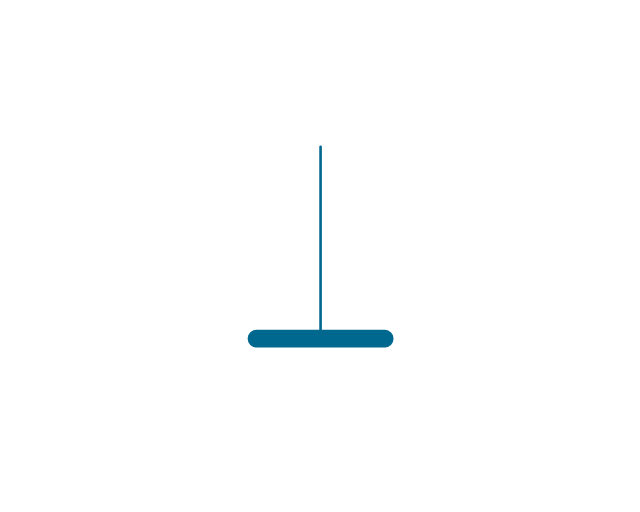
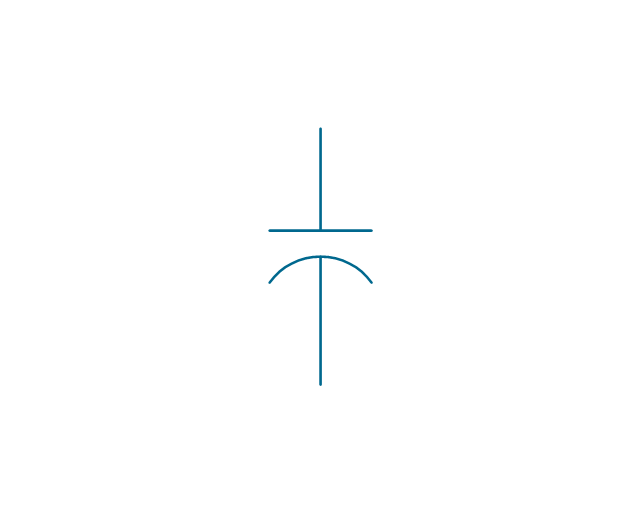
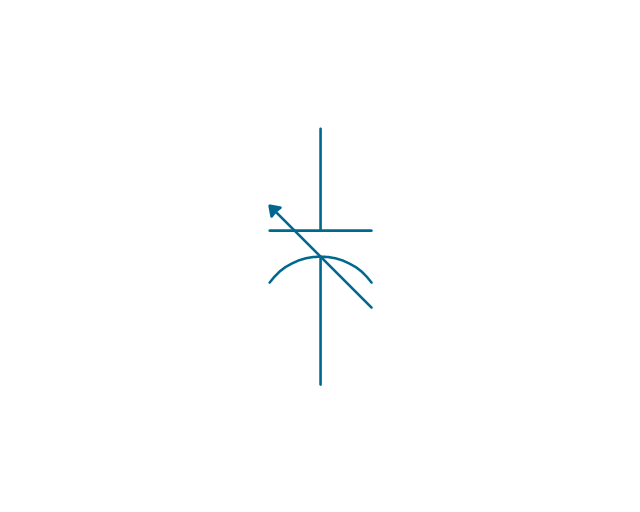
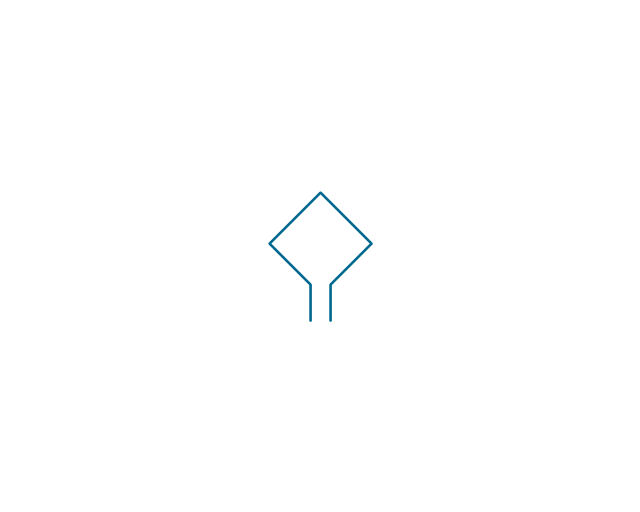
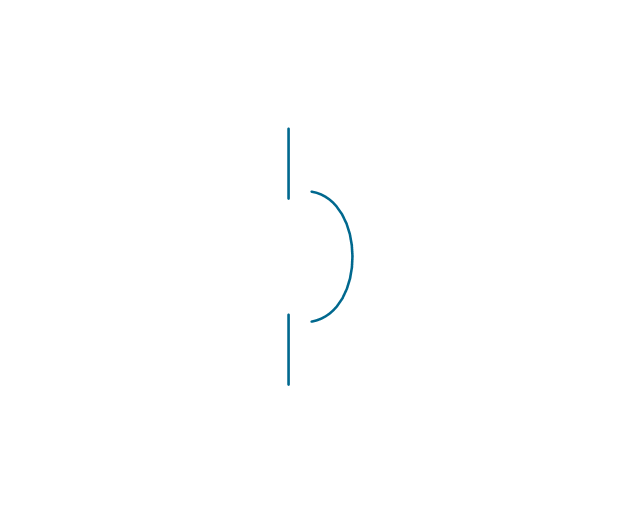
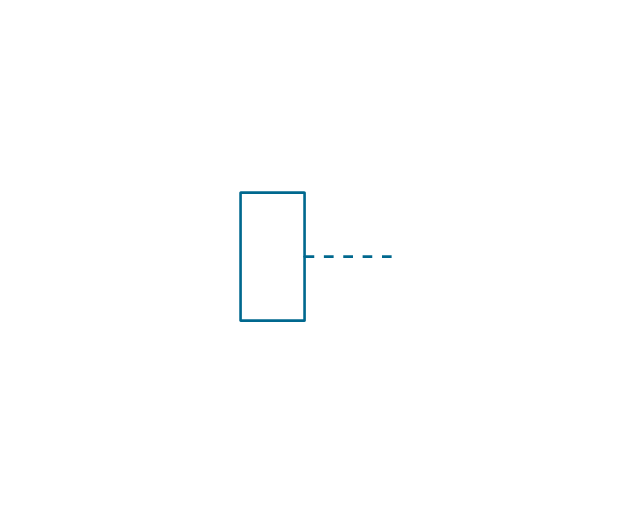
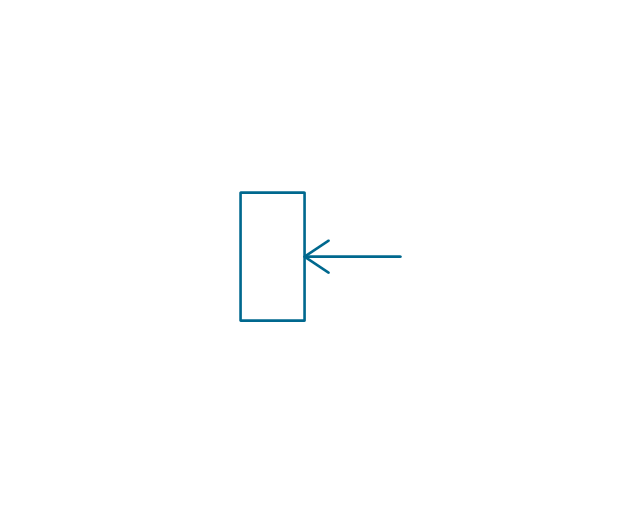
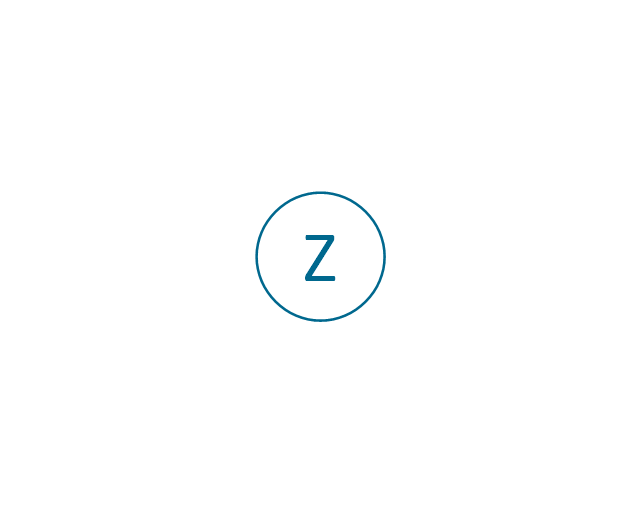
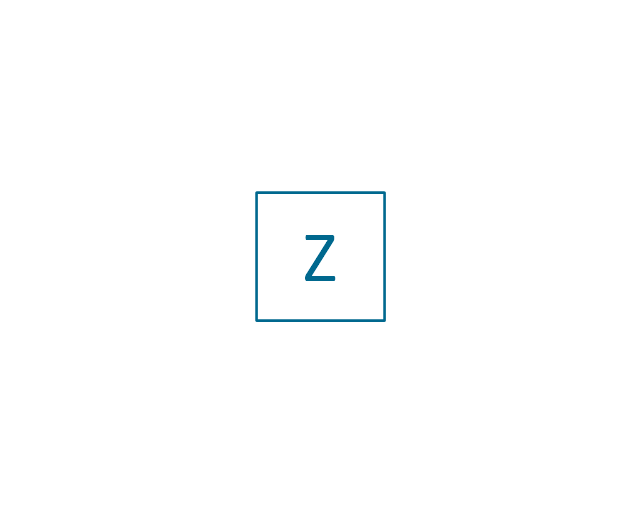
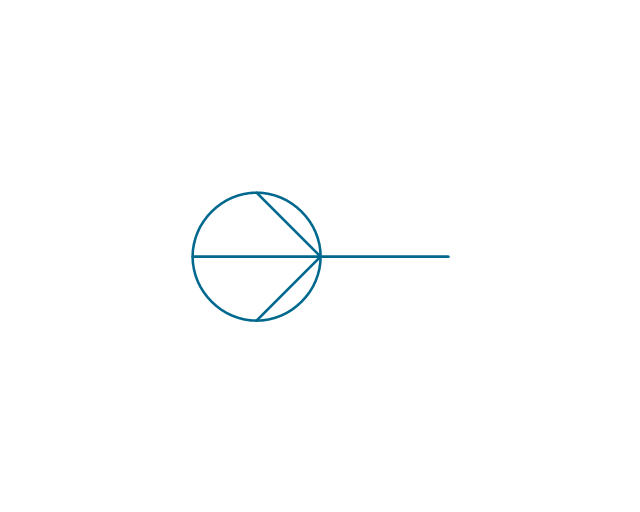
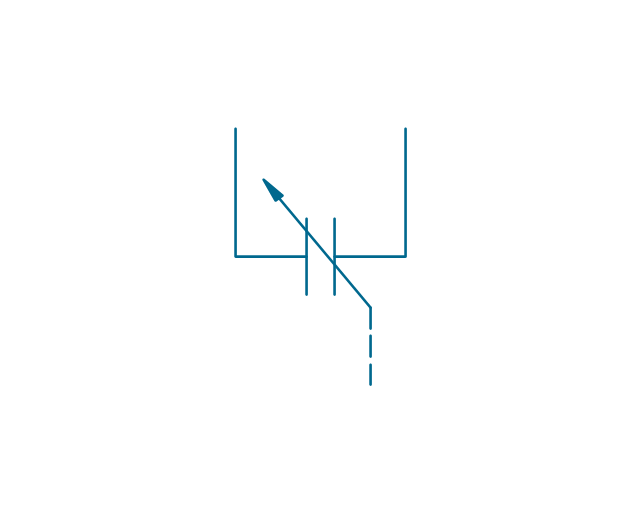
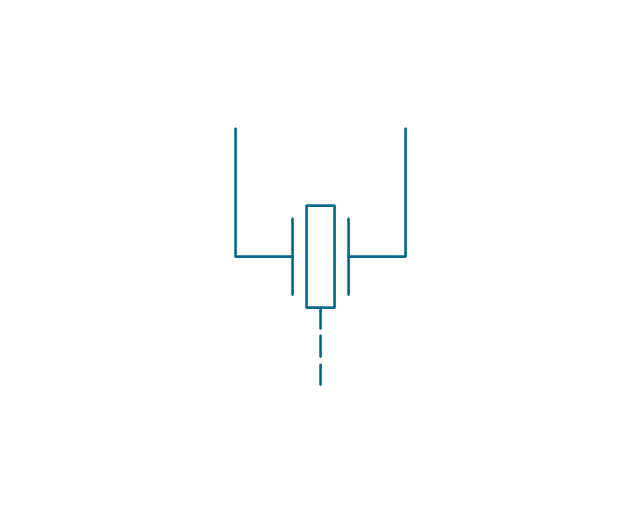
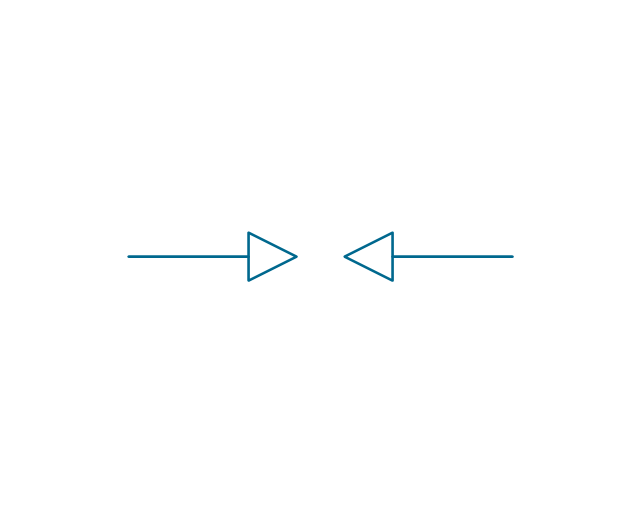
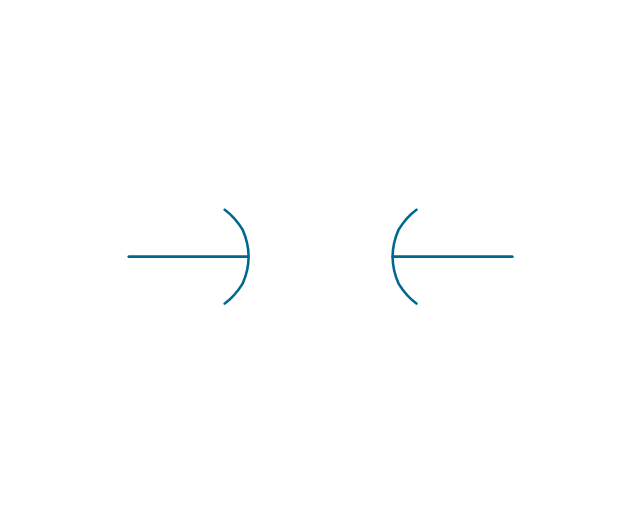
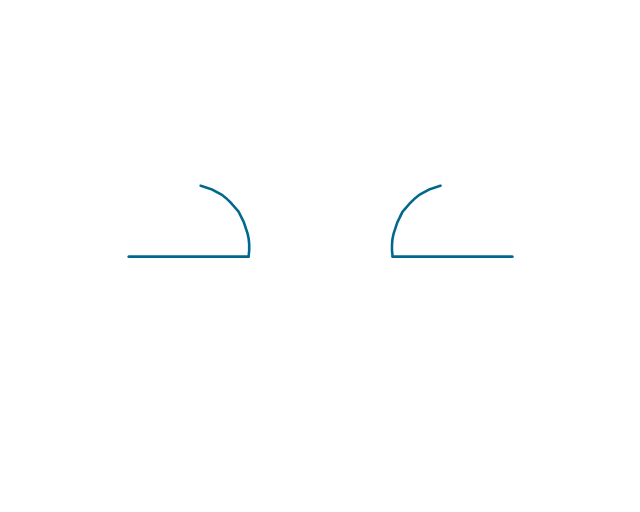
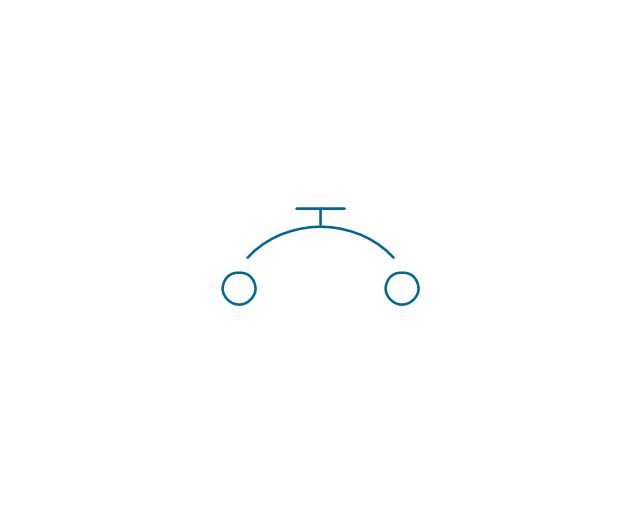
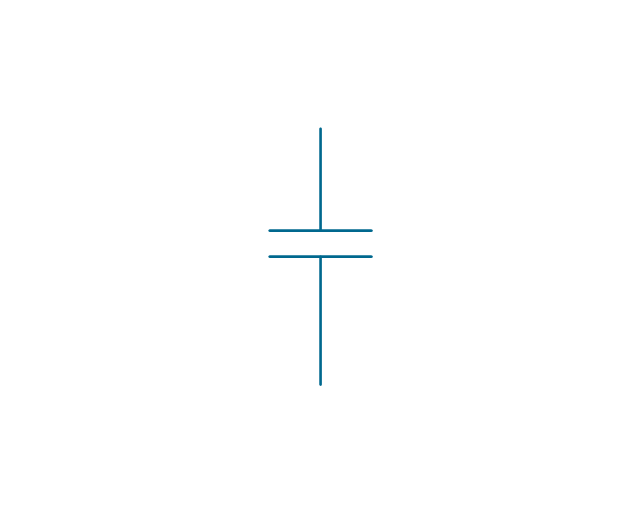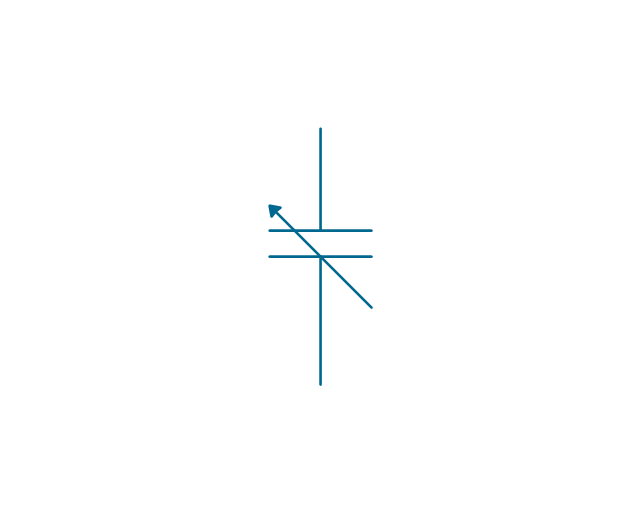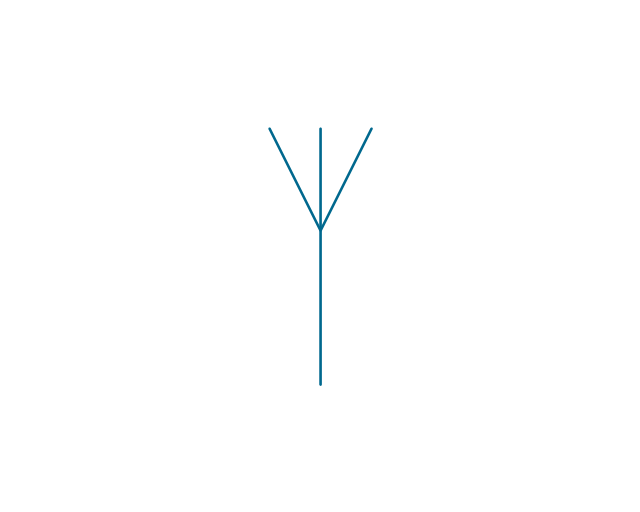The vector stencils library "Electrical circuits" contains 49 element symbols of electrical and electronic devices, including ignitors, starters, transmitters, circuit protectors, transducers, radio and audio equipment.
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
The vector stencils library "Electrical circuits" contains 49 element symbols of electrical and electronic devices, including ignitors, starters, transmitters, circuit protectors, transducers, radio and audio equipment.
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
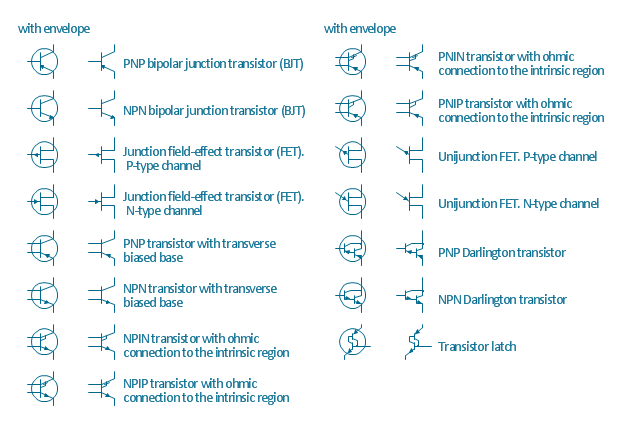
The vector stencils library "Transistors" contains 30 symbols of transistors drawing electronic schematics and circuit diagrams.
"A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.
The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. ...
Transistors are categorized by:
(1) Semiconductor material...: the metalloids germanium ... and silicon ... in amorphous, polycrystalline and monocrystalline form; the compounds gallium arsenide ... and silicon carbide ..., the alloy silicon-germanium ..., the allotrope of carbon graphene ...
(2) Structure: BJT, JFET, IGFET (MOSFET), insulated-gate bipolar transistor, "other types"
(3) Electrical polarity (positive and negative): n–p–n, p–n–p (BJTs); n-channel, p-channel (FETs)
(4) Maximum power rating: low, medium, high
(5) Maximum operating frequency: low, medium, high, radio (RF), microwave frequency...
(6) Application: switch, general purpose, audio, high voltage, super-beta, matched pair
(7) Physical packaging: through-hole metal, through-hole plastic, surface mount, ball grid array, power modules...
(8) Amplification factor..." [Transistor. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transistors" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.
The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. ...
Transistors are categorized by:
(1) Semiconductor material...: the metalloids germanium ... and silicon ... in amorphous, polycrystalline and monocrystalline form; the compounds gallium arsenide ... and silicon carbide ..., the alloy silicon-germanium ..., the allotrope of carbon graphene ...
(2) Structure: BJT, JFET, IGFET (MOSFET), insulated-gate bipolar transistor, "other types"
(3) Electrical polarity (positive and negative): n–p–n, p–n–p (BJTs); n-channel, p-channel (FETs)
(4) Maximum power rating: low, medium, high
(5) Maximum operating frequency: low, medium, high, radio (RF), microwave frequency...
(6) Application: switch, general purpose, audio, high voltage, super-beta, matched pair
(7) Physical packaging: through-hole metal, through-hole plastic, surface mount, ball grid array, power modules...
(8) Amplification factor..." [Transistor. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transistors" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Semiconductor diodes" contains 24 symbols of semiconductor diodes for drawing electronic schematics and circuit diagrams.
"In electronics, a diode is a two-terminal electronic component with asymmetric conductance; it has low (ideally zero) resistance to current in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. A vacuum tube diode has two electrodes, a plate (anode) and a heated cathode. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. ...
Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconductors such as selenium or germanium are sometimes used." [Diode. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Semiconductor diodes" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In electronics, a diode is a two-terminal electronic component with asymmetric conductance; it has low (ideally zero) resistance to current in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. A vacuum tube diode has two electrodes, a plate (anode) and a heated cathode. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. ...
Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconductors such as selenium or germanium are sometimes used." [Diode. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Semiconductor diodes" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
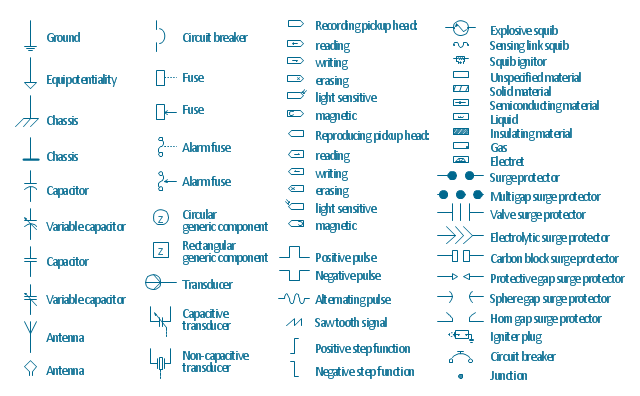
The vector stencils library "Electrical circuits" contains 49 element symbols of electrical and electronic devices, including ignitors, starters, transmitters, circuit protectors, transducers, radio and audio equipment.
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics.
"An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Linear electrical networks, a special type consisting only of sources (voltage or current), linear lumped elements (resistors, capacitors, inductors), and linear distributed elements (transmission lines), have the property that signals are linearly superimposable. They are thus more easily analyzed, using powerful frequency domain methods such as Laplace transforms, to determine DC response, AC response, and transient response.
A resistive circuit is a circuit containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive circuits is less complicated than analysis of circuits containing capacitors and inductors. If the sources are constant (DC) sources, the result is a DC circuit.
A network that contains active electronic components is known as an electronic circuit. Such networks are generally nonlinear and require more complex design and analysis tools." [Electrical network. Wikipedia]
The symbils example "Design elements - Electrical circuits" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for drawing electronic circuit diagrams and electrical schematics.
"An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Linear electrical networks, a special type consisting only of sources (voltage or current), linear lumped elements (resistors, capacitors, inductors), and linear distributed elements (transmission lines), have the property that signals are linearly superimposable. They are thus more easily analyzed, using powerful frequency domain methods such as Laplace transforms, to determine DC response, AC response, and transient response.
A resistive circuit is a circuit containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive circuits is less complicated than analysis of circuits containing capacitors and inductors. If the sources are constant (DC) sources, the result is a DC circuit.
A network that contains active electronic components is known as an electronic circuit. Such networks are generally nonlinear and require more complex design and analysis tools." [Electrical network. Wikipedia]
The symbils example "Design elements - Electrical circuits" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
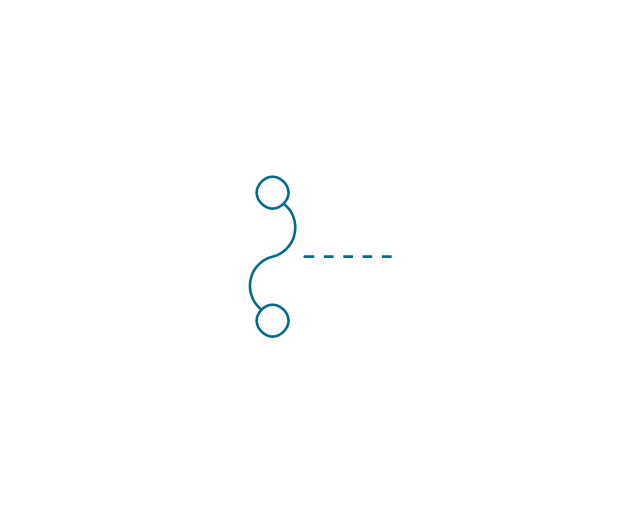
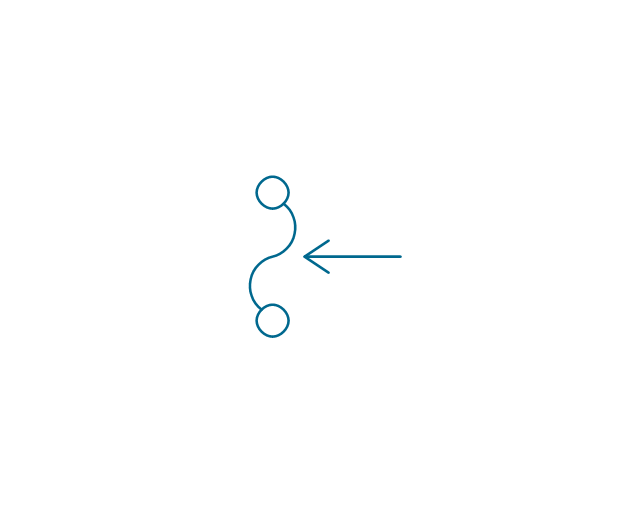
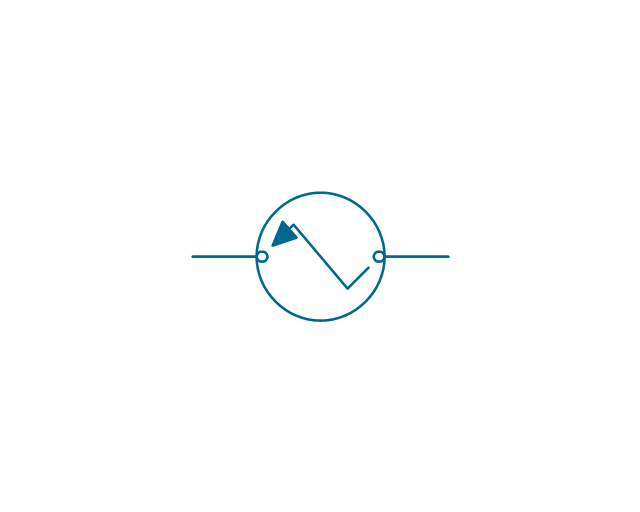
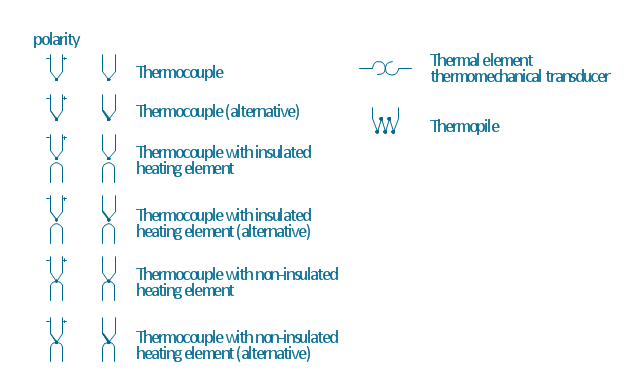
The vector stencils library "Thermo" contains 14 symbols of thermoelectric elements: thermal element, thermocouples with and without heating elements, thermoplile.
Use it for drawing electrical layouts, electronic schematics, and circuit diagrams.
"The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa. A thermoelectric device creates voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, it creates a temperature difference. At the atomic scale, an applied temperature gradient causes charge carriers in the material to diffuse from the hot side to the cold side.
This effect can be used to generate electricity, measure temperature or change the temperature of objects. Because the direction of heating and cooling is determined by the polarity of the applied voltage, thermoelectric devices can be used as temperature controllers.
The term "thermoelectric effect" encompasses three separately identified effects: the Seebeck effect, Peltier effect, and Thomson effect. Textbooks may refer to it as the Peltier–Seebeck effect. ...
Thermocouples and thermopiles are devices that use the Seebeck effect to measure the temperature difference between two objects, one connected to a voltmeter and the other to the probe. The temperature of the voltmeter, and hence that of the material being measured by the probe, can be measured separately using cold junction compensation techniques." [Thermoelectric effect. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Thermo" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for drawing electrical layouts, electronic schematics, and circuit diagrams.
"The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa. A thermoelectric device creates voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, it creates a temperature difference. At the atomic scale, an applied temperature gradient causes charge carriers in the material to diffuse from the hot side to the cold side.
This effect can be used to generate electricity, measure temperature or change the temperature of objects. Because the direction of heating and cooling is determined by the polarity of the applied voltage, thermoelectric devices can be used as temperature controllers.
The term "thermoelectric effect" encompasses three separately identified effects: the Seebeck effect, Peltier effect, and Thomson effect. Textbooks may refer to it as the Peltier–Seebeck effect. ...
Thermocouples and thermopiles are devices that use the Seebeck effect to measure the temperature difference between two objects, one connected to a voltmeter and the other to the probe. The temperature of the voltmeter, and hence that of the material being measured by the probe, can be measured separately using cold junction compensation techniques." [Thermoelectric effect. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Thermo" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
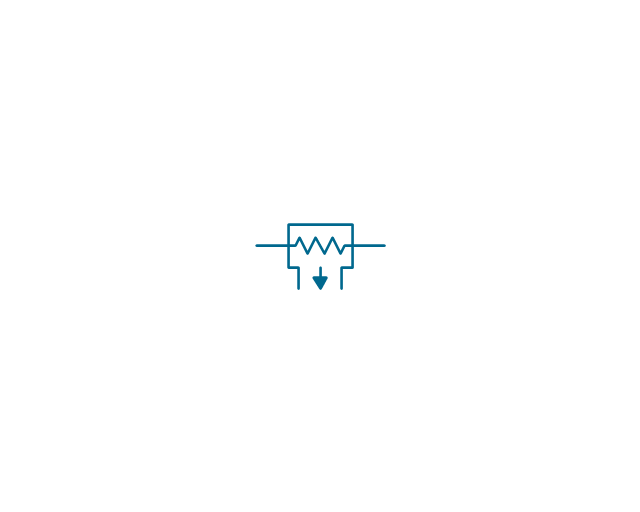
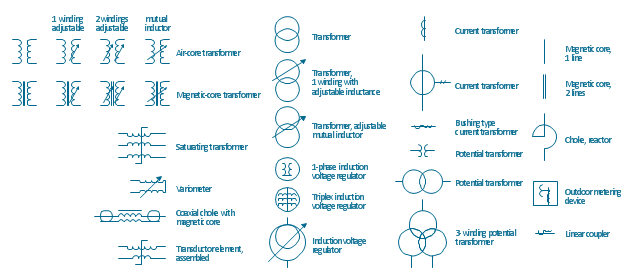
The vector stencils library "Transformers and windings" contains 29 element symbols of transformers, windings, couplers, metering devices, transductors, magnetic cores, chokes, and a variometer.
Use it to design the electromechanical device schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers may be used in step-up or step-down voltage conversion, which 'transforms' an AC voltage from one voltage level on the input of the device to another level at the output terminals. This special function of transformers can provide control of specified requirements of current level as an alternating current source, or it may be used for impedance matching between mismatched electrical circuits to effect maximum power transfer between the circuits.
A transformer most commonly consists of two windings of wire that are wound around a common core to induce tight electromagnetic coupling between the windings. The core material is often a laminated iron core. The coil that receives the electrical input energy is referred to as the primary winding, while the output coil is called the secondary winding.
An alternating electric current flowing through the primary winding (coil) of a transformer generates an electromagnetic field in its surroundings and a varying magnetic flux in the core of the transformer. By electromagnetic induction this magnetic flux generates a varying electromotive force in the secondary winding, resulting in a voltage across the output terminals. If a load impedance is connected across the secondary winding, a current flows through the secondary winding drawing power from the primary winding and its power source." [Transformer. Wikipedia]
"An electromagnetic coil (or simply a "coil") is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet. When electricity is passed through a coil, it generates a magnetic field. One loop of wire is usually referred to as a turn or a winding, and a coil consists of one or more turns. For use in an electronic circuit, electrical connection terminals called taps are often connected to a coil. Coils are often coated with varnish or wrapped with insulating tape to provide additional insulation and secure them in place. A completed coil assembly with one or more set of coils and taps is often called the windings.
Windings are used in transformers, electric motors, inductors, solenoids, loudspeakers, and many other applications." [Electromagnetic coil. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transformers and windings" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to design the electromechanical device schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers may be used in step-up or step-down voltage conversion, which 'transforms' an AC voltage from one voltage level on the input of the device to another level at the output terminals. This special function of transformers can provide control of specified requirements of current level as an alternating current source, or it may be used for impedance matching between mismatched electrical circuits to effect maximum power transfer between the circuits.
A transformer most commonly consists of two windings of wire that are wound around a common core to induce tight electromagnetic coupling between the windings. The core material is often a laminated iron core. The coil that receives the electrical input energy is referred to as the primary winding, while the output coil is called the secondary winding.
An alternating electric current flowing through the primary winding (coil) of a transformer generates an electromagnetic field in its surroundings and a varying magnetic flux in the core of the transformer. By electromagnetic induction this magnetic flux generates a varying electromotive force in the secondary winding, resulting in a voltage across the output terminals. If a load impedance is connected across the secondary winding, a current flows through the secondary winding drawing power from the primary winding and its power source." [Transformer. Wikipedia]
"An electromagnetic coil (or simply a "coil") is formed when a conductor is wound around a core or form to create an inductor or electromagnet. When electricity is passed through a coil, it generates a magnetic field. One loop of wire is usually referred to as a turn or a winding, and a coil consists of one or more turns. For use in an electronic circuit, electrical connection terminals called taps are often connected to a coil. Coils are often coated with varnish or wrapped with insulating tape to provide additional insulation and secure them in place. A completed coil assembly with one or more set of coils and taps is often called the windings.
Windings are used in transformers, electric motors, inductors, solenoids, loudspeakers, and many other applications." [Electromagnetic coil. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Transformers and windings" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Semiconductors" contains 22 symbols of rectifiers, diodes, charge transfer and electronic conduction devices, switches, cathodes, transistors, thyristors, and transceivers for semiconductor (SIS) design.
"Semiconductor devices are electronic components that exploit the electronic properties of semiconductor materials, principally silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, as well as organic semiconductors. Semiconductor devices have replaced thermionic devices (vacuum tubes) in most applications. They use electronic conduction in the solid state as opposed to the gaseous state or thermionic emission in a high vacuum.
Semiconductor devices are manufactured both as single discrete devices and as integrated circuits (ICs), which consist of a number - from a few (as low as two) to billions - of devices manufactured and interconnected on a single semiconductor substrate, or wafer. ...
All transistor types can be used as the building blocks of logic gates, which are fundamental in the design of digital circuits. In digital circuits like microprocessors, transistors act as on-off switches; in the MOSFET, for instance, the voltage applied to the gate determines whether the switch is on or off.
Transistors used for analog circuits do not act as on-off switches; rather, they respond to a continuous range of inputs with a continuous range of outputs. Common analog circuits include amplifiers and oscillators.
Circuits that interface or translate between digital circuits and analog circuits are known as mixed-signal circuits.
Power semiconductor devices are discrete devices or integrated circuits intended for high current or high voltage applications. Power integrated circuits combine IC technology with power semiconductor technology, these are sometimes referred to as "smart" power devices. Several companies specialize in manufacturing power semiconductors." [Semiconductor device. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Semiconductors" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Semiconductor devices are electronic components that exploit the electronic properties of semiconductor materials, principally silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, as well as organic semiconductors. Semiconductor devices have replaced thermionic devices (vacuum tubes) in most applications. They use electronic conduction in the solid state as opposed to the gaseous state or thermionic emission in a high vacuum.
Semiconductor devices are manufactured both as single discrete devices and as integrated circuits (ICs), which consist of a number - from a few (as low as two) to billions - of devices manufactured and interconnected on a single semiconductor substrate, or wafer. ...
All transistor types can be used as the building blocks of logic gates, which are fundamental in the design of digital circuits. In digital circuits like microprocessors, transistors act as on-off switches; in the MOSFET, for instance, the voltage applied to the gate determines whether the switch is on or off.
Transistors used for analog circuits do not act as on-off switches; rather, they respond to a continuous range of inputs with a continuous range of outputs. Common analog circuits include amplifiers and oscillators.
Circuits that interface or translate between digital circuits and analog circuits are known as mixed-signal circuits.
Power semiconductor devices are discrete devices or integrated circuits intended for high current or high voltage applications. Power integrated circuits combine IC technology with power semiconductor technology, these are sometimes referred to as "smart" power devices. Several companies specialize in manufacturing power semiconductors." [Semiconductor device. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Semiconductors" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Quality Mind Map
Quality Mind Map
This solution extends ConceptDraw MINDMAP software with Quality Management Mind Maps (Presentations, Meeting Agendas, Problem to be solved).
 Health Food
Health Food
The Health Food solution contains the set of professionally designed samples and large collection of vector graphic libraries of healthy foods symbols of fruits, vegetables, herbs, nuts, beans, seafood, meat, dairy foods, drinks, which give powerful possi
 eLearning for Skype
eLearning for Skype
This solution extends ConceptDraw MINDMAP software with the ability to prepare and run remote learning sessions by using Skype
- Power socket outlet layout | Plant Layout Plans | Electrical and ...
- Electrical Drawing Software | How To use House Electrical Plan ...
- Chemical and Process Engineering | Engineering | Mechanical ...
- How To use House Electrical Plan Software | ConceptDraw Solution ...
- SWOT and TOWS Matrix Diagrams | ConceptDraw Solution Park ...
- Electrical and Telecom Plan Software
- Reflected Ceiling Plans | How to Create a Reflected Ceiling Floor ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Process Flowchart ...
- Classroom lighting - Reflected ceiling plan | Electric and Telecom ...
- Electrical and telecom - Vector stencils library | Design elements ...
- Engineering | Universal Diagramming Area | Design elements ...
- CAD Drawing Software for Making Mechanic Diagram and Electrical ...
- Electrical circuits - Vector stencils library | Security and Access Plans ...
- Mechanical Engineering | ConceptDraw Solution Park | How to ...
- Block Diagram | Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning ...
- How To use House Electrical Plan Software | Plumbing and Piping ...
- How To use House Electrical Plan Software | Network Layout Floor ...
- How To use House Electrical Plan Software | Engineering | How To ...
- Solid geometry - Vector stencils library | Vessels - Vector stencils ...
- Cross-Functional Flowchart | How To use House Electrical Plan ...