This example of bank ATM UML activity diagram was created on the base of UML use case diagram of automated teller machine from the course "Thinking in Java, 2nd edition, Revision 9" by Bruce Eckel published on the website of the Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Department of the University of Maryland, Baltimore (UMBC).
"If you are designing an auto-teller, for example, the use case for a particular aspect of the functionality of the system is able to describe what the auto-teller does in every possible situation. Each of these “situations” is referred to as a scenario, and a use case can be considered a collection of scenarios. You can think of a scenario as a question that starts with: “What does the system do if...?” For example, “What does the auto-teller do if a customer has just deposited a check within the last 24 hours, and there’s not enough in the account without the check having cleared to provide a desired withdrawal?”
Use case diagrams are intentionally simple to prevent you from getting bogged down in system implementation details prematurely...
Each stick person represents an “actor,” which is typically a human or some other kind of free agent. (These can even be other computer systems, as is the case with “ATM.”) The box represents the boundary of your system. The ellipses represent the use cases, which are descriptions of valuable work that can be performed with the system. The lines between the actors and the use cases represent the interactions.
It doesn’t matter how the system is actually implemented, as long as it looks like this to the user."
[csee.umbc.edu/ courses/ 331/ resources/ tij/ text/ TIJ213.gif]
This automated teller machine (ATM) UML use case diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"If you are designing an auto-teller, for example, the use case for a particular aspect of the functionality of the system is able to describe what the auto-teller does in every possible situation. Each of these “situations” is referred to as a scenario, and a use case can be considered a collection of scenarios. You can think of a scenario as a question that starts with: “What does the system do if...?” For example, “What does the auto-teller do if a customer has just deposited a check within the last 24 hours, and there’s not enough in the account without the check having cleared to provide a desired withdrawal?”
Use case diagrams are intentionally simple to prevent you from getting bogged down in system implementation details prematurely...
Each stick person represents an “actor,” which is typically a human or some other kind of free agent. (These can even be other computer systems, as is the case with “ATM.”) The box represents the boundary of your system. The ellipses represent the use cases, which are descriptions of valuable work that can be performed with the system. The lines between the actors and the use cases represent the interactions.
It doesn’t matter how the system is actually implemented, as long as it looks like this to the user."
[csee.umbc.edu/ courses/ 331/ resources/ tij/ text/ TIJ213.gif]
This automated teller machine (ATM) UML use case diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
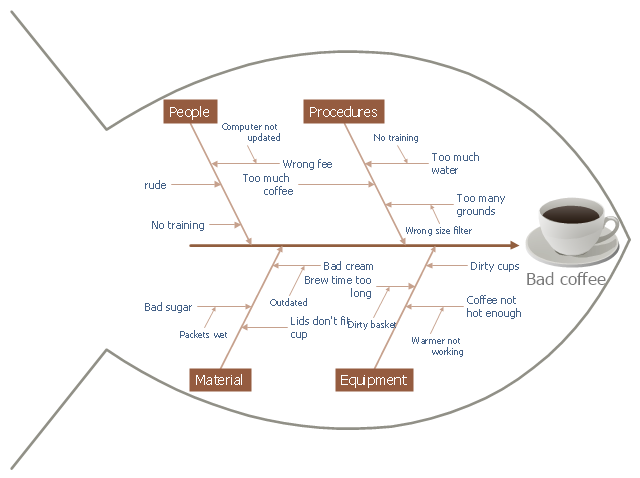
This cause and effect diagram sample was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Fishbone BadCoffeeExample.jpg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Fishbone_ BadCoffeeExample.jpg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
The fishbone diagram example "Bad coffee" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
The fishbone diagram example "Bad coffee" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fishbone Diagrams solution from the Management area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
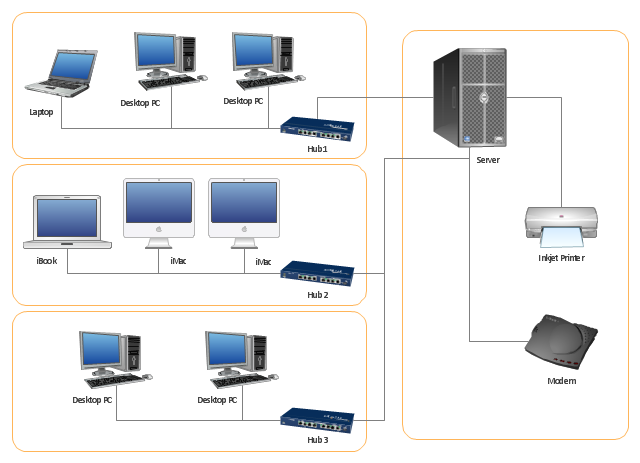
"A computer network or data network is a telecommunications network that allows computers to exchange data. In computer networks, networked computing devices (network nodes) pass data to each other along data connections. The connections (network links) between nodes are established using either cable media or wireless media. The best-known computer network is the Internet.
Network devices that originate, route and terminate the data are called network nodes. Nodes can include hosts such as servers and personal computers, as well as networking hardware. Two devices are said to be networked when a device is able to exchange information with another device." [Computer network. Wikipedia]
This computer communication network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Network devices that originate, route and terminate the data are called network nodes. Nodes can include hosts such as servers and personal computers, as well as networking hardware. Two devices are said to be networked when a device is able to exchange information with another device." [Computer network. Wikipedia]
This computer communication network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Physical topology refers to the placement of the network's various components, including device location and cable installation...
The shape of the cabling layout used to link devices is called the physical topology of the network. This refers to the layout of cabling, the locations of nodes, and the interconnections between the nodes and the cabling. The physical topology of a network is determined by the capabilities of the network access devices and media, the level of control or fault tolerance desired, and the cost associated with cabling or telecommunications circuits." [Network topology. Wikipedia]
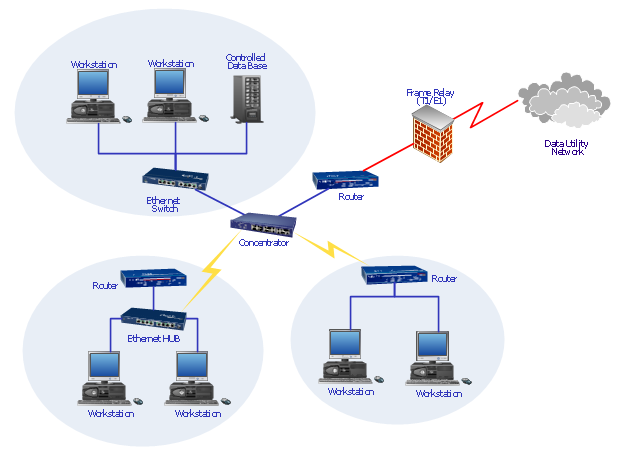
This physical LAN diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The shape of the cabling layout used to link devices is called the physical topology of the network. This refers to the layout of cabling, the locations of nodes, and the interconnections between the nodes and the cabling. The physical topology of a network is determined by the capabilities of the network access devices and media, the level of control or fault tolerance desired, and the cost associated with cabling or telecommunications circuits." [Network topology. Wikipedia]
This physical LAN diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Used Solutions
"There are two definitions for wireless LAN roaming:
Internal Roaming (1): The Mobile Station (MS) moves from one access point (AP) to another AP within a home network because the signal strength is too weak. An authentication server (RADIUS) performs the re-authentication of MS via 802.1x (e.g. with PEAP). The billing of QoS is in the home network. A Mobile Station roaming from one access point to another often interrupts the flow of data among the Mobile Station and an application connected to the network. The Mobile Station, for instance, periodically monitors the presence of alternative access points (ones that will provide a better connection). At some point, based on proprietary mechanisms, the Mobile Station decides to re-associate with an access point having a stronger wireless signal. The Mobile Station, however, may lose a connection with an access point before associating with another access point. In order to provide reliable connections with applications, the Mobile Station must generally include software that provides session persistence.
External Roaming (2): The MS (client) moves into a WLAN of another Wireless Internet Service Provider (WISP) and takes their services (Hotspot). The user can independently of his home network use another foreign network, if this is open for visitors. There must be special authentication and billing systems for mobile services in a foreign network." [Wireless LAN. Wikipedia]
This Cisco roaming wireless local area network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Internal Roaming (1): The Mobile Station (MS) moves from one access point (AP) to another AP within a home network because the signal strength is too weak. An authentication server (RADIUS) performs the re-authentication of MS via 802.1x (e.g. with PEAP). The billing of QoS is in the home network. A Mobile Station roaming from one access point to another often interrupts the flow of data among the Mobile Station and an application connected to the network. The Mobile Station, for instance, periodically monitors the presence of alternative access points (ones that will provide a better connection). At some point, based on proprietary mechanisms, the Mobile Station decides to re-associate with an access point having a stronger wireless signal. The Mobile Station, however, may lose a connection with an access point before associating with another access point. In order to provide reliable connections with applications, the Mobile Station must generally include software that provides session persistence.
External Roaming (2): The MS (client) moves into a WLAN of another Wireless Internet Service Provider (WISP) and takes their services (Hotspot). The user can independently of his home network use another foreign network, if this is open for visitors. There must be special authentication and billing systems for mobile services in a foreign network." [Wireless LAN. Wikipedia]
This Cisco roaming wireless local area network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Used Solutions
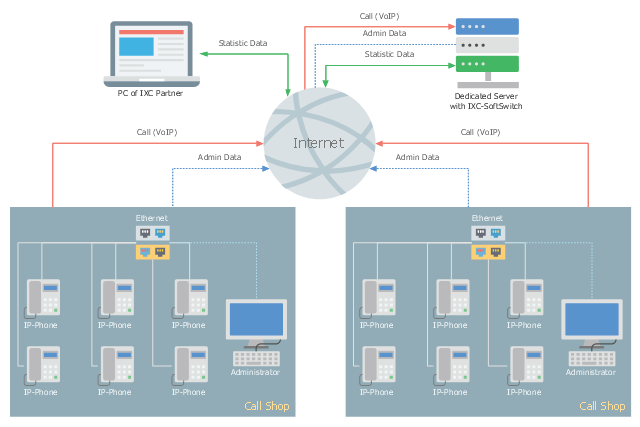
This telecom diagram sample illustrates the call shop solution. It was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Call shops.jpg.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Call_ shops.jpg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"A call shop is a business providing on-site access to telephones for long-distance calling in countries without widespread home long-distance service. Calls may be prepaid or postpaid." [Call shop. Wikipedia]
The telecommunication diagram example "Call shop solution" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computers and Communications solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Call_ shops.jpg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"A call shop is a business providing on-site access to telephones for long-distance calling in countries without widespread home long-distance service. Calls may be prepaid or postpaid." [Call shop. Wikipedia]
The telecommunication diagram example "Call shop solution" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computers and Communications solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Fault-tolerant computer systems are systems designed around the concepts of fault tolerance. In essence, they have to be able to keep working to a level of satisfaction in the presence of faults. ...
Most fault-tolerant computer systems are designed to be able to handle several possible failures, including hardware-related faults such as hard disk failures, input or output device failures, or other temporary or permanent failures; software bugs and errors; interface errors between the hardware and software, including driver failures; operator errors, such as erroneous keystrokes, bad command sequences, or installing unexpected software; and physical damage or other flaws introduced to the system from an outside source." [Fault-tolerant computer system. Wikipedia]
The computer network diagram example "Cisco LAN fault-tolerance system" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Most fault-tolerant computer systems are designed to be able to handle several possible failures, including hardware-related faults such as hard disk failures, input or output device failures, or other temporary or permanent failures; software bugs and errors; interface errors between the hardware and software, including driver failures; operator errors, such as erroneous keystrokes, bad command sequences, or installing unexpected software; and physical damage or other flaws introduced to the system from an outside source." [Fault-tolerant computer system. Wikipedia]
The computer network diagram example "Cisco LAN fault-tolerance system" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Used Solutions
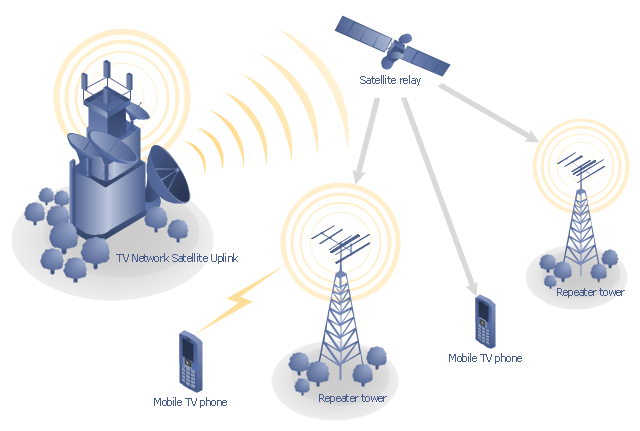
"Satellite television is television programming delivered by the means of communications satellite and received by an outdoor antenna, usually a parabolic reflector generally referred to as a satellite dish, and as far as household usage is concerned, a satellite receiver either in the form of an external set-top box or a satellite tuner module built into a TV set. Satellite TV tuners are also available as a card or a USB peripheral to be attached to a personal computer. In many areas of the world satellite television provides a wide range of channels and services, often to areas that are not serviced by terrestrial or cable providers.
Direct-broadcast satellite television comes to the general public in two distinct flavors - analog and digital. This necessitates either having an analog satellite receiver or a digital satellite receiver. Analog satellite television is being replaced by digital satellite television and the latter is becoming available in a better quality known as high-definition television." [Satellite television. Wikipedia]
"Mobile television is television watched on a small handheld or mobile device. It includes pay TV service delivered via mobile phone networks or received free-to-air via terrestrial television stations. Regular broadcast standards or special mobile TV transmission formats can be used. Additional features include downloading TV programs and podcasts from the internet and the ability to store programming for later viewing. ...
Mobile TV is among the features provided by many 3G phones." [Mobile television. Wikipedia]
"MobiTV, Inc. ... is a provider of end-to-end mobile media solutions. In 2011, the cloud-based MobiTV converged media platform delivered 1.6 billion minutes of live TV, video-on-demand and downloaded content for offline viewing to all tier-one wireless carriers and major mobile operating systems in the United States. ...
MobiTV furnishes programming from more than 40 television channels, offering live news and sports and a variety of full-episode on-demand shows for streaming or download on mobile devices, tablets, personal computers and other Internet-enabled consumer electronics.
MobiTV-powered TV services, which carry the operator’s brand, are accessible on hundreds of devices across multiple wireless carrier partners. ...
MobiTV’s converged media platform is an end-to-end managed service comprising components that work together to securely manage, deliver and play back video across devices both inside and outside the home." [MobiTV. Wikipedia]
This mobile satellite TV network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Direct-broadcast satellite television comes to the general public in two distinct flavors - analog and digital. This necessitates either having an analog satellite receiver or a digital satellite receiver. Analog satellite television is being replaced by digital satellite television and the latter is becoming available in a better quality known as high-definition television." [Satellite television. Wikipedia]
"Mobile television is television watched on a small handheld or mobile device. It includes pay TV service delivered via mobile phone networks or received free-to-air via terrestrial television stations. Regular broadcast standards or special mobile TV transmission formats can be used. Additional features include downloading TV programs and podcasts from the internet and the ability to store programming for later viewing. ...
Mobile TV is among the features provided by many 3G phones." [Mobile television. Wikipedia]
"MobiTV, Inc. ... is a provider of end-to-end mobile media solutions. In 2011, the cloud-based MobiTV converged media platform delivered 1.6 billion minutes of live TV, video-on-demand and downloaded content for offline viewing to all tier-one wireless carriers and major mobile operating systems in the United States. ...
MobiTV furnishes programming from more than 40 television channels, offering live news and sports and a variety of full-episode on-demand shows for streaming or download on mobile devices, tablets, personal computers and other Internet-enabled consumer electronics.
MobiTV-powered TV services, which carry the operator’s brand, are accessible on hundreds of devices across multiple wireless carrier partners. ...
MobiTV’s converged media platform is an end-to-end managed service comprising components that work together to securely manage, deliver and play back video across devices both inside and outside the home." [MobiTV. Wikipedia]
This mobile satellite TV network diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Telecommunication Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
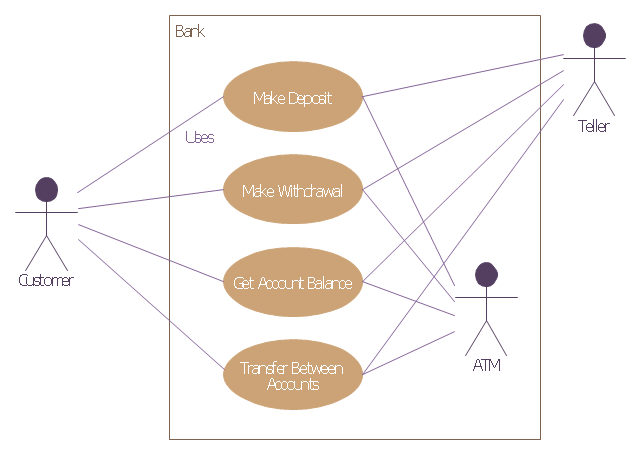
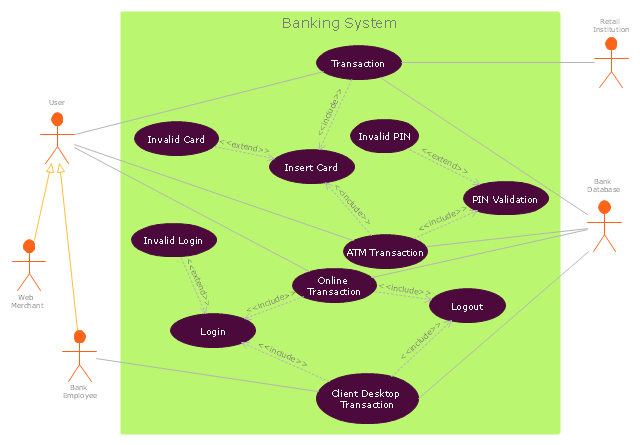
"Banks offer many different channels to access their banking and other services:
(1) Automated Teller Machines.
(2) A branch is a retail location.
(3) Call center.
(4) Mail: most banks accept cheque deposits via mail and use mail to communicate to their customers, e.g. by sending out statements.
(5) Mobile banking is a method of using one's mobile phone to conduct banking transactions.
(6) Online banking is a term used for performing multiple transactions, payments etc. over the Internet.
(7) Relationship Managers, mostly for private banking or business banking, often visiting customers at their homes or businesses.
(8) Telephone banking is a service which allows its customers to conduct transactions over the telephone with automated attendant or when requested with telephone operator.
(9) Video banking is a term used for performing banking transactions or professional banking consultations via a remote video and audio connection. Video banking can be performed via purpose built banking transaction machines (similar to an Automated teller machine), or via a video conference enabled bank branch clarification.
(10) DSA is a Direct Selling Agent, who works for the bank based on a contract. Its main job is to increase the customer base for the bank." [Bank. Wikipedia]
The UML use case diagram example "Banking system" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
(1) Automated Teller Machines.
(2) A branch is a retail location.
(3) Call center.
(4) Mail: most banks accept cheque deposits via mail and use mail to communicate to their customers, e.g. by sending out statements.
(5) Mobile banking is a method of using one's mobile phone to conduct banking transactions.
(6) Online banking is a term used for performing multiple transactions, payments etc. over the Internet.
(7) Relationship Managers, mostly for private banking or business banking, often visiting customers at their homes or businesses.
(8) Telephone banking is a service which allows its customers to conduct transactions over the telephone with automated attendant or when requested with telephone operator.
(9) Video banking is a term used for performing banking transactions or professional banking consultations via a remote video and audio connection. Video banking can be performed via purpose built banking transaction machines (similar to an Automated teller machine), or via a video conference enabled bank branch clarification.
(10) DSA is a Direct Selling Agent, who works for the bank based on a contract. Its main job is to increase the customer base for the bank." [Bank. Wikipedia]
The UML use case diagram example "Banking system" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
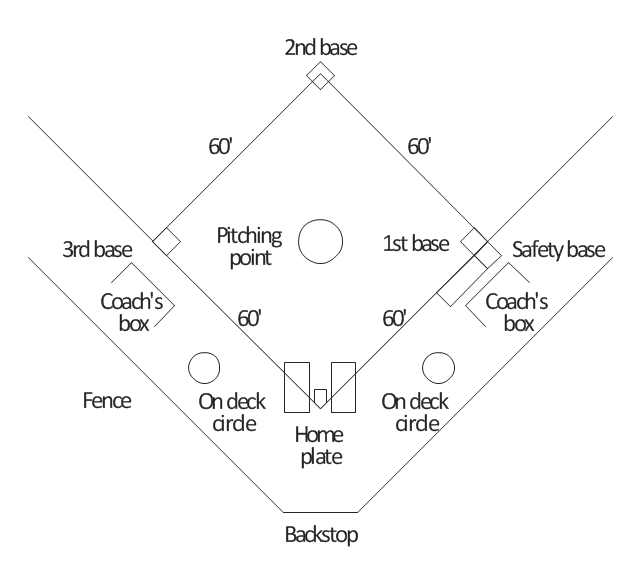
"A baseball field, also called a ball field or a baseball diamond, is the field upon which the game of baseball is played. The term is also used as a metonym for baseball park. ...
The starting point for much of the action on the field is home plate, which is a five-sided slab of whitened rubber, 17-inches square with two of the corners removed so that one edge is 17 inches long, two adjacent sides are 8½ inches and the remaining two sides are 12 inches and set at an angle to make a point. Adjacent to each of the two parallel 8½-inch sides is a batter's box. The point of home plate where the two 12-inch sides meet at right angles, is at one corner of a ninety-foot square. The other three corners of the square, in counterclockwise order from home plate, are called first base, second base, and third base. Three canvas bags fifteen inches (38 cm) square mark the three bases. These three bags along with home plate form the four bases at the corners of the infield." [Baseball field. Wikipedia]
The diagram example "Simple baseball field" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Baseball solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The starting point for much of the action on the field is home plate, which is a five-sided slab of whitened rubber, 17-inches square with two of the corners removed so that one edge is 17 inches long, two adjacent sides are 8½ inches and the remaining two sides are 12 inches and set at an angle to make a point. Adjacent to each of the two parallel 8½-inch sides is a batter's box. The point of home plate where the two 12-inch sides meet at right angles, is at one corner of a ninety-foot square. The other three corners of the square, in counterclockwise order from home plate, are called first base, second base, and third base. Three canvas bags fifteen inches (38 cm) square mark the three bases. These three bags along with home plate form the four bases at the corners of the infield." [Baseball field. Wikipedia]
The diagram example "Simple baseball field" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Baseball solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In the sport of association football, each of the eleven players on a team is assigned to a particular position on the field of play. A team is made up of one goalkeeper and ten outfield players who fill various defensive, midfield and attacking positions depending on the formation deployed. These positions describe both the player's main role and their area of operation on the pitch. ...
Goalkeeper is the most defensive position in football. The goalkeeper's main job is to stop the other team from scoring by catching, palming or punching the ball from shots, headers and crosses. ...
Defenders play behind the midfielders and their primary responsibility is to provide support to the team and to prevent the opposition from scoring a goal. They usually remain in the half of the field that contains the goal they are defending. Taller defenders will move forward to the opposing team's penalty box when their team takes corner kicks or free kicks, where scoring with one's head is a possibility. ...
Midfielders (originally called half-backs) are players whose position of play is midway between the attacking forwards and the defenders. Their main duties are to maintain possession of the ball, taking the ball from defenders and feeding it to the strikers, as well as dispossessing opposing players. ...
Forwards (or strikers) are the players who are positioned nearest to the opposing team's goal. The primary responsibility of forwards is to score goals and to create scoring chances for other players." [Association football positions. Wikipedia]
The diagram example "Association football (soccer) positions" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Football solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ sport-soccer
Goalkeeper is the most defensive position in football. The goalkeeper's main job is to stop the other team from scoring by catching, palming or punching the ball from shots, headers and crosses. ...
Defenders play behind the midfielders and their primary responsibility is to provide support to the team and to prevent the opposition from scoring a goal. They usually remain in the half of the field that contains the goal they are defending. Taller defenders will move forward to the opposing team's penalty box when their team takes corner kicks or free kicks, where scoring with one's head is a possibility. ...
Midfielders (originally called half-backs) are players whose position of play is midway between the attacking forwards and the defenders. Their main duties are to maintain possession of the ball, taking the ball from defenders and feeding it to the strikers, as well as dispossessing opposing players. ...
Forwards (or strikers) are the players who are positioned nearest to the opposing team's goal. The primary responsibility of forwards is to score goals and to create scoring chances for other players." [Association football positions. Wikipedia]
The diagram example "Association football (soccer) positions" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Football solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ sport-soccer
"In association football, the formation describes how the players in a team are positioned on the pitch. Different formations can be used depending on whether a team wishes to play more attacking or defensive football. ...
4–4–2.
This formation was the most common in football in the 1990s and early 2000s, so well known that it has even inspired a magazine title, FourFourTwo. The midfielders are required to work hard to support both the defence and the attack: typically one of the central midfielders is expected to go upfield as often as possible to support the forward pair, while the other will play a "holding role", shielding the defence; the two wide midfield players must move up the flanks to the goal line in attacks and yet also protect the fullback wide defenders." [Formation (association football). Wikipedia]
The diagram example "Association football (soccer) formation 4-4-2" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Football solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ sport-soccer
4–4–2.
This formation was the most common in football in the 1990s and early 2000s, so well known that it has even inspired a magazine title, FourFourTwo. The midfielders are required to work hard to support both the defence and the attack: typically one of the central midfielders is expected to go upfield as often as possible to support the forward pair, while the other will play a "holding role", shielding the defence; the two wide midfield players must move up the flanks to the goal line in attacks and yet also protect the fullback wide defenders." [Formation (association football). Wikipedia]
The diagram example "Association football (soccer) formation 4-4-2" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Football solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ sport-soccer
The vector stencils library "American football positions" contains 38 symbols for drawing diagrams of American football positions.
"In American football, each team has eleven players on the field at one time. The specific role that a player takes on the field is called their position. Under the modern rules of American football, teams are allowed unlimited substitutions, that is teams may change any number of players after any play. This has resulted in the development of three "platoons" of players, the offense (the team with the ball, who is trying to score), the defense (the team trying to prevent the other team from scoring, and to take the ball from them), and the special teams (who play in kicking situations). Within those platoons, various specific positions exist depending on what the player's main job is." [American football positions. Wikipedia]
The symbols example "Design elements - Football positions (for perspective view)" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Football solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In American football, each team has eleven players on the field at one time. The specific role that a player takes on the field is called their position. Under the modern rules of American football, teams are allowed unlimited substitutions, that is teams may change any number of players after any play. This has resulted in the development of three "platoons" of players, the offense (the team with the ball, who is trying to score), the defense (the team trying to prevent the other team from scoring, and to take the ball from them), and the special teams (who play in kicking situations). Within those platoons, various specific positions exist depending on what the player's main job is." [American football positions. Wikipedia]
The symbols example "Design elements - Football positions (for perspective view)" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Football solution from the Sport area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Computers and network isometric" contains 56 3D clipart images of computer and network devices and equipment for drawing network diagrams.
The clip art example "Computers and network isometric - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The clip art example "Computers and network isometric - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This pitch plan sample was designed on the base of the Wikipedia file: Comparison sport playing areas.svg.
[en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Comparison_ sport_ playing_ areas.svg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"A pitch is an outdoor playing area for various sports. The term is used in British and Australian English; the comparable term in American English is playing field. In most sports, the official technical term is field of play, although this is not regularly used by those outside of refereeing/ umpiring circles.
In the sport of cricket, the cricket pitch refers not to the entire field of play, but to the section of the field on which batting and bowling take place in the centre of the field. The pitch is prepared differently to the rest of the field, to provide a harder surface for bowling.
A pitch is often a regulation space, as in an association football pitch." [Pitch (sports field). Wikipedia]
The pitch plan example "Sport fields comparison" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Sport Field Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Comparison_ sport_ playing_ areas.svg]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"A pitch is an outdoor playing area for various sports. The term is used in British and Australian English; the comparable term in American English is playing field. In most sports, the official technical term is field of play, although this is not regularly used by those outside of refereeing/ umpiring circles.
In the sport of cricket, the cricket pitch refers not to the entire field of play, but to the section of the field on which batting and bowling take place in the centre of the field. The pitch is prepared differently to the rest of the field, to provide a harder surface for bowling.
A pitch is often a regulation space, as in an association football pitch." [Pitch (sports field). Wikipedia]
The pitch plan example "Sport fields comparison" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Sport Field Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Sport fields and recreation" contains 25 shapes for drawing sport fields and recreation plans.
"A pitch is an outdoor playing area for various sports. The term is used in British and Australian English; the comparable term in American English is playing field. In most sports, the official technical term is field of play, although this is not regularly used by those outside of refereeing/ umpiring circles.
In the sport of cricket, the cricket pitch refers not to the entire field of play, but to the section of the field on which batting and bowling take place in the centre of the field. The pitch is prepared differently to the rest of the field, to provide a harder surface for bowling.
A pitch is often a regulation space, as in an association football pitch." [Pitch (sports field). Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Sport fields and recreation" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Sport Field Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A pitch is an outdoor playing area for various sports. The term is used in British and Australian English; the comparable term in American English is playing field. In most sports, the official technical term is field of play, although this is not regularly used by those outside of refereeing/ umpiring circles.
In the sport of cricket, the cricket pitch refers not to the entire field of play, but to the section of the field on which batting and bowling take place in the centre of the field. The pitch is prepared differently to the rest of the field, to provide a harder surface for bowling.
A pitch is often a regulation space, as in an association football pitch." [Pitch (sports field). Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Sport fields and recreation" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Sport Field Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- UML Class Diagram Generalization Example UML Diagrams | UML ...
- Plant Layout Plans | Pollution Example Of Fishbone Diagran
- Pyramid Diagram and Pyramid Chart | Marketing Flow Chart ...
- Network Diagram Examples | Network Diagram Software Logical ...
- Example Of Residential Building Bubble Diagram
- UML activity diagram (swimlanes) - Template | Cross-Functional ...
- UML Class Diagram Example - Buildings and Rooms | Data Flow ...
- Roaming wireless local area network diagram | Network Diagram ...
- Flow chart Example . Warehouse Flowchart | What Is Information ...
- Example of DFD for Online Store (Data Flow Diagram ) | Data Flow ...
- Entity Relationship Diagram Software | Drawing ER diagrams on a ...
- Applications | Sentence Diagrammer | Design elements - Sport fields ...
- Fishbone Diagram | HVAC Plans | Basic Pie Charts | Using ...
- ERD Symbols and Meanings | Entity Relationship Diagram Symbols ...
- Diagram of a Wireless Network | Wireless Network Diagram ...
- UML Use Case Diagram Example - Taxi Service | Taxi Service Data ...
- Flow chart Example . Warehouse Flowchart | Dfd On Inventory ...
- | Flow Chart Diagran
- Fishbone Diagram | Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) | Software ...


-positions-diagram-association-football-(soccer)-positions.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-formation-diagram-association-football-(soccer)-formation-4-4-2.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)