"Logical topology, or signal topology, is the arrangement of devices on a computer network and how they communicate with one another. How devices are connected to the network through the actual cables that transmit data, or the physical structure of the network, is called the physical topology. Physical topology defines how the systems are physically connected. It represents the physical layout of the devices on the network. The logical topology defines how the systems communicate across the physical topologies.
Logical topologies are bound to network protocols and describe how data is moved across the network. ...
EXAMPLE : twisted pair Ethernet is a logical bus topology in a physical star topology layout. while IBM's token ring is a logical ring topology, it is physically set up in star topology." [Logical topology. Wikipedia]
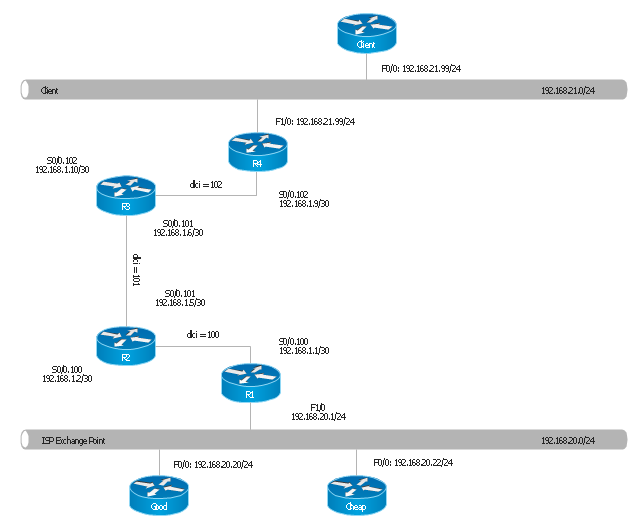
This Cisco logical computer network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Logical topologies are bound to network protocols and describe how data is moved across the network. ...
EXAMPLE : twisted pair Ethernet is a logical bus topology in a physical star topology layout. while IBM's token ring is a logical ring topology, it is physically set up in star topology." [Logical topology. Wikipedia]
This Cisco logical computer network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
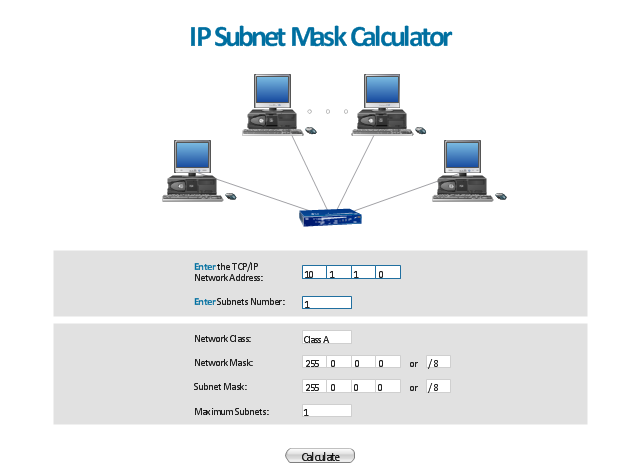
"A subnetwork, or subnet, is a logically visible subdivision of an IP network. The practice of dividing a network into two or more networks is called subnetting.
All computers that belong to a subnet are addressed with a common, identical, most-significant bit-group in their IP address. This results in the logical division of an IP address into two fields, a network or routing prefix and the rest field or host identifier. The rest field is an identifier for a specific host or network interface.
The routing prefix is expressed in CIDR notation. It is written as the first address of a network, followed by a slash character (/ ), and ending with the bit-length of the prefix. ...
The IPv6 address specification 2001:db8::/ 32 is a large address block with 296 addresses, having a 32-bit routing prefix. In IPv4 the routing prefix is also specified in the form of the subnet mask, which is expressed in quad-dotted decimal representation like an address. ...
Traffic between subnetworks is exchanged or routed with special gateways called routers which constitute the logical or physical boundaries between the subnets.
The benefits of subnetting vary with each deployment scenario. In the address allocation architecture of the Internet using Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) and in large organizations, it is necessary to allocate address space efficiently. It may also enhance routing efficiency, or have advantages in network management when subnetworks are administratively controlled by different entities in a larger organization. Subnets may be arranged logically in a hierarchical architecture, partitioning an organization's network address space into a tree-like routing structure." [Subnetwork. Wikipedia]
The template "IP Subnet mask calculator" for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
All computers that belong to a subnet are addressed with a common, identical, most-significant bit-group in their IP address. This results in the logical division of an IP address into two fields, a network or routing prefix and the rest field or host identifier. The rest field is an identifier for a specific host or network interface.
The routing prefix is expressed in CIDR notation. It is written as the first address of a network, followed by a slash character (/ ), and ending with the bit-length of the prefix. ...
The IPv6 address specification 2001:db8::/ 32 is a large address block with 296 addresses, having a 32-bit routing prefix. In IPv4 the routing prefix is also specified in the form of the subnet mask, which is expressed in quad-dotted decimal representation like an address. ...
Traffic between subnetworks is exchanged or routed with special gateways called routers which constitute the logical or physical boundaries between the subnets.
The benefits of subnetting vary with each deployment scenario. In the address allocation architecture of the Internet using Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) and in large organizations, it is necessary to allocate address space efficiently. It may also enhance routing efficiency, or have advantages in network management when subnetworks are administratively controlled by different entities in a larger organization. Subnets may be arranged logically in a hierarchical architecture, partitioning an organization's network address space into a tree-like routing structure." [Subnetwork. Wikipedia]
The template "IP Subnet mask calculator" for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Logical symbols" contains 49 logical symbols for drawing logical network topology diagrams.
"Logical topology, or signal topology, is the arrangement of devices on a computer network and how they communicate with one another. How devices are connected to the network through the actual cables that transmit data, or the physical structure of the network, is called the physical topology. Physical topology defines how the systems are physically connected. It represents the physical layout of the devices on the network. The logical topology defines how the systems communicate across the physical topologies.
Logical topologies are bound to network protocols and describe how data is moved across the network. ... EXAMPLE : twisted pair Ethernet is a logical bus topology in a physical star topology layout. While IBM's token ring is a logical ring topology, it is physically set up in star topology." [Logical topology. Wikipedia]
The icons example "Logical symbols - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ computer-and-networks
"Logical topology, or signal topology, is the arrangement of devices on a computer network and how they communicate with one another. How devices are connected to the network through the actual cables that transmit data, or the physical structure of the network, is called the physical topology. Physical topology defines how the systems are physically connected. It represents the physical layout of the devices on the network. The logical topology defines how the systems communicate across the physical topologies.
Logical topologies are bound to network protocols and describe how data is moved across the network. ... EXAMPLE : twisted pair Ethernet is a logical bus topology in a physical star topology layout. While IBM's token ring is a logical ring topology, it is physically set up in star topology." [Logical topology. Wikipedia]
The icons example "Logical symbols - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ computer-and-networks
 Computer Network Diagrams
Computer Network Diagrams
Computer Network Diagrams solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with samples, templates and libraries of vector icons and objects of computer network devices and network components to help you create professional-looking Computer Network Diagrams, to plan simple home networks and complex computer network configurations for large buildings, to represent their schemes in a comprehensible graphical view, to document computer networks configurations, to depict the interactions between network's components, the used protocols and topologies, to represent physical and logical network structures, to compare visually different topologies and to depict their combinations, to represent in details the network structure with help of schemes, to study and analyze the network configurations, to communicate effectively to engineers, stakeholders and end-users, to track network working and troubleshoot, if necessary.
Network Diagram Software Logical Network
ConceptDraw Network Diagram is ideal for network engineers and network designers who need to draw Logical Network diagrams.
- Logical network topology diagram | Network diagrams with ...
- Cisco Routers . Cisco icons, shapes, stencils and symbols | Logical ...
- Logical network topology diagram | Bus Network Topology | Network ...
- Diagram Physical Topologies | Network Topologies | Physical LAN ...
- Router And Gateway Arrangement Images
- Cisco Logical Computer Network Diagram Example
- Logical network topology diagram | Local area network (LAN ...
- Logical Network Diagrams
- Router Setup With Bus Topology
- Logical symbols - Vector stencils library | Logical symbols - Vector ...
- Logical network topology diagram | Local area network (LAN ...
- Home area networks (HAN). Computer and Network Examples ...
- Wireless router network diagram | Cisco Routers . Cisco icons ...
- Logical network topology diagram | Network Diagram Software ...
- Computer Router Switch Diagram
- Network Topologies | Fully Connected Network Topology Diagram ...
- Hotel Network Topology Diagram. Hotel Guesthouse WiFi Network ...
- Network Gateway Router | Star Network Topology | Hotel Network ...
- Network Gateway Router | Cisco Routers . Cisco icons, shapes ...




-logical-symbols---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)