 Chemical and Process Engineering
Chemical and Process Engineering
This chemical engineering solution extends ConceptDraw PRO v.9.5 (or later) with process flow diagram symbols, samples, process diagrams templates and libraries of design elements for creating process and instrumentation diagrams, block flow diagrams (BFD
"A process flow diagram (PFD) is a diagram commonly used in chemical and process engineering to indicate the general flow of plant processes and equipment. The PFD displays the relationship between major equipment of a plant facility and does not show minor details such as piping details and designations. Another commonly used term for a PFD is a flowsheet. ...
Process flow diagrams of multiple process units within a large industrial plant will usually contain less detail and may be called block flow diagrams or schematic flow diagrams." [Process flow diagram. Wikipedia]
The process flow diagram (PFD) template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Process flow diagrams of multiple process units within a large industrial plant will usually contain less detail and may be called block flow diagrams or schematic flow diagrams." [Process flow diagram. Wikipedia]
The process flow diagram (PFD) template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This is a schematic process flow diagram of the processes used in a typical oil refinery.
This process flow diagram (PFD) example was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: RefineryFlow.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:RefineryFlow.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units. In many ways, oil refineries use much of the technology of, and can be thought of, as types of chemical plants. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot (tank farm) at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.
An oil refinery is considered an essential part of the downstream side of the petroleum industry." [Oil refinery. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This process flow diagram (PFD) example was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: RefineryFlow.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:RefineryFlow.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units. In many ways, oil refineries use much of the technology of, and can be thought of, as types of chemical plants. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot (tank farm) at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.
An oil refinery is considered an essential part of the downstream side of the petroleum industry." [Oil refinery. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
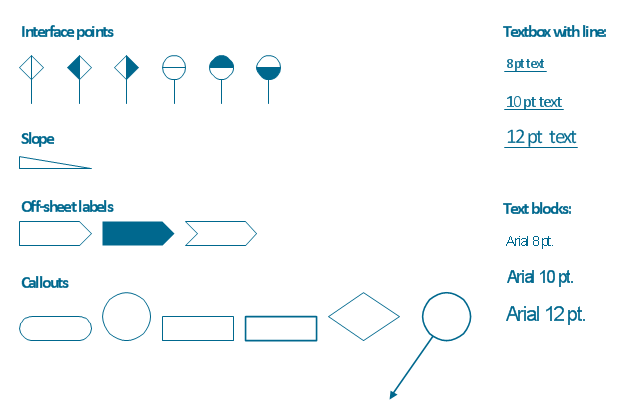
The vector stencils library "Process annotations" contains 22 symbols of interface points, slope, off-sheet labels, callouts and textboxes.
Use these shapes for setting automatic labels to display a datasheet field for a pipeline shape, labels, captions, outlines, off-sheet labels, text balloons, annotations, outlines, tags, and descriptions.
"In engineering a process is a set of interrelated tasks that, together, transform inputs into outputs. These tasks may be carried out by people, nature, or machines using resources; so an engineering process must be considered in the context of the agents carrying out the tasks, and the resource attributes involved. Systems Engineering normative documents and those related to Maturity Models are typically based on processes. For example, System Engineering processes of the EIA-632 and processes involved in the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) institutionalization and improvement approach. Constraints imposed on the tasks and resources required to implement them are essential for executing the tasks mentioned.
A chemical process is a series of unit operations used to produce a material in large quantities.
In the chemical industry, chemical engineers will use the following to define or illustrate a process:
Process Flow Diagram (PFD),
Piping and instrumentation diagram
(P&ID),
Simplified process description,
Detailed process description,
Project management,
Process simulation." [Process (engineering). Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Process annotations" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these shapes for setting automatic labels to display a datasheet field for a pipeline shape, labels, captions, outlines, off-sheet labels, text balloons, annotations, outlines, tags, and descriptions.
"In engineering a process is a set of interrelated tasks that, together, transform inputs into outputs. These tasks may be carried out by people, nature, or machines using resources; so an engineering process must be considered in the context of the agents carrying out the tasks, and the resource attributes involved. Systems Engineering normative documents and those related to Maturity Models are typically based on processes. For example, System Engineering processes of the EIA-632 and processes involved in the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) institutionalization and improvement approach. Constraints imposed on the tasks and resources required to implement them are essential for executing the tasks mentioned.
A chemical process is a series of unit operations used to produce a material in large quantities.
In the chemical industry, chemical engineers will use the following to define or illustrate a process:
Process Flow Diagram (PFD),
Piping and instrumentation diagram
(P&ID),
Simplified process description,
Detailed process description,
Project management,
Process simulation." [Process (engineering). Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Process annotations" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This process flow diagram (PFD) example shows an amine treating system for the removal of gaseous hydrogen sulfide from gas streams. It is used in oil refineries and chemical plants. This PFD sample was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: AmineTreating.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:AmineTreating.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Amine gas treating, also known as gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from gases. It is a common unit process used in refineries, and is also used in petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries.
Processes within oil refineries or chemical processing plants that remove hydrogen sulfide are referred to as "sweetening" processes because the odor of the processed products is improved by the absence of hydrogen sulfide. An alternative to the use of amines involves membrane technology. Membranes are attractive since no reagents are consumed.
Many different amines are used in gas treating:
Diethanolamine (DEA),
Monoethanolamine (MEA),
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA),
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA),
Aminoethoxyethanol (Diglycolamine) (DGA).
The most commonly used amines in industrial plants are the alkanolamines DEA, MEA, and MDEA. These amines are also used in many oil refineries to remove sour gases from liquid hydrocarbons such as liquified petroleum gas (LPG)." [Amine gas treating. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Amine treating unit schematic diagram" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Amine gas treating, also known as gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from gases. It is a common unit process used in refineries, and is also used in petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries.
Processes within oil refineries or chemical processing plants that remove hydrogen sulfide are referred to as "sweetening" processes because the odor of the processed products is improved by the absence of hydrogen sulfide. An alternative to the use of amines involves membrane technology. Membranes are attractive since no reagents are consumed.
Many different amines are used in gas treating:
Diethanolamine (DEA),
Monoethanolamine (MEA),
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA),
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA),
Aminoethoxyethanol (Diglycolamine) (DGA).
The most commonly used amines in industrial plants are the alkanolamines DEA, MEA, and MDEA. These amines are also used in many oil refineries to remove sour gases from liquid hydrocarbons such as liquified petroleum gas (LPG)." [Amine gas treating. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Amine treating unit schematic diagram" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Types Of Flow Sheet In Chemical Engineering
- Flow Sheet Chemical Engineering
- Flowsheeting In Chemical Engineering
- Chemical Engineering Flow Sheet Examples In Block Diagram
- Flowsheeting Solution In Chemical Engineering Pdf
- Chemical and Process Engineering | How to Draw a Chemical ...
- Flow Sheeting
- Chemical Engineering Symbols For Flow Sheet Pdf
- Uses Of Flow Sheet In Chemical Engineering
-template-process-flow-diagram-(pfd)-template.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-process-flow-diagram---typical-oil-refinery.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-amine-treating-unit-schematic-diagram.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)