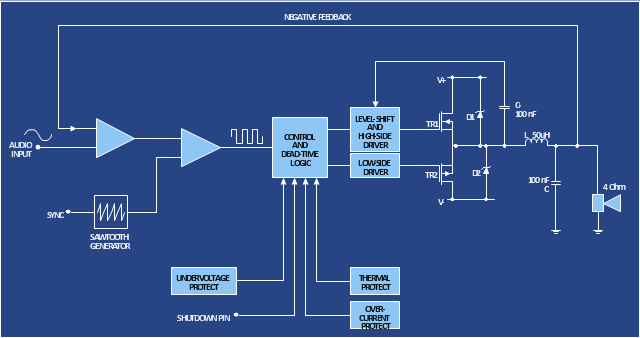
The circuit diagram example "Amplifier" was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Slika br.5.JPG.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Slika_ br.5.JPG]
This file is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication. [creativecommons.org/ publicdomain/ zero/ 1.0/ deed.en]
"An electronic amplifier, amplifier, or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal. It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply.
There are four basic types of electronic amplifier: the voltage amplifier, the current amplifier, the transconductance amplifier, and the transresistance amplifier. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain." [Amplifier. Wikipedia]
The circuit diagram example "Amplifier" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Slika_ br.5.JPG]
This file is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication. [creativecommons.org/ publicdomain/ zero/ 1.0/ deed.en]
"An electronic amplifier, amplifier, or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal. It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply.
There are four basic types of electronic amplifier: the voltage amplifier, the current amplifier, the transconductance amplifier, and the transresistance amplifier. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain." [Amplifier. Wikipedia]
The circuit diagram example "Amplifier" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Electrical Engineering
Electrical Engineering
This solution extends ConceptDraw PRO v.9.5 (or later) with electrical engineering samples, electrical schematic symbols, electrical diagram symbols, templates and libraries of design elements, to help you design electrical schematics, digital and analog
ConceptDraw Arrows10 Technology
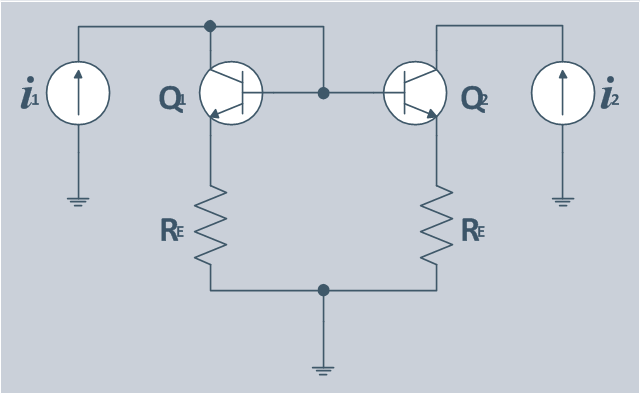
You can see that when you rotate a group, connectors change their angle, keeping their position inside of the grouped objects. If you decide to ungroup the objects, the connectors will adjust to keep lines parallel to the edges of the sheet. The magic of ConceptDraw Arrows10’s rotating group containing connectors, makes complex diagramming simple and easy. The way to connect objects has never been easier.The circuit diagram example "Bipolar current mirror" was redesigned from the Wikipedia file: Current mirror.png.
[en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Current_ mirror.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"A current mirror is a circuit designed to copy a current through one active device by controlling the current in another active device of a circuit, keeping the output current constant regardless of loading. The current being 'copied' can be, and sometimes is, a varying signal current. Conceptually, an ideal current mirror is simply an ideal inverting current amplifier that reverses the current direction as well or it is a current-controlled current source (CCCS). The current mirror is used to provide bias currents and active loads to circuits. ...
Basic BJT current mirror.
If a voltage is applied to the BJT base-emitter junction as an input quantity and the collector current is taken as an output quantity, the transistor will act as an exponential voltage-to-current converter. By applying a negative feedback (simply joining the base and collector) the transistor can be "reversed" and it will begin acting as the opposite logarithmic current-to-voltage converter; now it will adjust the "output" base-emitter voltage so as to pass the applied "input" collector current.
The simplest bipolar current mirror ... implements this idea. It consists of two cascaded transistor stages acting accordingly as a reversed and direct voltage-to-current converters." [Current mirror. Wikipedia]
The circuit diagram example "Bipolar current mirror" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Current_ mirror.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"A current mirror is a circuit designed to copy a current through one active device by controlling the current in another active device of a circuit, keeping the output current constant regardless of loading. The current being 'copied' can be, and sometimes is, a varying signal current. Conceptually, an ideal current mirror is simply an ideal inverting current amplifier that reverses the current direction as well or it is a current-controlled current source (CCCS). The current mirror is used to provide bias currents and active loads to circuits. ...
Basic BJT current mirror.
If a voltage is applied to the BJT base-emitter junction as an input quantity and the collector current is taken as an output quantity, the transistor will act as an exponential voltage-to-current converter. By applying a negative feedback (simply joining the base and collector) the transistor can be "reversed" and it will begin acting as the opposite logarithmic current-to-voltage converter; now it will adjust the "output" base-emitter voltage so as to pass the applied "input" collector current.
The simplest bipolar current mirror ... implements this idea. It consists of two cascaded transistor stages acting accordingly as a reversed and direct voltage-to-current converters." [Current mirror. Wikipedia]
The circuit diagram example "Bipolar current mirror" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Home Theater Amplifier Circuit Diagram With Volume Control In
- American Home Theater Amplifier Circuit Diagram And Layout
- Symbol Amplifier Diagram
- Home Theater Amplifier Circuit Diagram
- Amplifier - Circuit diagram | Bipolar current mirror - Circuit diagram ...
- Amplifier - Circuit diagram | Video and audio - Vector stencils library ...
- Circuit diagram - EL 34 schematics | Pentode Tube Amplifier
- Symbol Meaning Of Diagram Lay Out Of Amplifier
- Stereo Amplifier Circut Diagram Com
- Amplifier Circuit Schematics
- Circuits And Diagrams Of Amplifiers
- Audio Amplifier Circuit Diagram With Layout
- Electrical Amplifier Diagram Circuit
- Amplifier - Circuit diagram | Electrical Symbols — Logic Gate ...
- Power Full Home Theater Amplifier Circuit Diagram
- Amplifier - Circuit diagram
- Electrical Symbols, Electrical Diagram Symbols | Circuits and Logic ...
- Amplifier - Circuit diagram | Design elements - Composite ...
- Block Diagram Symbols Amplifier
- Amplifier Rack Mount Plan Diagrams