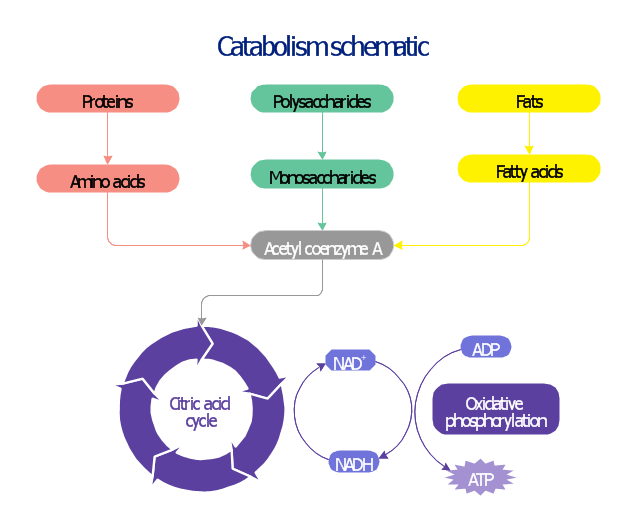
This biochemical chart display how proteins, polysaccharides and fats from food are digested into gastrointestinal tract into aminoacids, monosaccharides and fatty acids, and then broken down and oxidized to carbon dioxide and water in cellular processes of energy generation.
This metabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikipedia file: Catabolism schematic.svg. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Catabolism_ schematic.svg]
The biochemical diagram example "Catabolism schematic" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This metabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikipedia file: Catabolism schematic.svg. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Catabolism_ schematic.svg]
The biochemical diagram example "Catabolism schematic" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In biochemistry, metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. In each pathway, a principal chemical is modified by a series of chemical reactions. Enzymes catalyze these reactions, and often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors in order to function properly. Because of the many chemicals (a.k.a. "metabolites") that may be involved, metabolic pathways can be quite elaborate. In addition, numerous distinct pathways co-exist within a cell. This collection of pathways is called the metabolic network. Pathways are important to the maintenance of homeostasis within an organism. Catabolic (break-down) and Anabolic (synthesis) pathways often work interdependently to create new biomolecules as the final end-products." [Metabolic pathway. Wikipedia]
The biochemical diagram example "Metabolic pathway map" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The biochemical diagram example "Metabolic pathway map" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Biology
Biology
Biology solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with samples, templates and libraries containing biological vector symbols, to help you create scientific and educational designs in the field of biology.
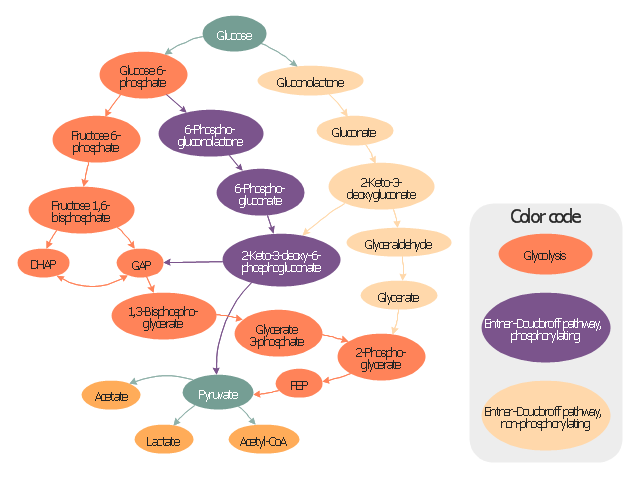
"Carbohydrate catabolism is the breakdown of carbohydrates into smaller units. Carbohydrates literally undergo combustion to retrieve the large amounts of energy in their bonds. Energy is secured by mitochondria in the form of ATP.
There are several different types of carbohydrates: polysaccharides (e.g., starch, amylopectin, glycogen, cellulose), monosaccharides (e.g., glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose) and the disaccharides (e.g., maltose, lactose).
Glucose reacts with oxygen in the following redox reaction, C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O, the carbon dioxide and water is a waste product and the chemical reaction is exothermic.
The breakdown of glucose into energy in the form of molecules of ATP is therefore one of the most important biochemical pathways found in living organisms." [Carbohydrate catabolism. Wikipedia]
This glucose catabolism pathways map shows glycolysis by orange color, Entner-Doudoroff phosphorylating pathway by green color, Entner-Doudoroff non-phosphorylating pathway by Yellow color.
This methabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikimedia file: Glucose catabolism pathways.svg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Glucose_ catabolism_ pathways.svg]
The biochemical diagram example "Glucose catabolism pathways map" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
There are several different types of carbohydrates: polysaccharides (e.g., starch, amylopectin, glycogen, cellulose), monosaccharides (e.g., glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose) and the disaccharides (e.g., maltose, lactose).
Glucose reacts with oxygen in the following redox reaction, C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O, the carbon dioxide and water is a waste product and the chemical reaction is exothermic.
The breakdown of glucose into energy in the form of molecules of ATP is therefore one of the most important biochemical pathways found in living organisms." [Carbohydrate catabolism. Wikipedia]
This glucose catabolism pathways map shows glycolysis by orange color, Entner-Doudoroff phosphorylating pathway by green color, Entner-Doudoroff non-phosphorylating pathway by Yellow color.
This methabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikimedia file: Glucose catabolism pathways.svg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Glucose_ catabolism_ pathways.svg]
The biochemical diagram example "Glucose catabolism pathways map" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
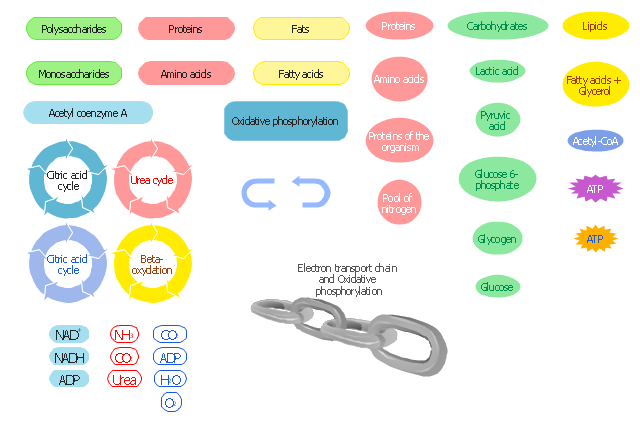
The vector stencils library " Biochemistry of metabolism" contains 46 metabolite symbols for drawing metabolic pathways maps, biochemical diagrams and metabolism process flow charts using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually restricted to small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Alcohol is an example of a primary metabolite produced in large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. ...
The metabolome forms a large network of metabolic reactions, where outputs from one enzymatic chemical reaction are inputs to other chemical reactions." [Metabolite. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Biochemistry of metabolism" is included in the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually restricted to small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Alcohol is an example of a primary metabolite produced in large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. ...
The metabolome forms a large network of metabolic reactions, where outputs from one enzymatic chemical reaction are inputs to other chemical reactions." [Metabolite. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Biochemistry of metabolism" is included in the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Catabolism schematic - Biochemical diagram | Metabolic pathway ...
- Metabolic pathway map - Biochemical diagram | Glycolysis overview ...
- Metabolic pathway map - Biochemical diagram | Biology ...
- An Overview Of Catabolism Diagram
- Biology Drawing Software | Catabolism schematic - Biochemical ...
- Flow Chart Or Diagram Polysaccharides
- Glycolysis overview | Biology | Glucose catabolism pathways map ...
- Metabolic pathway map - Biochemical diagram | Glucose catabolism ...
- Draw A Complete Overview Of Catabolic Pathways In Organisms
- Simple Sketch Of Polysaccharide
- Catabolism schematic - Biochemical diagram | Biology | Glucose ...
- Metabolic pathway map - Biochemical diagram | Catabolism ...
- Diagram Of Catabolism Of Protein
- Metabolic pathway map - Biochemical diagram | Metabolic pathway ...
- Glucose catabolism pathways map | Catabolism schematic ...
- Draw A Water Cycles Diagram In Biology
- Catabolism schematic - Biochemical diagram | Schematic Diagram ...
- Biology Drawing | Glycolysis overview | Biology | Drawing About ...
- Glycolysis overview | Biology | Biology Drawing | Draw The Embden ...
- Catabolism schematic - Biochemical diagram | Water Cycle ...