Basic Diagramming
Mathematics is an exact science, which studies the values, spatial forms and quantitative relations. It is a science, in which is built large number of various diagrams, charts and graphs that present the material in a clear, visual and colorful form, help to analyze the information and to make certain conclusions. A diagram is a graphical representation of data using the linear segments or geometric shapes, which allows to evaluate the ratio of several values. Depending on the types of solved tasks are used the diagrams of different kinds. A graph is a diagram that shows quantitative dependencies of various processes using the curves. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is a powerful intelligent and multifunctional vector engine for drawing different Mathematical diagrams and graphs, Mathematical illustrations, complex and simple Diagram mathematics, Flowcharts of equation solving process, Line graphs, Scatter plots, Histograms, Block diagrams, Bar charts, Divided bar diagrams, Pie charts, Area charts, Circular arrows diagrams, Venn diagrams, Bubble diagrams, Concept maps, and many others.
Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning
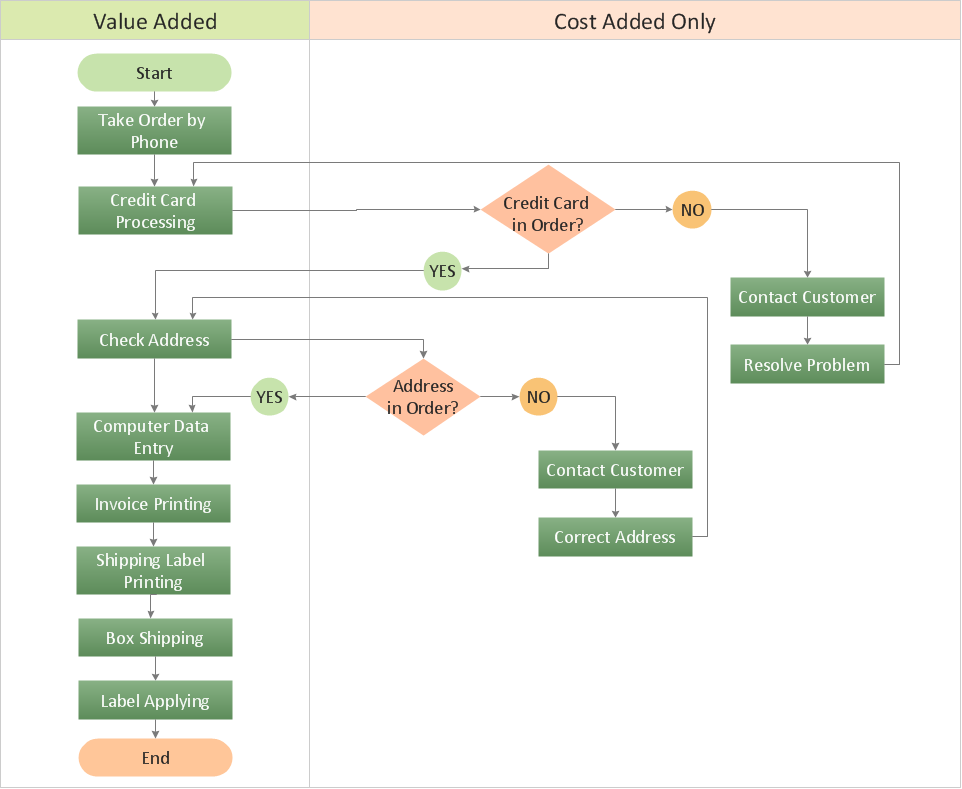
Flowcharts are the best for visually representation the business processes and the flow of a custom-order process through various departments within an organization. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Flowcharts solution offers the full set of predesigned basic flowchart symbols which are gathered at two libraries: Flowchart and Flowcharts Rapid Draw. Among them are: process, terminator, decision, data, document, display, manual loop, and many other specific symbols. The meaning for each symbol offered by ConceptDraw gives the presentation about their proposed use in professional Flowcharts for business and technical processes, software algorithms, well-developed structures of web sites, Workflow diagrams, Process flow diagram and correlation in developing on-line instructional projects or business process system. Use of ready flow chart symbols in diagrams is incredibly useful - you need simply drag desired from the libraries to your document and arrange them in required order. There are a few serious alternatives to Visio for Mac, one of them is ConceptDraw DIAGRAM. It is one of the main contender with the most similar features and capabilities.
Mathematical Diagrams
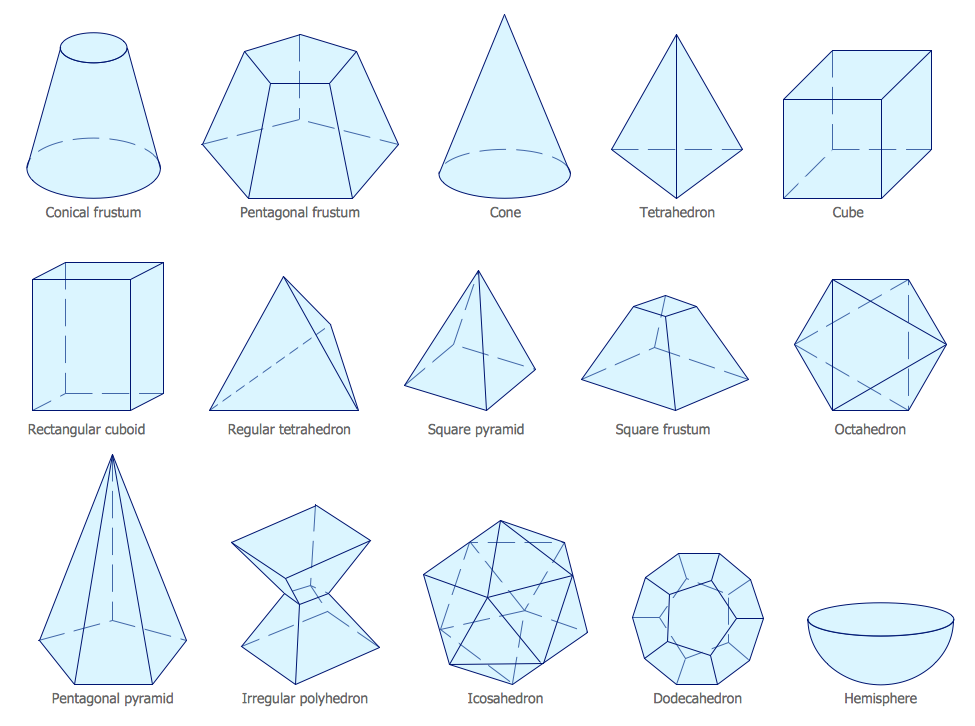
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area is the best for creating: mathematical diagrams, graphics, tape diagrams various mathematical illustrations of any complexity quick and easy. Mathematics solution provides 3 libraries: Plane Geometry Library, Solid Geometry Library, Trigonometric Functions Library.
 Mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software with templates, samples and libraries of vector stencils for drawing the mathematical illustrations, diagrams and charts.
Mathematics Symbols
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM extended with Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area is a powerful diagramming and vector drawing software that offers all needed tools for mathematical diagrams designing. Mathematics solution provides 3 libraries with predesigned vector mathematics symbols and figures: Solid Geometry Library, Plane Geometry Library and Trigonometric Functions Library."In mathematics, the Euclidean algorithm, or Euclid's algorithm, is a method for computing the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two (usually positive) integers, also known as the greatest common factor (GCF) or highest common factor (HCF). ...
The GCD of two positive integers is the largest integer that divides both of them without leaving a remainder (the GCD of two integers in general is defined in a more subtle way).
In its simplest form, Euclid's algorithm starts with a pair of positive integers, and forms a new pair that consists of the smaller number and the difference between the larger and smaller numbers. The process repeats until the numbers in the pair are equal. That number then is the greatest common divisor of the original pair of integers.
The main principle is that the GCD does not change if the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number. ... Since the larger of the two numbers is reduced, repeating this process gives successively smaller numbers, so this repetition will necessarily stop sooner or later - when the numbers are equal (if the process is attempted once more, one of the numbers will become 0)." [Euclidean algorithm. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Euclidean algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The GCD of two positive integers is the largest integer that divides both of them without leaving a remainder (the GCD of two integers in general is defined in a more subtle way).
In its simplest form, Euclid's algorithm starts with a pair of positive integers, and forms a new pair that consists of the smaller number and the difference between the larger and smaller numbers. The process repeats until the numbers in the pair are equal. That number then is the greatest common divisor of the original pair of integers.
The main principle is that the GCD does not change if the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number. ... Since the larger of the two numbers is reduced, repeating this process gives successively smaller numbers, so this repetition will necessarily stop sooner or later - when the numbers are equal (if the process is attempted once more, one of the numbers will become 0)." [Euclidean algorithm. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Euclidean algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Bar Diagram Math
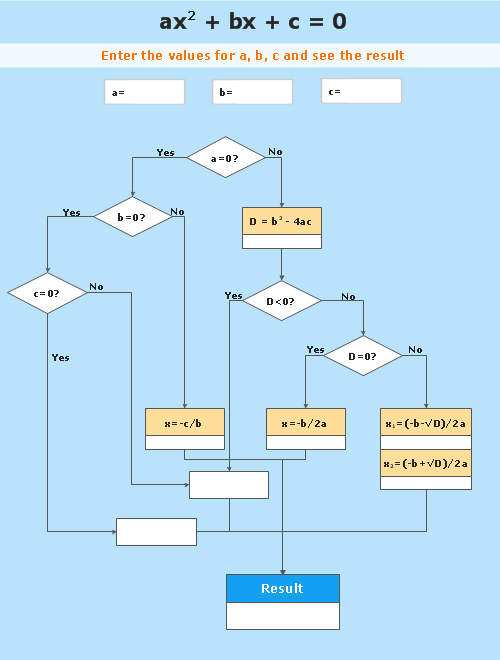
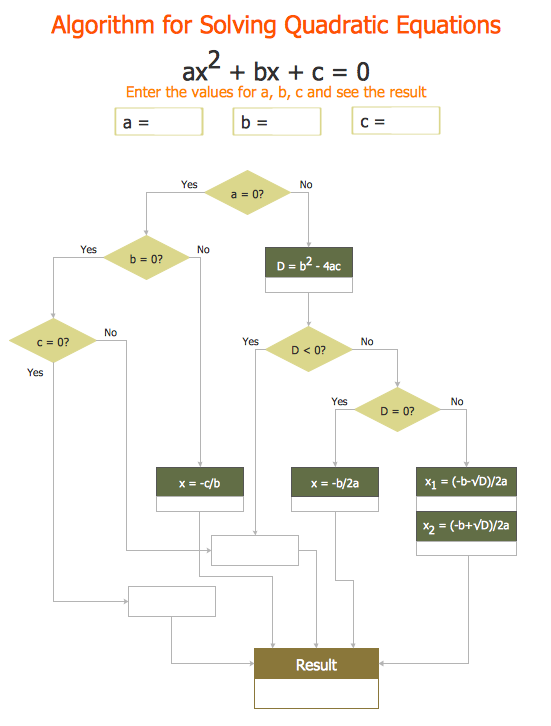
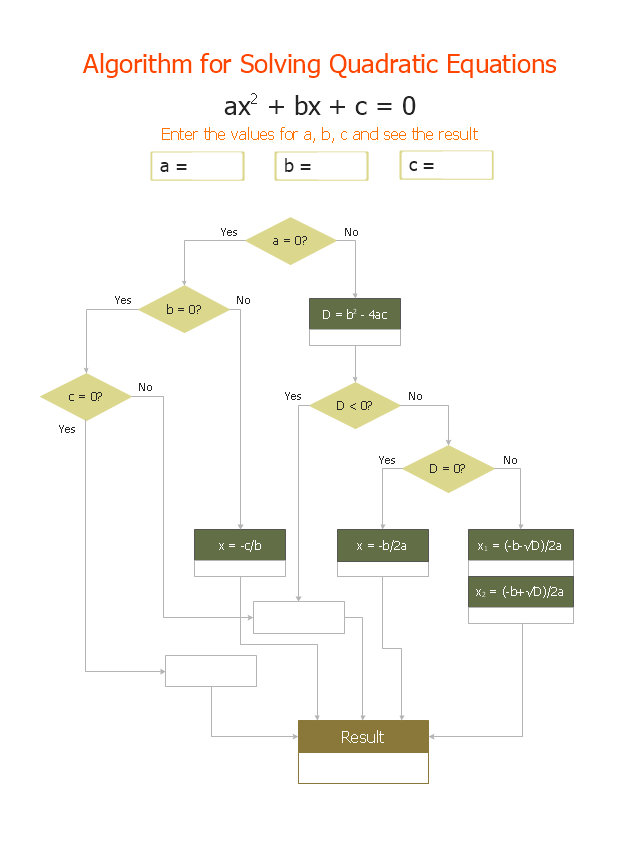
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM extended with Divided Bar Diagrams solution from Graphs and Charts area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is the best software for quick and simple drawing the Divided Bar Diagrams and Bar Diagram Math."In elementary algebra, a quadratic equation (from the Latin quadratus for "square") is any equation having the form
ax^2+bx+c=0
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c are constants with a not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The constants a, b, and c are called, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.
Because the quadratic equation involves only one unknown, it is called "univariate". The quadratic equation only contains powers of x that are non-negative integers, and therefore it is a polynomial equation, and in particular it is a second degree polynomial equation since the greatest power is two.
Quadratic equations can be solved by a process known in American English as factoring and in other varieties of English as factorising, by completing the square, by using the quadratic formula, or by graphing." [Quadratic equation. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Solving quadratic equation algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
ax^2+bx+c=0
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c are constants with a not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The constants a, b, and c are called, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.
Because the quadratic equation involves only one unknown, it is called "univariate". The quadratic equation only contains powers of x that are non-negative integers, and therefore it is a polynomial equation, and in particular it is a second degree polynomial equation since the greatest power is two.
Quadratic equations can be solved by a process known in American English as factoring and in other varieties of English as factorising, by completing the square, by using the quadratic formula, or by graphing." [Quadratic equation. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Solving quadratic equation algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Example Basic Flowchart. Flowchart Examples
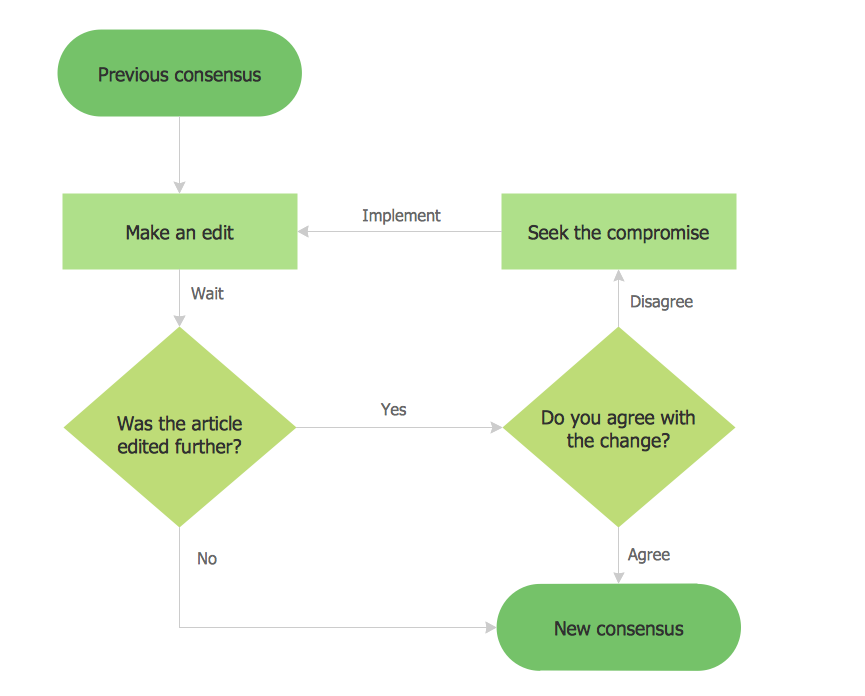
This sample shows the Flowchart that displays the process of the achievement the consensus, in other words solving for the acceptable solution. This Flowchart has start point. The rectangles on it represent the steps of the process and are connected with arrows that show the sequence of the actions. The diamonds with yes/no shows the decisions. The Flowcharts are widely used in marketing, business, analytics, government, politics, engineering, architecture, science, manufacturing, administration, etc.How to Create a Cross Functional Flow Chart
If neither of 45 vector shapes of the Cross-Functional Flowcharts solution don't fit your needs, you will want to learn How to create a unique Cross-Functional flowchart. ConceptDraw Arrows10 Technology - This is more than enough versatility to draw any type of diagram with any degree of complexity. Drawing software lets you to make horizontal and vertical, audit, opportunity and many more flowcharts.- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Basic Flowchart Symbols and ...
- Examples Of Flowcharts Designed To Solve Mathematical Problems
- Basic Diagramming | Bar Diagram Math | Basic Flowchart Symbols ...
- Math Topics Flow Chart Examples
- Flow Chart That Illustrate The Five Content Areas In Mathematics
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Mathematics | Diagram ...
- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Mathematics | Cross-Functional ...
- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Mathematics | Flow Chart Of Euclid ...
- Mathematics | Solving quadratic equation algorithm - Flowchart ...
- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Number System Flow Chart In Math