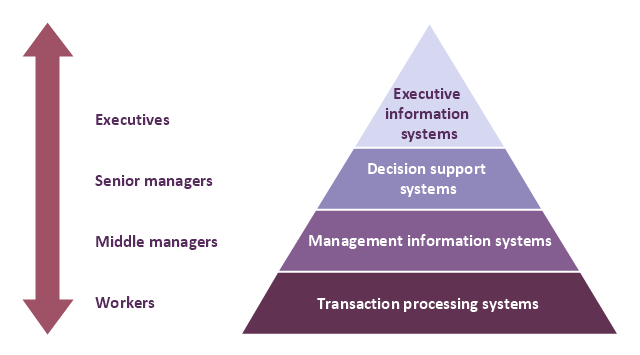
A four level pyramid model of different types of Information Systems based on the different levels of hierarchy in an organization. The first level represents transaction processing systems for workers. The second level represents management information systems for middle managers. The third level represents decision support systems for senior menegers. The fourth level represents executive information systems for executives.
"The "classic" view of Information systems found in the textbooks in the 1980s was of a pyramid of systems that reflected the hierarchy of the organization, usually transaction processing systems at the bottom of the pyramid, followed by management information systems, decision support systems, and ending with executive information systems at the top. Although the pyramid model remains useful, since it was first formulated a number of new technologies have been developed and new categories of information systems have emerged, some of which no longer fit easily into the original pyramid model.
Some examples of such systems are:
data warehouses,
enterprise resource planning,
enterprise systems,
expert systems,
search engines,
geographic information system,
global information system,
office automation." [Information systems. Wikipedia]
This diagram was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file Four-Level-Pyramid-model.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Four-Level-Pyramid-model.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
The triangle chart example "Information systems types" is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"The "classic" view of Information systems found in the textbooks in the 1980s was of a pyramid of systems that reflected the hierarchy of the organization, usually transaction processing systems at the bottom of the pyramid, followed by management information systems, decision support systems, and ending with executive information systems at the top. Although the pyramid model remains useful, since it was first formulated a number of new technologies have been developed and new categories of information systems have emerged, some of which no longer fit easily into the original pyramid model.
Some examples of such systems are:
data warehouses,
enterprise resource planning,
enterprise systems,
expert systems,
search engines,
geographic information system,
global information system,
office automation." [Information systems. Wikipedia]
This diagram was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file Four-Level-Pyramid-model.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Four-Level-Pyramid-model.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
The triangle chart example "Information systems types" is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
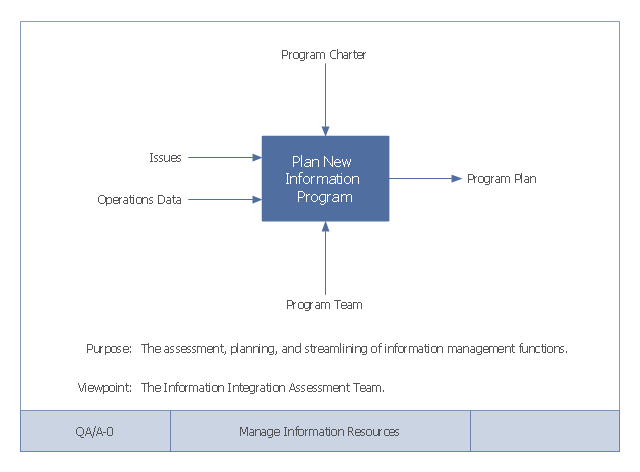
This example of a Top Level Context Diagram for an information system management process was redesigned from the Wikipedia file: IDEF Top-Level Context Diagram.jpg. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:IDEF_ Top-Level_ Context_ Diagram.jpg]
"Graphical notation.
IDEF0 is a model that consists of a hierarchical series of diagrams, text, and glossary cross referenced to each other. The two primary modeling components are:
(1) functions (represented on a diagram by boxes), and
(2) data and objects that interrelate those functions (represented by arrows).
... the position at which the arrow attaches to a box conveys the specific role of the interface. The controls enter the top of the box. The inputs, the data or objects acted upon by the operation, enter the box from the left. The outputs of the operation leave the right-hand side of the box. Mechanism arrows that provide supporting means for performing the function join (point up to) the bottom of the box.
The IDEF0 process.
The IDEF0 process starts with the identification of the prime function to be decomposed. This function is identified on a “Top Level Context Diagram,” that defines the scope of the particular IDEF0 analysis. ... From this diagram lower-level diagrams are generated." [IDEF0. Wikipedia]
The IDEF0 diagram example "Top-level context diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the IDEF0 Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Graphical notation.
IDEF0 is a model that consists of a hierarchical series of diagrams, text, and glossary cross referenced to each other. The two primary modeling components are:
(1) functions (represented on a diagram by boxes), and
(2) data and objects that interrelate those functions (represented by arrows).
... the position at which the arrow attaches to a box conveys the specific role of the interface. The controls enter the top of the box. The inputs, the data or objects acted upon by the operation, enter the box from the left. The outputs of the operation leave the right-hand side of the box. Mechanism arrows that provide supporting means for performing the function join (point up to) the bottom of the box.
The IDEF0 process.
The IDEF0 process starts with the identification of the prime function to be decomposed. This function is identified on a “Top Level Context Diagram,” that defines the scope of the particular IDEF0 analysis. ... From this diagram lower-level diagrams are generated." [IDEF0. Wikipedia]
The IDEF0 diagram example "Top-level context diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the IDEF0 Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
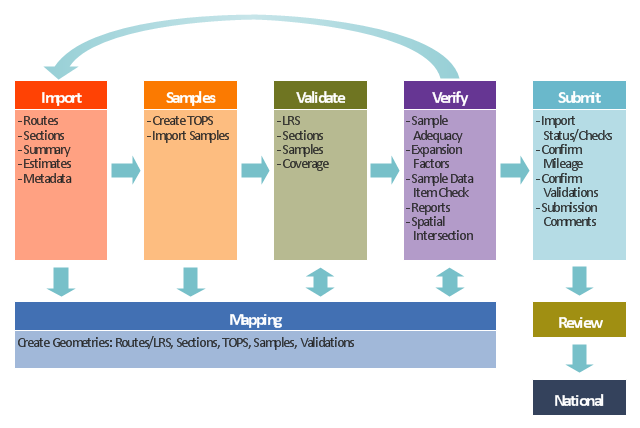
This TQM diagram example was redesigned from the illustration of the Highway Performance Monitoring System (HPMS) Field Manual from the website of the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA).
[fhwa.dot.gov/ policyinformation/ hpms/ fieldmanual/ chapter7.cfm]
"Highway Performance Monitoring System (HPMS).
The HPMS is a national level highway information system that includes data on the extent, condition, performance, use and operating characteristics of the nation's highways. The HPMS contains administrative and extent of system information on all public roads, while information on other characteristics is represented in HPMS as a mix of universe and sample data for arterial and collector functional systems. Limited information on travel and paved miles is included in summary form for the lowest functional systems.
HPMS was developed in 1978 as a continuing database, replacing the special biennial condition studies that had been conducted since 1965. The HPMS has been modified several times since its inception. Changes have been made to reflect changes in the highway systems, legislation, and national priorities, to reflect new technology, and to consolidate or streamline reporting requirements." [fhwa.dot.gov/ policyinformation/ hpms.cfm]
The TQM flowchart example "Software workflow diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Total Quality Management (TQM) Diagrams solution from the Quality area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[fhwa.dot.gov/ policyinformation/ hpms/ fieldmanual/ chapter7.cfm]
"Highway Performance Monitoring System (HPMS).
The HPMS is a national level highway information system that includes data on the extent, condition, performance, use and operating characteristics of the nation's highways. The HPMS contains administrative and extent of system information on all public roads, while information on other characteristics is represented in HPMS as a mix of universe and sample data for arterial and collector functional systems. Limited information on travel and paved miles is included in summary form for the lowest functional systems.
HPMS was developed in 1978 as a continuing database, replacing the special biennial condition studies that had been conducted since 1965. The HPMS has been modified several times since its inception. Changes have been made to reflect changes in the highway systems, legislation, and national priorities, to reflect new technology, and to consolidate or streamline reporting requirements." [fhwa.dot.gov/ policyinformation/ hpms.cfm]
The TQM flowchart example "Software workflow diagram" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Total Quality Management (TQM) Diagrams solution from the Quality area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- 4 Level pyramid model diagram - Information systems types | 5 Level ...
- Chart Of Management Information System With Diagram
- 4 Level pyramid model diagram - Information systems types ...
- Four Levels Of Information System
- Explain Four Level Of Information System
- Pyramid Diagram | 4 Level pyramid model diagram - Information ...
- Marketing Information System Example
- Three Levels Management Information System
- 4 Level pyramid model diagram - Information systems types
- Pyramid Diagram | Tactical Level Management Information System
- 5 Level pyramid model diagram - Information systems types ...
- Pyramid Diagram | 4 Level pyramid model diagram - Information ...
- Pyramid Diagram | 4 Level pyramid model diagram - Information ...
- What Are The 3 Levels Of Management Information System
- Information System At Various Levels Of Management
- Using Diagram Explain Types Of Management Information System
- Management Information System Triangle Diagram
- How to Create Flowcharts for an Accounting Information System ...
- 5 Level pyramid model diagram - Information systems types | 4 Level ...
- Pyramid Diagram | 4 Level pyramid model diagram - Information ...