This IVR diagram sample illustrates how ENUM works by giving an example: Subscriber A sets out to call Subscriber B:
1. The User Agent of an ENUM-enabled subscriber terminal device, or a PBX, or a Gateway, translates the request for the number +34 98 765 4321 in accordance with the rule described in RFC 3761 into the ENUM domain 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.4.3.e164.arpa.
2. A request is sent to the Domain Name System (DNS) asking it to look up the ENUM domain 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.4.3.e164.arpa.
3. The query returns a result in the form of so called Naming Authority Pointer Resource NAPTR records, as per RFC 3403. In the example above, the response is an address that can be reached in the Internet using the VoIP protocol, SIP per RFC 3261.
4. The terminal application now sets up a communication link, and the call is routed via the Internet.
This IVR diagram sample was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Ejemplo ENUM.jpg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Ejemplo_ ENUM.jpg]
"Being able to dial telephone numbers the way customers have come to expect is considered crucial for the convergence of classic telephone service (PSTN) and Internet telephony (Voice over IP, VoIP), and for the development of new IP multimedia services. The problem of a single universal personal identifier for multiple communication services can be solved with different approaches. One simple approach is the Electronic Number Mapping System (ENUM), developed by the IETF, using existing E.164 telephone numbers, protocols and infrastructure to indirectly access different services available under a single personal identifier. ENUM also permits connecting the IP world to the telephone system in a seamless manner." [Telephone number mapping. Wikipedia]
The IVR diagram example "Example ENUM" was designed using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Interactive Voice Response Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
1. The User Agent of an ENUM-enabled subscriber terminal device, or a PBX, or a Gateway, translates the request for the number +34 98 765 4321 in accordance with the rule described in RFC 3761 into the ENUM domain 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.4.3.e164.arpa.
2. A request is sent to the Domain Name System (DNS) asking it to look up the ENUM domain 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.4.3.e164.arpa.
3. The query returns a result in the form of so called Naming Authority Pointer Resource NAPTR records, as per RFC 3403. In the example above, the response is an address that can be reached in the Internet using the VoIP protocol, SIP per RFC 3261.
4. The terminal application now sets up a communication link, and the call is routed via the Internet.
This IVR diagram sample was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Ejemplo ENUM.jpg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Ejemplo_ ENUM.jpg]
"Being able to dial telephone numbers the way customers have come to expect is considered crucial for the convergence of classic telephone service (PSTN) and Internet telephony (Voice over IP, VoIP), and for the development of new IP multimedia services. The problem of a single universal personal identifier for multiple communication services can be solved with different approaches. One simple approach is the Electronic Number Mapping System (ENUM), developed by the IETF, using existing E.164 telephone numbers, protocols and infrastructure to indirectly access different services available under a single personal identifier. ENUM also permits connecting the IP world to the telephone system in a seamless manner." [Telephone number mapping. Wikipedia]
The IVR diagram example "Example ENUM" was designed using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Interactive Voice Response Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
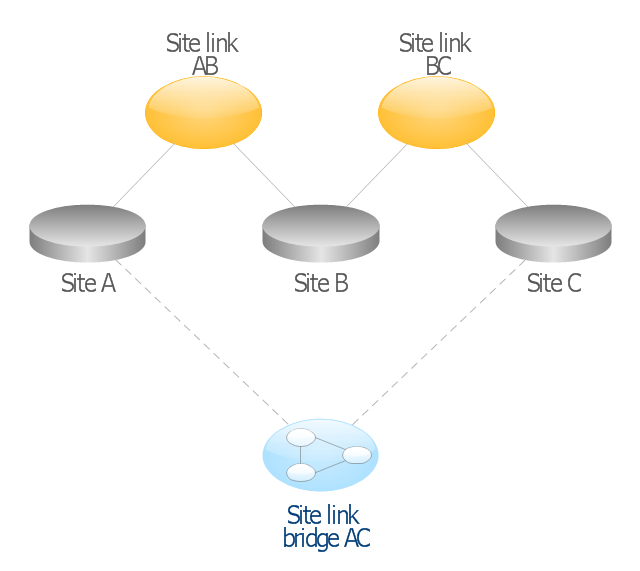
This AD diagram example was redesigned from the picture "Site links" from the book "Active Directory for Dummies".
"Site links represent the Active Directory replication paths between sites.
These paths are manually defined so that the designer has control over which network links the replication traffic occurs on. These site links also control how clients are directed to domain controllers when there’s no DC in the client’s local site. Each site link has the following attributes:
(1) Connected sites: A site link is defined by the sites to which it connects. A site link can connect two or more sites together.
(2) Network transport: Site links support replication communication over IP-based RPCs or with the Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP). You normally want to use RPC whenever possible, but you can use SMTP when the sites you’re linking don’t support RPC.
(3) Cost: Each site link has a cost associated with it. Costs are used to assign preferences to links that determine which link should be followed when multiple link paths are available between sites. The cost represents what it “costs” to use this site link relative to the other site links and affects replication traffic as well as how users are assigned a domain controller. Links with lower cost values have preference over links with higher cost values. Cost values range from 1–32,767; the default being 100.
(4) Frequency: The frequency value defines how often a replication occurs
when using this site link (the replication latency). You can configure the time between replications from a minimum of 15 minutes to a maximum of 10,080 minutes (one week). The default frequency is 180 minutes.
(5) Schedule: The schedule dictates when this link is active and available for replication between the sites. The schedule can also control which days of the week the link is available. Normally, the schedule is set so that the link is available 24 hours a day, but you can set up different schedules on a per-day-of-the-week basis.
By creating a site link, you enable two or more sites to be connected and to share the same site link attributes (transport, cost, frequency, and schedule). By default, site links create transitive connectivity between sites.
If you create a site link between sites A and B and another site link between
sites B and C, an automatic connection (known as a site link bridge) is created between sites A and C..." [Steve Clines and Marcia Loughry, Active Directory® For Dummies®, 2nd Edition. 2008]
The Active Directory diagram example "Site links" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Active Directory Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Site links represent the Active Directory replication paths between sites.
These paths are manually defined so that the designer has control over which network links the replication traffic occurs on. These site links also control how clients are directed to domain controllers when there’s no DC in the client’s local site. Each site link has the following attributes:
(1) Connected sites: A site link is defined by the sites to which it connects. A site link can connect two or more sites together.
(2) Network transport: Site links support replication communication over IP-based RPCs or with the Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP). You normally want to use RPC whenever possible, but you can use SMTP when the sites you’re linking don’t support RPC.
(3) Cost: Each site link has a cost associated with it. Costs are used to assign preferences to links that determine which link should be followed when multiple link paths are available between sites. The cost represents what it “costs” to use this site link relative to the other site links and affects replication traffic as well as how users are assigned a domain controller. Links with lower cost values have preference over links with higher cost values. Cost values range from 1–32,767; the default being 100.
(4) Frequency: The frequency value defines how often a replication occurs
when using this site link (the replication latency). You can configure the time between replications from a minimum of 15 minutes to a maximum of 10,080 minutes (one week). The default frequency is 180 minutes.
(5) Schedule: The schedule dictates when this link is active and available for replication between the sites. The schedule can also control which days of the week the link is available. Normally, the schedule is set so that the link is available 24 hours a day, but you can set up different schedules on a per-day-of-the-week basis.
By creating a site link, you enable two or more sites to be connected and to share the same site link attributes (transport, cost, frequency, and schedule). By default, site links create transitive connectivity between sites.
If you create a site link between sites A and B and another site link between
sites B and C, an automatic connection (known as a site link bridge) is created between sites A and C..." [Steve Clines and Marcia Loughry, Active Directory® For Dummies®, 2nd Edition. 2008]
The Active Directory diagram example "Site links" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Active Directory Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Communication Links Examples
- Microwave Communication Link Design Devices
- Communication network diagram | Telecommunication Network ...
- Diagram Of Link And Node In Data Communication
- Telecommunication Network Diagrams | Telecommunication ...
- Communication network diagram
- Diagram Of Link In Data Communication
- Telecommunication networks. Computer and Network Examples ...
- Link Diagram Software Free
- Wireless Communication Example
- What Is Link
- Wide area network (WAN) topology. Computer and Network Examples
- Concept Mapping Of Communication
- Personal area (PAN) networks. Computer and Network Examples ...
- Network Communication
- Communication Media In Networking
- Network Topologies | Near field communication (NFC). Computer ...
- Concept Map About Communication
- Concept Map In Communication
- Telecommunication Network Diagrams | Digital Communications ...