This PFD sample was redesigned from the Wikipedia file: NaturalGasCondensate.png.
"This is a schematic flow diagram of a typical facility for separating and recovering liquid condensate from raw natural gas."
[en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:NaturalGasCondensate.png]
"Natural-gas condensate is a low-density mixture of hydrocarbon liquids that are present as gaseous components in the raw natural gas produced from many natural gas fields. It condenses out of the raw gas if the temperature is reduced to below the hydrocarbon dew point temperature of the raw gas.
The natural gas condensate is also referred to as simply condensate, or gas condensate, or sometimes natural gasoline because it contains hydrocarbons within the gasoline boiling range. Raw natural gas may come from any one of three types of gas wells:
(1) Crude oil wells - Raw natural gas that comes from crude oil wells is called associated gas. This gas can exist separate from the crude oil in the underground formation, or dissolved in the crude oil.
(2) Dry gas wells - These wells typically produce only raw natural gas that does not contain any hydrocarbon liquids. Such gas is called non-associated gas.
(3) Condensate wells - These wells produce raw natural gas along with natural gas liquid. Such gas is also non-associated gas and often referred to as wet gas." [Natural-gas condensate. Wikipedia]
The process flow diagram example "Natural gas condensate - PFD" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"This is a schematic flow diagram of a typical facility for separating and recovering liquid condensate from raw natural gas."
[en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:NaturalGasCondensate.png]
"Natural-gas condensate is a low-density mixture of hydrocarbon liquids that are present as gaseous components in the raw natural gas produced from many natural gas fields. It condenses out of the raw gas if the temperature is reduced to below the hydrocarbon dew point temperature of the raw gas.
The natural gas condensate is also referred to as simply condensate, or gas condensate, or sometimes natural gasoline because it contains hydrocarbons within the gasoline boiling range. Raw natural gas may come from any one of three types of gas wells:
(1) Crude oil wells - Raw natural gas that comes from crude oil wells is called associated gas. This gas can exist separate from the crude oil in the underground formation, or dissolved in the crude oil.
(2) Dry gas wells - These wells typically produce only raw natural gas that does not contain any hydrocarbon liquids. Such gas is called non-associated gas.
(3) Condensate wells - These wells produce raw natural gas along with natural gas liquid. Such gas is also non-associated gas and often referred to as wet gas." [Natural-gas condensate. Wikipedia]
The process flow diagram example "Natural gas condensate - PFD" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
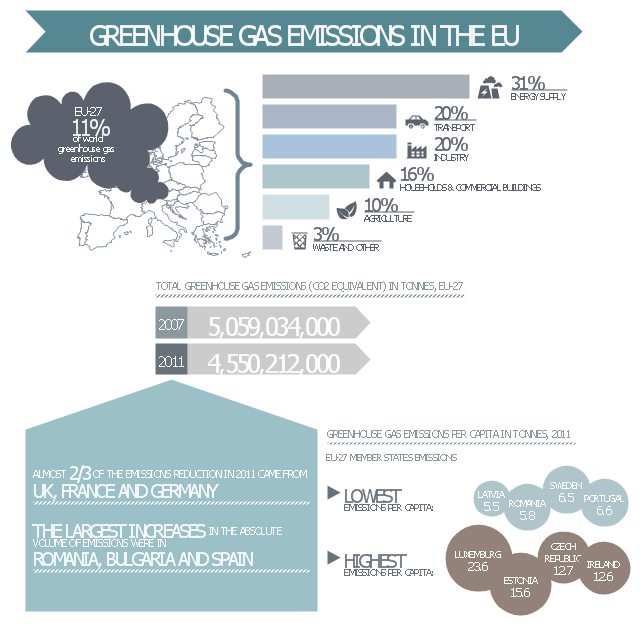
This ecology infographic example was created on the base of the infographics "Greenhouse gas emissions in the EU" from the Debating Europe website. [debatingeurope.eu/ wp-content/ uploads/ 2013/ 06/ TH_ 2_ social.png]
"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. Greenhouse gases greatly affect the temperature of the Earth; without them, Earth's surface would average about 33 °C colder, which is about 59 °F below the present average of 14 °C (57 °F)." [Greenhouse gas. Wikipedia]
The ecology infographic example "EU greenhouse gas emissions" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Management Infographics solition from the area "Business Infographics" in ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. Greenhouse gases greatly affect the temperature of the Earth; without them, Earth's surface would average about 33 °C colder, which is about 59 °F below the present average of 14 °C (57 °F)." [Greenhouse gas. Wikipedia]
The ecology infographic example "EU greenhouse gas emissions" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Management Infographics solition from the area "Business Infographics" in ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Used Solutions
This process flow diagram (PFD) example shows an amine treating system for the removal of gaseous hydrogen sulfide from gas streams. It is used in oil refineries and chemical plants. This PFD sample was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: AmineTreating.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:AmineTreating.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Amine gas treating, also known as gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from gases. It is a common unit process used in refineries, and is also used in petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries.
Processes within oil refineries or chemical processing plants that remove hydrogen sulfide are referred to as "sweetening" processes because the odor of the processed products is improved by the absence of hydrogen sulfide. An alternative to the use of amines involves membrane technology. Membranes are attractive since no reagents are consumed.
Many different amines are used in gas treating:
Diethanolamine (DEA),
Monoethanolamine (MEA),
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA),
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA),
Aminoethoxyethanol (Diglycolamine) (DGA).
The most commonly used amines in industrial plants are the alkanolamines DEA, MEA, and MDEA. These amines are also used in many oil refineries to remove sour gases from liquid hydrocarbons such as liquified petroleum gas (LPG)." [Amine gas treating. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Amine treating unit schematic diagram" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Amine gas treating, also known as gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from gases. It is a common unit process used in refineries, and is also used in petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries.
Processes within oil refineries or chemical processing plants that remove hydrogen sulfide are referred to as "sweetening" processes because the odor of the processed products is improved by the absence of hydrogen sulfide. An alternative to the use of amines involves membrane technology. Membranes are attractive since no reagents are consumed.
Many different amines are used in gas treating:
Diethanolamine (DEA),
Monoethanolamine (MEA),
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA),
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA),
Aminoethoxyethanol (Diglycolamine) (DGA).
The most commonly used amines in industrial plants are the alkanolamines DEA, MEA, and MDEA. These amines are also used in many oil refineries to remove sour gases from liquid hydrocarbons such as liquified petroleum gas (LPG)." [Amine gas treating. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Amine treating unit schematic diagram" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This PFD of jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating was redrawn from Wikipedia file: ConvLPGMerox.png. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:ConvKeroMerox.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported icense. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Merox is an acronym for mercaptan oxidation. It is a proprietary catalytic chemical process developed by UOP used in oil refineries and natural gas processing plants to remove mercaptans from LPG, propane, butanes, light naphthas, kerosene and jet fuel by converting them to liquid hydrocarbon disulfides.
The Merox process requires an alkaline environment which, in some of the process versions, is provided by an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a strong base, commonly referred to as caustic. In other versions of the process, the alkalinity is provided by ammonia, which is a weak base.
The catalyst in some versions of the process is a water-soluble liquid. In other versions, the catalyst is impregnated onto charcoal granules.
Processes within oil refineries or natural gas processing plants that remove mercaptans and/ or hydrogen sulfide (H2S) are commonly referred to as sweetening processes because they results in products which no longer have the sour, foul odors of mercaptans and hydrogen sulfide. The liquid hydrocarbon disulfides may remain in the sweetened products, they may be used as part of the refinery or natural gas processing plant fuel, or they may be processed further.
The Merox process is usually more economical than using a catalytic hydrodesulfurization process for much the same purpose." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ Merox]
The process flow diagram (PFD) example "Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported icense. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Merox is an acronym for mercaptan oxidation. It is a proprietary catalytic chemical process developed by UOP used in oil refineries and natural gas processing plants to remove mercaptans from LPG, propane, butanes, light naphthas, kerosene and jet fuel by converting them to liquid hydrocarbon disulfides.
The Merox process requires an alkaline environment which, in some of the process versions, is provided by an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a strong base, commonly referred to as caustic. In other versions of the process, the alkalinity is provided by ammonia, which is a weak base.
The catalyst in some versions of the process is a water-soluble liquid. In other versions, the catalyst is impregnated onto charcoal granules.
Processes within oil refineries or natural gas processing plants that remove mercaptans and/ or hydrogen sulfide (H2S) are commonly referred to as sweetening processes because they results in products which no longer have the sour, foul odors of mercaptans and hydrogen sulfide. The liquid hydrocarbon disulfides may remain in the sweetened products, they may be used as part of the refinery or natural gas processing plant fuel, or they may be processed further.
The Merox process is usually more economical than using a catalytic hydrodesulfurization process for much the same purpose." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ Merox]
The process flow diagram (PFD) example "Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This is a schematic process flow diagram of the processes used in a typical oil refinery.
This process flow diagram (PFD) example was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: RefineryFlow.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:RefineryFlow.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units. In many ways, oil refineries use much of the technology of, and can be thought of, as types of chemical plants. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot (tank farm) at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.
An oil refinery is considered an essential part of the downstream side of the petroleum industry." [Oil refinery. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This process flow diagram (PFD) example was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: RefineryFlow.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:RefineryFlow.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units. In many ways, oil refineries use much of the technology of, and can be thought of, as types of chemical plants. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot (tank farm) at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.
An oil refinery is considered an essential part of the downstream side of the petroleum industry." [Oil refinery. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
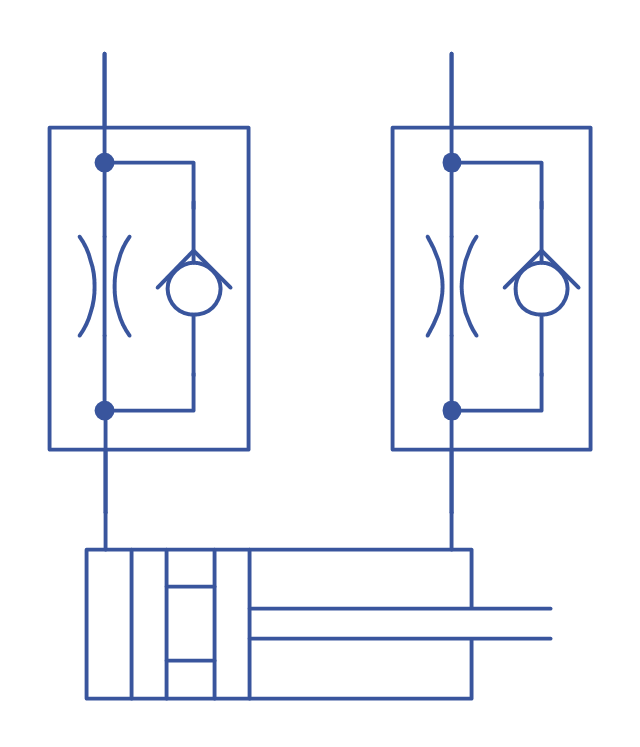
Retract resistor check valve application: pneumatic cylinder, piston driven by Compressed air through 2 Retract resistor check valves.
"A check valve, clack valve, non-return valve or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid (liquid or gas) to flow through it in only one direction.
Check valves are two-port valves, meaning they have two openings in the body, one for fluid to enter and the other for fluid to leave. There are various types of check valves used in a wide variety of applications. Check valves are often part of common household items. Although they are available in a wide range of sizes and costs, check valves generally are very small, simple, or inexpensive. Check valves work automatically and most are not controlled by a person or any external control; accordingly, most do not have any valve handle or stem. The bodies (external shells) of most check valves are made of plastic or metal.
An important concept in check valves is the cracking pressure which is the minimum upstream pressure at which the valve will operate. Typically the check valve is designed for and can therefore be specified for a specific cracking pressure.
Heart valves are essentially inlet and outlet check valves for the heart ventricles, since the ventricles act as pumps." [Check valve. Wikipedia]
This hydraulic schematic example was redrawn using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from the Wikimedia Commons file: Retract resistor check valve application.png.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Retract_ resistor_ check_ valve_ application.png]
The hydraulic engineering drawing example "Retract resistor check valve application" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mechanical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A check valve, clack valve, non-return valve or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid (liquid or gas) to flow through it in only one direction.
Check valves are two-port valves, meaning they have two openings in the body, one for fluid to enter and the other for fluid to leave. There are various types of check valves used in a wide variety of applications. Check valves are often part of common household items. Although they are available in a wide range of sizes and costs, check valves generally are very small, simple, or inexpensive. Check valves work automatically and most are not controlled by a person or any external control; accordingly, most do not have any valve handle or stem. The bodies (external shells) of most check valves are made of plastic or metal.
An important concept in check valves is the cracking pressure which is the minimum upstream pressure at which the valve will operate. Typically the check valve is designed for and can therefore be specified for a specific cracking pressure.
Heart valves are essentially inlet and outlet check valves for the heart ventricles, since the ventricles act as pumps." [Check valve. Wikipedia]
This hydraulic schematic example was redrawn using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from the Wikimedia Commons file: Retract resistor check valve application.png.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Retract_ resistor_ check_ valve_ application.png]
The hydraulic engineering drawing example "Retract resistor check valve application" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mechanical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This process flow diagram (PFD) of a typical crude oil distillation unit as used in petroleum crude oil refineries was redrawn from Wikipedia file: Crude Oil Distillation Unit.png. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:Crude_ Oil_ Distillation_ Unit.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units. In many ways, oil refineries use much of the technology of, and can be thought of, as types of chemical plants. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot (tank farm) at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.
An oil refinery is considered an essential part of the midstream side of the petroleum industry." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ Oil_ refinery]
The process flow diagram (PFD) example "Crude oil distillation" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units. In many ways, oil refineries use much of the technology of, and can be thought of, as types of chemical plants. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot (tank farm) at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.
An oil refinery is considered an essential part of the midstream side of the petroleum industry." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ Oil_ refinery]
The process flow diagram (PFD) example "Crude oil distillation" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Resources and energy" contains 19 clipart images for drawing illustrations on resources and energy.
"Natural resources occur naturally within environments that exist relatively undisturbed by humanity, in a natural form. A natural resource is often characterized by amounts of biodiversity and geodiversity existent in various ecosystems.
Natural resources are derived from the environment. Some of them are essential for our survival while most are used for satisfying our wants. Natural resources may be further classified in different ways.
Natural resources are materials and components (something that can be used) that can be found within the environment. Every man-made product is composed of natural resources (at its fundamental level). A natural resource may exist as a separate entity such as fresh water, and air, as well as a living organism such as a fish, or it may exist in an alternate form which must be processed to obtain the resource such as metal ores, oil, and most forms of energy." [Natural resource. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Resources and energy - Vector stencils library" was created in ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software using the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Natural resources occur naturally within environments that exist relatively undisturbed by humanity, in a natural form. A natural resource is often characterized by amounts of biodiversity and geodiversity existent in various ecosystems.
Natural resources are derived from the environment. Some of them are essential for our survival while most are used for satisfying our wants. Natural resources may be further classified in different ways.
Natural resources are materials and components (something that can be used) that can be found within the environment. Every man-made product is composed of natural resources (at its fundamental level). A natural resource may exist as a separate entity such as fresh water, and air, as well as a living organism such as a fish, or it may exist in an alternate form which must be processed to obtain the resource such as metal ores, oil, and most forms of energy." [Natural resource. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Resources and energy - Vector stencils library" was created in ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software using the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Appliances" contains 36 shapes for kitchen appliances, laundry appliances, stoves, cooking appliances, and laundry equipment. Use it for drawing kitchens, laundry rooms, utility rooms, kitchen floor plans, and kitchen design in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Floor Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Resources and energy" contains 19 clipart images for drawing illustrations on resources and energy.
"Natural resources occur naturally within environments that exist relatively undisturbed by humanity, in a natural form. A natural resource is often characterized by amounts of biodiversity and geodiversity existent in various ecosystems.
Natural resources are derived from the environment. Some of them are essential for our survival while most are used for satisfying our wants. Natural resources may be further classified in different ways.
Natural resources are materials and components (something that can be used) that can be found within the environment. Every man-made product is composed of natural resources (at its fundamental level). A natural resource may exist as a separate entity such as fresh water, and air, as well as a living organism such as a fish, or it may exist in an alternate form which must be processed to obtain the resource such as metal ores, oil, and most forms of energy." [Natural resource. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Resources and energy - Vector stencils library" was created in ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software using the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Natural resources occur naturally within environments that exist relatively undisturbed by humanity, in a natural form. A natural resource is often characterized by amounts of biodiversity and geodiversity existent in various ecosystems.
Natural resources are derived from the environment. Some of them are essential for our survival while most are used for satisfying our wants. Natural resources may be further classified in different ways.
Natural resources are materials and components (something that can be used) that can be found within the environment. Every man-made product is composed of natural resources (at its fundamental level). A natural resource may exist as a separate entity such as fresh water, and air, as well as a living organism such as a fish, or it may exist in an alternate form which must be processed to obtain the resource such as metal ores, oil, and most forms of energy." [Natural resource. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Resources and energy - Vector stencils library" was created in ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software using the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Landmarks" contains 69 landmark symbols of buildings, waterways, scale and directional indicators for labeling transportation and directional maps, road and route maps, street and transit maps, locator and tourist maps.
The pictograms example "Landmarks - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Directional Maps solution from the Maps area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The pictograms example "Landmarks - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Directional Maps solution from the Maps area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Fire and emergency planning" contains 52 symbols of firefighting equipment.
Use these shapes for drawing fire and emergency floor plans, equipment layouts, and evacuation schemes in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fire and Emergency Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ building-fire-emergency-plans
Use these shapes for drawing fire and emergency floor plans, equipment layouts, and evacuation schemes in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Fire and Emergency Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ building-fire-emergency-plans
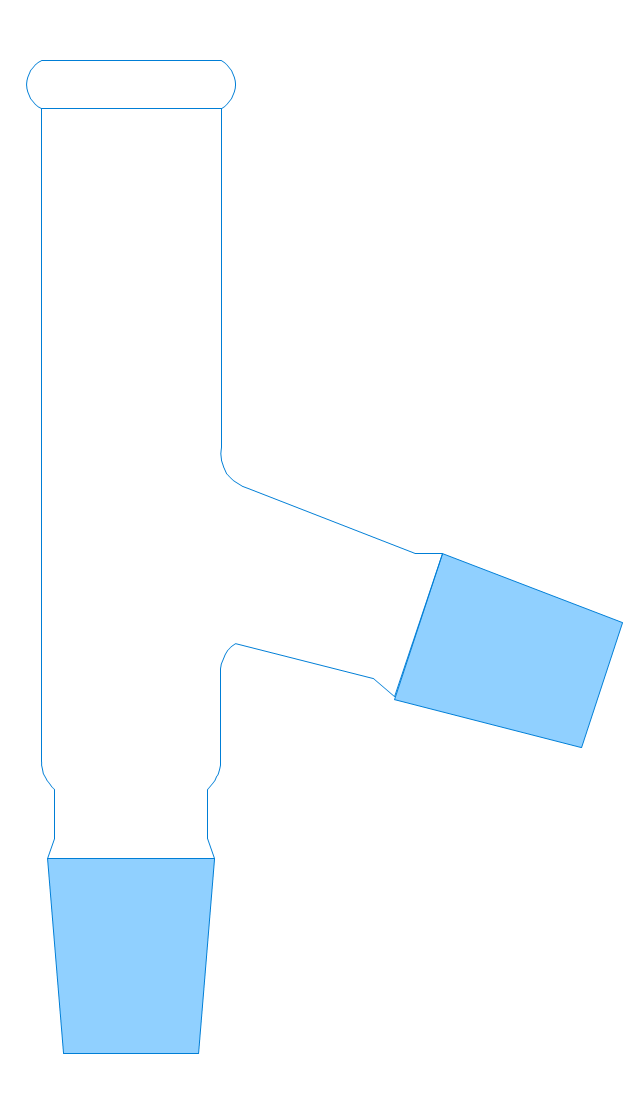
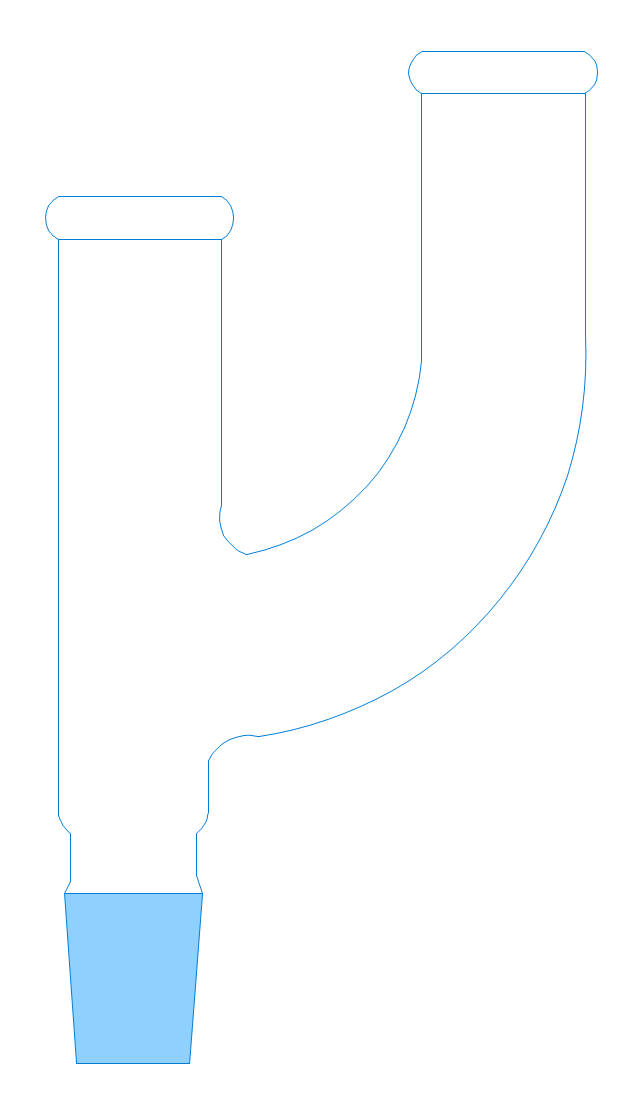
The vector stencils library "Laboratory equipment" contains 31 clipart icons of chemical laboratory equipment and labware.
Use these shapes for drawing part assembly and mounting schemes of glassware apparatus in chemical experiment diagrams and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these shapes for drawing part assembly and mounting schemes of glassware apparatus in chemical experiment diagrams and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Natural Gas Png
- Laboratory equipment - Vector stencils library | Gas Burner Icon Png
- Gas Fields In Png With Diagram
- Crude oil distillation unit - PFD | Process flow diagram (PFD ...
- Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery | Natural gas condensate ...
- Natural gas condensate - PFD | Amine treating unit schematic ...
- EU greenhouse gas emissions - Management infogram | Design ...
- Natural gas condensate - PFD | Process flow diagram - Typical oil ...
- Wind Power Png
- Petroleum Gas In Png
- Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating - PFD | Natural gas condensate ...
- Natural gas condensate - PFD | Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating ...
- Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery | Natural gas condensate ...
- Electric Tower Hd Png
- Process Flow Diagram Symbols | Chemical Engineering | Process ...
- Natural gas condensate - PFD | Bar Diagram Math | Affinity Diagram ...
- EU greenhouse gas emissions - Management infogram | Natural ...
- Electrical Tower Png
- Natural gas condensate - PFD | Chemical and Process Engineering ...
- Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery | Crude oil distillation unit ...
-natural-gas-condensate---pfd.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-amine-treating-unit-schematic-diagram.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-jet-fuel-mercaptan-oxidation-treating---pfd.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-process-flow-diagram---typical-oil-refinery.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-crude-oil-distillation-unit---pfd.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)















-appliances---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-appliances---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-appliances---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)































































































--laboratory-equipment---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-laboratory-equipment---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-laboratory-equipment---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)