The vector stencils library "UML timing diagrams" contains 15 symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
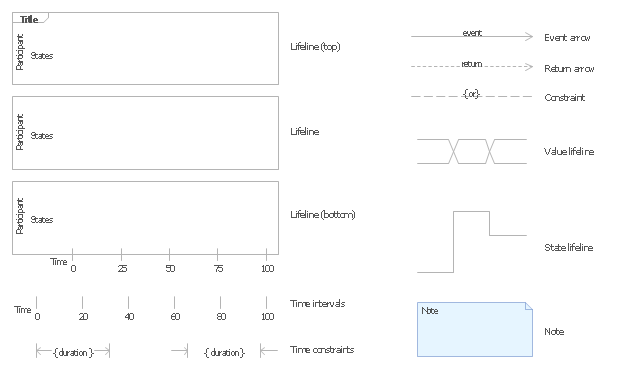
"The following nodes and edges are typically drawn in a UML timing diagram: lifeline, state or condition timeline, destruction event, duration constraint, time constraint. ...
Lifeline is a named element which represents an individual participant in the interaction. ... lifelines represent only one interacting entity. ...
Lifeline on the timing diagrams is represented by the name of classifier or the instance it represents. It could be placed inside diagram frame or a "swimlane". ...
Timing diagram could show states of the participating classifier or attribute, or some testable conditions, such as a discrete or enumerable value of an attribute. ...
UML also allows the state/ condition dimension be continuous. It could be used in scenarios where entities undergo continuous state changes, such as temperature or density. ...
Destruction occurrence is a message occurrence which represents the destruction of the instance described by the lifeline. It may result in the subsequent destruction of other objects that this object owns by composition. No other occurrence may appear after the destruction event on a given lifeline.
Complete UML name of the occurrence is destruction occurrence specification. Until UML 2.4 it was called destruction event, and earlier - stop.
The destruction event is depicted by a cross in the form of an X at the end of a timeline. ...
Duration constraint is an interval constraint that refers to a duration interval. The duration interval is duration used to determine whether the constraint is satisfied.
The semantics of a duration constraint is inherited from constraints. If constraints are violated, traces become negative which means that system is considered as failed.
Duration constraint is shown as some graphical association between a duration interval and the constructs that it constrains. ...
Time constraint is an interval constraint that refers to a time interval. The time interval is time expression used to determine whether the constraint is satisfied.
The semantics of a time constraint is inherited from constraints. All traces where the constraints are violated are negative traces, i.e., if they occur, the system is considered as failed.
Time constraint is shown as graphical association between a time interval and the construct that it constrains. Typically this graphical association is a small line, e.g., between an occurrence specification and a time interval." [uml-diagrams.org/ timing-diagrams.html]
The example "Design elements - UML timing diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"The following nodes and edges are typically drawn in a UML timing diagram: lifeline, state or condition timeline, destruction event, duration constraint, time constraint. ...
Lifeline is a named element which represents an individual participant in the interaction. ... lifelines represent only one interacting entity. ...
Lifeline on the timing diagrams is represented by the name of classifier or the instance it represents. It could be placed inside diagram frame or a "swimlane". ...
Timing diagram could show states of the participating classifier or attribute, or some testable conditions, such as a discrete or enumerable value of an attribute. ...
UML also allows the state/ condition dimension be continuous. It could be used in scenarios where entities undergo continuous state changes, such as temperature or density. ...
Destruction occurrence is a message occurrence which represents the destruction of the instance described by the lifeline. It may result in the subsequent destruction of other objects that this object owns by composition. No other occurrence may appear after the destruction event on a given lifeline.
Complete UML name of the occurrence is destruction occurrence specification. Until UML 2.4 it was called destruction event, and earlier - stop.
The destruction event is depicted by a cross in the form of an X at the end of a timeline. ...
Duration constraint is an interval constraint that refers to a duration interval. The duration interval is duration used to determine whether the constraint is satisfied.
The semantics of a duration constraint is inherited from constraints. If constraints are violated, traces become negative which means that system is considered as failed.
Duration constraint is shown as some graphical association between a duration interval and the constructs that it constrains. ...
Time constraint is an interval constraint that refers to a time interval. The time interval is time expression used to determine whether the constraint is satisfied.
The semantics of a time constraint is inherited from constraints. All traces where the constraints are violated are negative traces, i.e., if they occur, the system is considered as failed.
Time constraint is shown as graphical association between a time interval and the construct that it constrains. Typically this graphical association is a small line, e.g., between an occurrence specification and a time interval." [uml-diagrams.org/ timing-diagrams.html]
The example "Design elements - UML timing diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
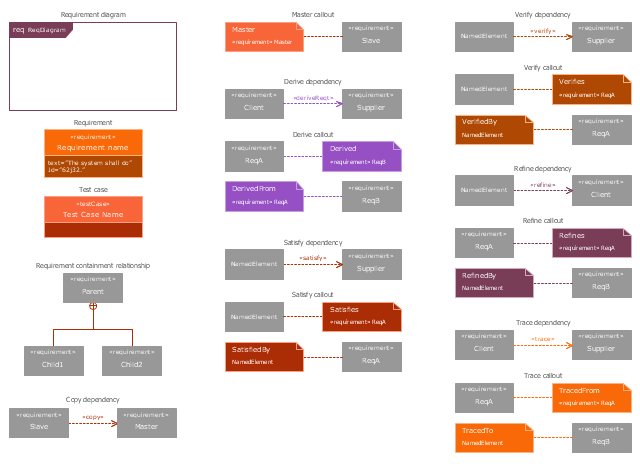
The vector stencils library "Requirement diagram" contains 21 SysML symbols.
Use it to design your requirement diagrams using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"A requirement specifies a capability or condition that must (or should) be satisfied. A requirement may specify a function that a system must perform or a performance condition a system must achieve. SysML provides modeling constructs to represent text-based requirements and relate them to other modeling elements. The requirements diagram described in this clause can depict the requirements in graphical, tabular, or tree structure format. A requirement can also appear on other diagrams to show its relationship to other modeling elements. The requirements modeling constructs are intended to provide a bridge between traditional requirements management tools and the other SysML models.
A requirement is defined as a stereotype of UML Class subject to a set of constraints. A standard requirement includes properties to specify its unique identifier and text requirement. Additional properties such as verification status, can be specified by the user.
Several requirements relationships are specified that enable the modeler to relate requirements to other requirements as well as to other model elements. These include relationships for defining a requirements hierarchy, deriving requirements, satisfying requirements, verifying requirements, and refining requirements." [www.omg.org/ spec/ SysML/ 1.3/ PDF]
The SysML shapes example "Design elements - Requirement diagram" is included in the SysML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to design your requirement diagrams using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"A requirement specifies a capability or condition that must (or should) be satisfied. A requirement may specify a function that a system must perform or a performance condition a system must achieve. SysML provides modeling constructs to represent text-based requirements and relate them to other modeling elements. The requirements diagram described in this clause can depict the requirements in graphical, tabular, or tree structure format. A requirement can also appear on other diagrams to show its relationship to other modeling elements. The requirements modeling constructs are intended to provide a bridge between traditional requirements management tools and the other SysML models.
A requirement is defined as a stereotype of UML Class subject to a set of constraints. A standard requirement includes properties to specify its unique identifier and text requirement. Additional properties such as verification status, can be specified by the user.
Several requirements relationships are specified that enable the modeler to relate requirements to other requirements as well as to other model elements. These include relationships for defining a requirements hierarchy, deriving requirements, satisfying requirements, verifying requirements, and refining requirements." [www.omg.org/ spec/ SysML/ 1.3/ PDF]
The SysML shapes example "Design elements - Requirement diagram" is included in the SysML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- How To Represent Or Condition In Flowchart
- On An Activity Diagram The Diamond Represents An And Condition
- Fishbone Diagram On 4m Condition
- Condition Meaning In Flowchart
- How can you illustrate the weather condition | Nature | Illustration ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Workflow Diagram | Types ...
- Circuit Symbol For Air Condition Switch
- How to Track Your Project Plan vs. the Actual Project Condition ...
- HVAC Plans | Er Diagram Of Heating Ventilation Air Condition
- Air Condition Lay Out Plan
- How to Track Your Project Plan vs. the Actual Project Condition ...
- How to Track Your Project Plan vs. the Actual Project Condition ...
- Process Control Block Diagram For Air Condition
- How to Track Your Project Plan vs. the Actual Project Condition ...
- How to Track Your Project Plan vs. the Actual Project Condition ...
- Basic Diagramming | Pie Charts | How can you illustrate the weather ...
- How to Create a HVAC Plan | Interior Design Registers, Drills and ...
- Mechanical Drawing Symbols | Interior Design Registers, Drills and ...
- How to Track Your Project Plan vs. the Actual Project Condition ...
- Drawing Illustration | How can you illustrate the weather condition ...