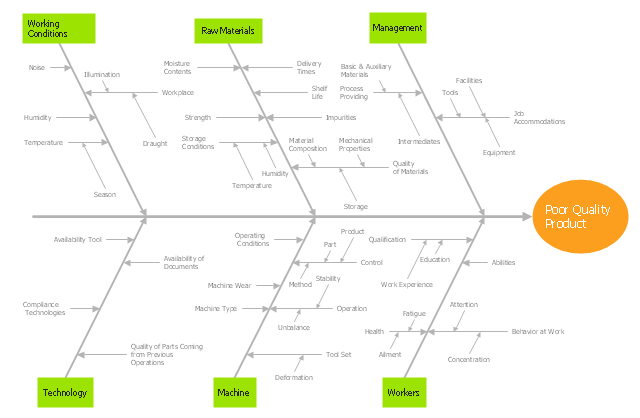
"Ishikawa diagrams (also called fishbone diagrams, herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, or Fishikawa) are causal diagrams created by Kaoru Ishikawa (1968) that show the causes of a specific event. Common uses of the Ishikawa diagram are product design and quality defect prevention, to identify potential factors causing an overall effect. Each cause or reason for imperfection is a source of variation. Causes are usually grouped into major categories to identify these sources of variation. The categories typically include:
- People: Anyone involved with the process
- Methods: How the process is performed and the specific requirements for doing it, such as policies, procedures, rules, regulations and laws
- Machines: Any equipment, computers, tools, etc. required to accomplish the job
- Materials: Raw materials, parts, pens, paper, etc. used to produce the final product
- Measurements: Data generated from the process that are used to evaluate its quality
- Environment: The conditions, such as location, time, temperature, and culture in which the process operates" [Ishikawa diagram. Wikipedia]
The fishbone diagram example "Causes of low-quality output" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- People: Anyone involved with the process
- Methods: How the process is performed and the specific requirements for doing it, such as policies, procedures, rules, regulations and laws
- Machines: Any equipment, computers, tools, etc. required to accomplish the job
- Materials: Raw materials, parts, pens, paper, etc. used to produce the final product
- Measurements: Data generated from the process that are used to evaluate its quality
- Environment: The conditions, such as location, time, temperature, and culture in which the process operates" [Ishikawa diagram. Wikipedia]
The fishbone diagram example "Causes of low-quality output" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Total Quality Management with ConceptDraw
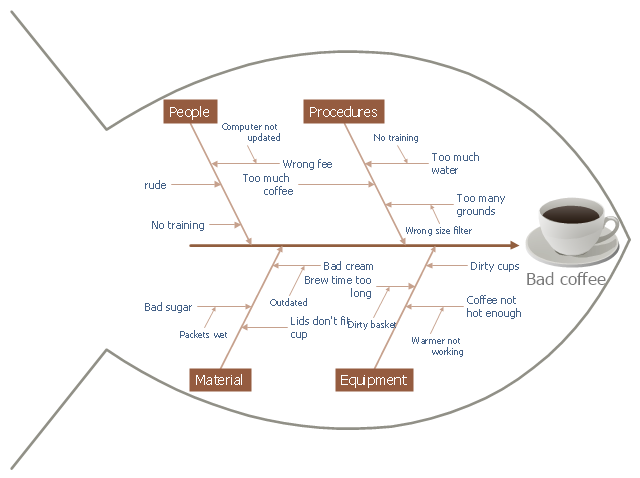
Total Quality Management (TQM) system is the management method where the confidence in quality of all organization processes is placed foremost. The given method is widely used in production, in educational system, in government organizations and so on.This cause and effect diagram sample was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Fishbone BadCoffeeExample.jpg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Fishbone_ BadCoffeeExample.jpg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
The fishbone diagram example "Bad coffee" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
The fishbone diagram example "Bad coffee" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
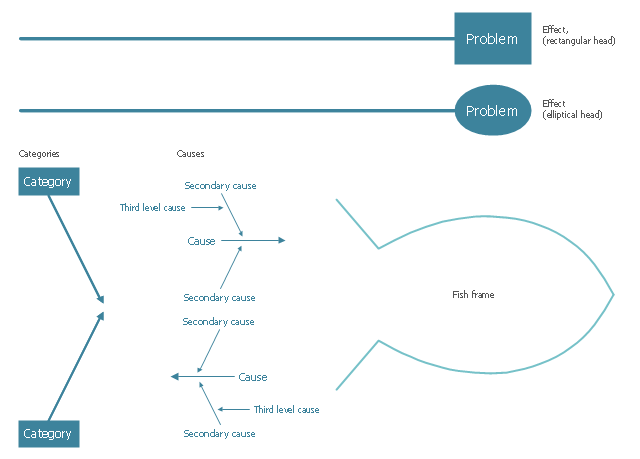
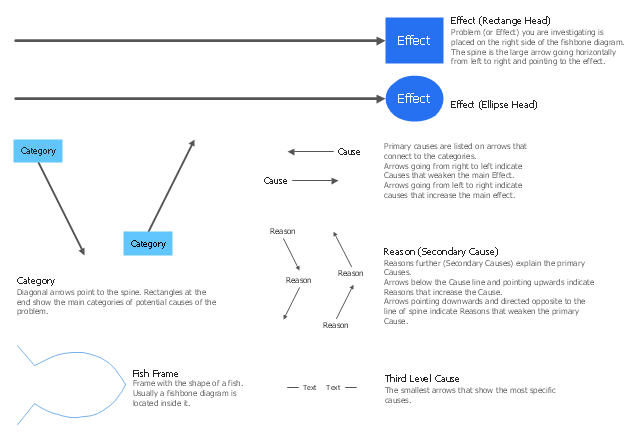
The vector stencils library "Cause-and-effect diagram" contains 13 elements of fishbone diagram.
Use it to design your Ishikawa diagrams with ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"Ishikawa diagrams (also called fishbone diagrams, herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, or Fishikawa) are causal diagrams created by Kaoru Ishikawa (1968) that show the causes of a specific event. Common uses of the Ishikawa diagram are product design and quality defect prevention to identify potential factors causing an overall effect. Each cause or reason for imperfection is a source of variation. Causes are usually grouped into major categories to identify these sources of variation. ...
The basic concept was first used in the 1920s, and is considered one of the seven basic tools of quality control." [Ishikawa diagram. Wikipedia]
The example of fishbone diagram shapes "Design elements - Cause-and-effect diagram" is included in the Seven Basic Tools of Quality solution from the Quality area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to design your Ishikawa diagrams with ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"Ishikawa diagrams (also called fishbone diagrams, herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, or Fishikawa) are causal diagrams created by Kaoru Ishikawa (1968) that show the causes of a specific event. Common uses of the Ishikawa diagram are product design and quality defect prevention to identify potential factors causing an overall effect. Each cause or reason for imperfection is a source of variation. Causes are usually grouped into major categories to identify these sources of variation. ...
The basic concept was first used in the 1920s, and is considered one of the seven basic tools of quality control." [Ishikawa diagram. Wikipedia]
The example of fishbone diagram shapes "Design elements - Cause-and-effect diagram" is included in the Seven Basic Tools of Quality solution from the Quality area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
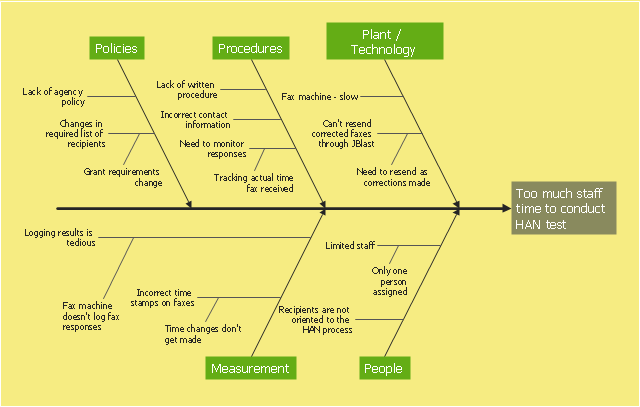
This example was created on the base of the figure from the website of Minnesota Department of Health. [health.state.mn.us/ divs/ opi/ qi/ images/ fishbone_ ex.png]
"Minnesota’s Health Alert Network (HAN) enables public health staff, tribal governments, health care providers, emergency workers, and others working to protect the public to exchange information during a disease outbreak, environmental threat, natural disaster, or act of terrorism." [health.state.mn.us/ han/ ]
The fishbone diagram example "HAN project" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Minnesota’s Health Alert Network (HAN) enables public health staff, tribal governments, health care providers, emergency workers, and others working to protect the public to exchange information during a disease outbreak, environmental threat, natural disaster, or act of terrorism." [health.state.mn.us/ han/ ]
The fishbone diagram example "HAN project" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
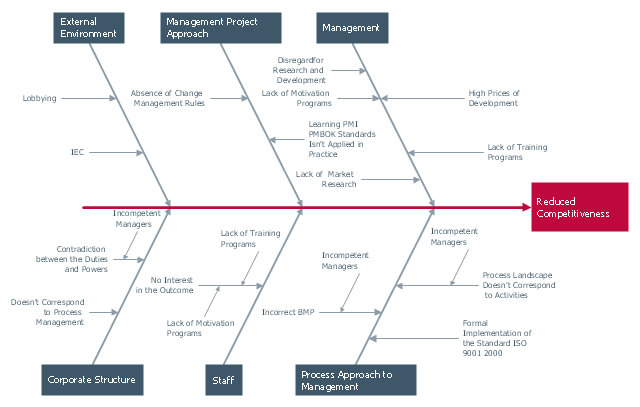
"Cause-and-effect diagrams can reveal key relationships among various variables, and the possible causes provide additional insight into process behavior.
Causes can be derived from brainstorming sessions. These groups can then be labeled as categories of the fishbone. They will typically be one of the traditional categories mentioned above but may be something unique to the application in a specific case. Causes can be traced back to root causes with the 5 Whys technique." [Ishikawa diagram. Wikipedia]
The Ishikawa diagram (cause and effect diagram, fishbone diagram) example "Factors reducing competitiveness" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Causes can be derived from brainstorming sessions. These groups can then be labeled as categories of the fishbone. They will typically be one of the traditional categories mentioned above but may be something unique to the application in a specific case. Causes can be traced back to root causes with the 5 Whys technique." [Ishikawa diagram. Wikipedia]
The Ishikawa diagram (cause and effect diagram, fishbone diagram) example "Factors reducing competitiveness" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
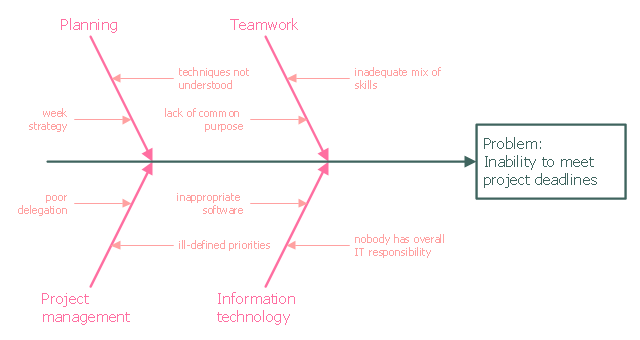
This example was created on the base of the figure from the website of the Iowa State University Center for Excellence in Learning and Teaching.
"Fishbone.
What: The fishbone technique uses a visual organizer to identify the possible causes of a problem.
Benefits: This technique discourages partial or premature solutions and demonstrates the relative importance of, and interactions between, different parts of a problem.
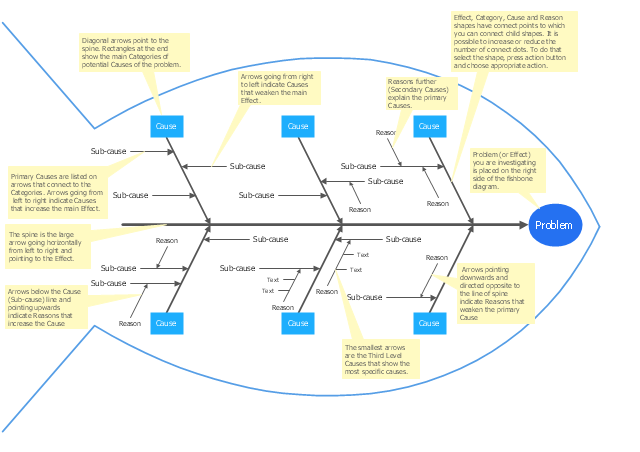
How: On a broad sheet of paper, draw a long arrow horizontally across the middle of the page pointing to the right. Label the arrowhead with the title of the issue to be explained. This is the "backbone" of the "fish." Draw "spurs" from this "backbone" at about 45 degrees, one for every likely cause of the problem that the group can think of; and label each. Sub-spurs can represent subsidiary causes. The group considers each spur/ sub-spur, taking the simplest first, partly for clarity but also because a simple explanation may make more complex ones unnecessary. Ideally, the fishbone is redrawn so that position along the backbone reflects the relative importance of the different parts of the problem, with the most important at the head." [celt.iastate.edu/ creativity/ techniques.html]
The fishbone diagram example "Inability to meet project deadlines" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Fishbone.
What: The fishbone technique uses a visual organizer to identify the possible causes of a problem.
Benefits: This technique discourages partial or premature solutions and demonstrates the relative importance of, and interactions between, different parts of a problem.
How: On a broad sheet of paper, draw a long arrow horizontally across the middle of the page pointing to the right. Label the arrowhead with the title of the issue to be explained. This is the "backbone" of the "fish." Draw "spurs" from this "backbone" at about 45 degrees, one for every likely cause of the problem that the group can think of; and label each. Sub-spurs can represent subsidiary causes. The group considers each spur/ sub-spur, taking the simplest first, partly for clarity but also because a simple explanation may make more complex ones unnecessary. Ideally, the fishbone is redrawn so that position along the backbone reflects the relative importance of the different parts of the problem, with the most important at the head." [celt.iastate.edu/ creativity/ techniques.html]
The fishbone diagram example "Inability to meet project deadlines" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The library of vector stencils "Fishbone diagrams" contains 13 symbols for drawing the Ishikawa diagrams using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"Ishikawa diagrams were popularized by Kaoru Ishikawa in the 1960s, who pioneered quality management processes in the Kawasaki shipyards, and in the process became one of the founding fathers of modern management.
The basic concept was first used in the 1920s, and is considered one of the seven basic tools of quality control. It is known as a fishbone diagram because of its shape, similar to the side view of a fish skeleton." [Ishikawa diagram. Wikipedia]
"The Seven Basic Tools of Quality is a designation given to a fixed set of graphical techniques identified as being most helpful in troubleshooting issues related to quality. They are called basic because they are suitable for people with little formal training in statistics and because they can be used to solve the vast majority of quality-related issues.
The seven tools are:
(1) Cause-and-effect diagram (also known as the "fishbone" or Ishikawa diagram);
(2) Check sheet;
(3) Control chart;
(4) Histogram;
(5) Pareto chart;
(6) Scatter diagram;
(7) Stratification (alternately, flow chart or run chart)." [Seven Basic Tools of Quality. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Fishbone diagram" is included in the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Ishikawa diagrams were popularized by Kaoru Ishikawa in the 1960s, who pioneered quality management processes in the Kawasaki shipyards, and in the process became one of the founding fathers of modern management.
The basic concept was first used in the 1920s, and is considered one of the seven basic tools of quality control. It is known as a fishbone diagram because of its shape, similar to the side view of a fish skeleton." [Ishikawa diagram. Wikipedia]
"The Seven Basic Tools of Quality is a designation given to a fixed set of graphical techniques identified as being most helpful in troubleshooting issues related to quality. They are called basic because they are suitable for people with little formal training in statistics and because they can be used to solve the vast majority of quality-related issues.
The seven tools are:
(1) Cause-and-effect diagram (also known as the "fishbone" or Ishikawa diagram);
(2) Check sheet;
(3) Control chart;
(4) Histogram;
(5) Pareto chart;
(6) Scatter diagram;
(7) Stratification (alternately, flow chart or run chart)." [Seven Basic Tools of Quality. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Fishbone diagram" is included in the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Ishikawa diagrams (also called fishbone diagrams, herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, or Fishikawa) are causal diagrams created by Kaoru Ishikawa (1968) that show the causes of a specific event. Common uses of the Ishikawa diagram are product design and quality defect prevention, to identify potential factors causing an overall effect. Each cause or reason for imperfection is a source of variation. Causes are usually grouped into major categories to identify these sources of variation. The categories typically include:
- People: Anyone involved with the process
- Methods: How the process is performed and the specific requirements for doing it, such as policies, procedures, rules, regulations and laws
- Machines: Any equipment, computers, tools, etc. required to accomplish the job
- Materials: Raw materials, parts, pens, paper, etc. used to produce the final product
- Measurements: Data generated from the process that are used to evaluate its quality
- Environment: The conditions, such as location, time, temperature, and culture in which the process operates" [Ishikawa diagram. Wikipedia]
The fishbone diagram example "Causes of low-quality output" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- People: Anyone involved with the process
- Methods: How the process is performed and the specific requirements for doing it, such as policies, procedures, rules, regulations and laws
- Machines: Any equipment, computers, tools, etc. required to accomplish the job
- Materials: Raw materials, parts, pens, paper, etc. used to produce the final product
- Measurements: Data generated from the process that are used to evaluate its quality
- Environment: The conditions, such as location, time, temperature, and culture in which the process operates" [Ishikawa diagram. Wikipedia]
The fishbone diagram example "Causes of low-quality output" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Cause-and-effect diagrams can reveal key relationships among various variables, and the possible causes provide additional insight into process behavior.
Causes can be derived from brainstorming sessions. These groups can then be labeled as categories of the fishbone. They will typically be one of the traditional categories mentioned above but may be something unique to the application in a specific case. Causes can be traced back to root causes with the 5 Whys technique." [Ishikawa diagram. Wikipedia]
"The 5 Whys is an iterative question-asking technique used to explore the cause-and-effect relationships underlying a particular problem. The primary goal of the technique is to determine the root cause of a defect or problem. (The "5" in the name derives from an empirical observation on the number of iterations typically required to resolve the problem.)" [5 Whys. Wikipedia]
This Ishikawa diagram (cause and effect diagram) template is included in the Fishbone Diagram solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Causes can be derived from brainstorming sessions. These groups can then be labeled as categories of the fishbone. They will typically be one of the traditional categories mentioned above but may be something unique to the application in a specific case. Causes can be traced back to root causes with the 5 Whys technique." [Ishikawa diagram. Wikipedia]
"The 5 Whys is an iterative question-asking technique used to explore the cause-and-effect relationships underlying a particular problem. The primary goal of the technique is to determine the root cause of a defect or problem. (The "5" in the name derives from an empirical observation on the number of iterations typically required to resolve the problem.)" [5 Whys. Wikipedia]
This Ishikawa diagram (cause and effect diagram) template is included in the Fishbone Diagram solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Reason
- Fishbone diagram - Template | Design elements - Cause-and-effect ...
- Ishikawa Diagram | Ishikawa fishbone diagram | How to Draw a ...
- Design elements - Cause-and-effect diagram | Ishikawa fishbone ...
- Ishikawa fishbone diagram | Fishbone diagram - Bad coffee | Cause ...
- Fishbone Diagram
- Cause and Effect Analysis - Fishbone Diagrams for Problem Solving ...
- Fishbone diagram - HAN project | Relations diagram - Health care ...
- Fishbone diagram - Causes of low-quality output | Fishbone ...
- Fishbone diagram - Bad coffee | Cause and effect diagram ...
- Design elements - Fishbone diagram | Fishbone diagram - Template ...
- Fishbone Diagram | Quality fishbone diagram - Template | Fishbone ...
- Fishbone diagram - Template | Ishikawa diagram - Factors reducing ...
- Fishbone Diagram Causes Of Low Quality Output
- Cause and Effect Analysis - Fishbone Diagrams for Problem Solving ...
- Fishbone diagram - Inability to meet project deadlines | Fishbone ...
- Cause and Effect Analysis - Fishbone Diagrams for Problem Solving ...
- Fishbone diagram - Bad coffee | Fishbone Diagrams | Using ...
- Fishbone diagram - Bad coffee | Fishbone Diagrams | Fishbone ...
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Timing Diagrams | UML ...