"In mathematics, the Euclidean algorithm, or Euclid's algorithm, is a method for computing the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two (usually positive) integers, also known as the greatest common factor (GCF) or highest common factor (HCF). ...
The GCD of two positive integers is the largest integer that divides both of them without leaving a remainder (the GCD of two integers in general is defined in a more subtle way).
In its simplest form, Euclid's algorithm starts with a pair of positive integers, and forms a new pair that consists of the smaller number and the difference between the larger and smaller numbers. The process repeats until the numbers in the pair are equal. That number then is the greatest common divisor of the original pair of integers.
The main principle is that the GCD does not change if the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number. ... Since the larger of the two numbers is reduced, repeating this process gives successively smaller numbers, so this repetition will necessarily stop sooner or later - when the numbers are equal (if the process is attempted once more, one of the numbers will become 0)." [Euclidean algorithm. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Euclidean algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The GCD of two positive integers is the largest integer that divides both of them without leaving a remainder (the GCD of two integers in general is defined in a more subtle way).
In its simplest form, Euclid's algorithm starts with a pair of positive integers, and forms a new pair that consists of the smaller number and the difference between the larger and smaller numbers. The process repeats until the numbers in the pair are equal. That number then is the greatest common divisor of the original pair of integers.
The main principle is that the GCD does not change if the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number. ... Since the larger of the two numbers is reduced, repeating this process gives successively smaller numbers, so this repetition will necessarily stop sooner or later - when the numbers are equal (if the process is attempted once more, one of the numbers will become 0)." [Euclidean algorithm. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Euclidean algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
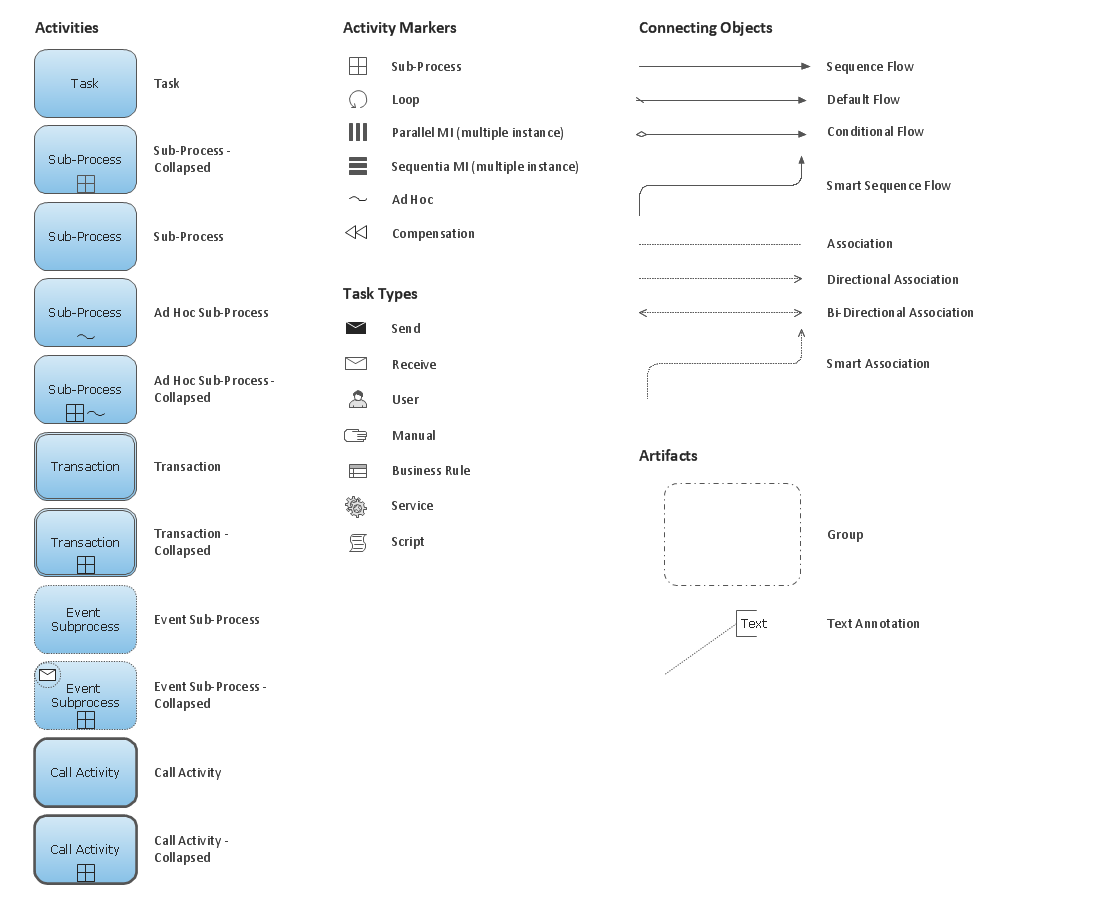
Business Process Elements: Activities
Create professional business process diagrams using ConceptDraw Activities library with 34 objects from BPMN.
- Rectangle Flowchart Represent
- A Rectangle Is Used To Display A Decision In The Flow Chart
- Flow Chart Area Of Rectangle
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Divided Bar Diagrams ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | How to Draw a Divided Bar ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Process Flow Chart Symbol ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Flowchart Definition ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Divided Bar Diagrams ...
- How to Draw a Divided Bar Chart in ConceptDraw PRO | Basic ...
- Flow Chart For Area Of Rectangle Mathematics
- Divided Bar Diagrams | Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning ...
- Workflow Diagram Template | Basic Flowchart Symbols and ...
- A Flow Chart Symbol Represented With Rectangle With Rounded
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | London election results ...
- Examples Of Divided Rectangles
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Divided Bar Diagrams ...
- Entity Relationship Diagram Symbols | Rectangle Flow Chart Png
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Competitor Analysis ...
- How to Draw a Divided Bar Chart in ConceptDraw PRO | Basic ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Business Process Workflow ...