"In mathematics, the Euclidean algorithm, or Euclid's algorithm, is a method for computing the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two (usually positive) integers, also known as the greatest common factor (GCF) or highest common factor (HCF). ...
The GCD of two positive integers is the largest integer that divides both of them without leaving a remainder (the GCD of two integers in general is defined in a more subtle way).
In its simplest form, Euclid's algorithm starts with a pair of positive integers, and forms a new pair that consists of the smaller number and the difference between the larger and smaller numbers. The process repeats until the numbers in the pair are equal. That number then is the greatest common divisor of the original pair of integers.
The main principle is that the GCD does not change if the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number. ... Since the larger of the two numbers is reduced, repeating this process gives successively smaller numbers, so this repetition will necessarily stop sooner or later - when the numbers are equal (if the process is attempted once more, one of the numbers will become 0)." [Euclidean algorithm. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Euclidean algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The GCD of two positive integers is the largest integer that divides both of them without leaving a remainder (the GCD of two integers in general is defined in a more subtle way).
In its simplest form, Euclid's algorithm starts with a pair of positive integers, and forms a new pair that consists of the smaller number and the difference between the larger and smaller numbers. The process repeats until the numbers in the pair are equal. That number then is the greatest common divisor of the original pair of integers.
The main principle is that the GCD does not change if the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number. ... Since the larger of the two numbers is reduced, repeating this process gives successively smaller numbers, so this repetition will necessarily stop sooner or later - when the numbers are equal (if the process is attempted once more, one of the numbers will become 0)." [Euclidean algorithm. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Euclidean algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
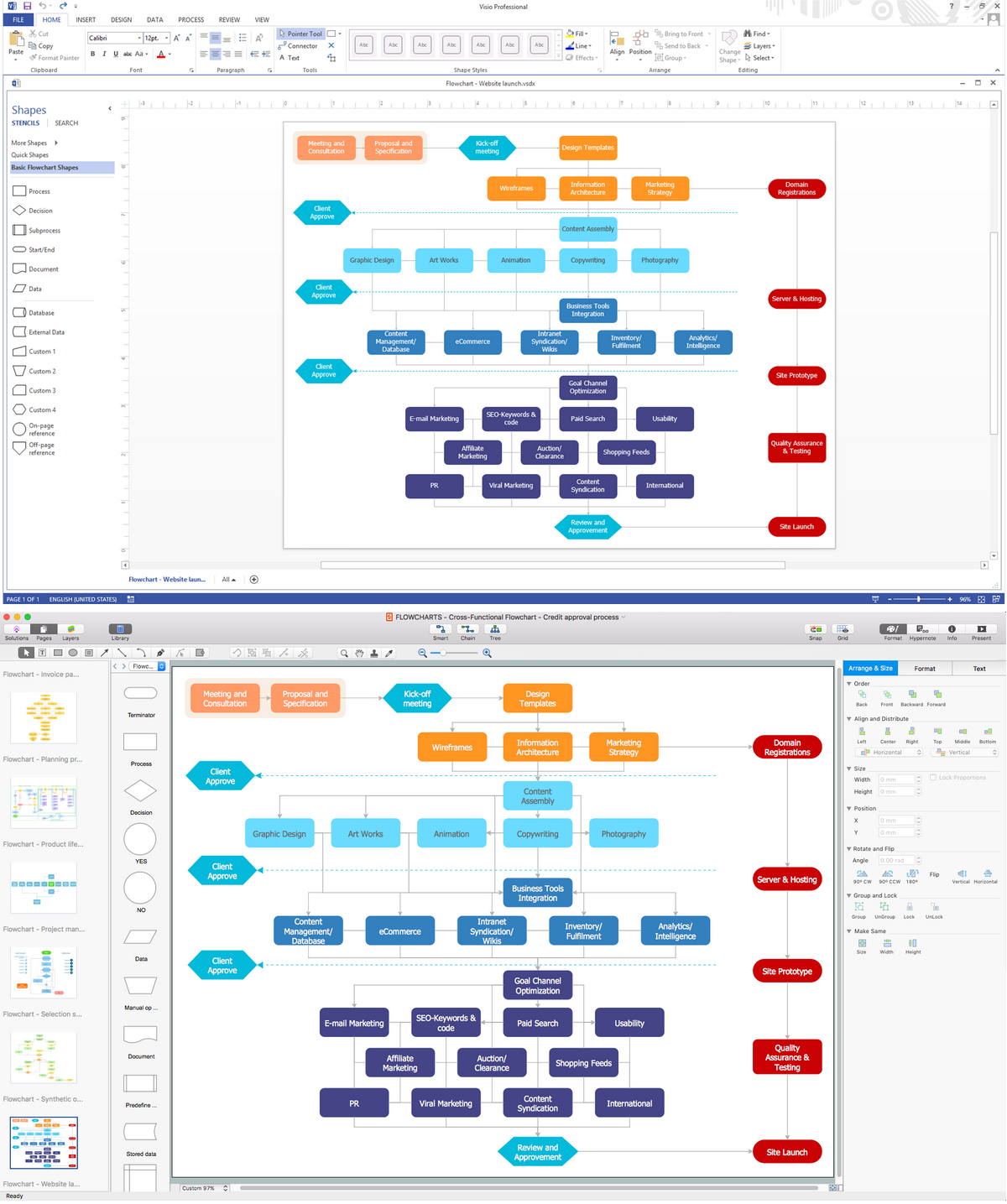
In searching of alternative to MS Visio for MAC and PC with ConceptDraw DIAGRAM
Undoubtedly MS Visio is a powerful and multifunctional tool, but however at times occur the instances, when it turns unable of meeting certain users' requirements. At this cases you may need to use an alternative program software, preferably it will be simple, convenient, and at the same time powerful and professional. In searching the alternative to MS Visio for MAC and PC we recommend you to pay attention for ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software, which was developed to satisfy all your drawing needs and requirements. It is a fully-functioned alternative product to MS Visio for both platforms. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software has many advantages, the main among them are the cross-platform compatibility, a reasonable price, widespread ConceptDraw Solution Park with huge variety of different solutions that offer numerous libraries of specialized vector objects, useful examples, samples, and quick-start templates, extensive import / export capabilities, built-in script language, MS Visio support and certainly free technical support.Cross Functional Flowchart Examples
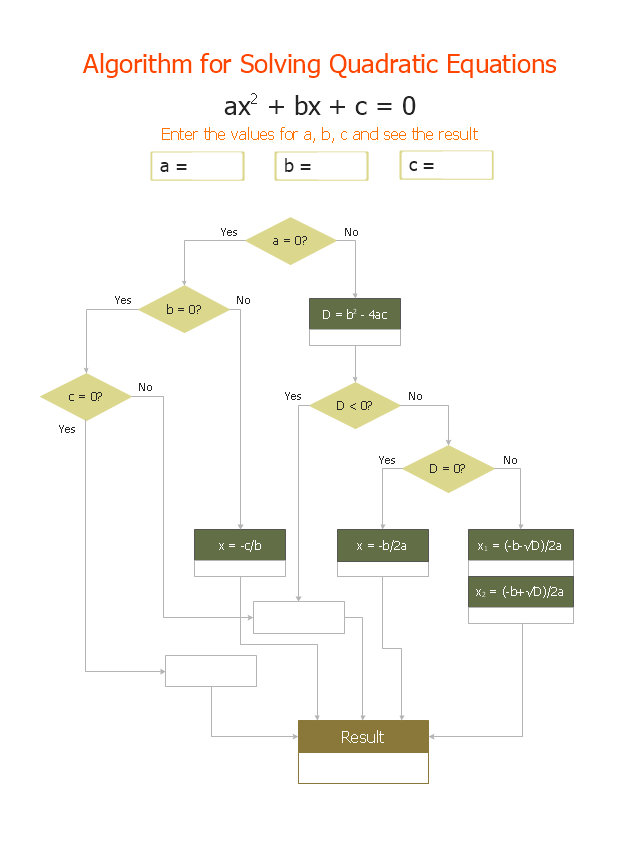
Take a look on an example of Cross-Functional-Flowchart, showing the software service cross-function process flowcharts among the different departments. It presents a simple flowchart among the customer, sales, technical support, tester and development. Try now Flowchart Software and Cross-Functional library with 2 libraries and 45 vector shapes of the Cross-Functional Flowcharts solution. Then you can use built-in templates to create and present your software service cross-function process flowcharts."In elementary algebra, a quadratic equation (from the Latin quadratus for "square") is any equation having the form
ax^2+bx+c=0
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c are constants with a not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The constants a, b, and c are called, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.
Because the quadratic equation involves only one unknown, it is called "univariate". The quadratic equation only contains powers of x that are non-negative integers, and therefore it is a polynomial equation, and in particular it is a second degree polynomial equation since the greatest power is two.
Quadratic equations can be solved by a process known in American English as factoring and in other varieties of English as factorising, by completing the square, by using the quadratic formula, or by graphing." [Quadratic equation. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Solving quadratic equation algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
ax^2+bx+c=0
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c are constants with a not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The constants a, b, and c are called, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.
Because the quadratic equation involves only one unknown, it is called "univariate". The quadratic equation only contains powers of x that are non-negative integers, and therefore it is a polynomial equation, and in particular it is a second degree polynomial equation since the greatest power is two.
Quadratic equations can be solved by a process known in American English as factoring and in other varieties of English as factorising, by completing the square, by using the quadratic formula, or by graphing." [Quadratic equation. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Solving quadratic equation algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
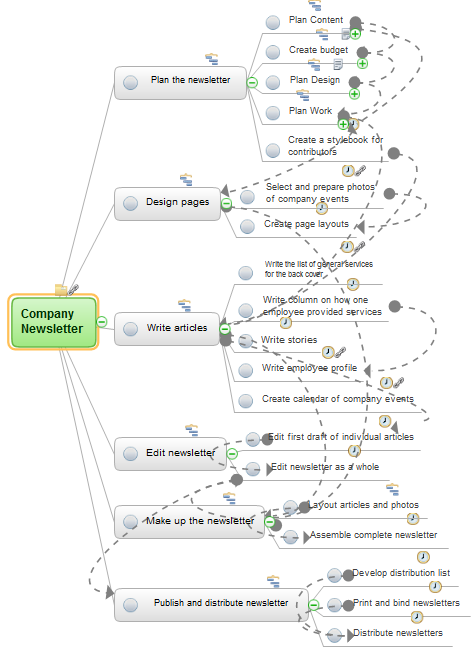
Think and act effectively
Many people who use mind mapping software for personal organizing find ConceptDraw MINDMAP sufficiently useful mind mapping tool in their business and daily life. Especially many positive responses receive ConceptDraw MINDMAP as cross platform tool to mind maps for Macintosh and Windows.Total Quality Management with ConceptDraw
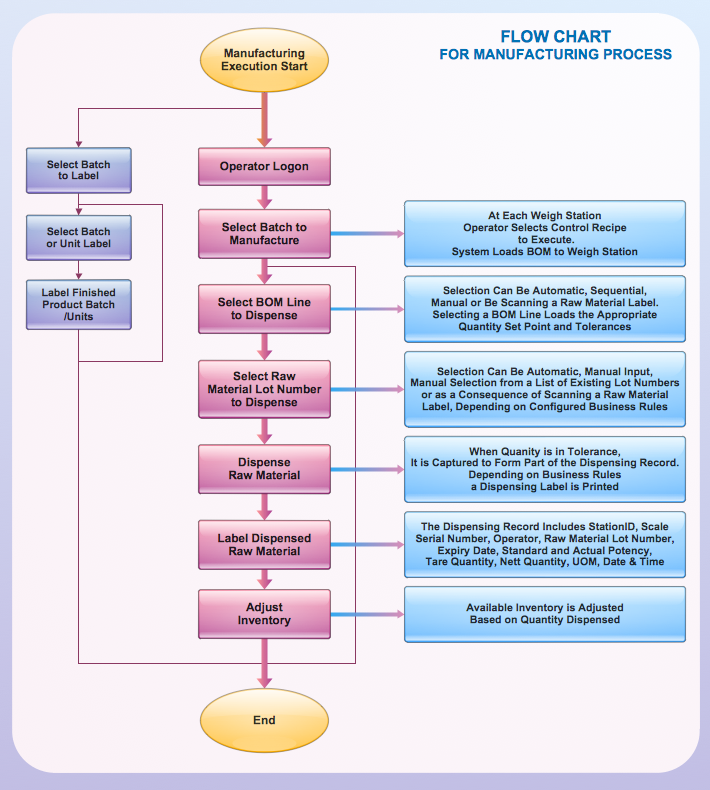
Total Quality Management (TQM) system is the management method where the confidence in quality of all organization processes is placed foremost. The given method is widely used in production, in educational system, in government organizations and so on.- Draw Flow Chart To Find Factors Of A Number
- Draw A Flow Chart Of Finding Factors Of Given Number
- Flowchart To Find GCD Of Two Number
- Flow Chart For Greatest Common Division Of Two Numbers
- Draw The Flowchart To Find Factors Between Two Numbers
- Flowchart To Find Factors Of A Given Number
- What Are Factors And Solutions Flow Chart
- Factor Of Numbers In C With Flow Chart
- A Flowchart To Find The Sum Of A Given Numbers
- Visual Basic Program And Flowchart On Gcd Of Two Numbers
- Alogarithm For Finding The Larger Of Two Numbers
- Flowchart To Subtract Two Number
- Algorithm To Find The Greatest Of Two Numbers
- Flow Chart For Division Of Two Numbers
- Flow Chart In C To Find The Sum Of Gp Series
- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Sales Process Flowchart ...
- Draw The Flowchart To Find All Of A Quadratic Eqation
- Solving quadratic equation algorithm - Flowchart | Types of ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Types of Flowcharts ...
- Process Flowchart | PROBLEM ANALYSIS. Root Cause Analysis ...