Telecommunication Network Diagrams
Telecommunication Network Diagrams
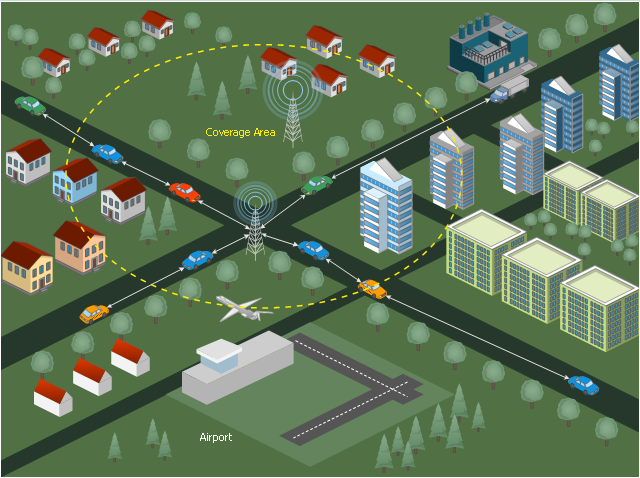
Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software with samples, templates, and great collection of vector stencils to help the specialists in a field of networks and telecommunications, as well as other users to create Computer systems networking and Telecommunication network diagrams for various fields, to organize the work of call centers, to design the GPRS networks and GPS navigational systems, mobile, satellite and hybrid communication networks, to construct the mobile TV networks and wireless broadband networks.
Network Diagram Examples
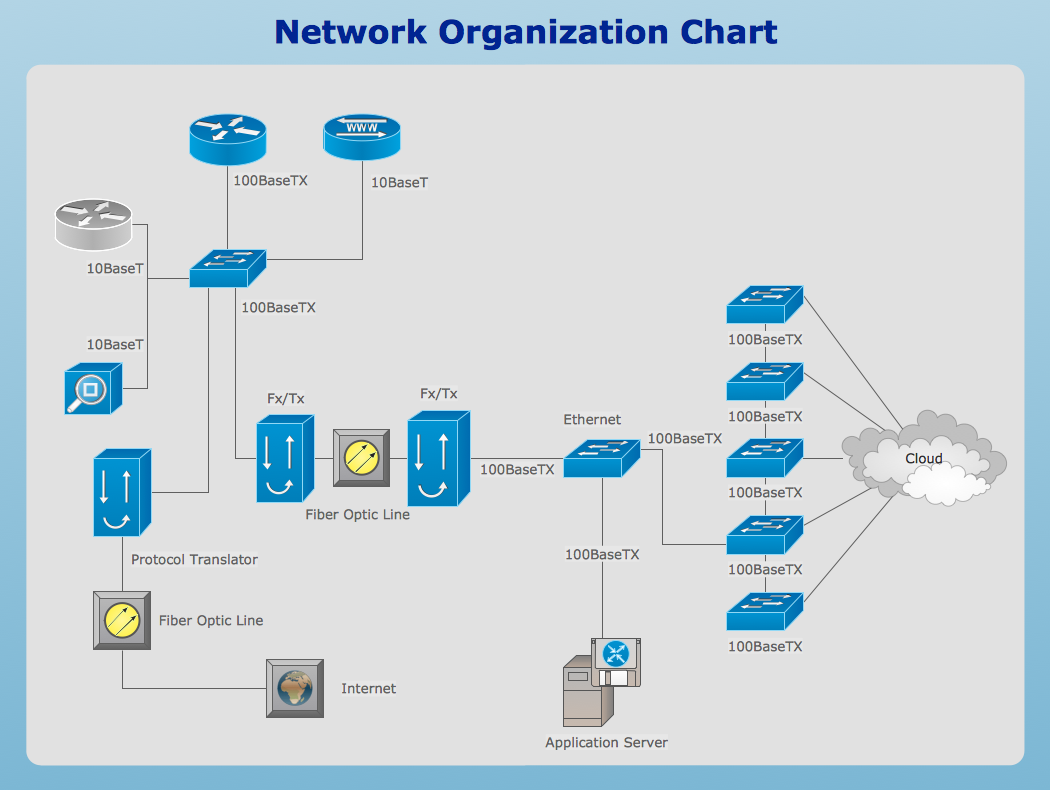
Network diagram is a chart which represents nodes and connections between them in computer network or any telecommunication network, it is a visual depiction of network architecture, physical or logical network topology. There are used common icons for the Network diagrams design, such as icons of various network appliances, computer devices, routers, clouds, peripheral devices, digital devices, etc. Network diagrams can represent networks of different scales (LAN level, WAN level) and detailization. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming software enhanced with Computer Network Diagrams solution from Computer and Networks area includes huge collection of computer and network templates, design objects and stencils, and numerous quantity of Network diagram examples and samples, among them: Basic Computer Network Diagrams, Communication Network Diagram, Wireless Router Network Diagram, LAN Topology Diagram, Computer Network System Design Diagram, Mobile Satellite Communication Network, Web-based Network Diagram, Hybrid Network Diagram, and many others.
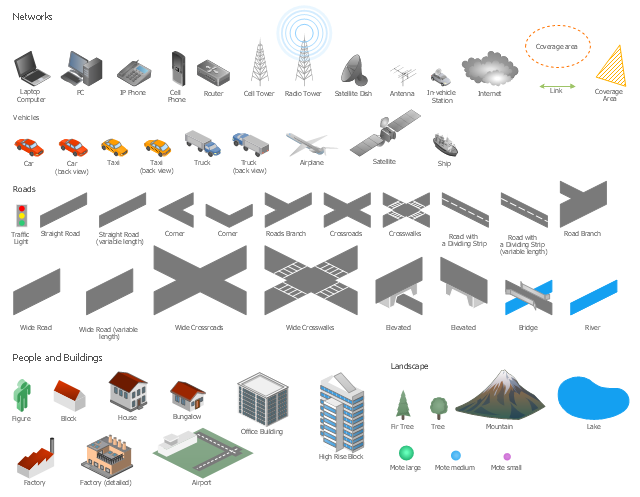
The vector stencils library "Local vehicular networking" contains 88 symbols for drawing the vehicular computer telecommunication network diagrams using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"A vehicular ad hoc network (VANET) uses cars as mobile nodes in a MANET to create a mobile network.[1] A VANET turns every participating car into a wireless router or node, allowing cars approximately 100 to 300 metres of each other to connect and, in turn, create a network with a wide range. As cars fall out of the signal range and drop out of the network, other cars can join in, connecting vehicles to one another so that a mobile Internet is created. It is estimated that the first systems that will integrate this technology are police and fire vehicles to communicate with each other for safety purposes. ...
Vehicular ad hocal networks are expected to implement wireless technologies such as dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) which is a type of Wi-Fi. Other candidate wireless technologies are cellular, satellite, and WiMAX. Vehicular ad hoc networks can be viewed as component of the intelligent transportation systems (ITS).
As promoted in ITS, vehicles communicate with each other via inter-vehicle communication (IVC) as well as with roadside base stations via roadside-to-vehicle communication (RVC)." [Vehicular ad hoc network. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Local vehicular networking" is included in the Vehicular Networking solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A vehicular ad hoc network (VANET) uses cars as mobile nodes in a MANET to create a mobile network.[1] A VANET turns every participating car into a wireless router or node, allowing cars approximately 100 to 300 metres of each other to connect and, in turn, create a network with a wide range. As cars fall out of the signal range and drop out of the network, other cars can join in, connecting vehicles to one another so that a mobile Internet is created. It is estimated that the first systems that will integrate this technology are police and fire vehicles to communicate with each other for safety purposes. ...
Vehicular ad hocal networks are expected to implement wireless technologies such as dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) which is a type of Wi-Fi. Other candidate wireless technologies are cellular, satellite, and WiMAX. Vehicular ad hoc networks can be viewed as component of the intelligent transportation systems (ITS).
As promoted in ITS, vehicles communicate with each other via inter-vehicle communication (IVC) as well as with roadside base stations via roadside-to-vehicle communication (RVC)." [Vehicular ad hoc network. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Local vehicular networking" is included in the Vehicular Networking solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Local vehicular networking" contains 88 icon symbols for drawing local vehicular computer network diagrams.
"A vehicular ad hoc network (VANET) uses cars as mobile nodes in a MANET to create a mobile network. A VANET turns every participating car into a wireless router or node, allowing cars approximately 100 to 300 metres of each other to connect and, in turn, create a network with a wide range. As cars fall out of the signal range and drop out of the network, other cars can join in, connecting vehicles to one another so that a mobile Internet is created. It is estimated that the first systems that will integrate this technology are police and fire vehicles to communicate with each other for safety purposes." [Vehicular ad hoc network. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Local vehicular networking - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Vehicular Networking solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ vehicular-networking
"A vehicular ad hoc network (VANET) uses cars as mobile nodes in a MANET to create a mobile network. A VANET turns every participating car into a wireless router or node, allowing cars approximately 100 to 300 metres of each other to connect and, in turn, create a network with a wide range. As cars fall out of the signal range and drop out of the network, other cars can join in, connecting vehicles to one another so that a mobile Internet is created. It is estimated that the first systems that will integrate this technology are police and fire vehicles to communicate with each other for safety purposes." [Vehicular ad hoc network. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Local vehicular networking - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Vehicular Networking solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ vehicular-networking
Network Drawing Software
ConceptDraw Network Drawing Software - Network design software for network drawings with abundant examples and templates. Create computer network designs, diagrams and schematics using ConceptDraw.
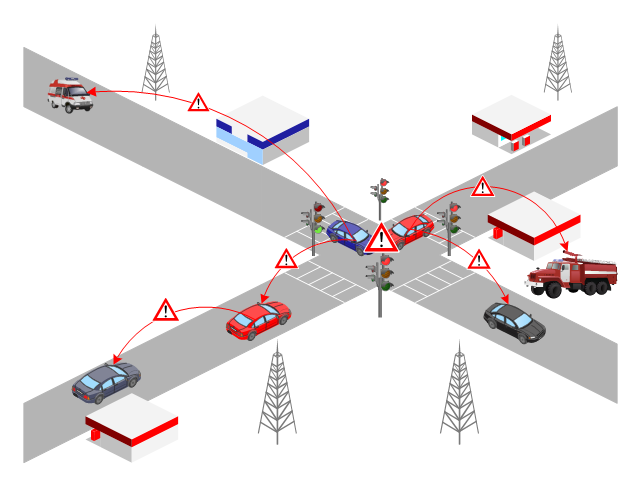
This VANET diagram example was drawn on the base of picture from the webpage "Security and Privacy in Location-based MANETs/ VANETs" from the Donald Bren School of Information and Computer Sciences, the University of California, Irvine. [ics.uci.edu/ ~keldefra/ manet.htm]
"A vehicular ad hoc network (VANET) uses cars as mobile nodes in a MANET to create a mobile network. A VANET turns every participating car into a wireless router or node, allowing cars approximately 100 to 300 metres of each other to connect and, in turn, create a network with a wide range. As cars fall out of the signal range and drop out of the network, other cars can join in, connecting vehicles to one another so that a mobile Internet is created. It is estimated that the first systems that will integrate this technology are police and fire vehicles to communicate with each other for safety purposes. Automotive companies like General Motors, Toyota, Nissan, DaimlerChrysler, BMW and Ford promote this term." [Vehicular ad hoc network. Wikipedia]
The VANET diagram example "Vehicular ad-hoc network" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Vehicular Networking solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A vehicular ad hoc network (VANET) uses cars as mobile nodes in a MANET to create a mobile network. A VANET turns every participating car into a wireless router or node, allowing cars approximately 100 to 300 metres of each other to connect and, in turn, create a network with a wide range. As cars fall out of the signal range and drop out of the network, other cars can join in, connecting vehicles to one another so that a mobile Internet is created. It is estimated that the first systems that will integrate this technology are police and fire vehicles to communicate with each other for safety purposes. Automotive companies like General Motors, Toyota, Nissan, DaimlerChrysler, BMW and Ford promote this term." [Vehicular ad hoc network. Wikipedia]
The VANET diagram example "Vehicular ad-hoc network" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Vehicular Networking solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This diagram sample illustrates the cooperative vehicular delay-tolerant network operation.
"Delay-tolerant networking (DTN) is an approach to computer network architecture that seeks to address the technical issues in heterogeneous networks that may lack continuous network connectivity. Examples of such networks are those operating in mobile or extreme terrestrial environments, or planned networks in space.
Recently, the term disruption-tolerant networking has gained currency in the United States due to support from DARPA, which has funded many DTN projects. Disruption may occur because of the limits of wireless radio range, sparsity of mobile nodes, energy resources, attack, and noise." [Delay-tolerant networking. Wikipedia]
"Routing in delay-tolerant networking concerns itself with the ability to transport, or route, data from a source to a destination, which is a fundamental ability all communication networks must have. Delay- and disruption-tolerant networks (DTNs) are characterized by their lack of connectivity, resulting in a lack of instantaneous end-to-end paths. In these challenging environments, popular ad hoc routing protocols such as AODV and DSR fail to establish routes. This is due to these protocols trying to first establish a complete route and then, after the route has been established, forward the actual data. However, when instantaneous end-to-end paths are difficult or impossible to establish, routing protocols must take to a "store and forward" approach, where data is incrementally moved and stored throughout the network in hopes that it will eventually reach its destination. A common technique used to maximize the probability of a message being successfully transferred is to replicate many copies of the message in hopes that one will succeed in reaching its destination." [Routing in delay-tolerant networking. Wikipedia]
The example "Cooperative vehicular delay-tolerant network diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Vehicular Networking solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Delay-tolerant networking (DTN) is an approach to computer network architecture that seeks to address the technical issues in heterogeneous networks that may lack continuous network connectivity. Examples of such networks are those operating in mobile or extreme terrestrial environments, or planned networks in space.
Recently, the term disruption-tolerant networking has gained currency in the United States due to support from DARPA, which has funded many DTN projects. Disruption may occur because of the limits of wireless radio range, sparsity of mobile nodes, energy resources, attack, and noise." [Delay-tolerant networking. Wikipedia]
"Routing in delay-tolerant networking concerns itself with the ability to transport, or route, data from a source to a destination, which is a fundamental ability all communication networks must have. Delay- and disruption-tolerant networks (DTNs) are characterized by their lack of connectivity, resulting in a lack of instantaneous end-to-end paths. In these challenging environments, popular ad hoc routing protocols such as AODV and DSR fail to establish routes. This is due to these protocols trying to first establish a complete route and then, after the route has been established, forward the actual data. However, when instantaneous end-to-end paths are difficult or impossible to establish, routing protocols must take to a "store and forward" approach, where data is incrementally moved and stored throughout the network in hopes that it will eventually reach its destination. A common technique used to maximize the probability of a message being successfully transferred is to replicate many copies of the message in hopes that one will succeed in reaching its destination." [Routing in delay-tolerant networking. Wikipedia]
The example "Cooperative vehicular delay-tolerant network diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Vehicular Networking solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Mobile Network Architecture Diagram
- Diagram In Mobile Networking
- Hybrid satellite and common carrier network diagram | Mobile ...
- Network Diagram Examples | Network Diagram Software (PRO ...
- Project Of Mobile Networking Tower
- Mobile satellite TV network diagram | Building Networks | Phone ...
- Mobile Network Infrastructure Diagram
- Telecommunication Network Diagrams | Mobile satellite TV network ...
- Mobile Network Layout
- Mobile Vehicular Network
- Structure Of Mobile Networking
- Phone networks . Computer and Network Examples | Mobile satellite ...
- Telecommunication Network Diagrams | Providing telecom services ...
- Mobile satellite communication network diagram | Hybrid satellite ...
- Telecommunication Network Diagrams | Network Architecture | How ...
- UML Use Case Diagram Example Social Networking Sites Project ...
- Vehicular ad-hoc network | Network Glossary Definition | Mobile ...
- Gprs Mobile Network
- Telecommunication Network Diagrams | Mobile satellite ...









-local-vehicular-networking---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)

-local-vehicular-networking---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)

-local-vehicular-networking---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)

-local-vehicular-networking---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)

-local-vehicular-networking---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)















-local-vehicular-networking---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)