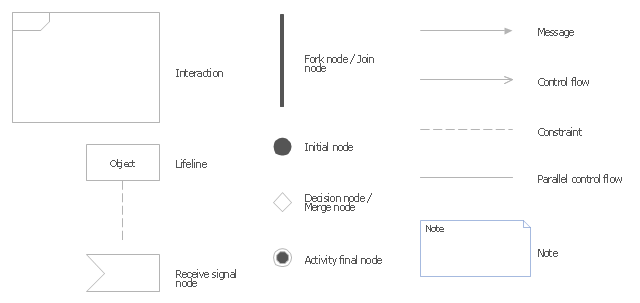
The vector stencils library "UML interaction overview diagrams" contains 13 symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"Interaction Overview Diagram is one of the fourteen types of diagrams of the Unified Modeling Language (UML), which can picture a control flow with nodes that can contain interaction diagrams.
The interaction overview diagram is similar to the activity diagram, in that both visualize a sequence of activities. The difference is that, for an interaction overview, each individual activity is pictured as a frame which can contain a nested interaction diagrams." [Interaction overview diagram. Wikipedia]
"Interaction diagrams.
Interaction diagrams, a subset of behavior diagrams, emphasize the flow of control and data among the things in the system being modeled:
(1) Communication diagram: shows the interactions between objects or parts in terms of sequenced messages. They represent a combination of information taken from Class, Sequence, and Use Case Diagrams describing both the static structure and dynamic behavior of a system.
(2) Interaction overview diagram: provides an overview in which the nodes represent interaction diagrams.
(3) Sequence diagram: shows how objects communicate with each other in terms of a sequence of messages. Also indicates the lifespans of objects relative to those messages.
(4) Timing diagrams: a specific type of interaction diagram where the focus is on timing constraints." [Unified Modeling Language. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - UML interaction overview diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Interaction Overview Diagram is one of the fourteen types of diagrams of the Unified Modeling Language (UML), which can picture a control flow with nodes that can contain interaction diagrams.
The interaction overview diagram is similar to the activity diagram, in that both visualize a sequence of activities. The difference is that, for an interaction overview, each individual activity is pictured as a frame which can contain a nested interaction diagrams." [Interaction overview diagram. Wikipedia]
"Interaction diagrams.
Interaction diagrams, a subset of behavior diagrams, emphasize the flow of control and data among the things in the system being modeled:
(1) Communication diagram: shows the interactions between objects or parts in terms of sequenced messages. They represent a combination of information taken from Class, Sequence, and Use Case Diagrams describing both the static structure and dynamic behavior of a system.
(2) Interaction overview diagram: provides an overview in which the nodes represent interaction diagrams.
(3) Sequence diagram: shows how objects communicate with each other in terms of a sequence of messages. Also indicates the lifespans of objects relative to those messages.
(4) Timing diagrams: a specific type of interaction diagram where the focus is on timing constraints." [Unified Modeling Language. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - UML interaction overview diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
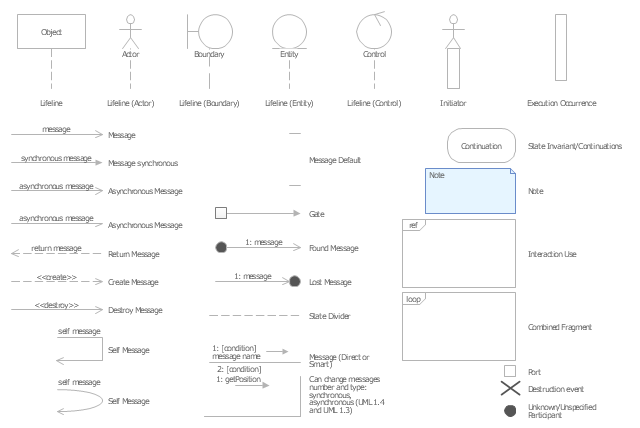
The vector stencils library "UML sequence diagrams" contains 50 symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"Sequence diagram ... building blocks.
If the lifeline is that of an object, it demonstrates a role. Note that leaving the instance name blank can represent anonymous and unnamed instances.
Messages, written with horizontal arrows with the message name written above them, display interaction. Solid arrow heads represent synchronous calls, open arrow heads represent asynchronous messages, and dashed lines represent reply messages. If a caller sends a synchronous message, it must wait until the message is done, such as invoking a subroutine. If a caller sends an asynchronous message, it can continue processing and doesn’t have to wait for a response. Asynchronous calls are present in multithreaded applications and in message-oriented middleware. Activation boxes, or method-call boxes, are opaque rectangles drawn on top of lifelines to represent that processes are being performed in response to the message (ExecutionSpecifications in UML).
Objects calling methods on themselves use messages and add new activation boxes on top of any others to indicate a further level of processing.
When an object is destroyed (removed from memory), an X is drawn on top of the lifeline, and the dashed line ceases to be drawn below it (this is not the case in the first example though). It should be the result of a message, either from the object itself, or another.
A message sent from outside the diagram can be represented by a message originating from a filled-in circle (found message in UML) or from a border of the sequence diagram (gate in UML)." [Sequence diagram. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - UML sequence diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Sequence diagram ... building blocks.
If the lifeline is that of an object, it demonstrates a role. Note that leaving the instance name blank can represent anonymous and unnamed instances.
Messages, written with horizontal arrows with the message name written above them, display interaction. Solid arrow heads represent synchronous calls, open arrow heads represent asynchronous messages, and dashed lines represent reply messages. If a caller sends a synchronous message, it must wait until the message is done, such as invoking a subroutine. If a caller sends an asynchronous message, it can continue processing and doesn’t have to wait for a response. Asynchronous calls are present in multithreaded applications and in message-oriented middleware. Activation boxes, or method-call boxes, are opaque rectangles drawn on top of lifelines to represent that processes are being performed in response to the message (ExecutionSpecifications in UML).
Objects calling methods on themselves use messages and add new activation boxes on top of any others to indicate a further level of processing.
When an object is destroyed (removed from memory), an X is drawn on top of the lifeline, and the dashed line ceases to be drawn below it (this is not the case in the first example though). It should be the result of a message, either from the object itself, or another.
A message sent from outside the diagram can be represented by a message originating from a filled-in circle (found message in UML) or from a border of the sequence diagram (gate in UML)." [Sequence diagram. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - UML sequence diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Collaboration Diagrams ...
- UML Sequence Diagram Example. SVG Vectored UML Diagrams ...
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Collaboration Diagrams ...
- UML Diagram | Design elements - UML interaction overview ...
- UML Diagram | Bank Sequence Diagram | UML Sequence Diagram ...
- UML sequence diagram - Template | Diagramming Software for ...
- Design elements - UML interaction overview diagrams ...
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Interaction Overview Diagrams
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Interaction Overview ...
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Interaction Overview Diagrams
- UML Sequence Diagram
- Diagramming Software for designing UML Sequence Diagrams ...
- UML Collaboration Diagram (UML2.0) | Diagramming Software for ...
- UML Diagram | Bank Sequence Diagram | Interactive Voice ...
- UML Block Diagram | About UML | Design elements - UML ...
- UML Sequence Diagram . Design Elements | Diagramming Software ...
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Collaboration Diagrams ...
- UML Interaction Overview Diagram . Design Elements | UML ...
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Collaboration Diagrams ...