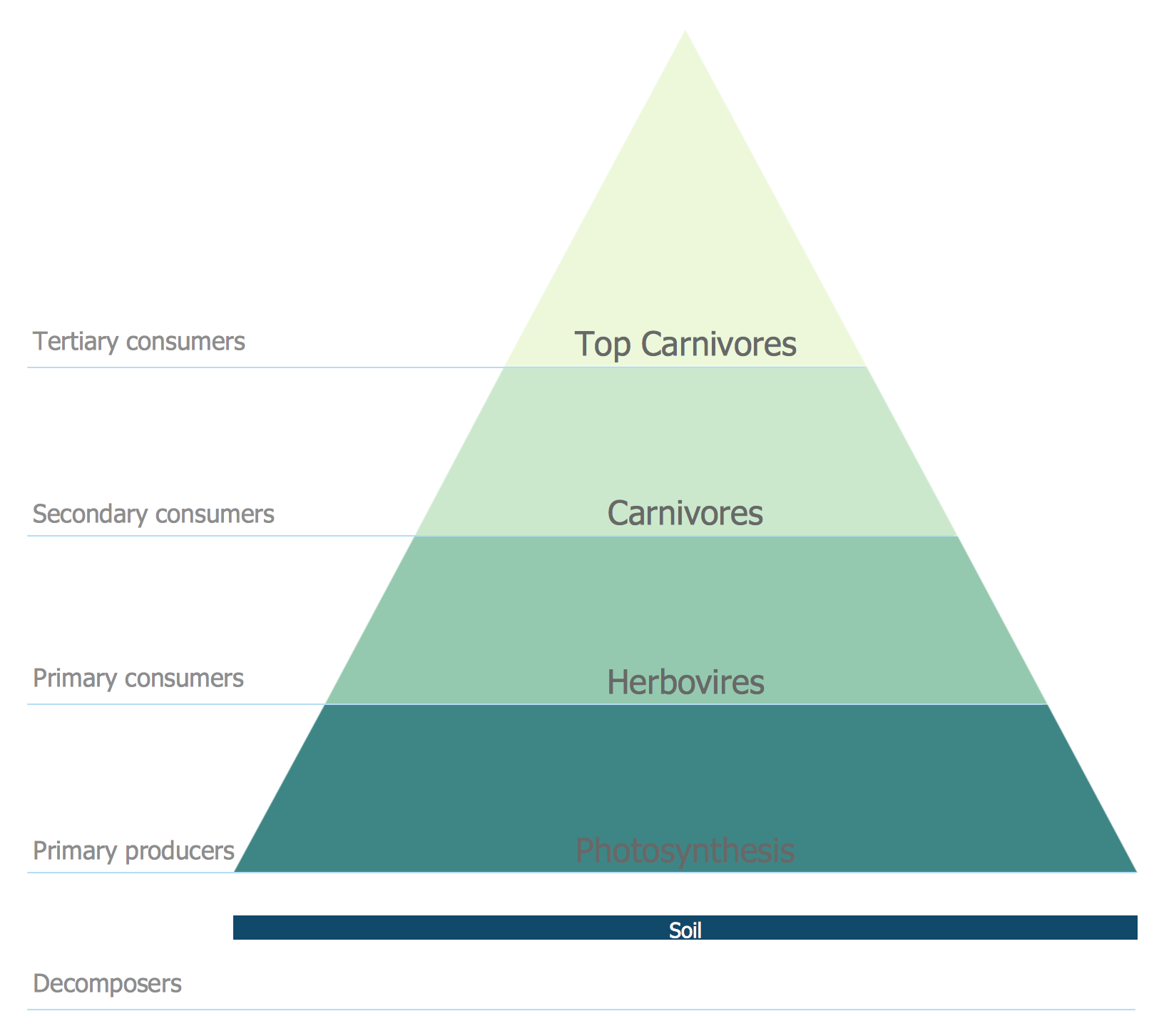
Energy Pyramid Diagram
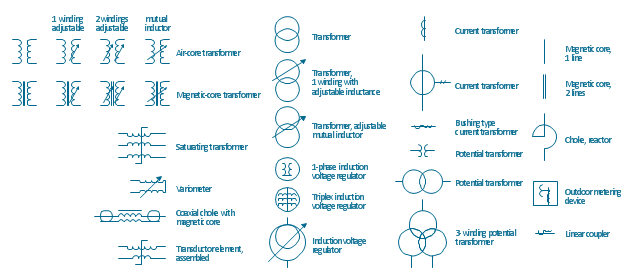
Energy Pyramid Diagram is a visual graphical representation of the biomass productivity on the each trophic level in a given ecosystem. Its designing in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM will not take much time thanks to the unique Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Energy Pyramid Diagram begins from the producers (plants) and proceeds through a few trophic levels of consumers (herbivores which eat these plants, the carnivores which eat these herbivores, then carnivores which eat those carnivores, and so on) to the top of the food chain.The vector stencils library "Transformers and windings" contains 29 element symbols of transformers, windings, couplers, metering devices, transductors, magnetic cores, chokes, and a variometer.
Use it to design the electromechanical device schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers may be used in step-up or step-down voltage conversion, which 'transforms' an AC voltage from one voltage level on the input of the device to another level at the output terminals. This special function of transformers can provide control of specified requirements of current level as an alternating current source, or it may be used for impedance matching between mismatched electrical circuits to effect maximum power transfer between the circuits.
A transformer most commonly consists of two windings of wire that are wound around a common core to induce tight electromagnetic coupling between the windings. The core material is often a laminated iron core. The coil that receives the electrical input energy is referred to as the primary winding, while the output coil is called the secondary winding.
An alternating electric current flowing through the primary winding (coil) of a transformer generates an electromagnetic field in its surroundings and a varying magnetic flux in the core of the transformer. By electromagnetic induction this magnetic flux generates a varying electromotive force in the secondary winding, resulting in a voltage across the output terminals. If a load impedance is connected across the secondary winding, a current flows through the secondary winding drawing power from the primary winding and its power source." [Transformer. Wikipedia]
"An electromagnetic coil (or simply a "coil") is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet. When electricity is passed through a coil, it generates a magnetic field. One loop of wire is usually referred to as a turn or a winding, and a coil consists of one or more turns. For use in an electronic circuit, electrical connection terminals called taps are often connected to a coil. Coils are often coated with varnish or wrapped with insulating tape to provide additional insulation and secure them in place. A completed coil assembly with one or more set of coils and taps is often called the windings.
Windings are used in transformers, electric motors, inductors, solenoids, loudspeakers, and many other applications." [Electromagnetic coil. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transformers and windings" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to design the electromechanical device schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers may be used in step-up or step-down voltage conversion, which 'transforms' an AC voltage from one voltage level on the input of the device to another level at the output terminals. This special function of transformers can provide control of specified requirements of current level as an alternating current source, or it may be used for impedance matching between mismatched electrical circuits to effect maximum power transfer between the circuits.
A transformer most commonly consists of two windings of wire that are wound around a common core to induce tight electromagnetic coupling between the windings. The core material is often a laminated iron core. The coil that receives the electrical input energy is referred to as the primary winding, while the output coil is called the secondary winding.
An alternating electric current flowing through the primary winding (coil) of a transformer generates an electromagnetic field in its surroundings and a varying magnetic flux in the core of the transformer. By electromagnetic induction this magnetic flux generates a varying electromotive force in the secondary winding, resulting in a voltage across the output terminals. If a load impedance is connected across the secondary winding, a current flows through the secondary winding drawing power from the primary winding and its power source." [Transformer. Wikipedia]
"An electromagnetic coil (or simply a "coil") is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet. When electricity is passed through a coil, it generates a magnetic field. One loop of wire is usually referred to as a turn or a winding, and a coil consists of one or more turns. For use in an electronic circuit, electrical connection terminals called taps are often connected to a coil. Coils are often coated with varnish or wrapped with insulating tape to provide additional insulation and secure them in place. A completed coil assembly with one or more set of coils and taps is often called the windings.
Windings are used in transformers, electric motors, inductors, solenoids, loudspeakers, and many other applications." [Electromagnetic coil. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transformers and windings" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Biology Drawing
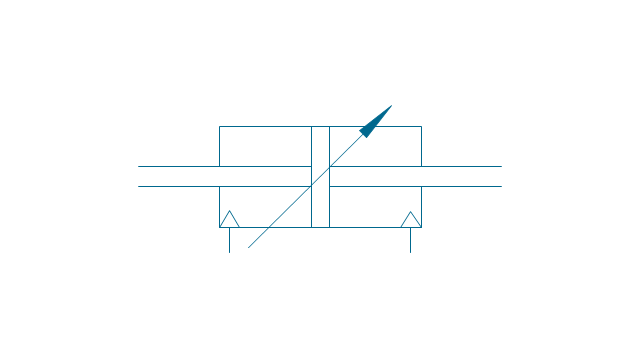
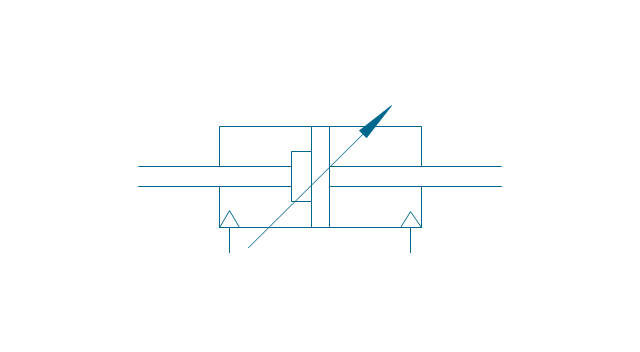
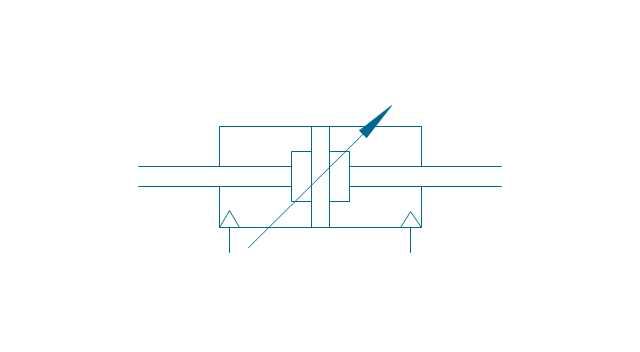
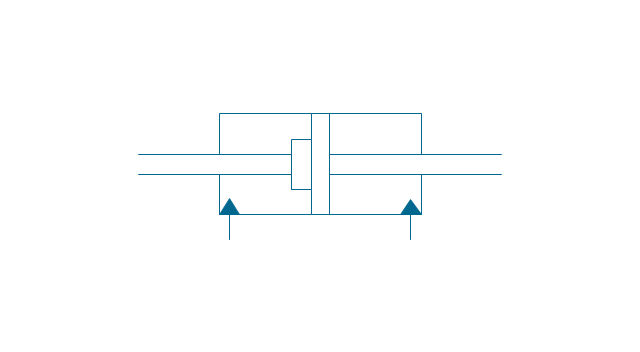
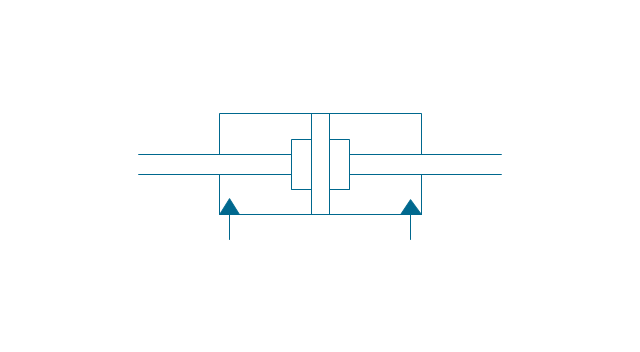
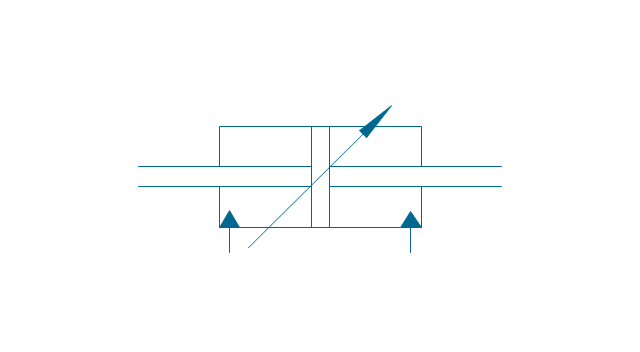
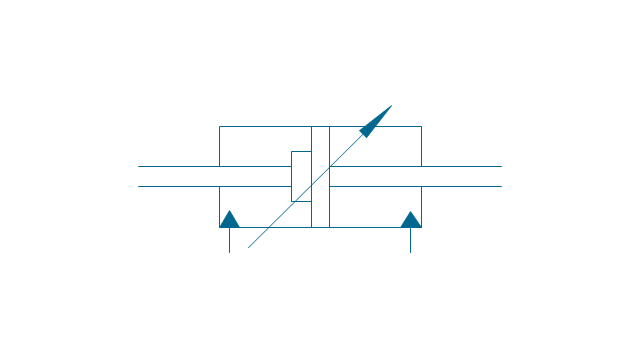
It is impossible to imagine the biology science without drawings. Drawings are very convenient way to explain the different biological knowledge and processes. If you dream to design any biology drawing quick and easy – the ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software is exactly what you need. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Biology solution from the Science and Education area offers the useful tools for easy biology drawing.The vector stencils library "Fluid power equipment" contains 113 symbols of hydraulic and pneumatic equipment including pumps, motors, air compressors, cylinders, meters, gauges, and actuators.
Use it to design fluid power and hydraulic control systems in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mechanical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-mechanical
Use it to design fluid power and hydraulic control systems in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mechanical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-mechanical
How To use House Electrical Plan Software
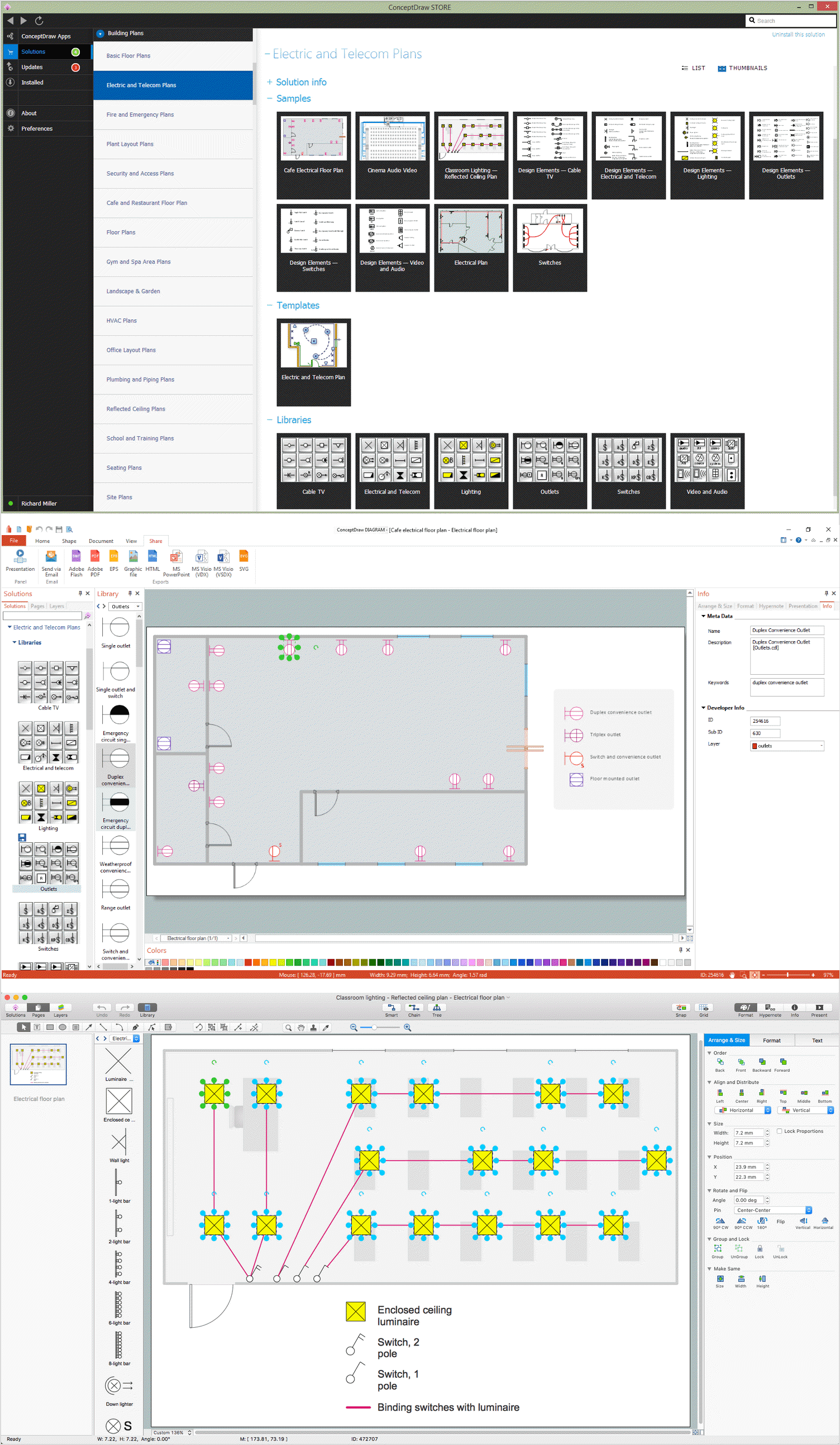
How we can conduct the electricity at house correctly without a plan? It is impossible. The House electrical diagram depicts locations of switches, outlets, dimmers and lights, and lets understand how you will connect them. But design of House Electrical Plan looks a complex task at a glance, which requires a lot of tools and special experience. But now all is simple with all-inclusive floor plan software - ConceptDraw DIAGRAM. As a house electrical plan software, the ConceptDraw DIAGRAM contains libraries with a large range of professional lighting and electrical symbols, ready-to-use electrical plans samples and examples, and built-in templates for creating great-looking Home floor electrical plans. It is a fastest way to draw Electrical circuit diagrams, Electrical wiring and Circuit schematics, Digital circuits, Electrical equipment, House electrical plans, Satellite television, Cable television, Home cinema, Closed-circuit television when are used the tools of Electric and Telecom Plans Solution from ConceptDraw Solution Park. Files created in Visio for Mac app can be easily imported to ConceptDraw DIAGRAM. Also you may import stencils and even libraries. Try for free an alternative to Visio that Apple users recommend.
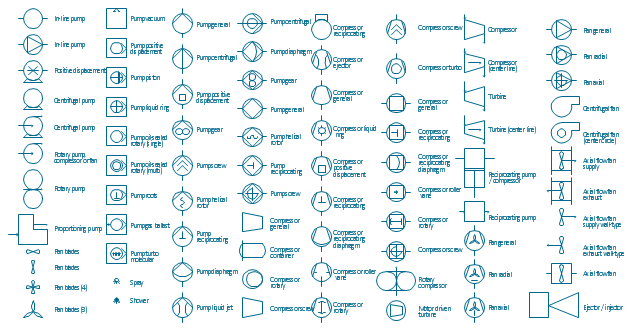
The vector stencils library "Pumps" contains 82 symbols of pumps, compressors, fans, turbines, and power generators.
Use these icons to design pumping systems, air and fluid compression systems, and industrial process diagrams.
"A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they use to move the fluid: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps.
Pumps operate by some mechanism (typically reciprocating or rotary), and consume energy to perform mechanical work by moving the fluid. Pumps operate via many energy sources, including manual operation, electricity, engines, or wind power, come in many sizes, from microscopic for use in medical applications to large industrial pumps.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of applications such as pumping water from wells, aquarium filtering, pond filtering and aeration, in the car industry for water-cooling and fuel injection, in the energy industry for pumping oil and natural gas or for operating cooling towers. In the medical industry, pumps are used for biochemical processes in developing and manufacturing medicine, and as artificial replacements for body parts, in particular the artificial heart and penile prosthesis.
In biology, many different types of chemical and bio-mechanical pumps have evolved, and biomimicry is sometimes used in developing new types of mechanical pumps." [Pump. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Pumps" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these icons to design pumping systems, air and fluid compression systems, and industrial process diagrams.
"A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they use to move the fluid: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps.
Pumps operate by some mechanism (typically reciprocating or rotary), and consume energy to perform mechanical work by moving the fluid. Pumps operate via many energy sources, including manual operation, electricity, engines, or wind power, come in many sizes, from microscopic for use in medical applications to large industrial pumps.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of applications such as pumping water from wells, aquarium filtering, pond filtering and aeration, in the car industry for water-cooling and fuel injection, in the energy industry for pumping oil and natural gas or for operating cooling towers. In the medical industry, pumps are used for biochemical processes in developing and manufacturing medicine, and as artificial replacements for body parts, in particular the artificial heart and penile prosthesis.
In biology, many different types of chemical and bio-mechanical pumps have evolved, and biomimicry is sometimes used in developing new types of mechanical pumps." [Pump. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Pumps" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Plumbing and Piping Plans
Plumbing and Piping Plans
Plumbing and Piping Plans solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM.2.2 software with samples, templates and libraries of pipes, plumbing, and valves design elements for developing of water and plumbing systems, and for drawing Plumbing plan, Piping plan, PVC Pipe plan, PVC Pipe furniture plan, Plumbing layout plan, Plumbing floor plan, Half pipe plans, Pipe bender plans.
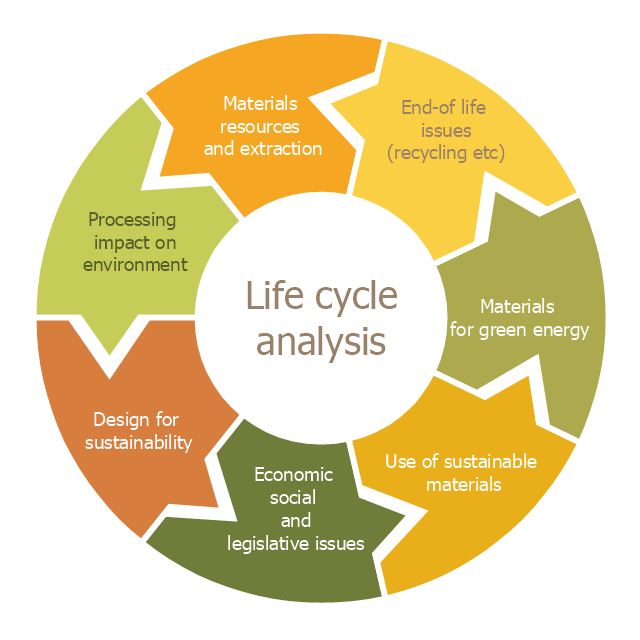
This cycle diagram sample was created on the base of the figure illustrating the article "Environmental Materials" by Cris Arnold from the website of the UK Centre for Materials Education of the Higher Education Academy. "The figure ... schematically shows how the disparate areas under the heading of 'environmental materials' can be linked via a life cycle analysis approach. ...
Life Cycle Analysis.
Life Cycle Analysis is essentially a method of considering the entire environmental impact, energy and resource usage of a material or product. It is often known as a 'cradle-to-grave' analysis and can encompass the entire lifetime from extraction to end-of-life disposal. Life cycle analysis can be an extremely effective way of linking many different aspects of the environmental impacts of materials usage. ...
Materials Extraction and Resource Implications.
The environmental impact of raw materials extraction and processing together with global resource issues provides a good place to start consideration of environmental aspects of materials. ...
Environmental Impacts of Processing.
... Topics that would come under this subject area include the specific environmental problems associated with processing of metals, polymers, ceramics, composites etc, and how these problems can be overcome.
Design for Sustainability.
This area ... will ... cover issues such as design for successful recycling, waste minimisation, energy efficiency and increased lifetime.
Economic, Social and Legislative Issues.
... For example, materials selection within the automotive industry is now heavily influenced by 'end-of-life vehicle' and 'hazardous material' regulations.
Use of Sustainable Materials.
... It is probably sensible to define such materials as those that have distinct differences that achieve environmental benefit compared to conventional materials. With this definition, the list would include:
(1) Materials of a significantly plant-based nature, including wood, natural fibre composites, natural polymers.
(2) Materials produced using a large proportion of waste material, including recycled polymers, composites made from waste mineral powders, and arguably also much steel and aluminium.
Materials for Green Energy.
The most exciting developments in Materials Science are in the realm of functional materials, and many of these serve an environmentally-beneficial purpose, particularly in the production of green energy.
These include:
(1) Solar-cell materials.
(2) Fuel-cell technology.
(3) Catalytic pollution control.
End-of-Life Issues.
The treatment of materials at the end of their lifetime is a significant subject area and encompasses aspects such as recycling techniques and materials limitations, biodegradabilty and composting, chemical recovery and energy recovery." [materials.ac.uk/ guides/ environmental.asp]
The ring chart example "Life cycle analysis" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ marketing-target-and-circular-diagrams
Life Cycle Analysis.
Life Cycle Analysis is essentially a method of considering the entire environmental impact, energy and resource usage of a material or product. It is often known as a 'cradle-to-grave' analysis and can encompass the entire lifetime from extraction to end-of-life disposal. Life cycle analysis can be an extremely effective way of linking many different aspects of the environmental impacts of materials usage. ...
Materials Extraction and Resource Implications.
The environmental impact of raw materials extraction and processing together with global resource issues provides a good place to start consideration of environmental aspects of materials. ...
Environmental Impacts of Processing.
... Topics that would come under this subject area include the specific environmental problems associated with processing of metals, polymers, ceramics, composites etc, and how these problems can be overcome.
Design for Sustainability.
This area ... will ... cover issues such as design for successful recycling, waste minimisation, energy efficiency and increased lifetime.
Economic, Social and Legislative Issues.
... For example, materials selection within the automotive industry is now heavily influenced by 'end-of-life vehicle' and 'hazardous material' regulations.
Use of Sustainable Materials.
... It is probably sensible to define such materials as those that have distinct differences that achieve environmental benefit compared to conventional materials. With this definition, the list would include:
(1) Materials of a significantly plant-based nature, including wood, natural fibre composites, natural polymers.
(2) Materials produced using a large proportion of waste material, including recycled polymers, composites made from waste mineral powders, and arguably also much steel and aluminium.
Materials for Green Energy.
The most exciting developments in Materials Science are in the realm of functional materials, and many of these serve an environmentally-beneficial purpose, particularly in the production of green energy.
These include:
(1) Solar-cell materials.
(2) Fuel-cell technology.
(3) Catalytic pollution control.
End-of-Life Issues.
The treatment of materials at the end of their lifetime is a significant subject area and encompasses aspects such as recycling techniques and materials limitations, biodegradabilty and composting, chemical recovery and energy recovery." [materials.ac.uk/ guides/ environmental.asp]
The ring chart example "Life cycle analysis" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Target and Circular Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ marketing-target-and-circular-diagrams
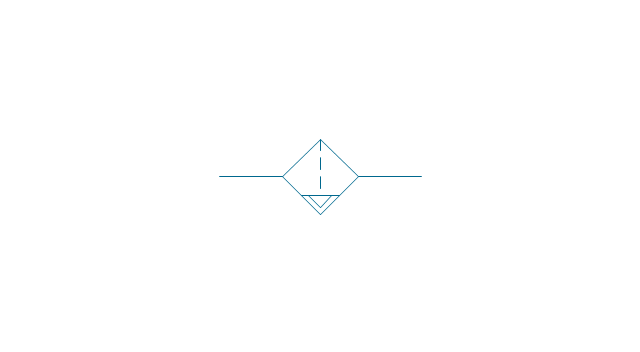
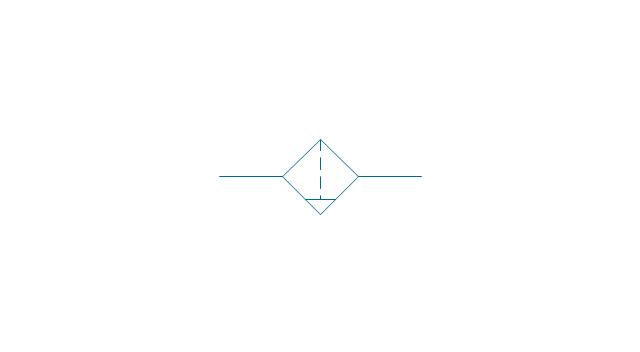
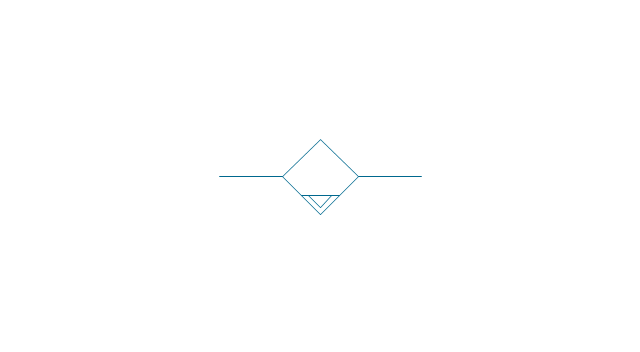
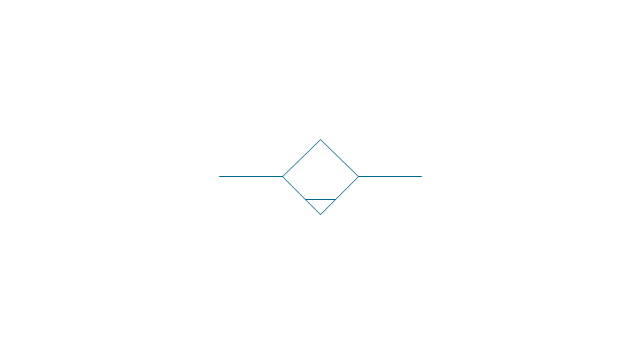
Electrical Symbols — Transformers and Windings
A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction produces an electromotive force within a conductor which is exposed to time varying magnetic fields. Transformers are used to increase or decrease the alternating voltages in electric power applications. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw DIAGRAM make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.- Drawings And Diagrams For Conventional Sources Of Energy
- Pie Charts | Energy resources diagram | Manufacturing and ...
- Energy resources diagram | CMP adaptive management cycle | Geo ...
- Energy resources diagram | Petroleum Conservation Resource ...
- Energy resources diagram | Fuel Conservation Drawing
- Energy resources diagram | Computer Network Architecture ...
- Energy Pyramid Diagram | Energy resources diagram | U.S. energy ...
- Resources and energy - Vector stencils library | Energy resources ...
- Resources and energy - Vector stencils library | Design elements ...
- Drawing Illustration | Drawing a Nature Scene | Resources and ...
- Energy resources diagram | Chemical and Process Engineering | Oil ...
- Chart Examples | Chemistry Drawings | Sources Of Energy ...
- Design elements - Resources and energy | Chemistry Drawings ...
- U.S. primary energy consumption by source and sector | U.S. energy ...
- Process Flow Diagram | Energy resources diagram | Interior Design ...
- Energy resources diagram | Manufacturing and Maintenance | Pie ...
- Chemical and Process Engineering | Energy resources diagram ...
- Design elements - Power sources | U.S. energy consumption by ...
- Energy resources diagram | Design elements - Resources and ...
















,-pneumatic-fluid-power-equipment---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
,-hydraulic-fluid-power-equipment---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)

-fluid-power-equipment---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-fluid-power-equipment---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-fluid-power-equipment---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-fluid-power-equipment---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)