"Decision-making can be regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief and/ or a course of action among several alternative possibilities. Every decision-making process produces a final choice that may or may not prompt action. ...
Decision-making can also be regarded as a problem-solving activity terminated by a solution deemed to be satisfactory. It is, therefore, a reasoning or emotional process which can be rational or irrational and can be based on explicit assumptions or tacit assumptions. Most decisions are followed by some form of cost-benefit analysis. Rational choice theory encompasses the notion that people try to maximize benefits while minimizing costs.
Some have argued that most decisions are made unconsciously, if not involuntarily. Jim Nightingale, author of Think Smart – Act Smart, states that "we simply decide without thinking much about the decision process. ...
A major part of decision-making involves the analysis of a finite set of alternatives described in terms of evaluative criteria. Information overload occurs when there is a substantial gap between the capacity of information and the ways in which people may or can adapt."" [Decision-making. Wikipedia]
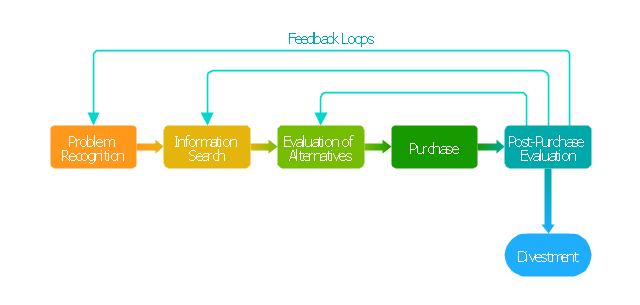
The block diagram example "Customer decision making" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Block Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Decision-making can also be regarded as a problem-solving activity terminated by a solution deemed to be satisfactory. It is, therefore, a reasoning or emotional process which can be rational or irrational and can be based on explicit assumptions or tacit assumptions. Most decisions are followed by some form of cost-benefit analysis. Rational choice theory encompasses the notion that people try to maximize benefits while minimizing costs.
Some have argued that most decisions are made unconsciously, if not involuntarily. Jim Nightingale, author of Think Smart – Act Smart, states that "we simply decide without thinking much about the decision process. ...
A major part of decision-making involves the analysis of a finite set of alternatives described in terms of evaluative criteria. Information overload occurs when there is a substantial gap between the capacity of information and the ways in which people may or can adapt."" [Decision-making. Wikipedia]
The block diagram example "Customer decision making" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Block Diagrams solution from the area "What is a Diagram" of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Block Diagram Of Rational Decision Making
- Decision Making | Block diagram - Customer decision making ...
- Block diagram - Customer decision making | Basic Flowchart ...
- Block diagram - Customer decision making | Block Diagram ...
- Block diagram - Customer decision making | Decision Making Can ...
- Block diagram - Customer decision making | Total Quality ...
- Block diagram - Customer decision making | Influence Diagram ...
- Block diagram - Customer decision making | Types of Flowcharts ...
- Block diagram - Customer decision making | Block Diagrams ...
- Block diagram - Customer decision making | Block Diagrams | Block ...
- Block diagram - Customer decision making | Workflow Diagram ...
- Block diagram - Customer decision making | How to Create an ...
- Block diagram - Gap model of service quality | Block diagram ...
- Block diagram - Total solution process | Process Flowchart | Block ...
- Block diagram - Customer decision making | Block Diagrams ...
- Decision Making | How To Make the Right Decision in Projects ...
- Block diagram - Sources of customer satisfaction | IVR customer ...
- Process Flowchart | How to Add a Workflow Diagram to a ...
- Decision Making | How To Make the Right Decision in Projects ...
- UML package diagram for Bank account | About UML | Booch OOD ...