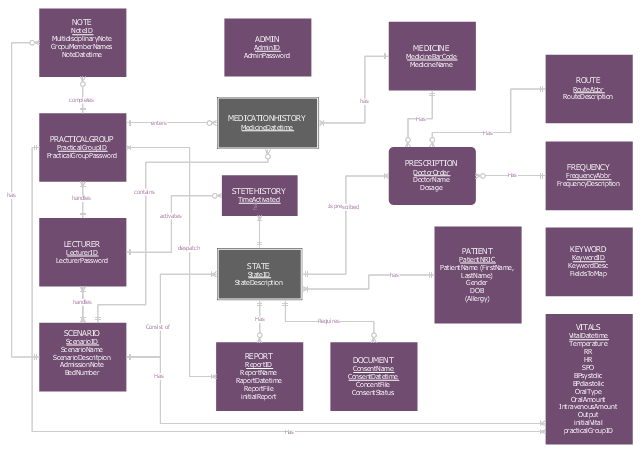
This ERD example was designed on the base of the entity-relationship diagram on the webpage "IS480 Team wiki: 2015T1 WhitePinnacle Documentation" from the Singapore Management University website. [wiki.smu.edu.sg/ is480/ IS480_ Team_ wiki%3A_ 2015T1_ WhitePinnacle_ Documentation]
This is ERD from the documentation of the High School Emergency Medical Responder (HS EMR) information system.
"Emergency medical responders are people who are specially trained to provide out-of-hospital care in medical emergencies. There are many different types of emergency medical responders, each with different levels of training, ranging from first aid and basic life support. Emergency Medical Responders have a very limited scope of practice and have the least amount of comprehensive education, clinical experience or clinical skills of EMS personnel. The Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) is not meant to replace the roles of Emergency Medical Technicians, Emergency Medical Technologists or Paramedics and their wide range of specialities. Emergency Medical Responders typically assist in rural regions providing basic life support where pre-hospital health professionals are not available due to limited resources or infrastructure." [Emergency medical responder. Wikipedia]
The example "Entity-Relationship Diagram" was drawn using ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This is ERD from the documentation of the High School Emergency Medical Responder (HS EMR) information system.
"Emergency medical responders are people who are specially trained to provide out-of-hospital care in medical emergencies. There are many different types of emergency medical responders, each with different levels of training, ranging from first aid and basic life support. Emergency Medical Responders have a very limited scope of practice and have the least amount of comprehensive education, clinical experience or clinical skills of EMS personnel. The Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) is not meant to replace the roles of Emergency Medical Technicians, Emergency Medical Technologists or Paramedics and their wide range of specialities. Emergency Medical Responders typically assist in rural regions providing basic life support where pre-hospital health professionals are not available due to limited resources or infrastructure." [Emergency medical responder. Wikipedia]
The example "Entity-Relationship Diagram" was drawn using ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
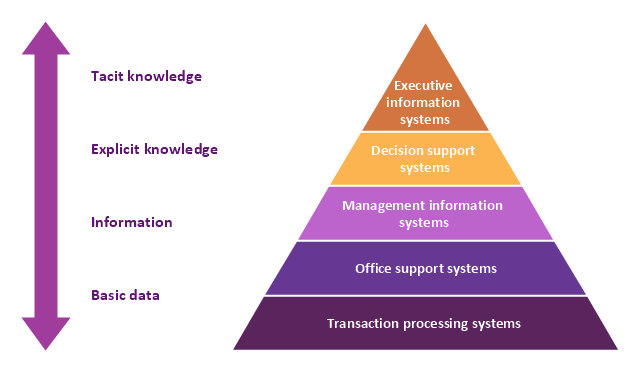
A five level pyramid model of different types of Information Systems based on the information processing requirement of different levels in the organization. The first level represents transaction processing systems to process basic data. The second level represents office support systems to process information in office. The third level represents management information systems to process information by managers. The fourth level represents decision support systems to process explicit knowledge. The fifth level represents executive information systems to process tacit knowledge.
"A Computer(-Based) Information System is essentially an IS using computer technology to carry out some or all of its planned tasks. The basic components of computer based information system are:
(1) Hardware - these are the devices like the monitor, processor, printer and keyboard, all of which work together to accept, process, show data and information.
(2) Software - are the programs that allow the hardware to process the data.
(3) Databases - are the gathering of associated files or tables containing related data.
(4) Networks - are a connecting system that allows diverse computers to distribute resources.
(5) Procedures - are the commands for combining the components above to process information and produce the preferred output.
The first four components (hardware, software, database and network) make up what is known as the information technology platform. Information technology workers could then use these components to create information systems that watch over safety measures, risk and the management of data. These actions are known as information technology services." [Information systems. Wikipedia]
This pyramid diagram was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file Five-Level-Pyramid-model.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Five-Level-Pyramid-model.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by/ 3.0/ deed.en]
The triangle chart example "Information systems types" is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A Computer(-Based) Information System is essentially an IS using computer technology to carry out some or all of its planned tasks. The basic components of computer based information system are:
(1) Hardware - these are the devices like the monitor, processor, printer and keyboard, all of which work together to accept, process, show data and information.
(2) Software - are the programs that allow the hardware to process the data.
(3) Databases - are the gathering of associated files or tables containing related data.
(4) Networks - are a connecting system that allows diverse computers to distribute resources.
(5) Procedures - are the commands for combining the components above to process information and produce the preferred output.
The first four components (hardware, software, database and network) make up what is known as the information technology platform. Information technology workers could then use these components to create information systems that watch over safety measures, risk and the management of data. These actions are known as information technology services." [Information systems. Wikipedia]
This pyramid diagram was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file Five-Level-Pyramid-model.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Five-Level-Pyramid-model.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by/ 3.0/ deed.en]
The triangle chart example "Information systems types" is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
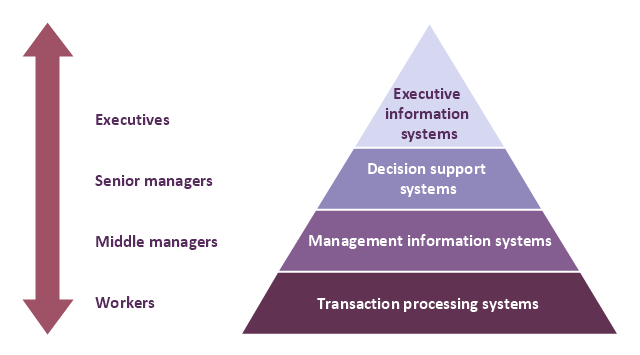
A four level pyramid model of different types of Information Systems based on the different levels of hierarchy in an organization. The first level represents transaction processing systems for workers. The second level represents management information systems for middle managers. The third level represents decision support systems for senior menegers. The fourth level represents executive information systems for executives.
"The "classic" view of Information systems found in the textbooks in the 1980s was of a pyramid of systems that reflected the hierarchy of the organization, usually transaction processing systems at the bottom of the pyramid, followed by management information systems, decision support systems, and ending with executive information systems at the top. Although the pyramid model remains useful, since it was first formulated a number of new technologies have been developed and new categories of information systems have emerged, some of which no longer fit easily into the original pyramid model.
Some examples of such systems are:
data warehouses,
enterprise resource planning,
enterprise systems,
expert systems,
search engines,
geographic information system,
global information system,
office automation." [Information systems. Wikipedia]
This diagram was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file Four-Level-Pyramid-model.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Four-Level-Pyramid-model.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
The triangle chart example "Information systems types" is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"The "classic" view of Information systems found in the textbooks in the 1980s was of a pyramid of systems that reflected the hierarchy of the organization, usually transaction processing systems at the bottom of the pyramid, followed by management information systems, decision support systems, and ending with executive information systems at the top. Although the pyramid model remains useful, since it was first formulated a number of new technologies have been developed and new categories of information systems have emerged, some of which no longer fit easily into the original pyramid model.
Some examples of such systems are:
data warehouses,
enterprise resource planning,
enterprise systems,
expert systems,
search engines,
geographic information system,
global information system,
office automation." [Information systems. Wikipedia]
This diagram was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file Four-Level-Pyramid-model.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Four-Level-Pyramid-model.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
The triangle chart example "Information systems types" is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
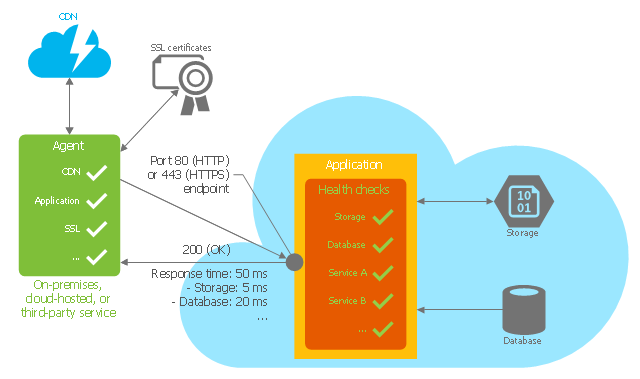
This Azure cloud architecture pattern diagram template was created on the base of figure in the article "Health Endpoint Monitoring Pattern" from the Microsoft Developer Network (MSDN) website.
"Health Endpoint Monitoring Pattern.
Implement functional checks within an application that external tools can access through exposed endpoints at regular intervals. This pattern can help to verify that applications and services are performing correctly. ...
It is good practice—and often a business requirement—to monitor web applications, and middle-tier and shared services, to ensure that they are available and performing correctly. However, it is more difficult to monitor services running in the cloud than it is to monitor on-premises services. ...
Implement health monitoring by sending requests to an endpoint on the application. The application should perform the necessary checks, and return an indication of its status.
A health monitoring check typically combines two factors: the checks (if any) performed by the application or service in response to the request to the health verification endpoint, and analysis of the result by the tool or framework that is performing the health verification check. The response code indicates the status of the application and, optionally, any components or services it uses. The latency or response time check is performed by the monitoring tool or framework." [msdn.microsoft.com/ ru-RU/ library/ dn589789.aspx]
The Azure cloud system architecture diagram template "Health endpoint monitoring pattern" for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Azure Architecture solutin from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Health Endpoint Monitoring Pattern.
Implement functional checks within an application that external tools can access through exposed endpoints at regular intervals. This pattern can help to verify that applications and services are performing correctly. ...
It is good practice—and often a business requirement—to monitor web applications, and middle-tier and shared services, to ensure that they are available and performing correctly. However, it is more difficult to monitor services running in the cloud than it is to monitor on-premises services. ...
Implement health monitoring by sending requests to an endpoint on the application. The application should perform the necessary checks, and return an indication of its status.
A health monitoring check typically combines two factors: the checks (if any) performed by the application or service in response to the request to the health verification endpoint, and analysis of the result by the tool or framework that is performing the health verification check. The response code indicates the status of the application and, optionally, any components or services it uses. The latency or response time check is performed by the monitoring tool or framework." [msdn.microsoft.com/ ru-RU/ library/ dn589789.aspx]
The Azure cloud system architecture diagram template "Health endpoint monitoring pattern" for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Azure Architecture solutin from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Er Diagram For Healthcare Management System
- How to Create a Healthcare Management Workflow Diagram ...
- Health Care Organization Er Diagram
- Er Diagram For Health Care System
- Components of ER Diagram | Healthcare Management Workflow ...
- Healthcare Management System Er Diagram
- Healthcare Management Workflow Diagrams | Developing Entity ...
- Uml Diagram Fot Health Care Management
- Entity-Relationship Diagram ( ERD ) | | Er Daigram Medical Shop ...
- Prioritization matrix - Health care problems | Relations diagram ...
- ER Diagram for Cloud Computing | Booch OOD Diagram | Example ...
- Erd Diagrams Of E Healthcare System
- Er Diagrams In Medicine
- Diagram Of Health Management
- Er Diagram For Health Care
- Relations diagram - Health care | Social determinants of health ...
- Uml Diagrams For Health Care System
- Healthcare Management Workflow Diagrams | Diagramming ...
- Healthcare Management Workflow Diagrams | Entity-Relationship ...
- Er Diagram Of Online Clinic System Dowanload