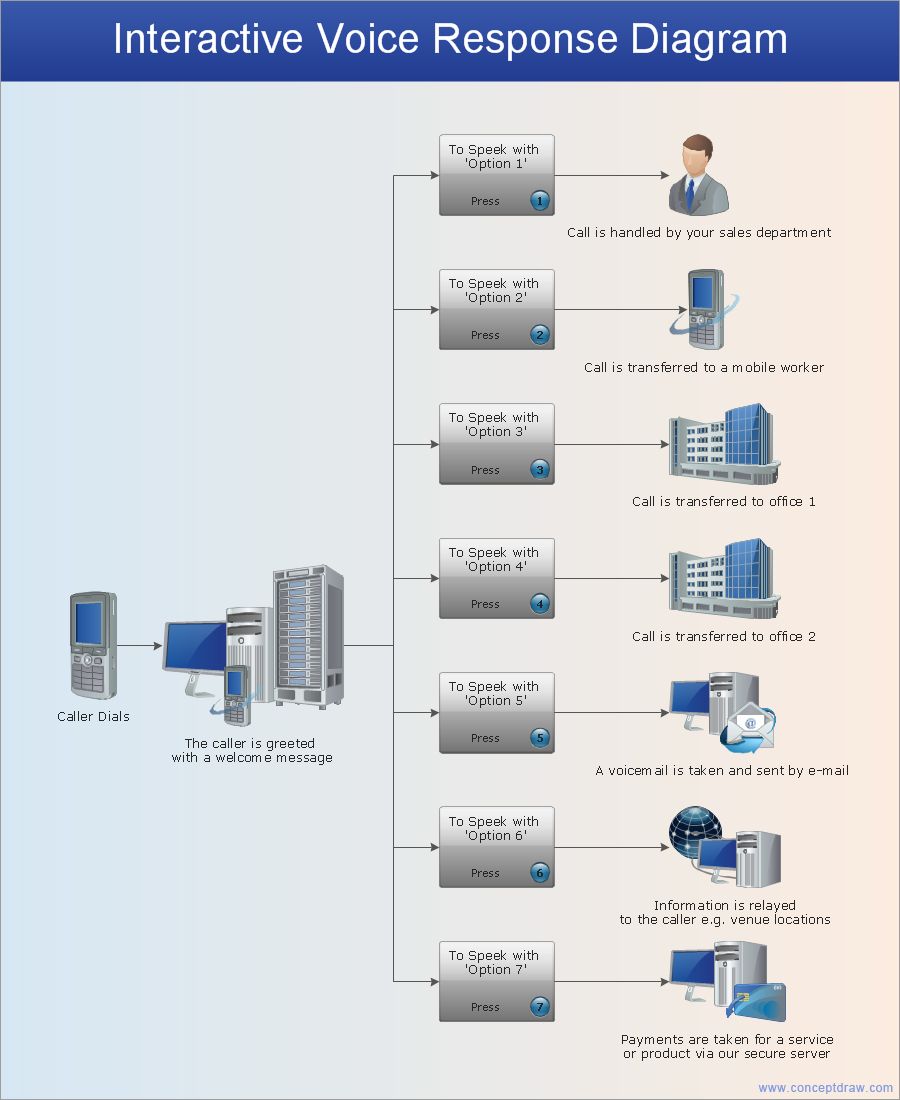
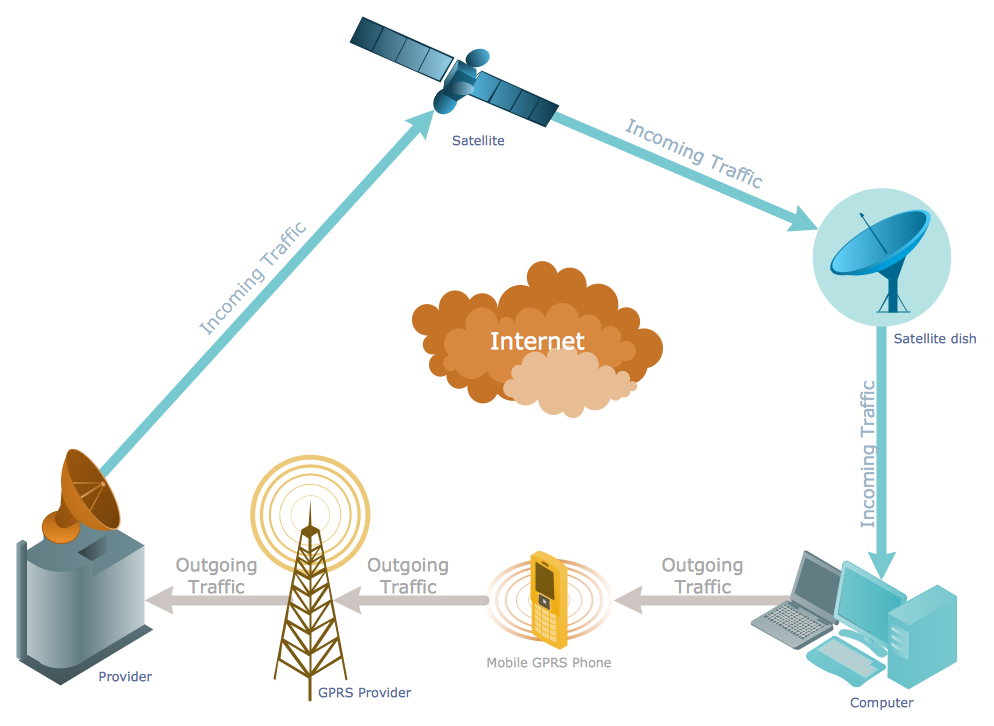
"General packet radio service (GPRS) is a packet oriented mobile data service on the 2G and 3G cellular communication system's global system for mobile communications (GSM). GPRS was originally standardized by European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) in response to the earlier CDPD and i-mode packet-switched cellular technologies. It is now maintained by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
GPRS usage is typically charged based on volume of data transferred, contrasting with circuit switched data, which is usually billed per minute of connection time. Usage above the bundle cap is either charged per megabyte or disallowed.
GPRS is a best-effort service, implying variable throughput and latency that depend on the number of other users sharing the service concurrently, as opposed to circuit switching, where a certain quality of service (QoS) is guaranteed during the connection. In 2G systems, GPRS provides data rates of 56–114 kbit/ second. 2G cellular technology combined with GPRS is sometimes described as 2.5G, that is, a technology between the second (2G) and third (3G) generations of mobile telephony. It provides moderate-speed data transfer, by using unused time division multiple access (TDMA) channels in, for example, the GSM system. GPRS is integrated into GSM Release 97 and newer releases." [General Packet Radio Service. Wikipedia]
This GPRS network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
GPRS usage is typically charged based on volume of data transferred, contrasting with circuit switched data, which is usually billed per minute of connection time. Usage above the bundle cap is either charged per megabyte or disallowed.
GPRS is a best-effort service, implying variable throughput and latency that depend on the number of other users sharing the service concurrently, as opposed to circuit switching, where a certain quality of service (QoS) is guaranteed during the connection. In 2G systems, GPRS provides data rates of 56–114 kbit/ second. 2G cellular technology combined with GPRS is sometimes described as 2.5G, that is, a technology between the second (2G) and third (3G) generations of mobile telephony. It provides moderate-speed data transfer, by using unused time division multiple access (TDMA) channels in, for example, the GSM system. GPRS is integrated into GSM Release 97 and newer releases." [General Packet Radio Service. Wikipedia]
This GPRS network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Network Drawing Software
ConceptDraw Network Drawing Software - Network design software for network drawings with abundant examples and templates. Create computer network designs, diagrams and schematics using ConceptDraw.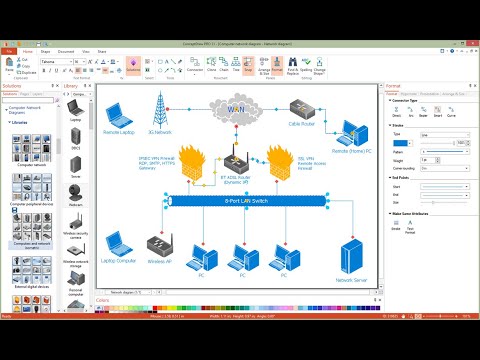
Network Diagram Software
Network Diagrams are used to visually represent the network architecture, to illustrate the network structure, how the computers and other elements of the network are connected each other using a variety of network symbols, clipart and connection lines. They are incredibly useful on the stages of projecting computer network, of its construction and exploitation. Professionally designed and accurate Network Diagrams are equally convenient for computer engineers and users. You can construct them by hand on the paper or use special network diagramming software, such as ConceptDraw DIAGRAM. Having at disposal the powerful network diagramming tools of Computer Network Diagrams solution included to ConceptDraw Solution Park, you can succeed in drawing various types of Computer Network Diagrams, among them Network Communication Plans, Logical Network Diagrams, Network Topology Diagrams, LAN and WAN Diagrams, Network Floor Plan Layouts, Computer Network System Diagrams, Web-based Network Diagrams, Wireless Network Diagrams, Cisco Network Diagram, and others.
The vector stencils library "Telecommunication networks" contains 32 clipart images of telecommunication network devices and equipment for drawing telecom network diagrams.
"A telecommunications network is a collection of terminal nodes, links and any intermediate nodes which are connected so as to enable telecommunication between the terminals.
The transmission links connect the nodes together. The nodes use circuit switching, message switching or packet switching to pass the signal through the correct links and nodes to reach the correct destination terminal.
Each terminal in the network usually has a unique address so messages or connections can be routed to the correct recipients. The collection of addresses in the network is called the address space." [Telecommunications network. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Telecommunication networks - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A telecommunications network is a collection of terminal nodes, links and any intermediate nodes which are connected so as to enable telecommunication between the terminals.
The transmission links connect the nodes together. The nodes use circuit switching, message switching or packet switching to pass the signal through the correct links and nodes to reach the correct destination terminal.
Each terminal in the network usually has a unique address so messages or connections can be routed to the correct recipients. The collection of addresses in the network is called the address space." [Telecommunications network. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Telecommunication networks - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "VHF UHF SHF" contains 52 symbols for VHF, UHF, and SHF circuit design, including capacitance measurers, nonreciprocal devices, modulators, phase shifters, field polarization devices, and filters.
"Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU-designated range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves from 30 MHz to 300 MHz, with corresponding wavelengths of one to ten meters. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted high frequency (HF), and the next higher frequencies are known as ultra high frequency (UHF).
Common uses for VHF are FM radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, land mobile stations (emergency, business, private use and military), long range data communication up to several tens of kilometres with radio modems, amateur radio, and marine communications. Air traffic control communications and air navigation systems (e.g. VOR, DME & ILS) work at distances of 100 kilometres or more to aircraft at cruising altitude.
VHF was previously used for analog television stations in the US." [Very high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Ultra-high frequency (UHF) designates the ITU radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz (3,000 MHz), also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres; that is 1 decimetre to 1 metre. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the SHF (super-high frequency) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is high enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting (digital and analogue), cordless phones, walkie-talkies, satellite communication, and numerous other applications.
The IEEE defines the UHF radar band as frequencies between 300 MHz and 1 GHz. Two other IEEE radar band overlap the ITU UHF band: the L band between 1 and 2 GHz and the S band between 2 and 4 GHz." [Ultra high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Super high frequency (or SHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3 GHz and 30 GHz. This band of frequencies is also known as the centimetre band or centimetre wave as the wavelengths range from ten to one centimetres. These frequencies fall within the microwave band, so radio waves with these frequencies are called microwaves. The small wavelength of microwaves allows them to be directed in narrow beams by aperture antennas such as parabolic dishes, so they are used for point-to-point communication and data links, and for radar. This frequency range is used for most radar transmitters, microwave ovens, wireless LANs, cell phones, satellite communication, microwave radio relay links, and numerous short range terrestrial data links. The commencing wireless USB technology will be using approximately 1/ 3 of this spectrum.
Frequencies in the SHF range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations." [Super high frequency. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - VHF UHF SHF" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU-designated range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves from 30 MHz to 300 MHz, with corresponding wavelengths of one to ten meters. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted high frequency (HF), and the next higher frequencies are known as ultra high frequency (UHF).
Common uses for VHF are FM radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, land mobile stations (emergency, business, private use and military), long range data communication up to several tens of kilometres with radio modems, amateur radio, and marine communications. Air traffic control communications and air navigation systems (e.g. VOR, DME & ILS) work at distances of 100 kilometres or more to aircraft at cruising altitude.
VHF was previously used for analog television stations in the US." [Very high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Ultra-high frequency (UHF) designates the ITU radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz (3,000 MHz), also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres; that is 1 decimetre to 1 metre. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the SHF (super-high frequency) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is high enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting (digital and analogue), cordless phones, walkie-talkies, satellite communication, and numerous other applications.
The IEEE defines the UHF radar band as frequencies between 300 MHz and 1 GHz. Two other IEEE radar band overlap the ITU UHF band: the L band between 1 and 2 GHz and the S band between 2 and 4 GHz." [Ultra high frequency. Wikipedia]
"Super high frequency (or SHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3 GHz and 30 GHz. This band of frequencies is also known as the centimetre band or centimetre wave as the wavelengths range from ten to one centimetres. These frequencies fall within the microwave band, so radio waves with these frequencies are called microwaves. The small wavelength of microwaves allows them to be directed in narrow beams by aperture antennas such as parabolic dishes, so they are used for point-to-point communication and data links, and for radar. This frequency range is used for most radar transmitters, microwave ovens, wireless LANs, cell phones, satellite communication, microwave radio relay links, and numerous short range terrestrial data links. The commencing wireless USB technology will be using approximately 1/ 3 of this spectrum.
Frequencies in the SHF range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations." [Super high frequency. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - VHF UHF SHF" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Network Glossary Definition
The network glossary contains a complete list of network, computer-related and technical terms in alphabetic order, explanations and definitions for them, among them there are words well known for you and also specific, rare-used, uncommon or newly introduced terms. This specialized glossary, also known as a vocabulary, is the best in its field and covers in details the various aspects of computer network technologies. This glossary was developed by specialists using the practical experience and many useful sources to help the ConceptDraw users in their work, you can read and learn it from the screen on-line or print, it can be also used as a perfect educational guide or tutorial. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software extended with Computer and Networks solution is easy to draw various types of Network diagrams, Network topology diagrams, Computer networking schematics, Network maps, Cisco network topology, Computer network architecture, Wireless networks, Vehicular networks, Rack diagrams, Logical, Physical, Cable networks, etc. Desktop ConceptDraw DIAGRAM Software is a good Visio for Mac Os X replacement. It gives you rich productivity and quality of the produced diagrams.
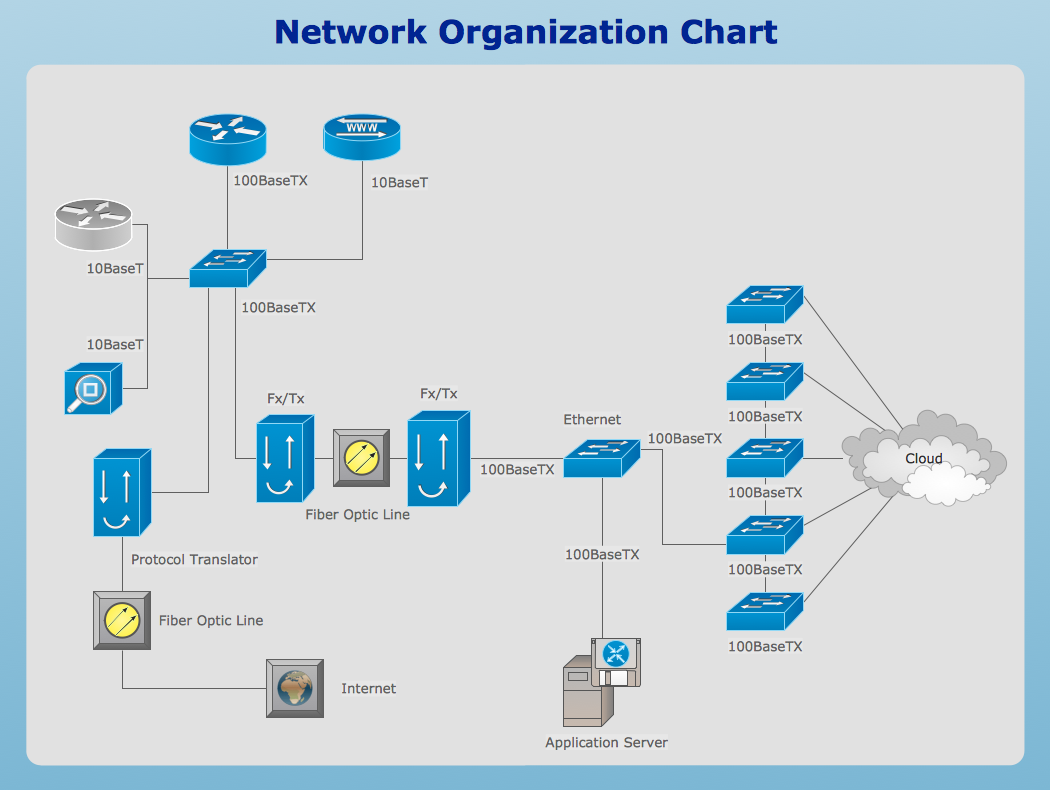
Telecommunications Networks
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software provides the Telecommunication Network Diagrams Solution from the Computer and Networks Area for quick and easy drawing the Telecommunications Networks.The vector stencils library "Cisco network topology" contains 89 symbols of Cisco network devices and design elements for drawing computer network topology diagrams.
"There are two basic categories of network topologies:
(1) Physical topologies,
(2) Logical topologies.
The shape of the cabling layout used to link devices is called the physical topology of the network. This refers to the layout of cabling, the locations of nodes, and the interconnections between the nodes and the cabling. The physical topology of a network is determined by the capabilities of the network access devices and media, the level of control or fault tolerance desired, and the cost associated with cabling or telecommunications circuits.
The logical topology in contrast, is the way that the signals act on the network media, or the way that the data passes through the network from one device to the next without regard to the physical interconnection of the devices." [Network topology. Wikipedia]
The symbols example "Cisco network topology - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ computer-networks-cisco
"There are two basic categories of network topologies:
(1) Physical topologies,
(2) Logical topologies.
The shape of the cabling layout used to link devices is called the physical topology of the network. This refers to the layout of cabling, the locations of nodes, and the interconnections between the nodes and the cabling. The physical topology of a network is determined by the capabilities of the network access devices and media, the level of control or fault tolerance desired, and the cost associated with cabling or telecommunications circuits.
The logical topology in contrast, is the way that the signals act on the network media, or the way that the data passes through the network from one device to the next without regard to the physical interconnection of the devices." [Network topology. Wikipedia]
The symbols example "Cisco network topology - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ computer-networks-cisco
Cisco Multimedia, Voice, Phone. Cisco icons, shapes, stencils and symbols
The ConceptDraw vector stencils library Cisco Multimedia, Voice, Phone contains equipment symbols for drawing the computer network diagrams.Network Security Architecture Diagram
Network Security Architecture Diagram visually reflects the network's structure and construction, and all actions undertaken for ensuring the network security which can be executed with help of software resources and hardware devices. You dream to find powerful software for easy designing Network Security Architecture Diagram? We recommend to use ConceptDraw DIAGRAM extended with Network Security Diagrams Solution from the Computer and Networks Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.HVAC Business Plan
Long time you have looked for the convenient and helpful software for drawing HVAC Business Plan? Now ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software offers you the HVAC Plans Solution from the Building Plans Area that will help you create any desired HVAC Business Plan.Wide area network (WAN) topology. Computer and Network Examples
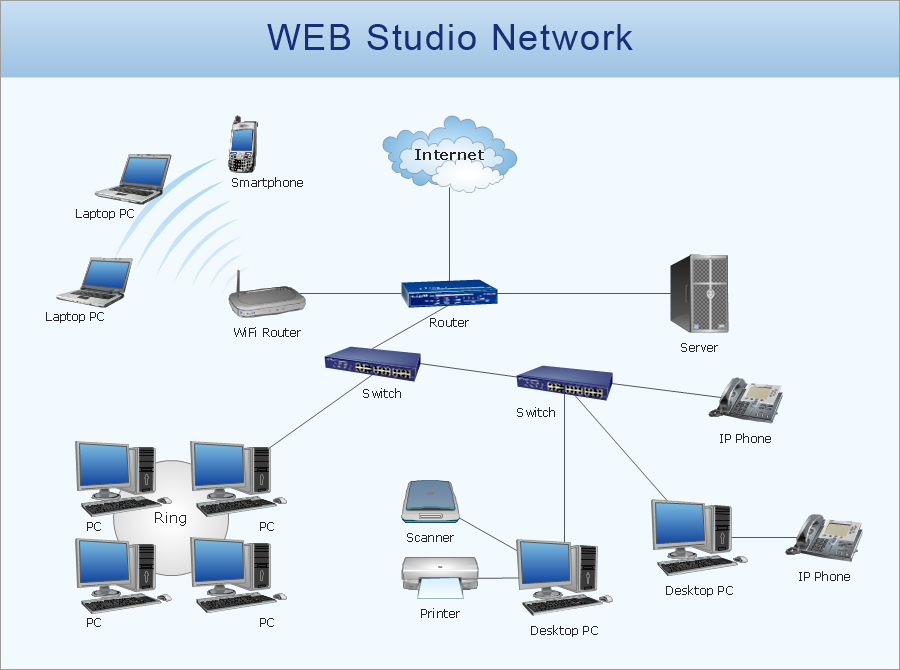
Wide area network (WAN) is a type of telecommunication network, which is used to connect the computers on a wide geographical area. WANs are quite popular and widely used networks, the most known and bright example of WAN is the Internet. They offer exceedingly convenient and quick way of exchanging information and data between employees, suppliers, and clients that are geographically remote each other. WANs are often constructed from several smaller networks (LANs, MANs, etc.) and use effectively different packet switching and circuit switching technologies. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is a powerful network diagramming software. Including Computer and Networks Area with extensive variety of solutions, ConceptDraw DIAGRAM offers a lot of ready-to-use predesigned vector stencils, wide set of examples and samples, helping the business and government entities effectively design professional-looking Wide area networks (WANs) and Wide area network topology diagrams of any complexity. Wide export capabilities of ConceptDraw DIAGRAM greatly extend your opportunities.
Telecommunications Network
How to draw Telecommunications Network Diagram quick, easy and effective? ConceptDraw DIAGRAM offers the unique Telecommunication Network Diagrams Solution from the Computer and Networks Area which will help you.- Satellite Mobile Circuit Diagram
- Mobile satellite communication network diagram
- Using Both Wired and Wireless Connections | Mobile satellite ...
- Satellite Network Circuit Diogram
- Gprs Circuit Diagram Mobile
- Satellite Dish Switching Circuits Schematic
- Circuit Diagram Of How To Connect To Satellite To Phone
- Mobile Network Tower Circuit
- Glossary Of Mobile Circuit Diagram
- Mobile Network Circuit Diagram
- Tv Tuner Circuit Diagram For Mobile
- Telecommunication Network Diagrams | Telecommunication ...
- Mobile Phone Networks
- Mobile Tower Wiring Diagram
- With Schematic Diagram Discuss The Satellite Connection
- For Transferring Data By Gprs From Mobile To Computer How The ...
- Mobile satellite communication network diagram | Mobile satellite TV ...
- Gprs Settilate Mobile
- Mobile T V Tuner Circuit Diagram
- Buiding Services Circuit Switching Drawings








































-cisco-network-topology---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-cisco-network-topology---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)














-cisco-network-topology---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)



-cisco-network-topology---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)













-cisco-network-topology---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)