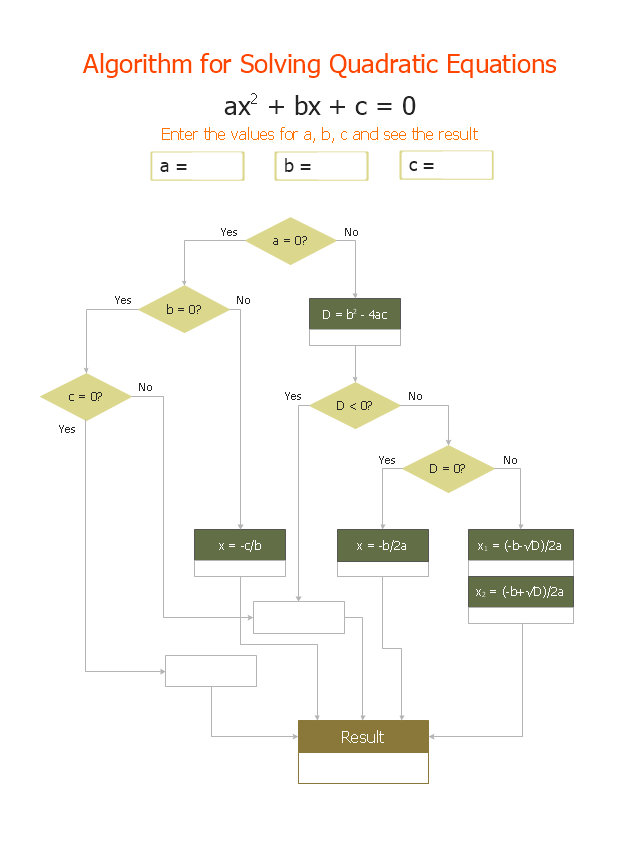
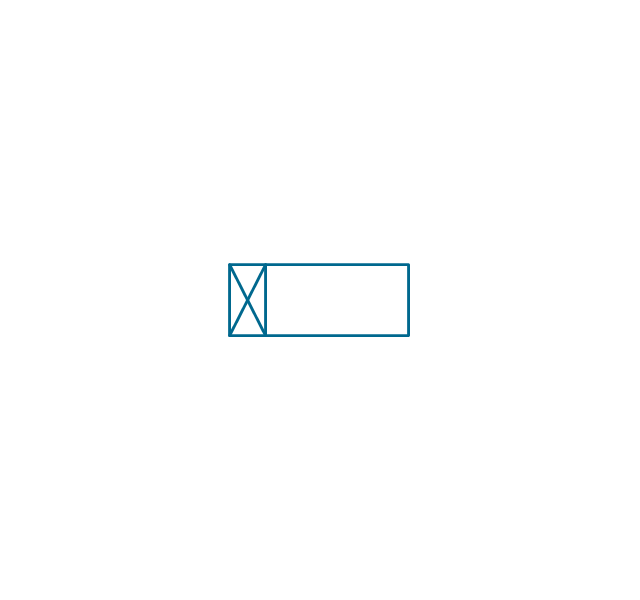
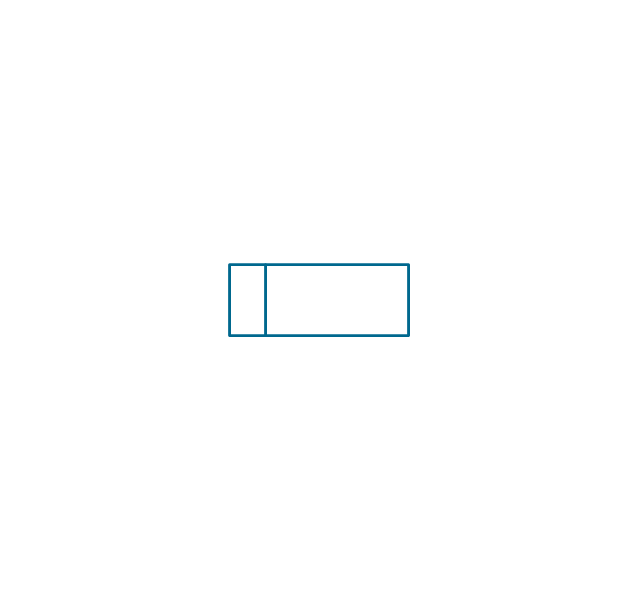
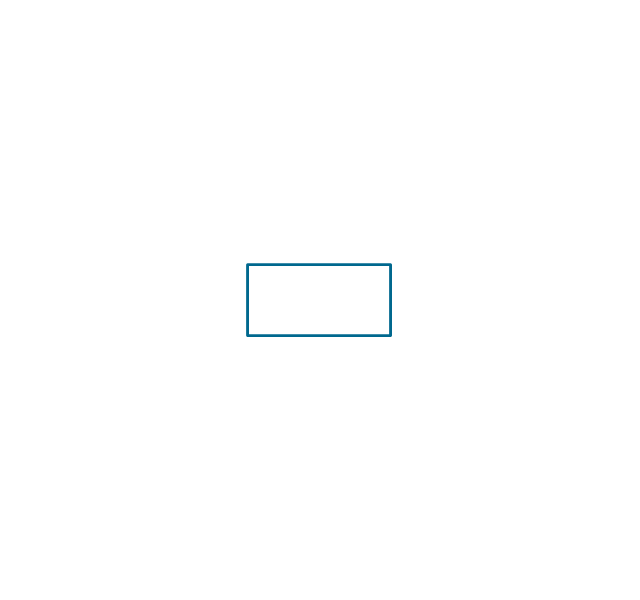
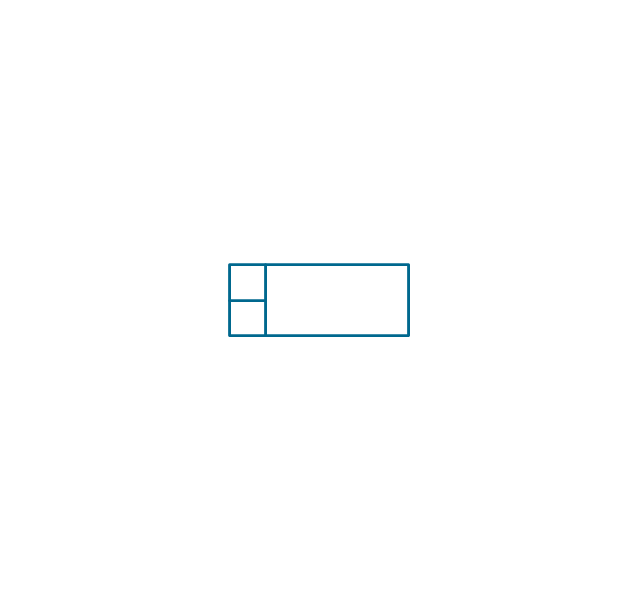
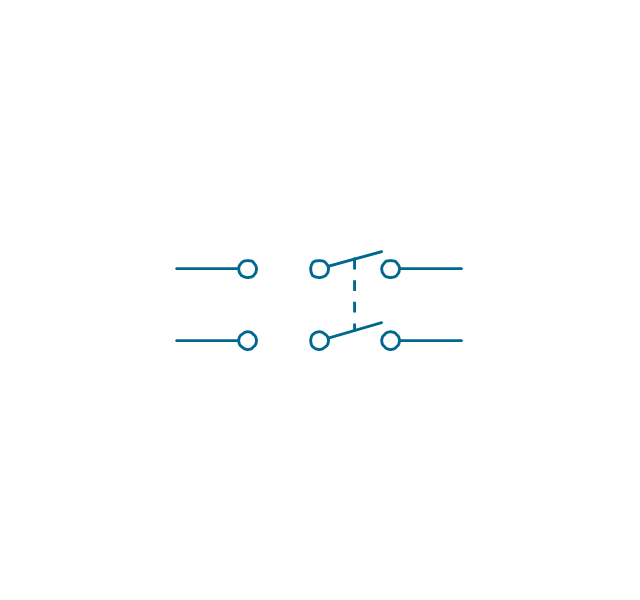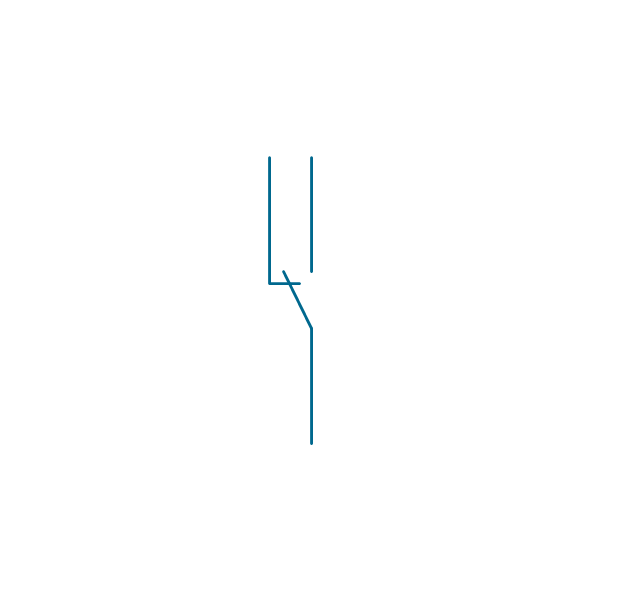"In elementary algebra, a quadratic equation (from the Latin quadratus for "square") is any equation having the form
ax^2+bx+c=0
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c are constants with a not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The constants a, b, and c are called, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.
Because the quadratic equation involves only one unknown, it is called "univariate". The quadratic equation only contains powers of x that are non-negative integers, and therefore it is a polynomial equation, and in particular it is a second degree polynomial equation since the greatest power is two.
Quadratic equations can be solved by a process known in American English as factoring and in other varieties of English as factorising, by completing the square, by using the quadratic formula, or by graphing." [Quadratic equation. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Solving quadratic equation algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
ax^2+bx+c=0
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c are constants with a not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The constants a, b, and c are called, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.
Because the quadratic equation involves only one unknown, it is called "univariate". The quadratic equation only contains powers of x that are non-negative integers, and therefore it is a polynomial equation, and in particular it is a second degree polynomial equation since the greatest power is two.
Quadratic equations can be solved by a process known in American English as factoring and in other varieties of English as factorising, by completing the square, by using the quadratic formula, or by graphing." [Quadratic equation. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Solving quadratic equation algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
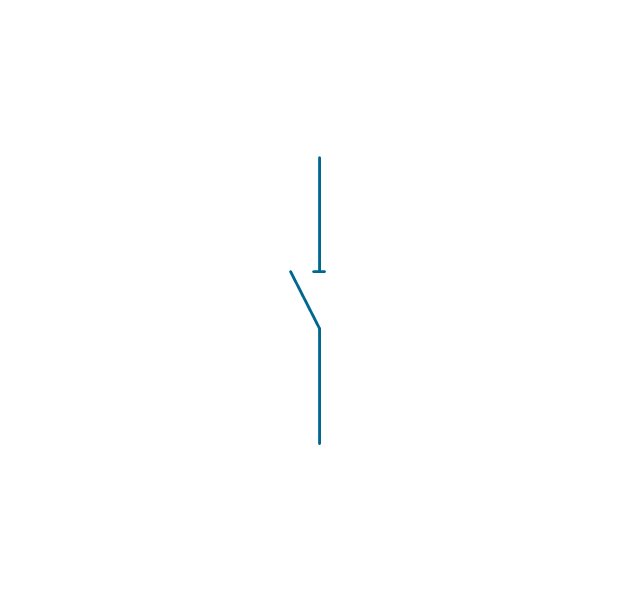
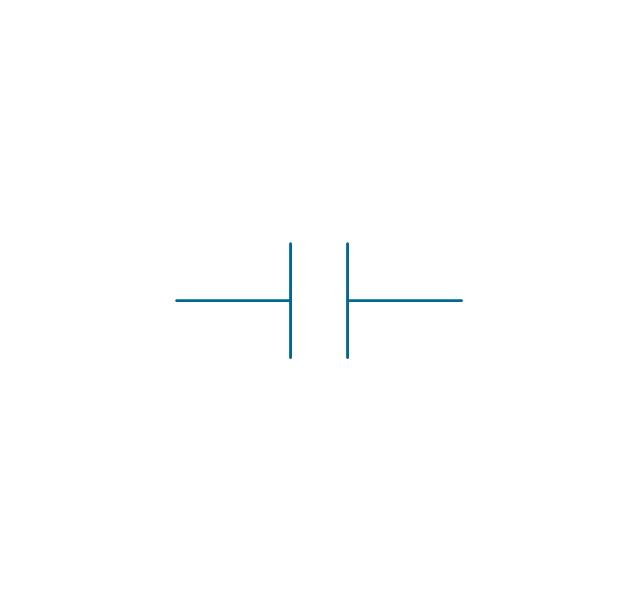
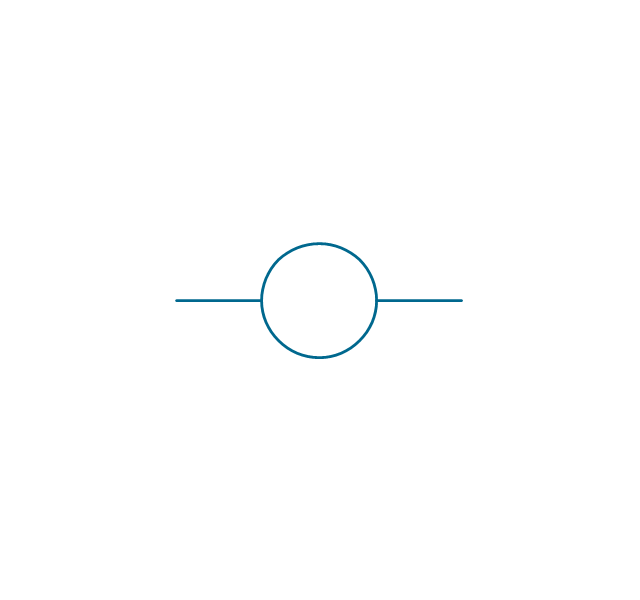
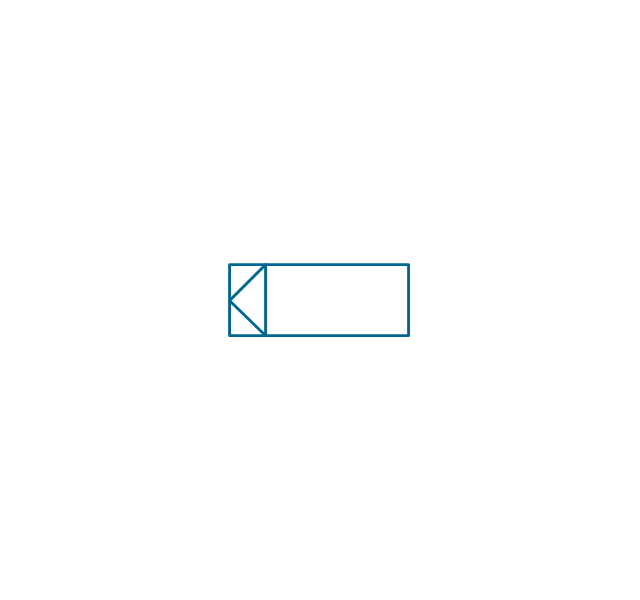
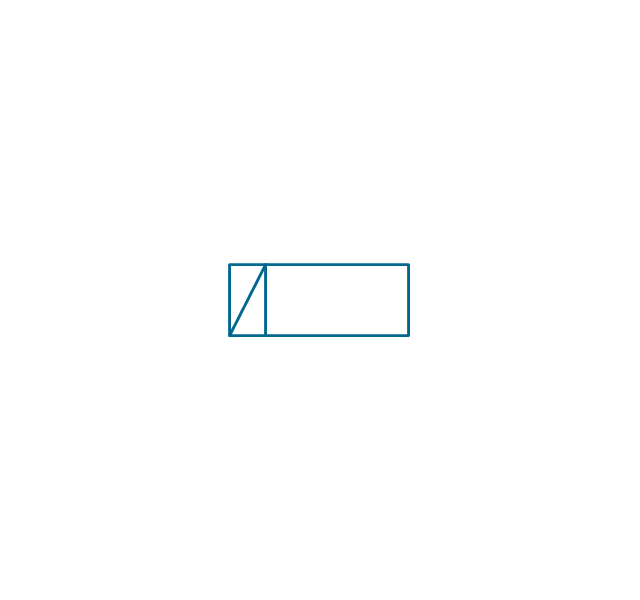
The vector stencils library "Switches and relays" contains 58 symbols of electrical contacts, switches, relays, circuit breakers, selectors, connectors, disconnect devices, switching circuits, current regulators, and thermostats for electrical devices.
Use these shapes for drawing electrical diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use these shapes for drawing electrical diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
HelpDesk
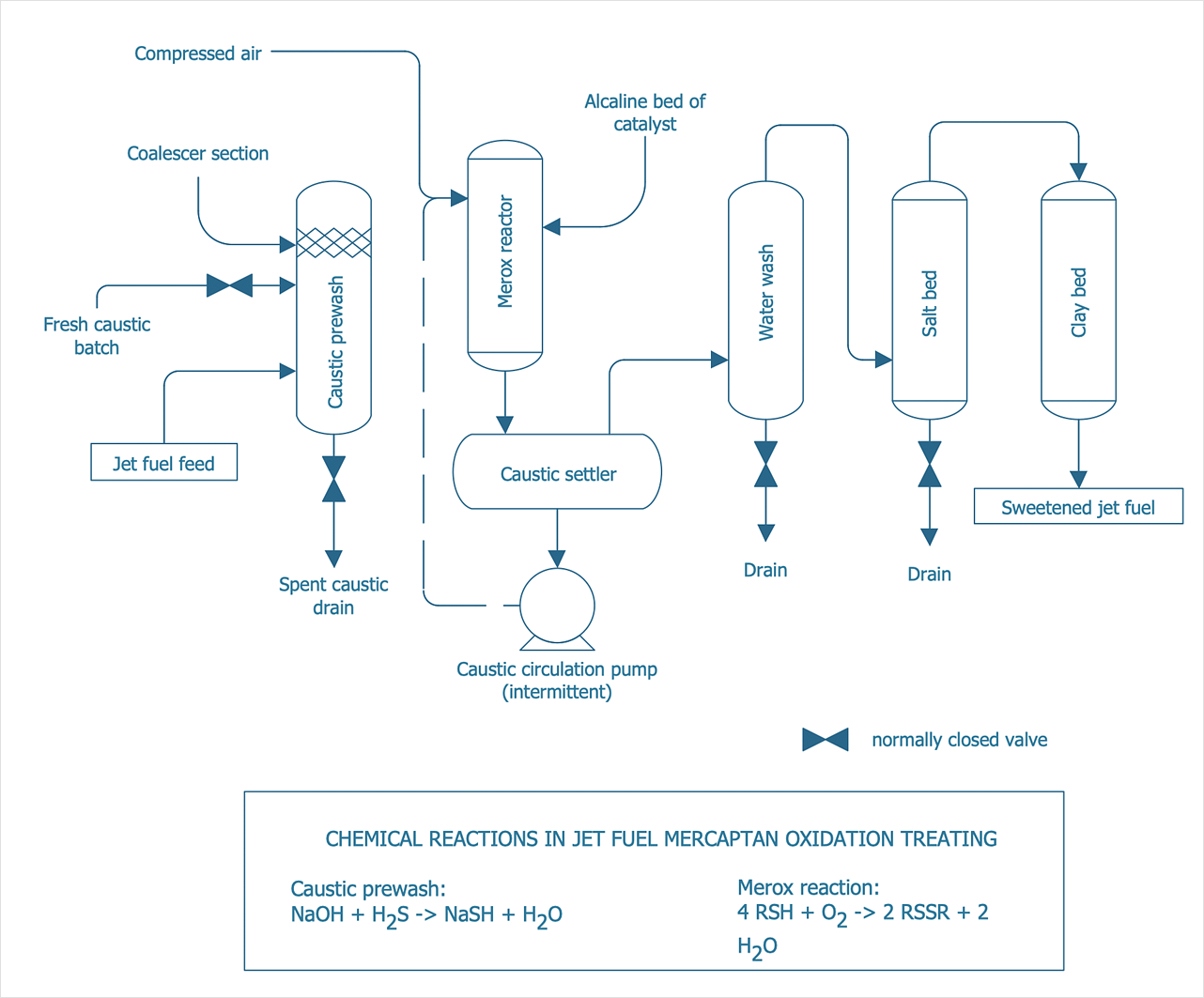
How to Draw a Chemical Process Flow Diagram
Process Flow Diagram widely used in modeling of processes in the chemical industry. A Chemical Process Flow diagram (PFD) is a specialized type of flowchart. With the help of Chemical Process Flow Diagram engineers can easily specify the general scheme of the processes and chemical plant equipment. Chemical Process Flow Diagram displays the real scheme of the chemical process, the relationship between the equipment and the technical characteristics of the process. Chemical Process Flow Diagram illustrates the connections between the basic equipment as well as the overall structure of pipelines and other supporting equipment. The purpose of the PFD is to build the image of the basic idea of the chemical process. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM together with its Chemical and Process Engineering solution delivers the possibility to design Chemical Process Flow diagrams. It is designed for chemical industry engineers and designers."In mathematics, the Euclidean algorithm, or Euclid's algorithm, is a method for computing the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two (usually positive) integers, also known as the greatest common factor (GCF) or highest common factor (HCF). ...
The GCD of two positive integers is the largest integer that divides both of them without leaving a remainder (the GCD of two integers in general is defined in a more subtle way).
In its simplest form, Euclid's algorithm starts with a pair of positive integers, and forms a new pair that consists of the smaller number and the difference between the larger and smaller numbers. The process repeats until the numbers in the pair are equal. That number then is the greatest common divisor of the original pair of integers.
The main principle is that the GCD does not change if the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number. ... Since the larger of the two numbers is reduced, repeating this process gives successively smaller numbers, so this repetition will necessarily stop sooner or later - when the numbers are equal (if the process is attempted once more, one of the numbers will become 0)." [Euclidean algorithm. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Euclidean algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The GCD of two positive integers is the largest integer that divides both of them without leaving a remainder (the GCD of two integers in general is defined in a more subtle way).
In its simplest form, Euclid's algorithm starts with a pair of positive integers, and forms a new pair that consists of the smaller number and the difference between the larger and smaller numbers. The process repeats until the numbers in the pair are equal. That number then is the greatest common divisor of the original pair of integers.
The main principle is that the GCD does not change if the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number. ... Since the larger of the two numbers is reduced, repeating this process gives successively smaller numbers, so this repetition will necessarily stop sooner or later - when the numbers are equal (if the process is attempted once more, one of the numbers will become 0)." [Euclidean algorithm. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Euclidean algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- A Diagram Of A Flow C
- Flow Chart For Ax^2 Bx C
- Flow Chart C Language App Android
- Flow Chart In C To Find The Sum Of Gp Series
- Quadratic Flow Chart In C Programming
- Flow Chart Of Quadratic Equation Ax 2 Bx C = 0
- Flowchart C
- Solving quadratic equation algorithm - Flowchart | Ax2 Bx C =0 Flow ...
- C Language Flow Charts App
- C Programming Flow Chart To Finding The Roots Of Quadratic
- Top 5 Android Flow Chart Apps | Flow Chat C App For Android
- Compute Area Of Circle C Program Flow Chart
- Quardartic Flow Chart Using C Programming
- Flow Chart Of Ax2 Bx C
- How To Draw Flow Chart Of C Pro Com
- Flow Chart Of Gp Series Program In C
- Graphics Calculator Flow Chart In C
- C Program To Display Pyramid Using Control Flow Charts
- Ax2 Bx C 0