 Workflow Diagrams
Workflow Diagrams
Workflow Diagrams solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software with samples, templates and vector stencils library for drawing the work process flowcharts.
This work flow chart sample was redesigned from the picture "Weather Forecast" from the article "Simulation Workflows".
[iaas.uni-stuttgart.de/ forschung/ projects/ simtech/ sim-workflows.php]
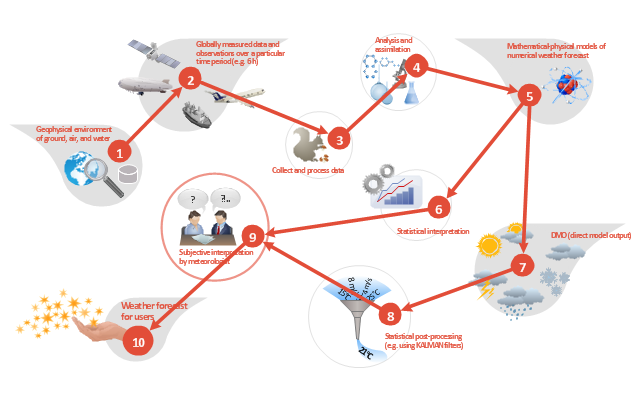
"(1) The weather is predicted for a particular geological area. Hence, the workflow is fed with a model of the geophysical environment of ground, air and water for a requested area.
(2) Over a specified period of time (e.g. 6 hours) several different variables are measured and observed. Ground stations, ships, airplanes, weather balloons, satellites and buoys measure the air pressure, air/ water temperature, wind velocity, air humidity, vertical temperature profiles, cloud velocity, rain fall, and more.
(3) This data needs to be collected from the different sources and stored for later access.
(4) The collected data is analyzed and transformed into a common format (e.g. Fahrenheit to Celsius scale). The normalized values are used to create the current state of the atmosphere.
(5) Then, a numerical weather forecast is made based on mathematical-physical models (e.g. GFS - Global Forecast System, UKMO - United Kingdom MOdel, GME - global model of Deutscher Wetterdienst). The environmental area needs to be discretized beforehand using grid cells. The physical parameters measured in Step 2 are exposed in 3D space as timely function. This leads to a system of partial differential equations reflecting the physical relations that is solved numerically.
(6) The results of the numerical models are complemented with a statistical interpretation (e.g. with MOS - Model-Output-Statistics). That means the forecast result of the numerical models is compared to statistical weather data. Known forecast failures are corrected.
(7) The numerical post-processing is done with DMO (Direct Model Output): the numerical results are interpolated for specific geological locations.
(8) Additionally, a statistical post-processing step removes failures of measuring devices (e.g. using KALMAN filters).
(9) The statistical interpretation and the numerical results are then observed and interpreted by meteorologists based on their subjective experiences.
(10) Finally, the weather forecast is visualized and presented to interested people." [iaas.uni-stuttgart.de/ forschung/ projects/ simtech/ sim-workflows.php]
The example "Workflow diagram - Weather forecast" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Workflow Diagrams solution from the Business Processes area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[iaas.uni-stuttgart.de/ forschung/ projects/ simtech/ sim-workflows.php]
"(1) The weather is predicted for a particular geological area. Hence, the workflow is fed with a model of the geophysical environment of ground, air and water for a requested area.
(2) Over a specified period of time (e.g. 6 hours) several different variables are measured and observed. Ground stations, ships, airplanes, weather balloons, satellites and buoys measure the air pressure, air/ water temperature, wind velocity, air humidity, vertical temperature profiles, cloud velocity, rain fall, and more.
(3) This data needs to be collected from the different sources and stored for later access.
(4) The collected data is analyzed and transformed into a common format (e.g. Fahrenheit to Celsius scale). The normalized values are used to create the current state of the atmosphere.
(5) Then, a numerical weather forecast is made based on mathematical-physical models (e.g. GFS - Global Forecast System, UKMO - United Kingdom MOdel, GME - global model of Deutscher Wetterdienst). The environmental area needs to be discretized beforehand using grid cells. The physical parameters measured in Step 2 are exposed in 3D space as timely function. This leads to a system of partial differential equations reflecting the physical relations that is solved numerically.
(6) The results of the numerical models are complemented with a statistical interpretation (e.g. with MOS - Model-Output-Statistics). That means the forecast result of the numerical models is compared to statistical weather data. Known forecast failures are corrected.
(7) The numerical post-processing is done with DMO (Direct Model Output): the numerical results are interpolated for specific geological locations.
(8) Additionally, a statistical post-processing step removes failures of measuring devices (e.g. using KALMAN filters).
(9) The statistical interpretation and the numerical results are then observed and interpreted by meteorologists based on their subjective experiences.
(10) Finally, the weather forecast is visualized and presented to interested people." [iaas.uni-stuttgart.de/ forschung/ projects/ simtech/ sim-workflows.php]
The example "Workflow diagram - Weather forecast" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Workflow Diagrams solution from the Business Processes area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This process flow diagram (PFD) example shows an amine treating system for the removal of gaseous hydrogen sulfide from gas streams. It is used in oil refineries and chemical plants. This PFD sample was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: AmineTreating.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:AmineTreating.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Amine gas treating, also known as gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from gases. It is a common unit process used in refineries, and is also used in petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries.
Processes within oil refineries or chemical processing plants that remove hydrogen sulfide are referred to as "sweetening" processes because the odor of the processed products is improved by the absence of hydrogen sulfide. An alternative to the use of amines involves membrane technology. Membranes are attractive since no reagents are consumed.
Many different amines are used in gas treating:
Diethanolamine (DEA),
Monoethanolamine (MEA),
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA),
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA),
Aminoethoxyethanol (Diglycolamine) (DGA).
The most commonly used amines in industrial plants are the alkanolamines DEA, MEA, and MDEA. These amines are also used in many oil refineries to remove sour gases from liquid hydrocarbons such as liquified petroleum gas (LPG)." [Amine gas treating. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Amine treating unit schematic diagram" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Amine gas treating, also known as gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from gases. It is a common unit process used in refineries, and is also used in petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries.
Processes within oil refineries or chemical processing plants that remove hydrogen sulfide are referred to as "sweetening" processes because the odor of the processed products is improved by the absence of hydrogen sulfide. An alternative to the use of amines involves membrane technology. Membranes are attractive since no reagents are consumed.
Many different amines are used in gas treating:
Diethanolamine (DEA),
Monoethanolamine (MEA),
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA),
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA),
Aminoethoxyethanol (Diglycolamine) (DGA).
The most commonly used amines in industrial plants are the alkanolamines DEA, MEA, and MDEA. These amines are also used in many oil refineries to remove sour gases from liquid hydrocarbons such as liquified petroleum gas (LPG)." [Amine gas treating. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Amine treating unit schematic diagram" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
This solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM.9 mechanical drawing software (or later) with samples of mechanical drawing symbols, templates and libraries of design elements, for help when drafting mechanical engineering drawings, or parts, assembly, pneumatic,
- Draw A Flow Chart To Show The Waste Water Treatment
- Water Treatment Process Flow Diagram Symbols
- How To Make Flow Chart Water Treatment
- Draw Flow Diagram Of Water Purification
- Water Purification Process Flow Chart
- Process Flow Chart | IDEF3 Standard | IDEF9 Standard | Solid ...
- Waste Flow Chart
- Workflow diagram - Weather forecast | Work Flow Chart | Workflow ...
- Types of Flowcharts | Workflow diagram - Weather forecast | Work ...
- Program to Make Flow Chart | Drawing Illustration | BPR Diagram ...
- Process Flowchart | Process Flow Diagram Symbols | Process Flow ...
- Outstanding trends of wastewater treatment plants | Building ...
- Mechanical Drawing Symbols | Process Flow Diagram Symbols ...
- Workflow Chart
- Workflow diagram - Weather forecast | Work Flow Chart | Workflow ...
- Screens Symbol Flow Diagram
- Process Flow Chart Symbols | Process Flow Diagram Symbols ...
- Plant Layout Plans | Onion Diagram Process Design | Process flow ...
- Mechanical Drawing Symbols | Process Flow Diagram Symbols ...
- How to Draw a Chemical Process Flow Diagram
-amine-treating-unit-schematic-diagram.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)