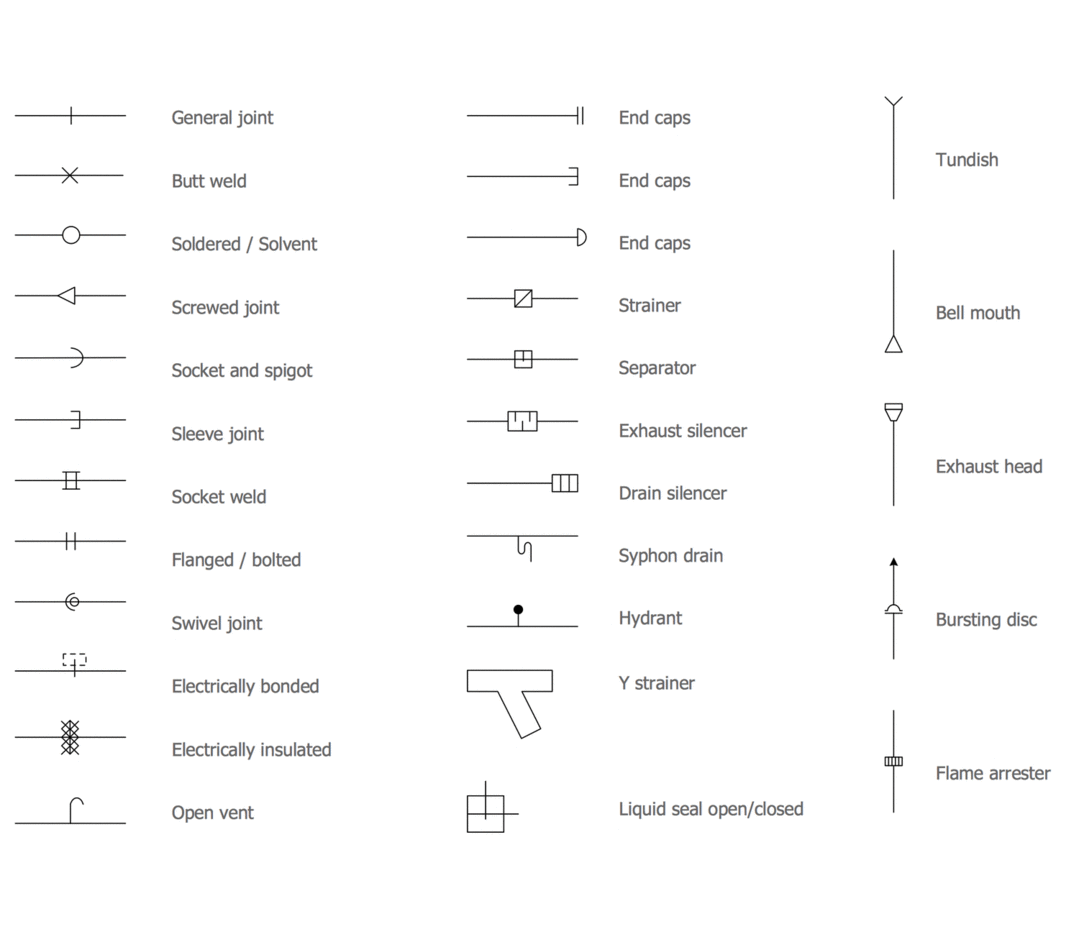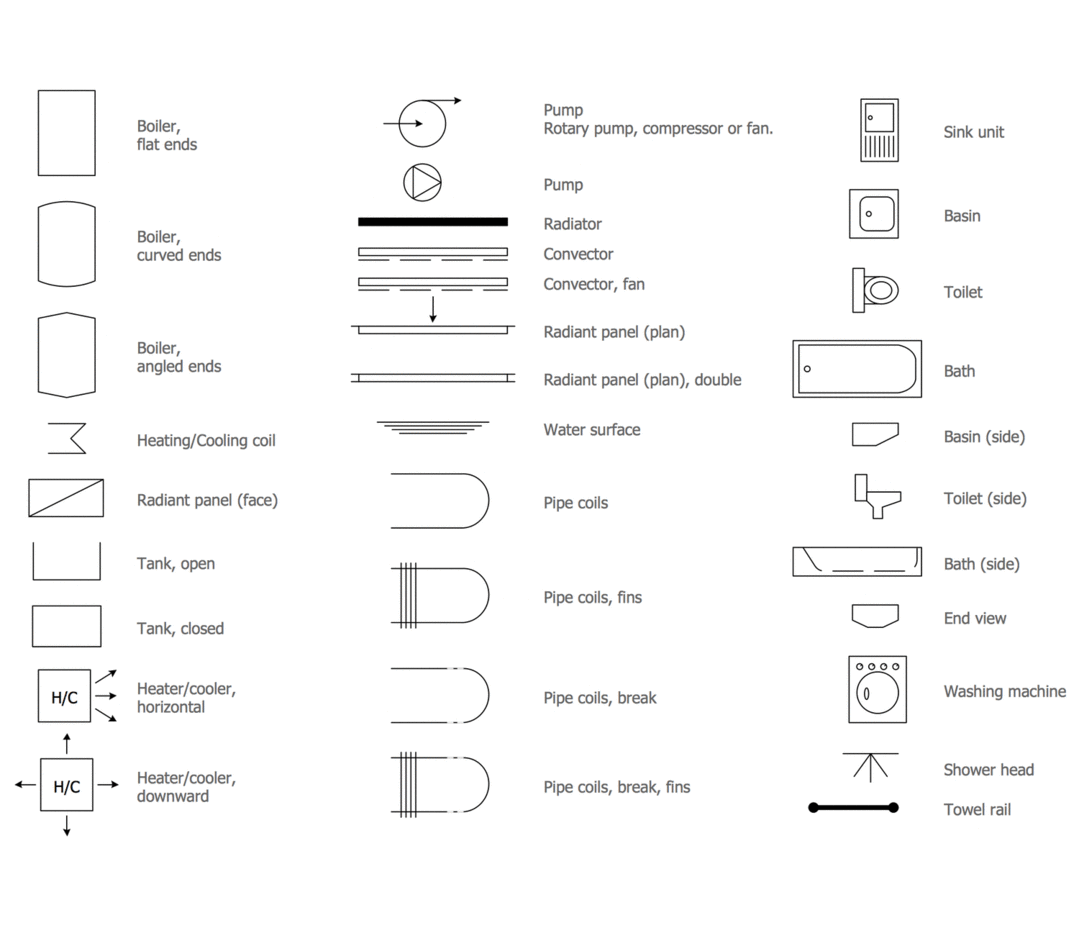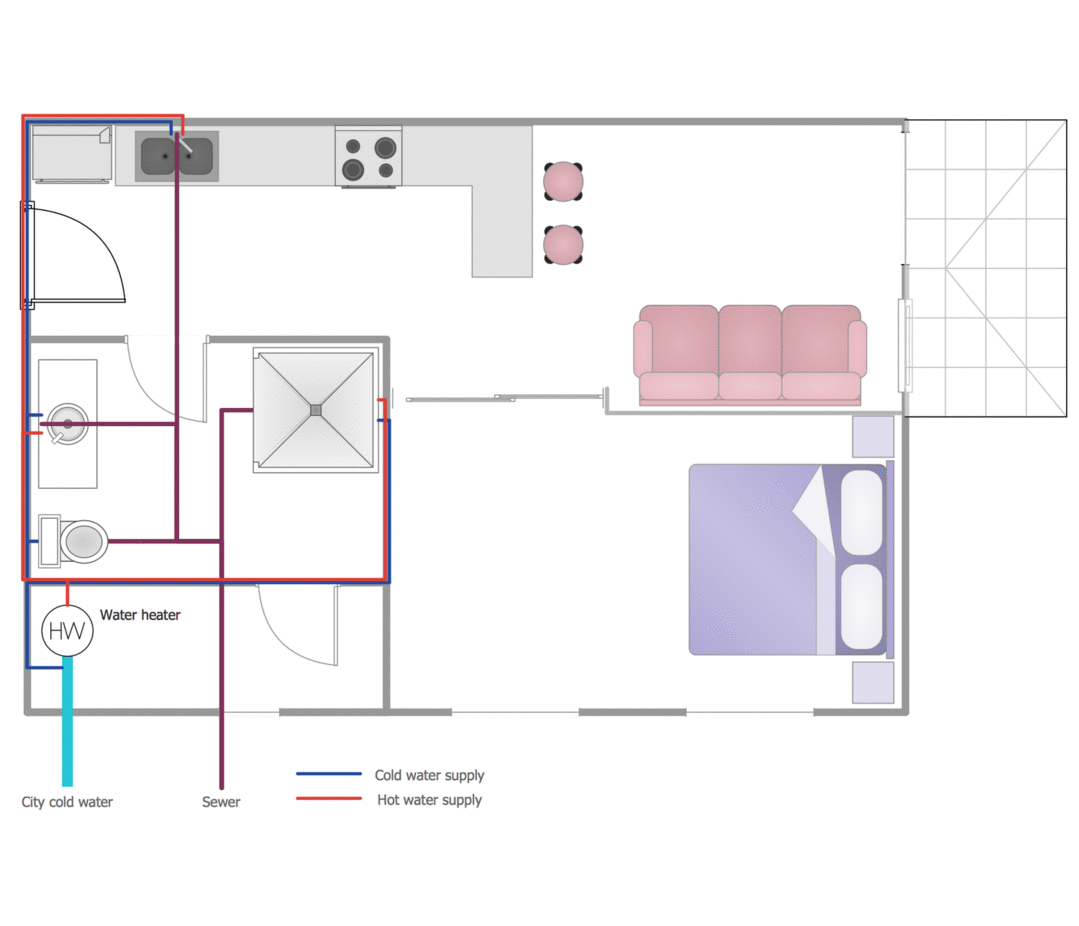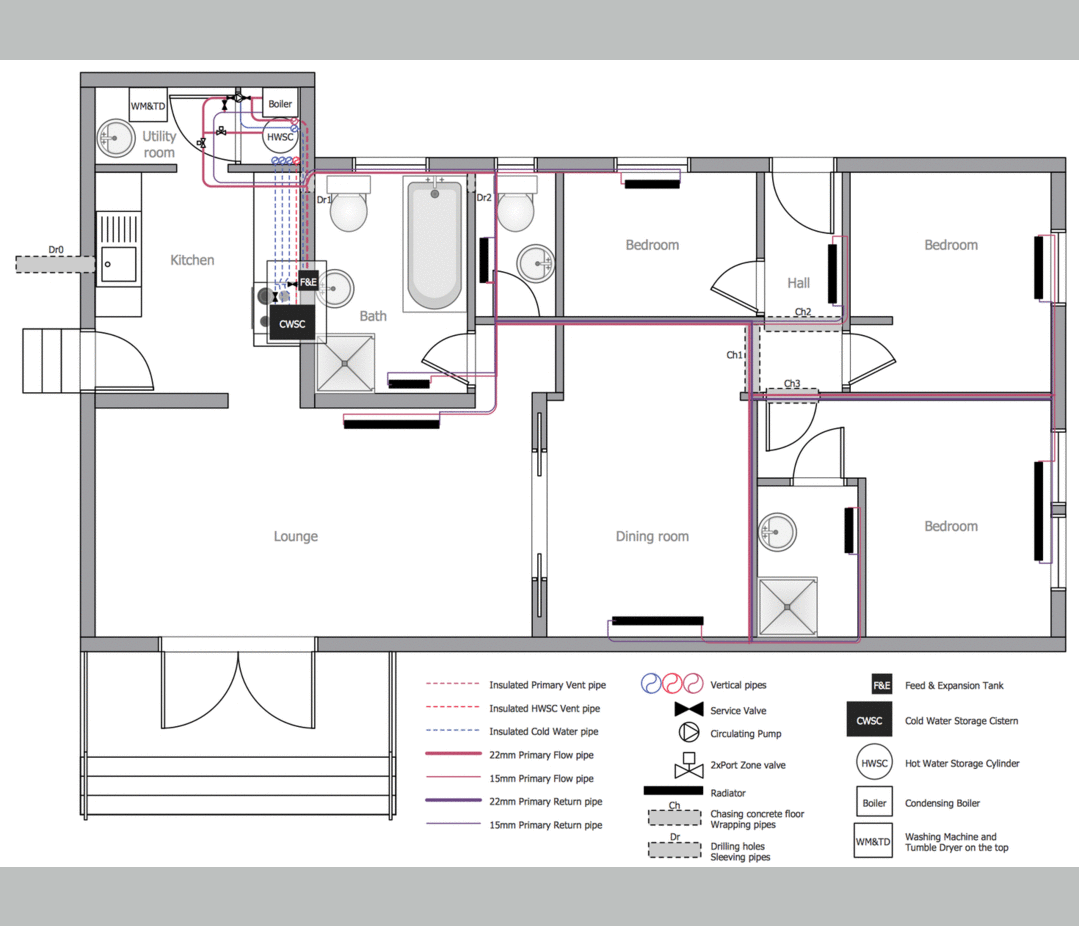
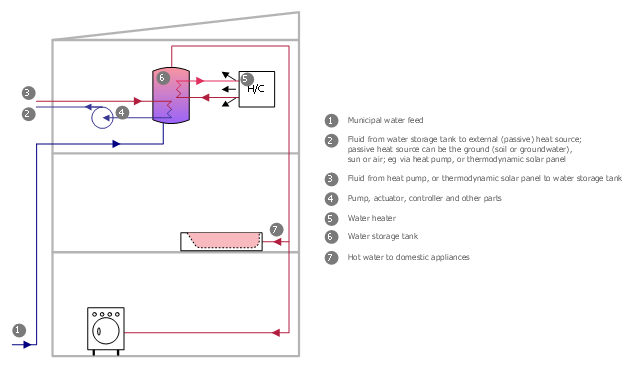
This plumbing and piping plan sample was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Active Indirect Water Heater Diagram.svg.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Active_ Indirect_ Water_ Heater_ Diagram.svg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Water heating is a thermodynamic process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated to steam have many uses.
Domestically, water is traditionally heated in vessels known as water heaters, kettles, cauldrons, pots, or coppers. These metal vessels that heat a batch of water do not produce a continual supply of heated water at a preset temperature. Rarely, hot water occurs naturally, usually from natural hot springs. The temperature varies based on the consumption rate, becoming cooler as flow increases.
Appliances that provide a continual supply of hot water are called water heaters, hot water heaters, hot water tanks, boilers, heat exchangers, geysers, or calorifiers. These names depend on region, and whether they heat potable or non-potable water, are in domestic or industrial use, and their energy source. In domestic installations, potable water heated for uses other than space heating is also called domestic hot water (DHW).
Fossil fuels (natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, oil), or solid fuels are commonly used for heating water. These may be consumed directly or may produce electricity that, in turn, heats water. Electricity to heat water may also come from any other electrical source, such as nuclear power or renewable energy. Alternative energy such as solar energy, heat pumps, hot water heat recycling, and geothermal heating can also heat water, often in combination with backup systems powered by fossil fuels or electricity." [Water heating. Wikipedia]
The plumbing plan example "Active indirect water heater diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Plumbing and Piping Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Active_ Indirect_ Water_ Heater_ Diagram.svg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Water heating is a thermodynamic process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated to steam have many uses.
Domestically, water is traditionally heated in vessels known as water heaters, kettles, cauldrons, pots, or coppers. These metal vessels that heat a batch of water do not produce a continual supply of heated water at a preset temperature. Rarely, hot water occurs naturally, usually from natural hot springs. The temperature varies based on the consumption rate, becoming cooler as flow increases.
Appliances that provide a continual supply of hot water are called water heaters, hot water heaters, hot water tanks, boilers, heat exchangers, geysers, or calorifiers. These names depend on region, and whether they heat potable or non-potable water, are in domestic or industrial use, and their energy source. In domestic installations, potable water heated for uses other than space heating is also called domestic hot water (DHW).
Fossil fuels (natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, oil), or solid fuels are commonly used for heating water. These may be consumed directly or may produce electricity that, in turn, heats water. Electricity to heat water may also come from any other electrical source, such as nuclear power or renewable energy. Alternative energy such as solar energy, heat pumps, hot water heat recycling, and geothermal heating can also heat water, often in combination with backup systems powered by fossil fuels or electricity." [Water heating. Wikipedia]
The plumbing plan example "Active indirect water heater diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Plumbing and Piping Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
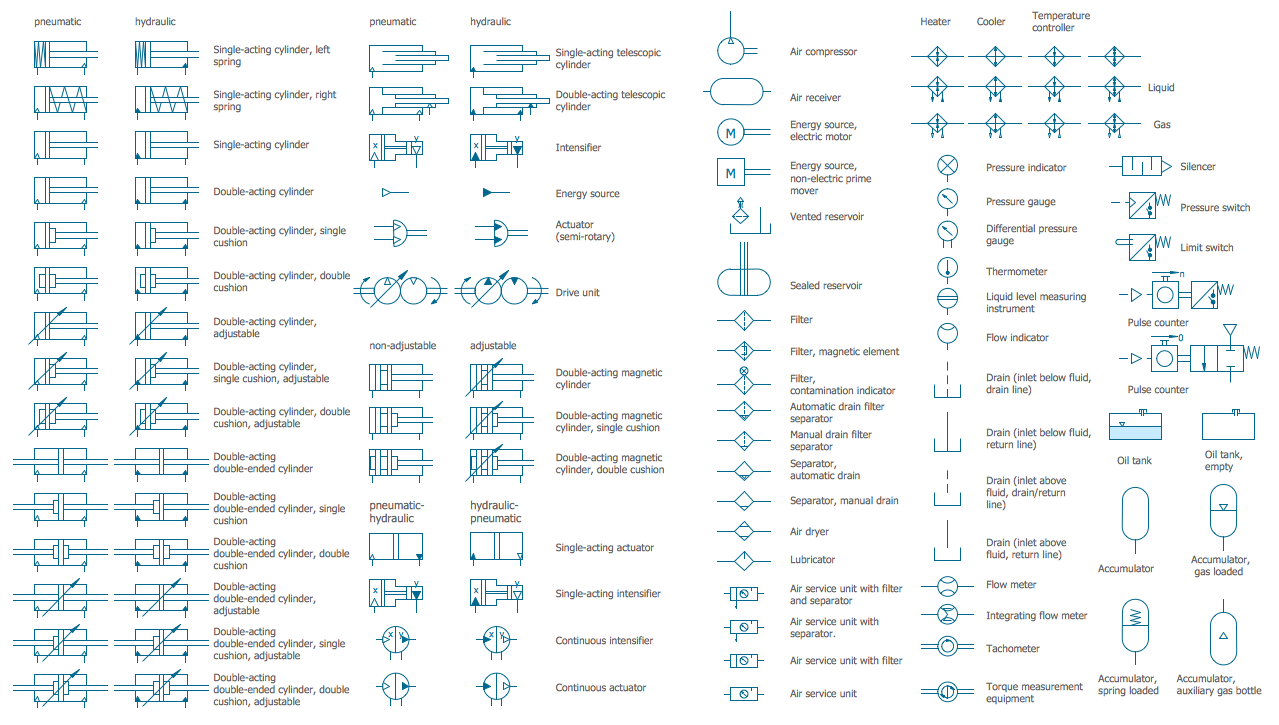
Process Flow Diagram Symbols
Chemical and Process Engineering Solution from the Industrial Engineering Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is a unique tool which contains variety of predesigned process flow diagram symbols for easy creating various Chemical and Process Flow Diagrams in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM.Piping and Instrumentation Diagram Software
Piping and Instrumentation Diagram is a technical sketch or drawing, which shows in details the piping system and instrumentation of a processing plant. Piping and Instrumentation Diagram is developed by process design engineers and technical engineers on the phase of plant design. This plan is necessary on the stages of plant construction and then is actively used by operators, instrumentation and piping engineers when operating the plant. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software provides unique Plumbing and Piping Plans solution from Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park with 10 libraries of ready-to-use predesigned vector elements, templates and samples, to help you create professional Piping diagrams and schematics, Instrumentation diagrams, Plumbing plans and blueprints, Schemes of hot and cold water supply systems, Heating schemes, Mechanical diagrams, Diagrams of fluids, hydraulics, air and gas pipings, Technical drawings of waste water disposal systems, Schematics of industrial piping systems, Diagrams of ventilation systems, etc.This process flow diagram (PFD) example shows an amine treating system for the removal of gaseous hydrogen sulfide from gas streams. It is used in oil refineries and chemical plants. This PFD sample was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: AmineTreating.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:AmineTreating.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Amine gas treating, also known as gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from gases. It is a common unit process used in refineries, and is also used in petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries.
Processes within oil refineries or chemical processing plants that remove hydrogen sulfide are referred to as "sweetening" processes because the odor of the processed products is improved by the absence of hydrogen sulfide. An alternative to the use of amines involves membrane technology. Membranes are attractive since no reagents are consumed.
Many different amines are used in gas treating:
Diethanolamine (DEA),
Monoethanolamine (MEA),
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA),
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA),
Aminoethoxyethanol (Diglycolamine) (DGA).
The most commonly used amines in industrial plants are the alkanolamines DEA, MEA, and MDEA. These amines are also used in many oil refineries to remove sour gases from liquid hydrocarbons such as liquified petroleum gas (LPG)." [Amine gas treating. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Amine treating unit schematic diagram" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Amine gas treating, also known as gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from gases. It is a common unit process used in refineries, and is also used in petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries.
Processes within oil refineries or chemical processing plants that remove hydrogen sulfide are referred to as "sweetening" processes because the odor of the processed products is improved by the absence of hydrogen sulfide. An alternative to the use of amines involves membrane technology. Membranes are attractive since no reagents are consumed.
Many different amines are used in gas treating:
Diethanolamine (DEA),
Monoethanolamine (MEA),
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA),
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA),
Aminoethoxyethanol (Diglycolamine) (DGA).
The most commonly used amines in industrial plants are the alkanolamines DEA, MEA, and MDEA. These amines are also used in many oil refineries to remove sour gases from liquid hydrocarbons such as liquified petroleum gas (LPG)." [Amine gas treating. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Amine treating unit schematic diagram" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This process flow diagram (PFD) of a typical crude oil distillation unit as used in petroleum crude oil refineries was redrawn from Wikipedia file: Crude Oil Distillation Unit.png. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Crude_ Oil_ Distillation_ Unit.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units. In many ways, oil refineries use much of the technology of, and can be thought of, as types of chemical plants. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot (tank farm) at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.
An oil refinery is considered an essential part of the midstream side of the petroleum industry." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ Oil_ refinery]
The process flow diagram (PFD) example "Crude oil distillation" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units. In many ways, oil refineries use much of the technology of, and can be thought of, as types of chemical plants. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot (tank farm) at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.
An oil refinery is considered an essential part of the midstream side of the petroleum industry." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ Oil_ refinery]
The process flow diagram (PFD) example "Crude oil distillation" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Plumbing and Piping Plans
Plumbing and Piping Plans
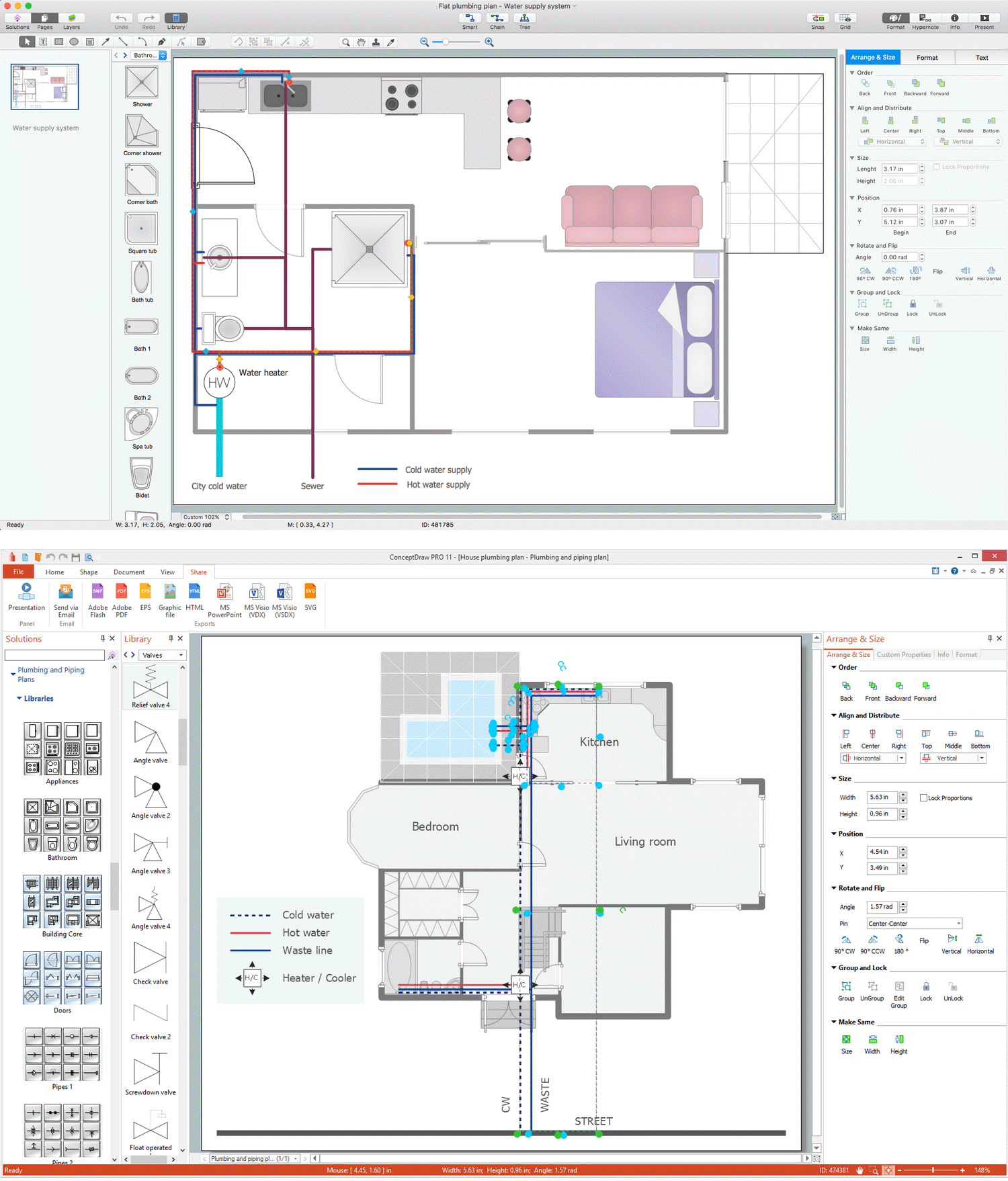
Plumbing and Piping Plans solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM.2.2 software with samples, templates and libraries of pipes, plumbing, and valves design elements for developing of water and plumbing systems, and for drawing Plumbing plan, Piping plan, PVC Pipe plan, PVC Pipe furniture plan, Plumbing layout plan, Plumbing floor plan, Half pipe plans, Pipe bender plans.
Building Drawing Software for Designing Plumbing
The construction project for any building obligatory must include the plans for systems of water supplying, sewerage, lighting and heating. From one side these are the documents required and indispensable for the construction, but from the other side this is a way of correct and effective selection of equipment, and subsequent its installation. Correctly performed calculations for these systems ensure a reliable, energy-efficient and cost-effective work. At this each project is fully individual decision taking into account all nuances - from the features of building to the personal preferences. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is a powerful building drawing software for designing Plumbing, Piping, Lighting and other building plans thanks to the included Plumbing and Piping Plans solution and other solutions from Building Plans area. Plumbing and Piping Plans solution includes variety of libraries with different design elements of pipes, valves and other sanitary equipment and helps easy develop the annotated schematics and diagrams of plumbing systems, piping, and waste water.
 Plant Layout Plans
Plant Layout Plans
Plant Layout Plans solution can be used for power plant design and plant layout design, for making the needed building plant plans and plant layouts looking professionally good. Having the newest plant layout software, the plant design solutions and in particular the ConceptDraw’s Plant Layout Plans solution, including the pre-made templates, examples of the plant layout plans, and the stencil libraries with the design elements, the architects, electricians, interior designers, builders, telecommunications managers, plant design engineers, and other technicians can use them to create the professionally looking drawings within only a few minutes.
 Chemical and Process Engineering
Chemical and Process Engineering
This chemical engineering solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM.9.5 (or later) with process flow diagram symbols, samples, process diagrams templates and libraries of design elements for creating process and instrumentation diagrams, block flow diagrams (BFD
Mechanical Drawing Symbols
Mechanical Drawings are the special type of technical diagrams that visualize the structure of complex systems and illustrate the information about ventilation, heating, air conditioning, i.e. HVAC systems. These drawings are created on the base of floor plans and reflected ceiling plans, and then become an obligatory part of construction project which is needed directly for construction a building and for receiving a permit on it. Mechanical drawings and diagrams help effectively represent construction, technical and engineering solutions, and also schematics of different mechanical equipment. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM ector drawing software enhanced with Mechanical Engineering solution from Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park provides wide set of effective drawing tools, predesigned mechanical drawing symbols, templates, samples and examples. Use of standardized and recognized mechanical vector symbols helps you design understandable mechanical drawings, diagrams and mechanical engineering schematics.- Active indirect water heater diagram | Amine treating unit schematic ...
- Active indirect water heater diagram | Pump Diagram With Name
- Flow Chart On Distillation Process Of Water
- Flow Diagram Of Pump
- Active indirect water heater diagram | House water heating | Flat ...
- Active indirect water heater diagram | Flat plumbing plan ...
- Process Flow Diagram Heater
- Active indirect water heater diagram | Central air pool heater ...
- Water cycle diagram | Active indirect water heater diagram | Drawing ...
- Schematic Drawing Sample In An Industrial Plant
-amine-treating-unit-schematic-diagram.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-crude-oil-distillation-unit---pfd.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)