In biochemistry, metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. In each pathway, a principal chemical is modified by a series of chemical reactions. Enzymes catalyze these reactions, and often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors in order to function properly. Because of the many chemicals (a.k.a. "metabolites") that may be involved, metabolic pathways can be quite elaborate. In addition, numerous distinct pathways co-exist within a cell. This collection of pathways is called the metabolic network. Pathways are important to the maintenance of homeostasis within an organism. Catabolic (break-down) and Anabolic (synthesis) pathways often work interdependently to create new biomolecules as the final end-products. [Metabolic pathway. Wikipedia]
This metabolic pathway map example was created using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Biology solution from Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
https:/ / www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-biology
This metabolic pathway map example was created using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Biology solution from Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
https:/ / www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-biology
- Citric acid cycle ( TCA cycle ) | Biochemical metabolic pathway map ...
- Biology | Bio Flowchart Lite | Glucose catabolism pathways map |
- Biochemical metabolic pathway map diagram ... - Conceptdraw.com
- Citric acid cycle ( TCA cycle ) |
- Physics | Language Learning | Astronomy |
- Drawing Illustration | Drawing a Nature Scene | Water Cycle |
- Drawing a Nature Scene | Drawing Illustration | Water Cycle |
- Physics | Biology | Language Learning |
- Business Diagram Software | Physics | ConceptDraw Arrows10 ...
- Conventional energy resources | Resources and energy vector ...
- Mathematics | Astronomy | Science and Education Area |
- Chemistry | Design elements - Chemical elements | Carbonyl ...
- Water cycle diagram | Drawing a Nature Scene | Drawing Illustration |
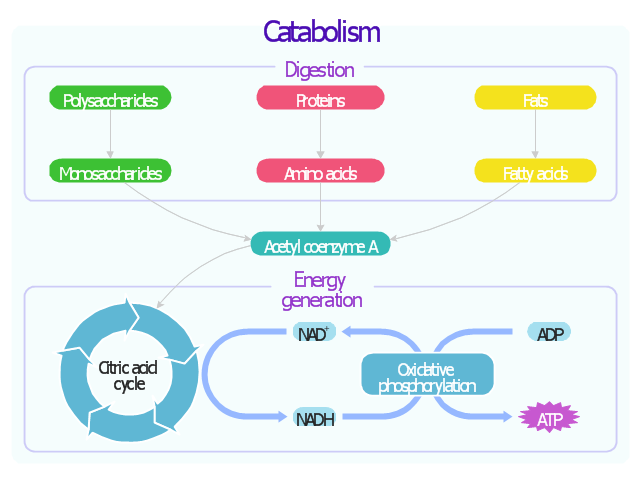
- Catabolism schematic | Glucose catabolism pathways map ...
- Biochemical pathway map - Key metabolic processes | Design ...
- Chemical and Process Engineering | Engineering | Process flow ...
- Design elements - Chemical drawings | Chemistry | Engineering |
- Biochemical pathway map - Key metabolic processes | Catabolism
- Biochemical pathway map - Key metabolic processes | Glucose ...
- Biochemical pathway map - Key metabolic processes | Glucose ...