The vector stencils library "Chemical elements" contains 118 icon symbols of chemical elements.
Use these shapes for drawing atoms, structural formulas of inorganic and organic molecules and ions, and schemes of chemical reaction mechanisms in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-chemistry
Use these shapes for drawing atoms, structural formulas of inorganic and organic molecules and ions, and schemes of chemical reaction mechanisms in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-chemistry
Electrical Symbols — Semiconductor Diodes
In electronics, a diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance to the flow of current in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A semiconductor diode is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconductors such as selenium or germanium are sometimes used. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw PRO make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.Electrical Symbols — VHF UHF SHF
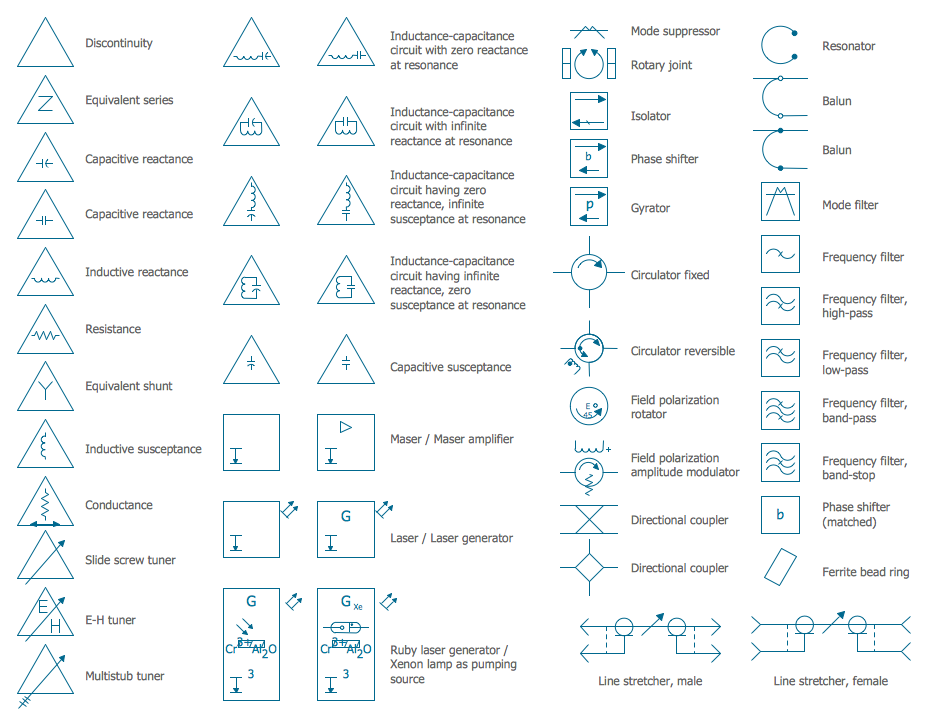
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 MHz and 3 GHz, also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one decimetre. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the SHF (super-high frequency) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, and numerous other applications. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw PRO make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.Electrical Symbols — Semiconductor
Semiconductors are crystalline or amorphous solids with distinct electrical characteristics. They are of high resistance — higher than typical resistance materials, but still of much lower resistance than insulators. Their resistance decreases as their temperature increases, which is behavior opposite to that of a metal. Finally, their conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by the deliberate, controlled introduction of impurities into the crystal structure, which lowers its resistance but also permits the creation of semiconductor junctions between differently-doped regions of the extrinsic semiconductor crystal. The behavior of charge carriers which include electrons, ions and electron holes at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors and all modern electronics. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw PRO make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.Electrical Symbols — Transistors
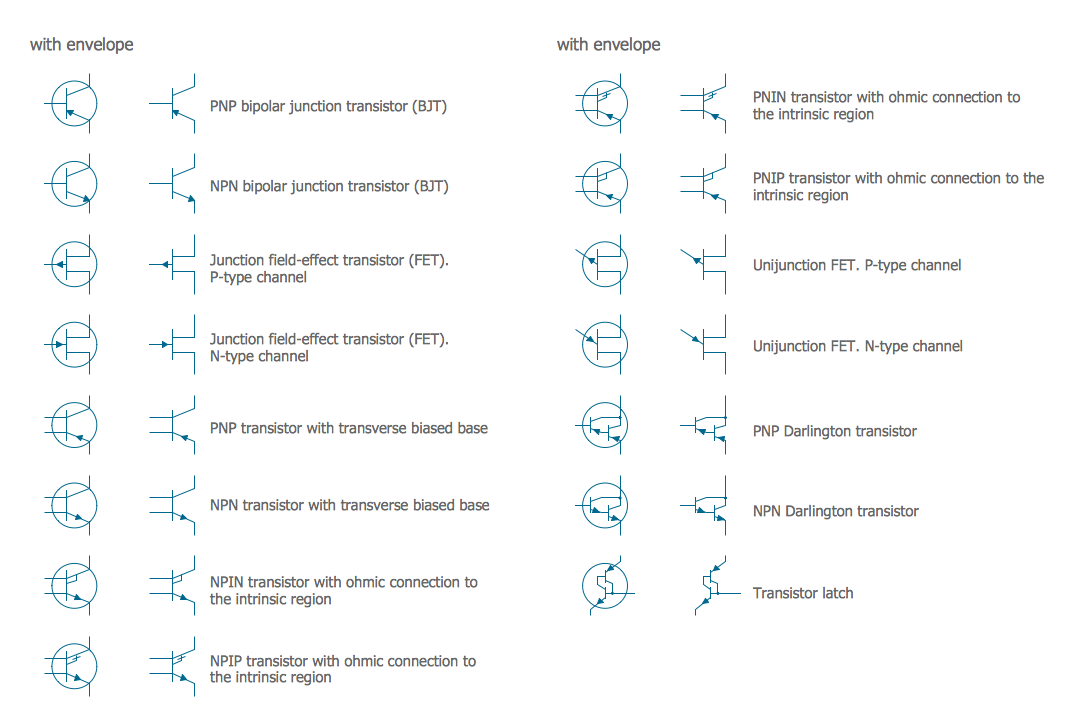
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw PRO make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.- Chemical elements - Vector stencils library | Potassium Icon
- Magnesium Icon
- Microwave Icons Meaning
- Chemical elements - Vector stencils library | Design elements ...
- Icon Microwave Visio
- Design elements - Periodic table of chemical elements | Chemical ...
- Chemical Element Icon
- Chemical elements - Vector stencils library | Mechanical Drawing ...
- Electrical Symbols — Semiconductor Diodes | Physical Security ...
- Cisco Products Additional. Cisco icons , shapes, stencils and ...
- Nitrogen Icon
- Carbon Element Icon
- Appearance Icon
- Design elements - Periodic table of chemical elements | Design ...
- Process Flow Diagram Symbols | Plumbing and Piping Plans ...
- Organic Chemistry Symbols | Chemistry Symbols and Meanings ...
- Electrical Symbols — Power Sources | Electrical Symbols — Thermo ...
- F&B | Chemical elements - Vector stencils library | Chemical ...
- Electrical Symbols, Electrical Diagram Symbols | Electrical Symbols ...
- Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating - PFD | Chemical elements ...
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)