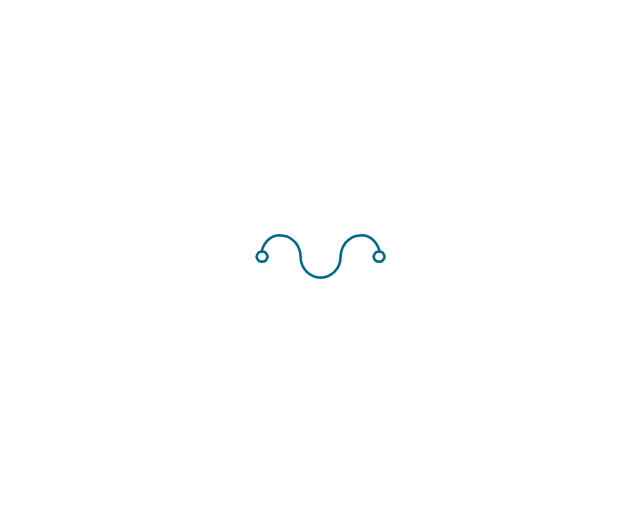
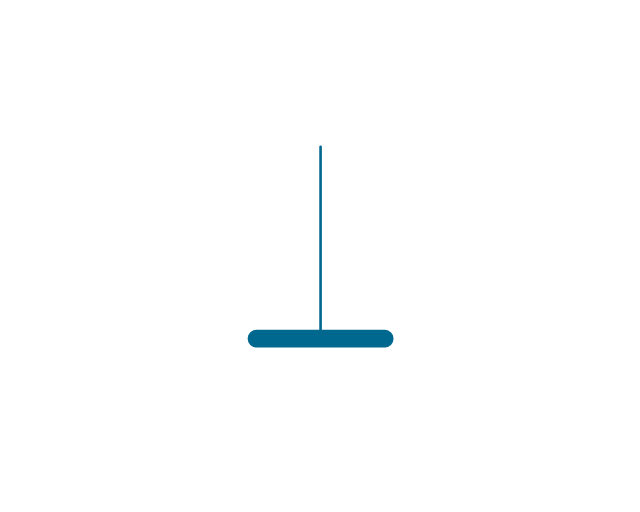
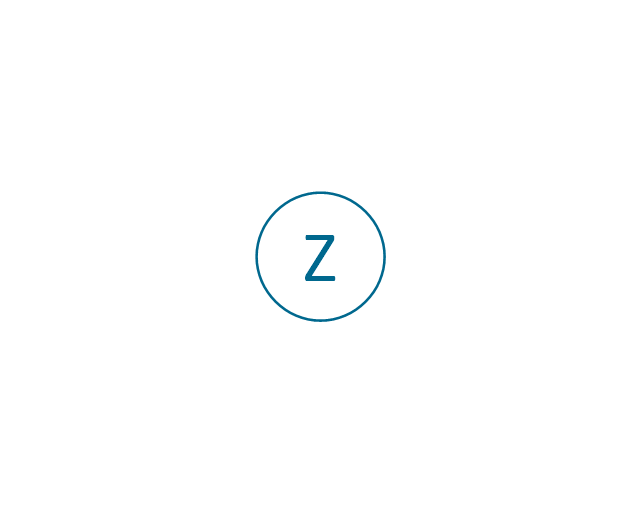
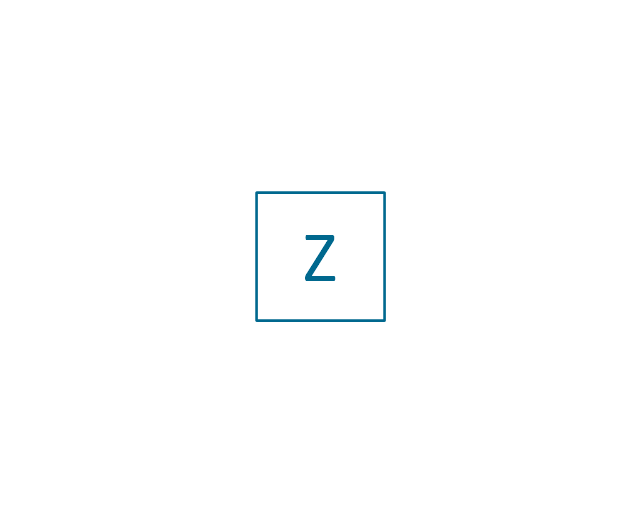
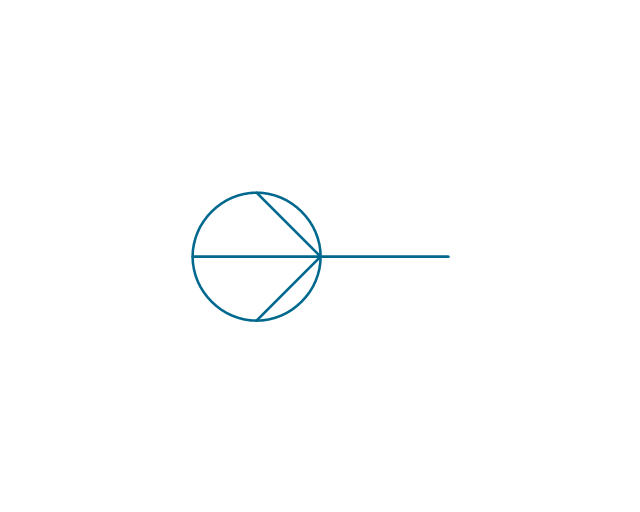
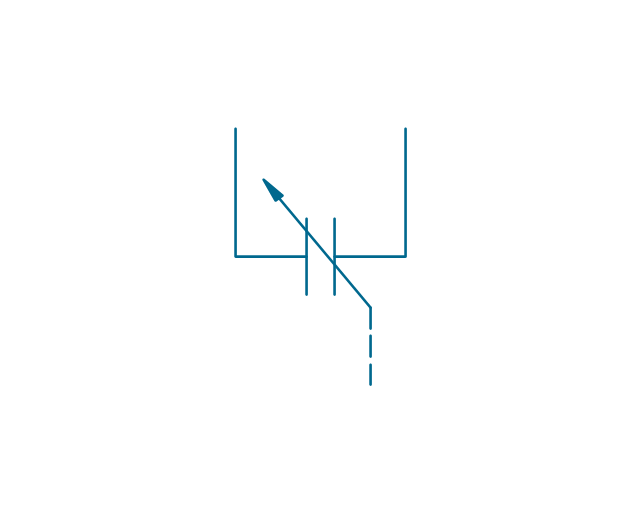
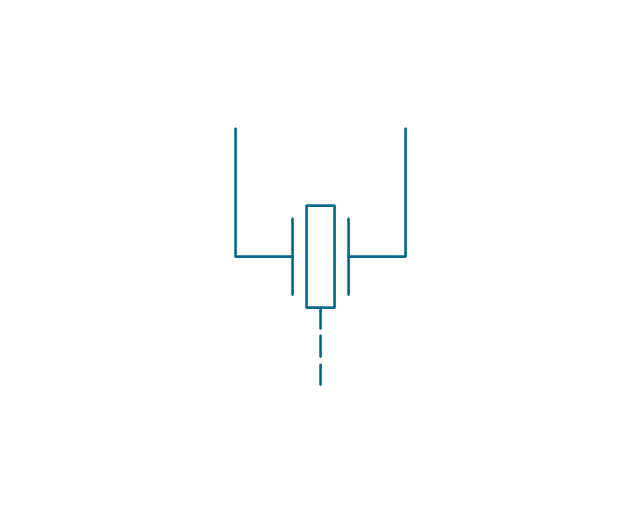
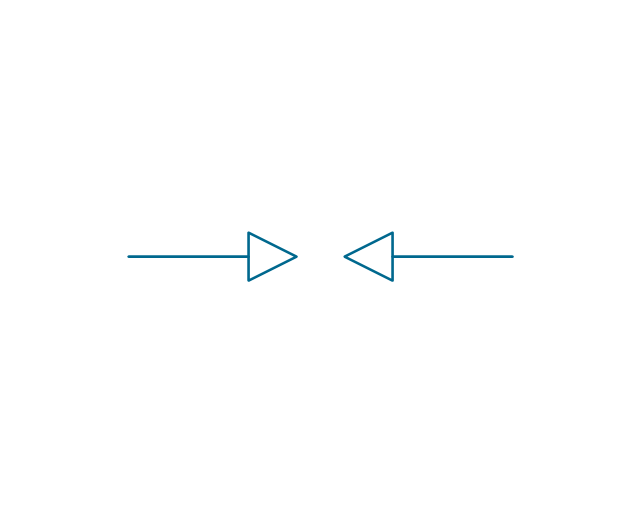
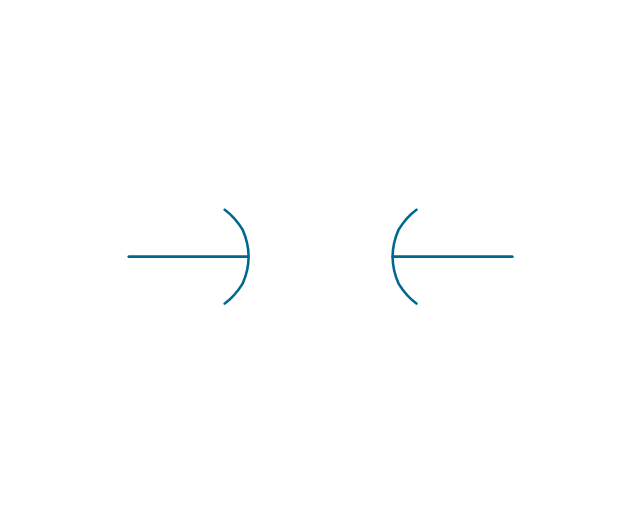
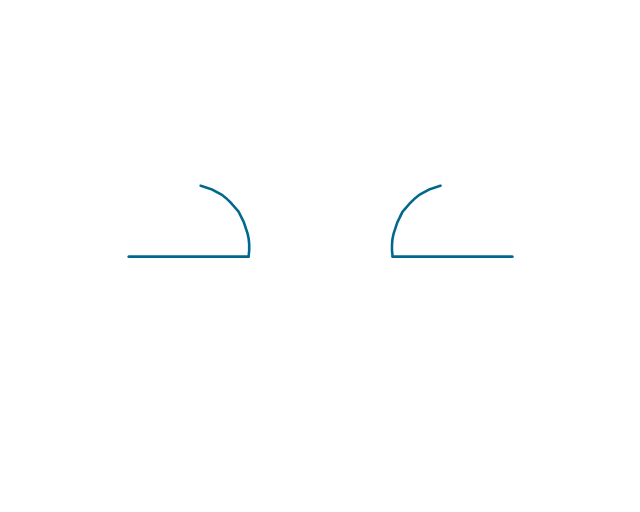
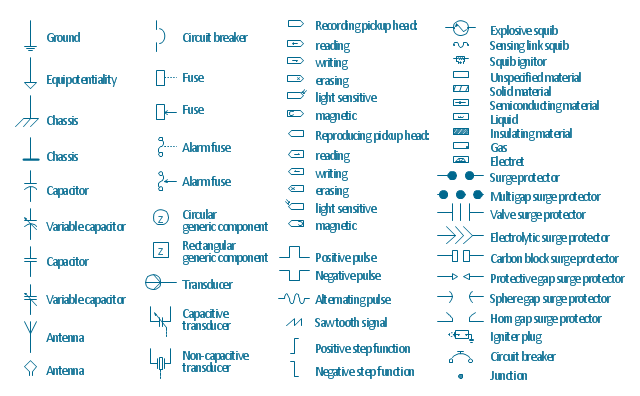
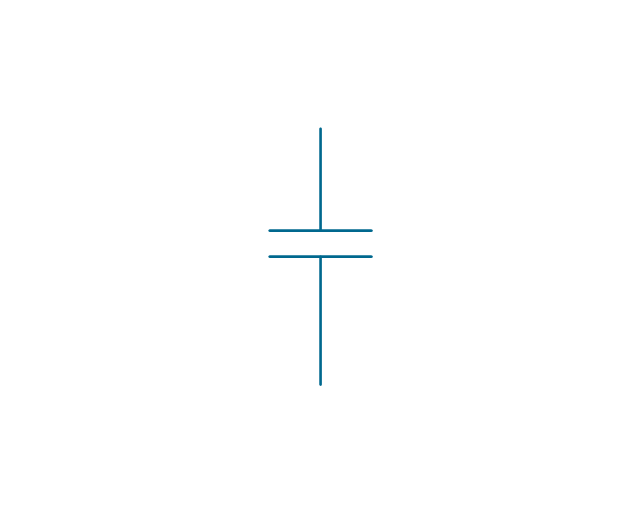The vector stencils library "Electrical circuits" contains 49 element symbols of electrical and electronic devices, including ignitors, starters, transmitters, circuit protectors, transducers, radio and audio equipment.
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
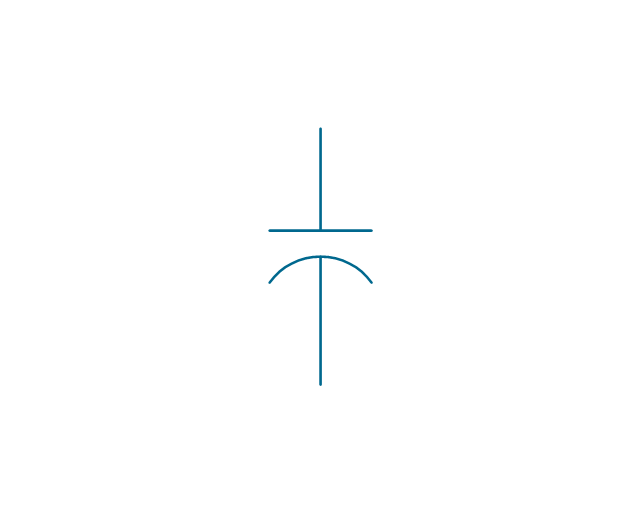
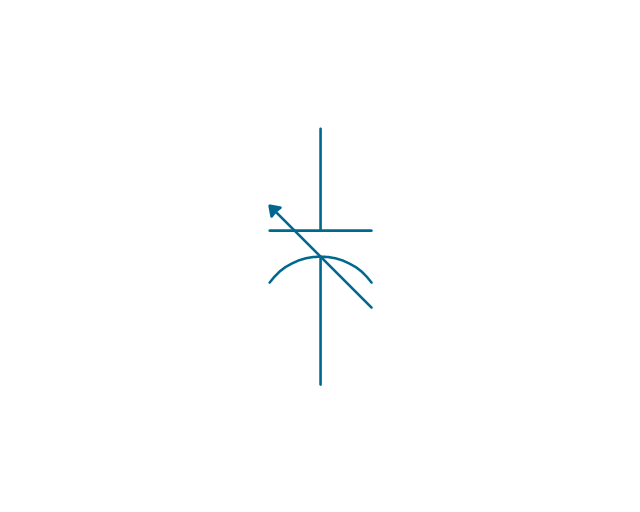
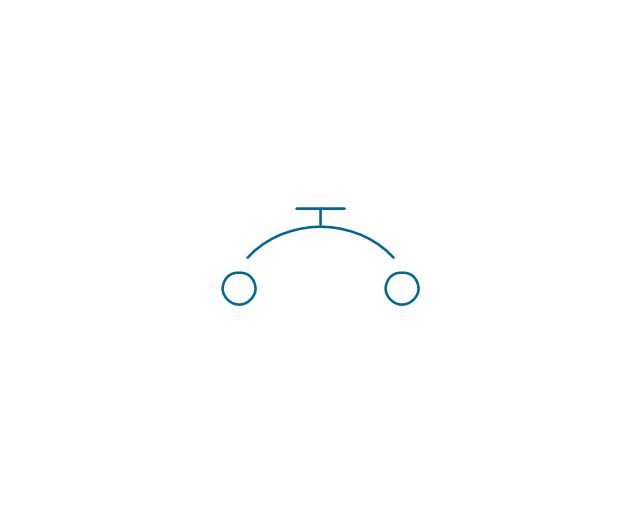
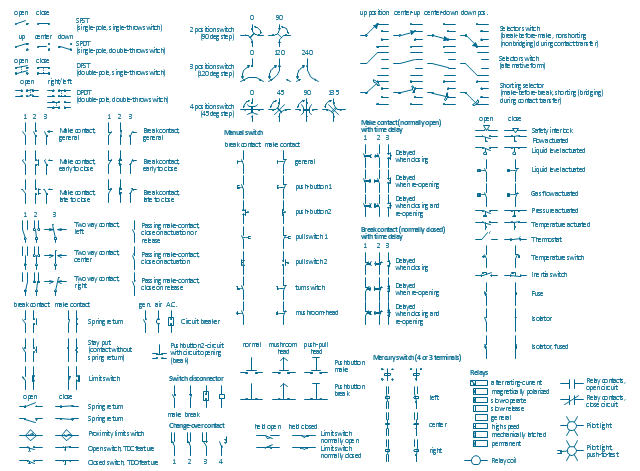
The vector stencils library "Switches and relays" contains 58 symbols of electrical contacts, switches, relays, circuit breakers, selectors, connectors, disconnect devices, switching circuits, current regulators, and thermostats for electrical devices.
"In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another.
The most familiar form of switch is a manually operated electromechanical device with one or more sets of electrical contacts, which are connected to external circuits. Each set of contacts can be in one of two states: either "closed" meaning the contacts are touching and electricity can flow between them, or "open", meaning the contacts are separated and the switch is nonconducting. The mechanism actuating the transition between these two states (open or closed) can be either a "toggle" (flip switch for continuous "on" or "off") or "momentary" (push-for "on" or push-for "off") type.
A switch may be directly manipulated by a human as a control signal to a system, such as a computer keyboard button, or to control power flow in a circuit, such as a light switch. Automatically operated switches can be used to control the motions of machines, for example, to indicate that a garage door has reached its full open position or that a machine tool is in a position to accept another workpiece. Switches may be operated by process variables such as pressure, temperature, flow, current, voltage, and force, acting as sensors in a process and used to automatically control a system. ... A switch that is operated by another electrical circuit is called a relay. Large switches may be remotely operated by a motor drive mechanism. Some switches are used to isolate electric power from a system, providing a visible point of isolation that can be padlocked if necessary to prevent accidental operation of a machine during maintenance, or to prevent electric shock." [Switch. Wikipedia]
"A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to mechanically operate a switch, but other operating principles are also used, such as solid-state relays. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal (with complete electrical isolation between control and controlled circuits), or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal. The first relays were used in long distance telegraph circuits as amplifiers: they repeated the signal coming in from one circuit and re-transmitted it on another circuit. Relays were used extensively in telephone exchanges and early computers to perform logical operations.
A type of relay that can handle the high power required to directly control an electric motor or other loads is called a contactor. Solid-state relays control power circuits with no moving parts, instead using a semiconductor device to perform switching. Relays with calibrated operating characteristics and sometimes multiple operating coils are used to protect electrical circuits from overload or faults; in modern electric power systems these functions are performed by digital instruments still called "protective relays"." [Relay. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Switches and relays" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another.
The most familiar form of switch is a manually operated electromechanical device with one or more sets of electrical contacts, which are connected to external circuits. Each set of contacts can be in one of two states: either "closed" meaning the contacts are touching and electricity can flow between them, or "open", meaning the contacts are separated and the switch is nonconducting. The mechanism actuating the transition between these two states (open or closed) can be either a "toggle" (flip switch for continuous "on" or "off") or "momentary" (push-for "on" or push-for "off") type.
A switch may be directly manipulated by a human as a control signal to a system, such as a computer keyboard button, or to control power flow in a circuit, such as a light switch. Automatically operated switches can be used to control the motions of machines, for example, to indicate that a garage door has reached its full open position or that a machine tool is in a position to accept another workpiece. Switches may be operated by process variables such as pressure, temperature, flow, current, voltage, and force, acting as sensors in a process and used to automatically control a system. ... A switch that is operated by another electrical circuit is called a relay. Large switches may be remotely operated by a motor drive mechanism. Some switches are used to isolate electric power from a system, providing a visible point of isolation that can be padlocked if necessary to prevent accidental operation of a machine during maintenance, or to prevent electric shock." [Switch. Wikipedia]
"A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to mechanically operate a switch, but other operating principles are also used, such as solid-state relays. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal (with complete electrical isolation between control and controlled circuits), or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal. The first relays were used in long distance telegraph circuits as amplifiers: they repeated the signal coming in from one circuit and re-transmitted it on another circuit. Relays were used extensively in telephone exchanges and early computers to perform logical operations.
A type of relay that can handle the high power required to directly control an electric motor or other loads is called a contactor. Solid-state relays control power circuits with no moving parts, instead using a semiconductor device to perform switching. Relays with calibrated operating characteristics and sometimes multiple operating coils are used to protect electrical circuits from overload or faults; in modern electric power systems these functions are performed by digital instruments still called "protective relays"." [Relay. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Switches and relays" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
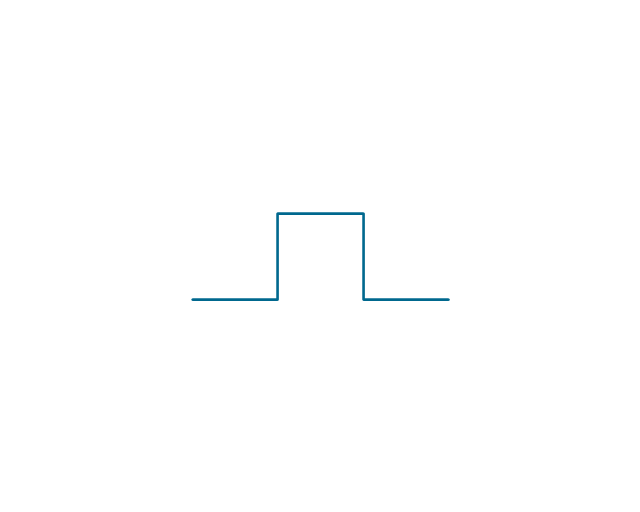
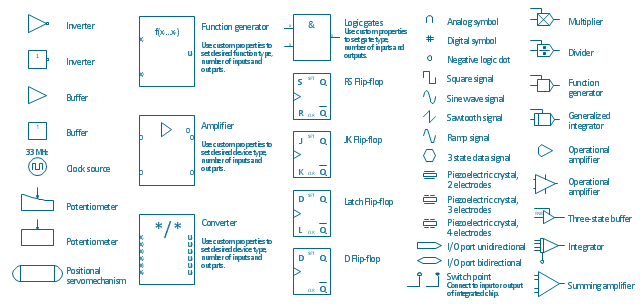
The vector stencils library "Analog and digital logic" contains 40 element symbols of logic (threshold) gates, bistable current switches, current controllers, regulators, electrical generators, and amplifiers.
Use it for drawing the digital and analog functions in electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics.
"Analogue electronics (or analog in American English) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two different levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal." [Analogue electronics. Wikipedia]
"Digital electronics, or digital (electronic) circuits, represent signals by discrete bands of analog levels, rather than by a continuous range. All levels within a band represent the same signal state. Relatively small changes to the analog signal levels due to manufacturing tolerance, signal attenuation or parasitic noise do not leave the discrete envelope, and as a result are ignored by signal state sensing circuitry.
In most cases the number of these states is two, and they are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as "ground" or zero volts) and a value near the supply voltage, corresponding to the "false" ("0") and "true" ("1") values of the Boolean domain respectively.
Digital techniques are useful because it is easier to get an electronic device to switch into one of a number of known states than to accurately reproduce a continuous range of values.
Digital electronic circuits are usually made from large assemblies of logic gates, simple electronic representations of Boolean logic functions." [Digital electronics. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Analog and digital logic" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for drawing the digital and analog functions in electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics.
"Analogue electronics (or analog in American English) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two different levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal." [Analogue electronics. Wikipedia]
"Digital electronics, or digital (electronic) circuits, represent signals by discrete bands of analog levels, rather than by a continuous range. All levels within a band represent the same signal state. Relatively small changes to the analog signal levels due to manufacturing tolerance, signal attenuation or parasitic noise do not leave the discrete envelope, and as a result are ignored by signal state sensing circuitry.
In most cases the number of these states is two, and they are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as "ground" or zero volts) and a value near the supply voltage, corresponding to the "false" ("0") and "true" ("1") values of the Boolean domain respectively.
Digital techniques are useful because it is easier to get an electronic device to switch into one of a number of known states than to accurately reproduce a continuous range of values.
Digital electronic circuits are usually made from large assemblies of logic gates, simple electronic representations of Boolean logic functions." [Digital electronics. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Analog and digital logic" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Electrical circuits" contains 49 element symbols of electrical and electronic devices, including ignitors, starters, transmitters, circuit protectors, transducers, radio and audio equipment.
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics.
"An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Linear electrical networks, a special type consisting only of sources (voltage or current), linear lumped elements (resistors, capacitors, inductors), and linear distributed elements (transmission lines), have the property that signals are linearly superimposable. They are thus more easily analyzed, using powerful frequency domain methods such as Laplace transforms, to determine DC response, AC response, and transient response.
A resistive circuit is a circuit containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive circuits is less complicated than analysis of circuits containing capacitors and inductors. If the sources are constant (DC) sources, the result is a DC circuit.
A network that contains active electronic components is known as an electronic circuit. Such networks are generally nonlinear and require more complex design and analysis tools." [Electrical network. Wikipedia]
The symbils example "Design elements - Electrical circuits" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics.
"An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Linear electrical networks, a special type consisting only of sources (voltage or current), linear lumped elements (resistors, capacitors, inductors), and linear distributed elements (transmission lines), have the property that signals are linearly superimposable. They are thus more easily analyzed, using powerful frequency domain methods such as Laplace transforms, to determine DC response, AC response, and transient response.
A resistive circuit is a circuit containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive circuits is less complicated than analysis of circuits containing capacitors and inductors. If the sources are constant (DC) sources, the result is a DC circuit.
A network that contains active electronic components is known as an electronic circuit. Such networks are generally nonlinear and require more complex design and analysis tools." [Electrical network. Wikipedia]
The symbils example "Design elements - Electrical circuits" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Design elements - Electrical circuits | Step Function In Dc Electrical ...
- Electrical Symbols — Electrical Circuits | Process Flowchart ...
- Electrical circuits - Vector stencils library | Electrical circuits - Vector ...
- Electrical Symbols And Functions Pdf
- Electronic Circuit Symbols And Function S In Pdf
- Electrical Symbols, Electrical Diagram Symbols | Local area network ...
- Electrical Devices And Their Symbols And Functions
- Electrical Symbols, Electrical Diagram Symbols | Electrical Drawing ...
- Different Electrical Symbols In An Electric Circuit And Their Uses
- Circuit Symbols And Functions
- Electrical Components Symbols And Function Pdf
- Design elements - Electrical circuits | Electrical Drawing Software ...
- Electronics Circuit Symbols And Functions Pdf
- Electrical Symbols, Electrical Diagram Symbols | Electrical Drawing ...
- Electrical Circuits
- Element Of Electricity And Functions
- Electrical Devices Symbols And Functions
- Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols | Block Diagram ...
- Element Of Electricity And Functions With Diagram
- Circuits and Logic Diagram Software | Electrical Drawing Software ...