This PFD of jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating was redrawn from Wikipedia file: ConvLPGMerox.png. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:ConvKeroMerox.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported icense. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Merox is an acronym for mercaptan oxidation. It is a proprietary catalytic chemical process developed by UOP used in oil refineries and natural gas processing plants to remove mercaptans from LPG, propane, butanes, light naphthas, kerosene and jet fuel by converting them to liquid hydrocarbon disulfides.
The Merox process requires an alkaline environment which, in some of the process versions, is provided by an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a strong base, commonly referred to as caustic. In other versions of the process, the alkalinity is provided by ammonia, which is a weak base.
The catalyst in some versions of the process is a water-soluble liquid. In other versions, the catalyst is impregnated onto charcoal granules.
Processes within oil refineries or natural gas processing plants that remove mercaptans and/ or hydrogen sulfide (H2S) are commonly referred to as sweetening processes because they results in products which no longer have the sour, foul odors of mercaptans and hydrogen sulfide. The liquid hydrocarbon disulfides may remain in the sweetened products, they may be used as part of the refinery or natural gas processing plant fuel, or they may be processed further.
The Merox process is usually more economical than using a catalytic hydrodesulfurization process for much the same purpose." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ Merox]
The process flow diagram (PFD) example "Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported icense. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Merox is an acronym for mercaptan oxidation. It is a proprietary catalytic chemical process developed by UOP used in oil refineries and natural gas processing plants to remove mercaptans from LPG, propane, butanes, light naphthas, kerosene and jet fuel by converting them to liquid hydrocarbon disulfides.
The Merox process requires an alkaline environment which, in some of the process versions, is provided by an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a strong base, commonly referred to as caustic. In other versions of the process, the alkalinity is provided by ammonia, which is a weak base.
The catalyst in some versions of the process is a water-soluble liquid. In other versions, the catalyst is impregnated onto charcoal granules.
Processes within oil refineries or natural gas processing plants that remove mercaptans and/ or hydrogen sulfide (H2S) are commonly referred to as sweetening processes because they results in products which no longer have the sour, foul odors of mercaptans and hydrogen sulfide. The liquid hydrocarbon disulfides may remain in the sweetened products, they may be used as part of the refinery or natural gas processing plant fuel, or they may be processed further.
The Merox process is usually more economical than using a catalytic hydrodesulfurization process for much the same purpose." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ Merox]
The process flow diagram (PFD) example "Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Chemical and Process Engineering
Chemical and Process Engineering
This chemical engineering solution extends ConceptDraw PRO v.9.5 (or later) with process flow diagram symbols, samples, process diagrams templates and libraries of design elements for creating process and instrumentation diagrams, block flow diagrams (BFD
 Biology
Biology
Biology solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with samples, templates and libraries containing biological vector symbols, to help you create scientific and educational designs in the field of biology.
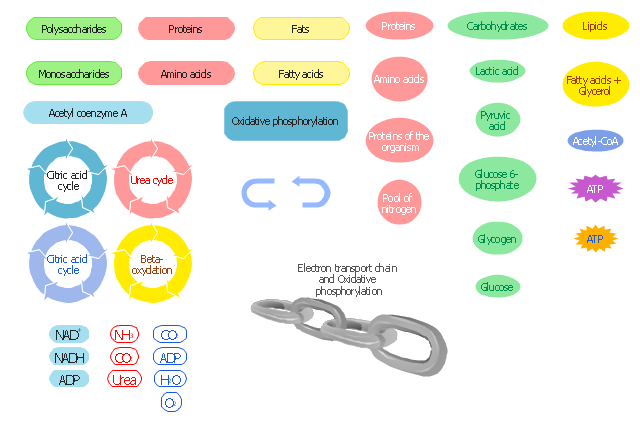
The vector stencils library " Biochemistry of metabolism" contains 46 metabolite symbols for drawing metabolic pathways maps, biochemical diagrams and metabolism process flow charts using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually restricted to small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Alcohol is an example of a primary metabolite produced in large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. ...
The metabolome forms a large network of metabolic reactions, where outputs from one enzymatic chemical reaction are inputs to other chemical reactions." [Metabolite. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Biochemistry of metabolism" is included in the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually restricted to small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Alcohol is an example of a primary metabolite produced in large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. ...
The metabolome forms a large network of metabolic reactions, where outputs from one enzymatic chemical reaction are inputs to other chemical reactions." [Metabolite. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Biochemistry of metabolism" is included in the Biology solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Process flow diagram (PFD) template | Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation ...
- Hydrodesulfurization Flow Chart
- Crude oil distillation unit - PFD | Process flow diagram (PFD ...
- Flow Chart For Centrifugals
- Process Flow Sheet Of Hydrocarbons
- Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery | Amine treating unit ...
- How to Draw a Chemical Process Flow Diagram | Chemical and ...
- Amine treating unit schematic diagram | Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation ...
- Chemical and Process Engineering | Process Flowchart | How to ...
- Process Flowchart | Process Flow app for Mac | Business process ...
- Design elements - Chemical engineering | Universal Diagramming ...
- Flow Chart Symbols | Process Flowchart | Basic Flowchart Symbols ...
- Process Flowchart | Process flow diagram (PFD) template | Business ...
- Centrifuge Process Flow Diagram
- How to Draw a Chemical Process Flow Diagram | Chemical and ...
- Process flow diagram (PFD) template | Crude oil distillation unit ...
- Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery | Crude oil distillation unit ...
- Chemical and Process Engineering | How to Draw a Chemical ...
- Natural gas condensate - PFD | Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating ...
- Replacing engine oil - Opportunity flowchart | Cross-Functional ...
-jet-fuel-mercaptan-oxidation-treating---pfd.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)