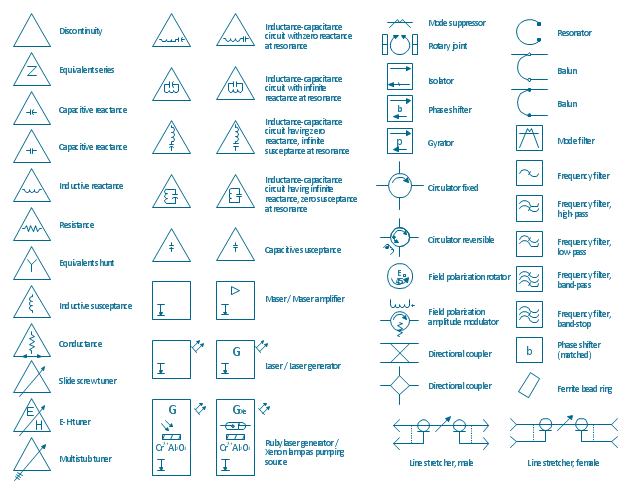
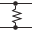
The vector stencils library "VHF UHF SHF" contains 52 symbols for VHF, UHF, and SHF circuit design, including capacitance measurers, nonreciprocal devices, modulators, phase shifters, field polarization devices, and filters.
"Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU-designated range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves from 30 MHz to 300 MHz, with corresponding wavelengths of one to ten meters. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted high frequency (HF), and the next higher frequencies are known as ultra high frequency (UHF).
Common uses for VHF are FM radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, land mobile stations (emergency, business, private use and military), long range data communication up to several tens of kilometres with radio modems, amateur radio, and marine communications. Air traffic control communications and air navigation systems (e.g. VOR, DME & ILS) work at distances of 100 kilometres or more to aircraft at cruising altitude.
VHF was previously used for analog television stations in the US." [Very high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Ultra-high frequency (UHF) designates the ITU radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz (3,000 MHz), also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres; that is 1 decimetre to 1 metre. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the SHF (super-high frequency) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is high enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting (digital and analogue), cordless phones, walkie-talkies, satellite communication, and numerous other applications.
The IEEE defines the UHF radar band as frequencies between 300 MHz and 1 GHz. Two other IEEE radar band overlap the ITU UHF band: the L band between 1 and 2 GHz and the S band between 2 and 4 GHz." [Ultra high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Super high frequency (or SHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3 GHz and 30 GHz. This band of frequencies is also known as the centimetre band or centimetre wave as the wavelengths range from ten to one centimetres. These frequencies fall within the microwave band, so radio waves with these frequencies are called microwaves. The small wavelength of microwaves allows them to be directed in narrow beams by aperture antennas such as parabolic dishes, so they are used for point-to-point communication and data links, and for radar. This frequency range is used for most radar transmitters, microwave ovens, wireless LANs, cell phones, satellite communication, microwave radio relay links, and numerous short range terrestrial data links. The commencing wireless USB technology will be using approximately 1/ 3 of this spectrum.
Frequencies in the SHF range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations." [Super high frequency. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - VHF UHF SHF" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU-designated range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves from 30 MHz to 300 MHz, with corresponding wavelengths of one to ten meters. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted high frequency (HF), and the next higher frequencies are known as ultra high frequency (UHF).
Common uses for VHF are FM radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, land mobile stations (emergency, business, private use and military), long range data communication up to several tens of kilometres with radio modems, amateur radio, and marine communications. Air traffic control communications and air navigation systems (e.g. VOR, DME & ILS) work at distances of 100 kilometres or more to aircraft at cruising altitude.
VHF was previously used for analog television stations in the US." [Very high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Ultra-high frequency (UHF) designates the ITU radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz (3,000 MHz), also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres; that is 1 decimetre to 1 metre. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the SHF (super-high frequency) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is high enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting (digital and analogue), cordless phones, walkie-talkies, satellite communication, and numerous other applications.
The IEEE defines the UHF radar band as frequencies between 300 MHz and 1 GHz. Two other IEEE radar band overlap the ITU UHF band: the L band between 1 and 2 GHz and the S band between 2 and 4 GHz." [Ultra high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Super high frequency (or SHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3 GHz and 30 GHz. This band of frequencies is also known as the centimetre band or centimetre wave as the wavelengths range from ten to one centimetres. These frequencies fall within the microwave band, so radio waves with these frequencies are called microwaves. The small wavelength of microwaves allows them to be directed in narrow beams by aperture antennas such as parabolic dishes, so they are used for point-to-point communication and data links, and for radar. This frequency range is used for most radar transmitters, microwave ovens, wireless LANs, cell phones, satellite communication, microwave radio relay links, and numerous short range terrestrial data links. The commencing wireless USB technology will be using approximately 1/ 3 of this spectrum.
Frequencies in the SHF range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations." [Super high frequency. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - VHF UHF SHF" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Electrical Engineering
Electrical Engineering
This solution extends ConceptDraw PRO v.9.5 (or later) with electrical engineering samples, electrical schematic symbols, electrical diagram symbols, templates and libraries of design elements, to help you design electrical schematics, digital and analog
HelpDesk
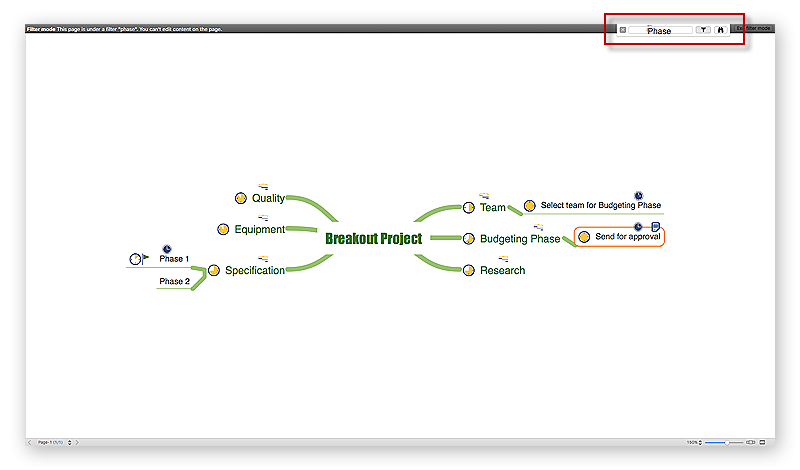
How to Use Mind Map Filtering in ConceptDraw MINDMAP
Many of us use mind maps for organizing, structuring or compiling our ideas or projects. Making mind map is the ability to take existing ideas and combine them in new ways. This is much easier to do when you can see all the ideas in front of you. Using mind maps for organizing and structuring information as the volume of data grows and the map expands can be a challenge. ConceptDraw MINDMAP allows you to sort and filter your mind map content even on the Full Screen.HelpDesk
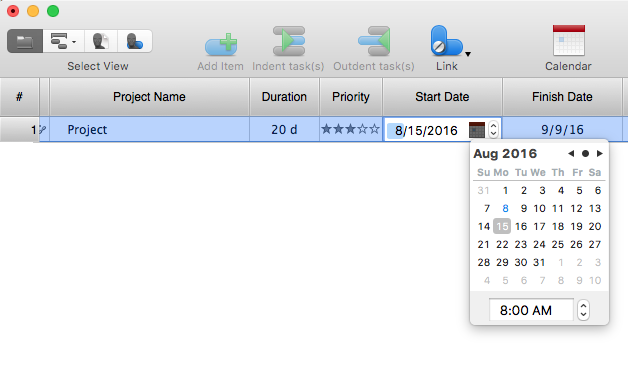
How to Operate with Project Time Frames in ConceptDraw PROJECT
ConceptDraw PROJECT applies an advanced scheduling facilities to enable you arrange your project's tasks with existing human and material resources. Comprehension of project scheduling principle allows you to plan the project the best way to execute it. Sometimes user is wondering why the task is moved to a different time than he supposed. Or he may be confused when a task's tardiness provoke the unwanted shift of other tasks. This article describes how do changes to the Start/Finish dates, or the Duration of the task affect the project schedule, created in ConceptDraw PROJECT.HelpDesk
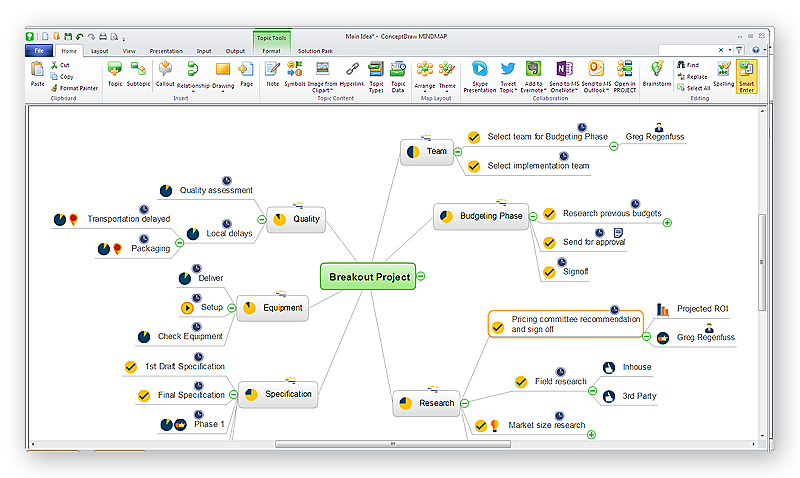
How to Draw a Mind Map on PC Using ConceptDraw MINDMAP
Mind maps are useful forcapturing ideas, organizing and structuring information in a visual form, that is easier to understand, and easier to explain to others. Mind map consists of a general Main Idea surrounded by other related topics and subtopics, which are displayed in a radial hierarchical structure. Read this step-by-step guide on how to create a mind map using ConceptDraw MINDMAP for Windows.
HelpDesk
How to Import Project Data From MS Excel File
You can import information into the project from MS Excel workbook using the entered fields - fields in which you can enter or edit information as opposed to calculated fields.GUI Prototyping with ConceptDraw PRO
All about prototyping. GUI Prototyping with ConceptDraw. Download prototyping software.- Variable Phase Shifter Symbol
- Level Shifter Symbol
- Electrical Symbols — Composite Assemblies | Composite ...
- Electrical Symbols — Composite Assemblies | Design elements ...
- Phase Symbol
- VHF UHF SHF - Vector stencils library | Waveguide Isolator Symbol
- VHF UHF SHF - Vector stencils library | Electrical Symbols — VHF ...
- Design elements - Composite assemblies | Design elements - Cable ...
- Electrical Symbols — Composite Assemblies | Composite ...
- Electrical Symbols — Composite Assemblies | Composite ...
- Design elements - Outlets | Design elements - Composite ...
- Symbol For Semiconductor Diode
- Electrical Symbols — Composite Assemblies | Composite ...
- Level Transducer Symbol
- Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols | Amplifier ...
- Electrical Symbols — Composite Assemblies | Electrical Symbols ...
- Design elements - VHF UHF SHF | Electrical Symbols ...
- Electromagnetic Wave Symbol
- Electrical Symbols — VHF UHF SHF
- How to Set Line Jumps for Smart Connectors in ConceptDraw PRO ...