Graphic User Interface
Graphic User Interface
Graphic User Interface solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with templates, samples and libraries of vector stencils for design of the GUI prototypes and diagrams for Windows, Mac OS and iOS software.
"Smaller mobile devices such as PDAs and smartphones typically use the WIMP elements with different unifying metaphors, due to constraints in space and available input devices. Applications for which WIMP is not well suited may use newer interaction techniques, collectively named as post-WIMP user interfaces.
As of 2011, some touch-screen-based operating systems such as Apple's iOS (iPhone) and Android use the class of GUIs named post-WIMP. These support styles of interaction using more than one finger in contact with a display, which allows actions such as pinching and rotating, which are unsupported by one pointer and mouse." [Graphical user interface. Wikipedia]
"In computing post-WIMP comprises work on user interfaces, mostly graphical user interfaces, which attempt to go beyond the paradigm of windows, icons, menus and a pointing device, i.e. WIMP interfaces. ...
However WIMP interfaces are not optimal for working with complex tasks such as computer-aided design, working on large amounts of data simultaneously, or interactive games. WIMPs are usually pixel-hungry, so given limited screen real estate they can distract attention from the task at hand. Thus, custom interfaces can better encapsulate workspaces, actions, and objects for specific complex tasks. Applications for which WIMP is not well suited include those requiring continuous input signals, showing 3D models, or simply portraying an interaction for which there is no defined standard widget.
Interfaces based on these considerations, now called "post-WIMP", have made their way to the general public. Examples include the interface of the classic MP3 player iPod and a bank's automated teller machine screen." [Post-WIMP. Wikipedia]
The example "iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - Activity indicator view" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
As of 2011, some touch-screen-based operating systems such as Apple's iOS (iPhone) and Android use the class of GUIs named post-WIMP. These support styles of interaction using more than one finger in contact with a display, which allows actions such as pinching and rotating, which are unsupported by one pointer and mouse." [Graphical user interface. Wikipedia]
"In computing post-WIMP comprises work on user interfaces, mostly graphical user interfaces, which attempt to go beyond the paradigm of windows, icons, menus and a pointing device, i.e. WIMP interfaces. ...
However WIMP interfaces are not optimal for working with complex tasks such as computer-aided design, working on large amounts of data simultaneously, or interactive games. WIMPs are usually pixel-hungry, so given limited screen real estate they can distract attention from the task at hand. Thus, custom interfaces can better encapsulate workspaces, actions, and objects for specific complex tasks. Applications for which WIMP is not well suited include those requiring continuous input signals, showing 3D models, or simply portraying an interaction for which there is no defined standard widget.
Interfaces based on these considerations, now called "post-WIMP", have made their way to the general public. Examples include the interface of the classic MP3 player iPod and a bank's automated teller machine screen." [Post-WIMP. Wikipedia]
The example "iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - Activity indicator view" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Designing the visual composition and temporal behavior of GUI is an important part of software application programming in the area of human-computer interaction. Its goal is to enhance the efficiency and ease of use for the underlying logical design of a stored program, a design discipline known as usability. Methods of user-centered design are used to ensure that the visual language introduced in the design is well tailored to the tasks.
The visible graphical interface features of an application are sometimes referred to as "chrome" or "Gui" (Goo-ee). Typically, the user interacts with information by manipulating visual widgets that allow for interactions appropriate to the kind of data they hold. The widgets of a well-designed interface are selected to support the actions necessary to achieve the goals of the user. A model-view-controller allows for a flexible structure in which the interface is independent from and indirectly linked to application functionality, so the GUI can be easily customized. This allows the user to select or design a different skin at will, and eases the designer's work to change the interface as the user needs evolve. Good user interface design relates to the user, not the system architecture.
Large widgets, such as windows, usually provide a frame or container for the main presentation content such as a web page, email message or drawing. Smaller ones usually act as a user-input tool." [Graphical user interface. Wikipedia]
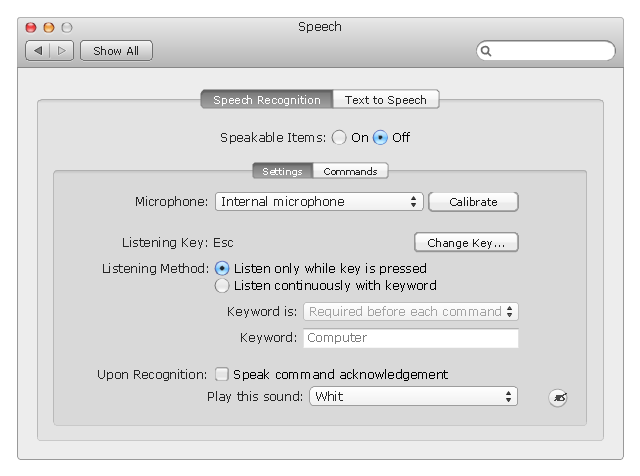
The example "ConceptDraw graphic user interface (Mac)" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The visible graphical interface features of an application are sometimes referred to as "chrome" or "Gui" (Goo-ee). Typically, the user interacts with information by manipulating visual widgets that allow for interactions appropriate to the kind of data they hold. The widgets of a well-designed interface are selected to support the actions necessary to achieve the goals of the user. A model-view-controller allows for a flexible structure in which the interface is independent from and indirectly linked to application functionality, so the GUI can be easily customized. This allows the user to select or design a different skin at will, and eases the designer's work to change the interface as the user needs evolve. Good user interface design relates to the user, not the system architecture.
Large widgets, such as windows, usually provide a frame or container for the main presentation content such as a web page, email message or drawing. Smaller ones usually act as a user-input tool." [Graphical user interface. Wikipedia]
The example "ConceptDraw graphic user interface (Mac)" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
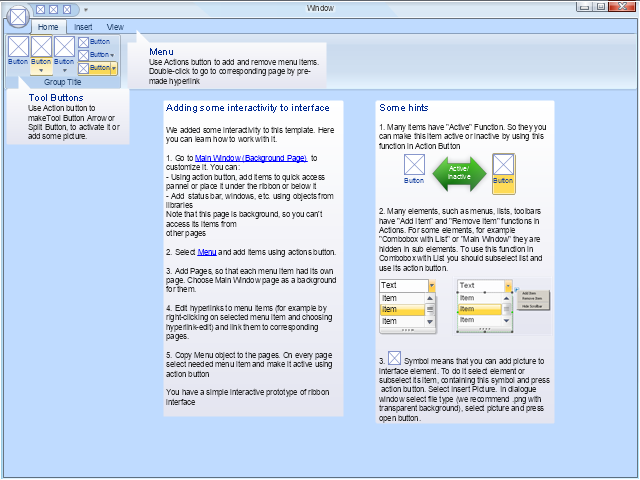
Use this template to prototype and design the Windows graphic user interface.
"In human–computer interaction, WIMP stands for "windows, icons, menus, pointer", denoting a style of interaction using these elements of the user interface. ... Other expansions are sometimes used, substituting "mouse" and "mice" or "pull-down menu" and "pointing", for menus and pointer, respectively. ...
In a WIMP system:
(1) A window runs a self-contained program, isolated from other programs that (if in a multi-program operating system) run at the same time in other windows.
(2) An icon acts as a shortcut to an action the computer performs (e.g., execute a program or task).
(3) A menu is a text or icon-based selection system that selects and executes programs or tasks.
(4) The pointer is an onscreen symbol that represents movement of a physical device that the user controls to select icons, data elements, etc.
(5) cut, copy, and paste.
This style of system improves human–computer interaction (HCI) by emulating real-world interactions and providing better ease of use for non-technical people - both novice and power users. Users can carry skill at a standardized interface from one application to another.
Due to the nature of the WIMP system, simple commands can be chained together to undertake a group of commands that would have taken several lines of command line instructions." [WIMP (computing). Wikipedia]
The Windows Vista graphic user interface template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In human–computer interaction, WIMP stands for "windows, icons, menus, pointer", denoting a style of interaction using these elements of the user interface. ... Other expansions are sometimes used, substituting "mouse" and "mice" or "pull-down menu" and "pointing", for menus and pointer, respectively. ...
In a WIMP system:
(1) A window runs a self-contained program, isolated from other programs that (if in a multi-program operating system) run at the same time in other windows.
(2) An icon acts as a shortcut to an action the computer performs (e.g., execute a program or task).
(3) A menu is a text or icon-based selection system that selects and executes programs or tasks.
(4) The pointer is an onscreen symbol that represents movement of a physical device that the user controls to select icons, data elements, etc.
(5) cut, copy, and paste.
This style of system improves human–computer interaction (HCI) by emulating real-world interactions and providing better ease of use for non-technical people - both novice and power users. Users can carry skill at a standardized interface from one application to another.
Due to the nature of the WIMP system, simple commands can be chained together to undertake a group of commands that would have taken several lines of command line instructions." [WIMP (computing). Wikipedia]
The Windows Vista graphic user interface template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"The interface is based around the home screen, a graphical list of available applications. iPhone applications normally run one at a time. Starting with the iPhone 4, a primitive version of multitasking came into play. Users could double click the home button to select recently opened. However, the apps never ran in the background. Starting with iOS 7, though, apps can truly multitask, and each open application runs in the background when not in use, although most functionality is still available when making a call or listening to music. The home screen can be accessed at any time by a hardware button below the screen, closing the open application in the process.
By default, the Home screen contains the following icons: Messages (SMS and MMS messaging), Calendar, Photos, Camera, YouTube, Stocks, Maps (Google Maps), Weather, Voice Memos, Notes, Clock, Calculator, Settings, iTunes (store), App Store, (on the iPhone 3GS and iPhone 4) Compass, FaceTime and GameCenter were added in iOS 4.0 and 4.1 respectively. In iOS 5, Reminders and Newsstand were added, as well as the iPod application split into separate Music and Videos applications. iOS 6 added Passbook as well as an updated version of Maps that relies on data provided by TomTom as well as other sources. iOS 6 also added a Clock application onto the iPad's homescreen. However, it also no longer support YouTube. Docked at the base of the screen, four icons for Phone, Mail, Safari (Internet), and Music delineate the iPhone's main purposes. On January 15, 2008, Apple released software update 1.1.3, allowing users to create "Web Clips", home screen icons that resemble apps that open a user-defined page in Safari. After the update, iPhone users can rearrange and place icons on up to nine other adjacent home screens, accessed by a horizontal swipe." [iPhone. Wikipedia]
The example "iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - Alarm setting" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
By default, the Home screen contains the following icons: Messages (SMS and MMS messaging), Calendar, Photos, Camera, YouTube, Stocks, Maps (Google Maps), Weather, Voice Memos, Notes, Clock, Calculator, Settings, iTunes (store), App Store, (on the iPhone 3GS and iPhone 4) Compass, FaceTime and GameCenter were added in iOS 4.0 and 4.1 respectively. In iOS 5, Reminders and Newsstand were added, as well as the iPod application split into separate Music and Videos applications. iOS 6 added Passbook as well as an updated version of Maps that relies on data provided by TomTom as well as other sources. iOS 6 also added a Clock application onto the iPad's homescreen. However, it also no longer support YouTube. Docked at the base of the screen, four icons for Phone, Mail, Safari (Internet), and Music delineate the iPhone's main purposes. On January 15, 2008, Apple released software update 1.1.3, allowing users to create "Web Clips", home screen icons that resemble apps that open a user-defined page in Safari. After the update, iPhone users can rearrange and place icons on up to nine other adjacent home screens, accessed by a horizontal swipe." [iPhone. Wikipedia]
The example "iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - Alarm setting" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"iOS (previously iPhone OS) is a mobile operating system developed and distributed by Apple Inc. ...
The user interface of iOS is based on the concept of direct manipulation, using multi-touch gestures. Interface control elements consist of sliders, switches, and buttons. Interaction with the OS includes gestures such as swipe, tap, pinch, and reverse pinch, all of which have specific definitions within the context of the iOS operating system and its multi-touch interface. Internal accelerometers are used by some applications to respond to shaking the device (one common result is the undo command) or rotating it in three dimensions (one common result is switching from portrait to landscape mode)." [iOS. Wikipedia]
The example "iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - More function view" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The user interface of iOS is based on the concept of direct manipulation, using multi-touch gestures. Interface control elements consist of sliders, switches, and buttons. Interaction with the OS includes gestures such as swipe, tap, pinch, and reverse pinch, all of which have specific definitions within the context of the iOS operating system and its multi-touch interface. Internal accelerometers are used by some applications to respond to shaking the device (one common result is the undo command) or rotating it in three dimensions (one common result is switching from portrait to landscape mode)." [iOS. Wikipedia]
The example "iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - More function view" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A world clock is a clock which displays the time for various cities around the world. The display can take various forms:
(1) The clock face can incorporate multiple round analogue clocks with moving hands or multiple digital clocks with numeric readouts, with each clock being labelled with the name of a major city or time zone in the world.
(2) It could also be a picture map of the world with embedded analog or digital time-displays.
(3) A moving circular map of the world, rotating inside a stationary 24 hour dial ring. Alternatively, the disc can be stationary and the ring moving.
(4) Light projection onto a map representing daytime, used in the Geochron, a brand of a particular form or world edvin.
There are also worldtime watches, both wrist watches and pocket watches. Sometime manufacturers of timekeepers erroneously apply the worldtime label to instruments that merely indicate time for two or a few time zones, but the term should be used only for timepieces that indicate time for all major time zones of the globe." [World clock. Wikipedia]
The example "iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - Clock application" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
(1) The clock face can incorporate multiple round analogue clocks with moving hands or multiple digital clocks with numeric readouts, with each clock being labelled with the name of a major city or time zone in the world.
(2) It could also be a picture map of the world with embedded analog or digital time-displays.
(3) A moving circular map of the world, rotating inside a stationary 24 hour dial ring. Alternatively, the disc can be stationary and the ring moving.
(4) Light projection onto a map representing daytime, used in the Geochron, a brand of a particular form or world edvin.
There are also worldtime watches, both wrist watches and pocket watches. Sometime manufacturers of timekeepers erroneously apply the worldtime label to instruments that merely indicate time for two or a few time zones, but the term should be used only for timepieces that indicate time for all major time zones of the globe." [World clock. Wikipedia]
The example "iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - Clock application" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"The iPhone ... is a line of smartphones designed and marketed by Apple Inc. It runs Apple's iOS mobile operating system. ...
The user interface is built around the device's multi-touch screen, including a virtual keyboard. The iPhone has Wi-Fi and can connect to many different cellular networks, including 1xRTT and GPRS (shown as a circle on the status bar), EDGE (shown as a capital E on the status bar), UMTS and EV-DO (shown as 3G), a faster version of UMTS and 4G (shown as a 4G symbol on the status bar), and LTE (shown as LTE on the status bar). An iPhone can shoot video (though this was not a standard feature until the iPhone 3GS), take photos, play music, send and receive email, browse the web, send texts, GPS navigation, tell jokes, record notes, do mathematical calculations, and receive visual voicemail. Other functions — video games, reference works, social networking, etc. — can be enabled by downloading application programs (‘apps’); as of October 2013, the App Store offered more than one million apps by Apple and third parties." [iPhone. Wikipedia]
The example "iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - Standby mode" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The user interface is built around the device's multi-touch screen, including a virtual keyboard. The iPhone has Wi-Fi and can connect to many different cellular networks, including 1xRTT and GPRS (shown as a circle on the status bar), EDGE (shown as a capital E on the status bar), UMTS and EV-DO (shown as 3G), a faster version of UMTS and 4G (shown as a 4G symbol on the status bar), and LTE (shown as LTE on the status bar). An iPhone can shoot video (though this was not a standard feature until the iPhone 3GS), take photos, play music, send and receive email, browse the web, send texts, GPS navigation, tell jokes, record notes, do mathematical calculations, and receive visual voicemail. Other functions — video games, reference works, social networking, etc. — can be enabled by downloading application programs (‘apps’); as of October 2013, the App Store offered more than one million apps by Apple and third parties." [iPhone. Wikipedia]
The example "iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - Standby mode" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use this template to prototype and design the iPhone user interface.
"At WWDC 2007 on June 11, 2007, Apple announced that the iPhone would support third-party web applications using Ajax that share the look and feel of the iPhone interface. On October 17, 2007, Steve Jobs, in an open letter posted to Apple's "Hot News" weblog, announced that a software development kit (SDK) would be made available to third-party developers in February 2008. The iPhone SDK was officially announced and released on March 6, 2008, at the Apple Town Hall facility.
It is a free download, with an Apple registration, that allows developers to develop native applications for the iPhone and iPod Touch, then test them in an "iPhone simulator". However, loading an application onto a real device is only possible after paying an Apple Developer Connection membership fee. Developers are free to set any price for their applications to be distributed through the App Store, of which they will receive a 70% share.
Developers can also opt to release the application for free and will not pay any costs to release or distribute the application beyond the membership fee. The App Store was launched with the release of iOS 2.0, on July 11, 2008. The update was free for iPhone users; owners of older iPod Touches were required to pay US$10 for it.
Once a developer has submitted an application to the App Store, Apple holds firm control over its distribution." [iPhone. Wikipedia]
The iPhone interface template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"At WWDC 2007 on June 11, 2007, Apple announced that the iPhone would support third-party web applications using Ajax that share the look and feel of the iPhone interface. On October 17, 2007, Steve Jobs, in an open letter posted to Apple's "Hot News" weblog, announced that a software development kit (SDK) would be made available to third-party developers in February 2008. The iPhone SDK was officially announced and released on March 6, 2008, at the Apple Town Hall facility.
It is a free download, with an Apple registration, that allows developers to develop native applications for the iPhone and iPod Touch, then test them in an "iPhone simulator". However, loading an application onto a real device is only possible after paying an Apple Developer Connection membership fee. Developers are free to set any price for their applications to be distributed through the App Store, of which they will receive a 70% share.
Developers can also opt to release the application for free and will not pay any costs to release or distribute the application beyond the membership fee. The App Store was launched with the release of iOS 2.0, on July 11, 2008. The update was free for iPhone users; owners of older iPod Touches were required to pay US$10 for it.
Once a developer has submitted an application to the App Store, Apple holds firm control over its distribution." [iPhone. Wikipedia]
The iPhone interface template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Designing the visual composition and temporal behavior of GUI is an important part of software application programming in the area of human-computer interaction. Its goal is to enhance the efficiency and ease of use for the underlying logical design of a stored program, a design discipline known as usability. Methods of user-centered design are used to ensure that the visual language introduced in the design is well tailored to the tasks.
The visible graphical interface features of an application are sometimes referred to as "chrome" or "Gui" (Goo-ee). Typically, the user interacts with information by manipulating visual widgets that allow for interactions appropriate to the kind of data they hold. The widgets of a well-designed interface are selected to support the actions necessary to achieve the goals of the user. A model-view-controller allows for a flexible structure in which the interface is independent from and indirectly linked to application functionality, so the GUI can be easily customized. This allows the user to select or design a different skin at will, and eases the designer's work to change the interface as the user needs evolve. Good user interface design relates to the user, not the system architecture.
Large widgets, such as windows, usually provide a frame or container for the main presentation content such as a web page, email message or drawing. Smaller ones usually act as a user-input tool." [Graphical user interface. Wikipedia]
The example "ConceptDraw graphic user interface (Mac)" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The visible graphical interface features of an application are sometimes referred to as "chrome" or "Gui" (Goo-ee). Typically, the user interacts with information by manipulating visual widgets that allow for interactions appropriate to the kind of data they hold. The widgets of a well-designed interface are selected to support the actions necessary to achieve the goals of the user. A model-view-controller allows for a flexible structure in which the interface is independent from and indirectly linked to application functionality, so the GUI can be easily customized. This allows the user to select or design a different skin at will, and eases the designer's work to change the interface as the user needs evolve. Good user interface design relates to the user, not the system architecture.
Large widgets, such as windows, usually provide a frame or container for the main presentation content such as a web page, email message or drawing. Smaller ones usually act as a user-input tool." [Graphical user interface. Wikipedia]
The example "ConceptDraw graphic user interface (Mac)" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"For text input, the iPhone implements a virtual keyboard on the touchscreen. It has automatic spell checking and correction, predictive word capabilities, and a dynamic dictionary that learns new words. The keyboard can predict what word the user is typing and complete it, and correct for the accidental pressing of keys near the presumed desired key.
The keys are somewhat larger and spaced farther apart when in landscape mode, which is supported by only a limited number of applications. Touching a section of text for a brief time brings up a magnifying glass, allowing users to place the cursor in the middle of existing text. The virtual keyboard can accommodate 21 languages, including character recognition for Chinese.
Alternate characters with accents (for example, letters from the alphabets of other languages) can be typed from the keyboard by pressing the letter for 2 seconds and selecting the alternate character from the popup. The 3.0 update brought support for cut, copy, or pasting text, as well as landscape keyboards in more applications." [iPhone. Wikipedia]
The example "iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - Horizontal mode" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The keys are somewhat larger and spaced farther apart when in landscape mode, which is supported by only a limited number of applications. Touching a section of text for a brief time brings up a magnifying glass, allowing users to place the cursor in the middle of existing text. The virtual keyboard can accommodate 21 languages, including character recognition for Chinese.
Alternate characters with accents (for example, letters from the alphabets of other languages) can be typed from the keyboard by pressing the letter for 2 seconds and selecting the alternate character from the popup. The 3.0 update brought support for cut, copy, or pasting text, as well as landscape keyboards in more applications." [iPhone. Wikipedia]
The example "iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - Horizontal mode" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use this template to prototype and design the Mac OS X Lion user interface.
"OS X, whose X is the Roman numeral for 10 and is a prominent part of its brand identity, is built on technologies developed at NeXT between the second half of the 1980s and Apple's purchase of the company in late 1996. The 'X' is also used to emphasize the relatedness between OS X and UNIX. Versions 10.5 "Leopard" running on Intel processors, 10.6 "Snow Leopard", 10.7 "Lion", 10.8 "Mountain Lion", and 10.9 "Mavericks" have obtained UNIX 03 certification. iOS, which runs on the iPhone, iPod Touch, iPad, and the 2nd and 3rd generation Apple TV, shares the Darwin core and many frameworks with OS X. An unnamed variant of v10.4 powered the first generation Apple TV.
Mac OS X 10.7 "Lion" was the first version of OS X to drop support for 32-bit Intel processors and run exclusively on 64-bit Intel CPUs." [OS X. Wikipedia]
The Mac OS X Lion user interface template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"OS X, whose X is the Roman numeral for 10 and is a prominent part of its brand identity, is built on technologies developed at NeXT between the second half of the 1980s and Apple's purchase of the company in late 1996. The 'X' is also used to emphasize the relatedness between OS X and UNIX. Versions 10.5 "Leopard" running on Intel processors, 10.6 "Snow Leopard", 10.7 "Lion", 10.8 "Mountain Lion", and 10.9 "Mavericks" have obtained UNIX 03 certification. iOS, which runs on the iPhone, iPod Touch, iPad, and the 2nd and 3rd generation Apple TV, shares the Darwin core and many frameworks with OS X. An unnamed variant of v10.4 powered the first generation Apple TV.
Mac OS X 10.7 "Lion" was the first version of OS X to drop support for 32-bit Intel processors and run exclusively on 64-bit Intel CPUs." [OS X. Wikipedia]
The Mac OS X Lion user interface template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
GUI Prototyping with ConceptDraw PRO
All about prototyping. GUI Prototyping with ConceptDraw. Download prototyping software.Use this template to prototype and design the wireframe graphic user interface (GUI).
"A website wireframe, also known as a page schematic or screen blueprint, is a visual guide that represents the skeletal framework of a website. Wireframes are created for the purpose of arranging elements to best accomplish a particular purpose. The purpose is usually being informed by a business objective and a creative idea. The wireframe depicts the page layout or arrangement of the website’s content, including interface elements and navigational systems, and how they work together. The wireframe usually lacks typographic style, color, or graphics, since the main focus lies in functionality, behavior, and priority of content. In other words, it focuses on what a screen does, not what it looks like. Wireframes can be pencil drawings or sketches on a whiteboard, or they can be produced by means of a broad array of free or commercial software applications. Wireframes are generally created by business analysts, user experience designers, developers, visual designers and other roles with expertise in interaction design, information architecture and user research.
Wireframes focus on:
(1) The kinds of information displayed.
(2) The range of functions available.
(3) The relative priorities of the information and functions.
(4) The rules for displaying certain kinds of information.
(5) The effect of different scenarios on the display.
The website wireframe connects the underlying conceptual structure, or information architecture, to the surface, or visual design of the website. Wireframes help establish functionality, and the relationships between different screen templates of a website. An iterative process, creating wireframes is an effective way to make rapid prototypes of pages, while measuring the practicality of a design concept. Wireframing typically begins between “high-level structural work - like flowcharts or site maps - and screen designs.” Within the process of building a website, wireframing is where thinking becomes tangible.
Aside from websites, wireframes are utilized for the prototyping of mobile sites, computer applications, or other screen-based products that involve human-computer interaction." [Website wireframe. Wikipedia]
The wireframe GUI template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A website wireframe, also known as a page schematic or screen blueprint, is a visual guide that represents the skeletal framework of a website. Wireframes are created for the purpose of arranging elements to best accomplish a particular purpose. The purpose is usually being informed by a business objective and a creative idea. The wireframe depicts the page layout or arrangement of the website’s content, including interface elements and navigational systems, and how they work together. The wireframe usually lacks typographic style, color, or graphics, since the main focus lies in functionality, behavior, and priority of content. In other words, it focuses on what a screen does, not what it looks like. Wireframes can be pencil drawings or sketches on a whiteboard, or they can be produced by means of a broad array of free or commercial software applications. Wireframes are generally created by business analysts, user experience designers, developers, visual designers and other roles with expertise in interaction design, information architecture and user research.
Wireframes focus on:
(1) The kinds of information displayed.
(2) The range of functions available.
(3) The relative priorities of the information and functions.
(4) The rules for displaying certain kinds of information.
(5) The effect of different scenarios on the display.
The website wireframe connects the underlying conceptual structure, or information architecture, to the surface, or visual design of the website. Wireframes help establish functionality, and the relationships between different screen templates of a website. An iterative process, creating wireframes is an effective way to make rapid prototypes of pages, while measuring the practicality of a design concept. Wireframing typically begins between “high-level structural work - like flowcharts or site maps - and screen designs.” Within the process of building a website, wireframing is where thinking becomes tangible.
Aside from websites, wireframes are utilized for the prototyping of mobile sites, computer applications, or other screen-based products that involve human-computer interaction." [Website wireframe. Wikipedia]
The wireframe GUI template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
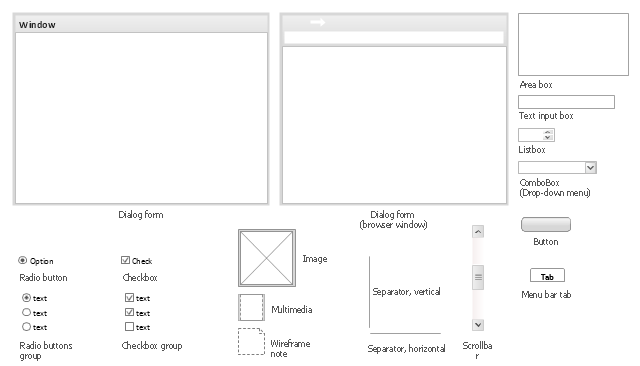
The vector stencils library "Wireframe" contains 18 elements for designing wireframe graphic user interface (GUI) of computer software.
"Wireframes may be utilized by ... designers ... to push the user interface (UI) process. ...
User interface design includes selecting and arranging interface elements to enable users to interact with the functionality of the system. The goal is to facilitate usability and efficiency as much as possible. Common elements found in interface design are action buttons, text fields, check boxes, radio buttons and drop-down menus." [Website wireframe. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Wireframe" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Wireframes may be utilized by ... designers ... to push the user interface (UI) process. ...
User interface design includes selecting and arranging interface elements to enable users to interact with the functionality of the system. The goal is to facilitate usability and efficiency as much as possible. Common elements found in interface design are action buttons, text fields, check boxes, radio buttons and drop-down menus." [Website wireframe. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Wireframe" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
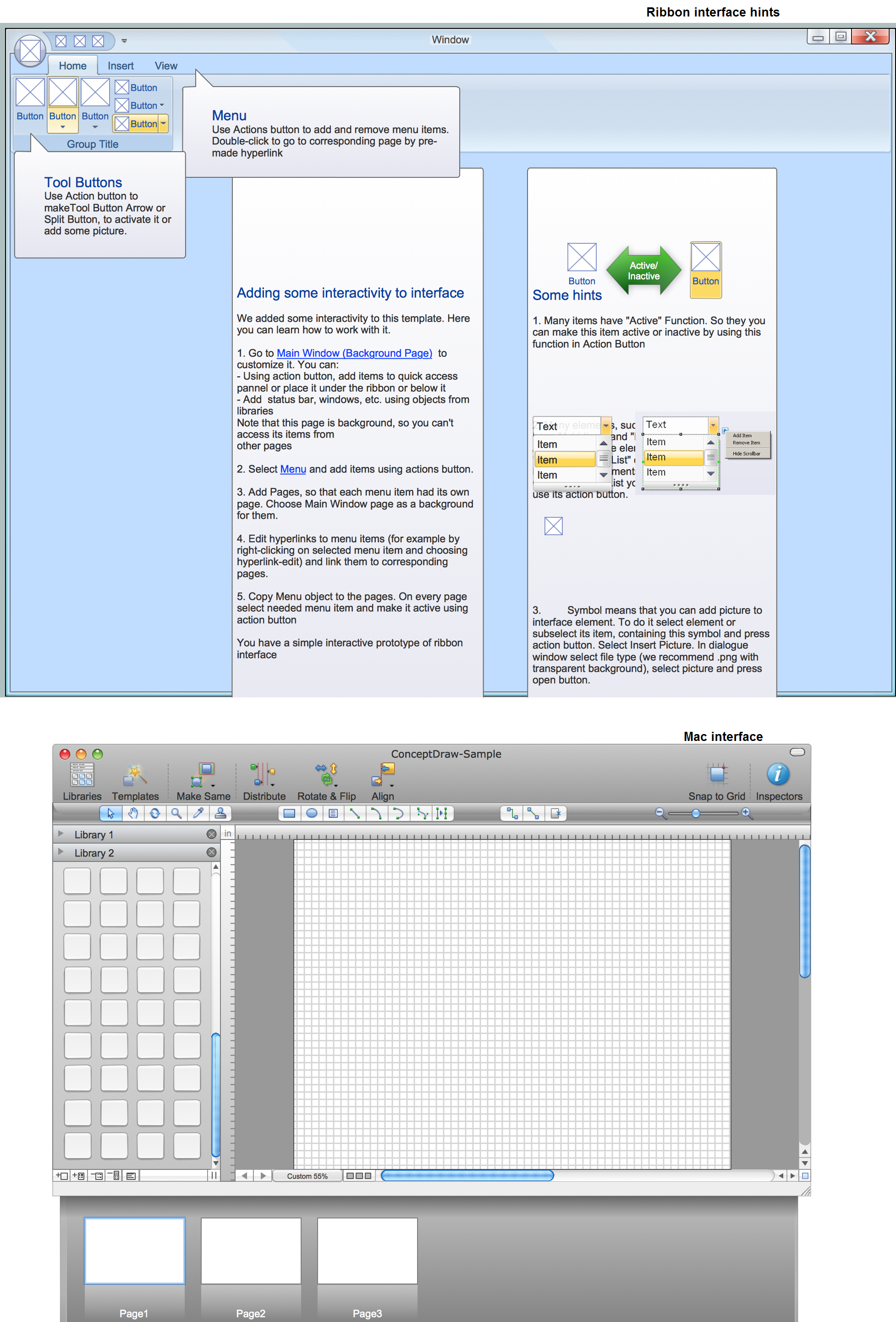
"In computing, a ribbon is a set of toolbars placed on several tabs. Microsoft products released since 2007 have introduced a form of modular ribbon as their main interface, where large tabbed toolbars, filled with graphical buttons and other controls, are grouped by functionality. Such ribbons use tabs to expose different sets of controls, eliminating the need for many parallel toolbars. Contextual tabs are tabs that appear only when the user needs them. For instance, in a word processor, an image-related tab may appear when the user selects an image in a document, allowing the user to interact with that image.
The usage of the term ribbon dates from the 1980s and was originally used as a synonym for what is now more commonly known as a (non-tabbed) toolbar. However, in 2007, Microsoft Office 2007 used the term to refer to its own implementation of tabbed toolbars bearing heterogeneous controls, which Microsoft calls "The Fluent UI". Thus, Microsoft popularized the term with a new meaning, although similar tabbed layouts of controls had existed in previous software from other vendors. The new design was intended to alleviate the problem of users not finding or knowing of the existence of available features in the Office suite." [Ribbon (computing). Wikipedia]
The example "Microsoft Windows ribbon interface hints" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The usage of the term ribbon dates from the 1980s and was originally used as a synonym for what is now more commonly known as a (non-tabbed) toolbar. However, in 2007, Microsoft Office 2007 used the term to refer to its own implementation of tabbed toolbars bearing heterogeneous controls, which Microsoft calls "The Fluent UI". Thus, Microsoft popularized the term with a new meaning, although similar tabbed layouts of controls had existed in previous software from other vendors. The new design was intended to alleviate the problem of users not finding or knowing of the existence of available features in the Office suite." [Ribbon (computing). Wikipedia]
The example "Microsoft Windows ribbon interface hints" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use this template to prototype and design the iPhone user interface.
"At WWDC 2007 on June 11, 2007, Apple announced that the iPhone would support third-party web applications using Ajax that share the look and feel of the iPhone interface. On October 17, 2007, Steve Jobs, in an open letter posted to Apple's "Hot News" weblog, announced that a software development kit (SDK) would be made available to third-party developers in February 2008. The iPhone SDK was officially announced and released on March 6, 2008, at the Apple Town Hall facility.
It is a free download, with an Apple registration, that allows developers to develop native applications for the iPhone and iPod Touch, then test them in an "iPhone simulator". However, loading an application onto a real device is only possible after paying an Apple Developer Connection membership fee. Developers are free to set any price for their applications to be distributed through the App Store, of which they will receive a 70% share.
Developers can also opt to release the application for free and will not pay any costs to release or distribute the application beyond the membership fee. The App Store was launched with the release of iOS 2.0, on July 11, 2008. The update was free for iPhone users; owners of older iPod Touches were required to pay US$10 for it.
Once a developer has submitted an application to the App Store, Apple holds firm control over its distribution." [iPhone. Wikipedia]
The iPhone interface template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"At WWDC 2007 on June 11, 2007, Apple announced that the iPhone would support third-party web applications using Ajax that share the look and feel of the iPhone interface. On October 17, 2007, Steve Jobs, in an open letter posted to Apple's "Hot News" weblog, announced that a software development kit (SDK) would be made available to third-party developers in February 2008. The iPhone SDK was officially announced and released on March 6, 2008, at the Apple Town Hall facility.
It is a free download, with an Apple registration, that allows developers to develop native applications for the iPhone and iPod Touch, then test them in an "iPhone simulator". However, loading an application onto a real device is only possible after paying an Apple Developer Connection membership fee. Developers are free to set any price for their applications to be distributed through the App Store, of which they will receive a 70% share.
Developers can also opt to release the application for free and will not pay any costs to release or distribute the application beyond the membership fee. The App Store was launched with the release of iOS 2.0, on July 11, 2008. The update was free for iPhone users; owners of older iPod Touches were required to pay US$10 for it.
Once a developer has submitted an application to the App Store, Apple holds firm control over its distribution." [iPhone. Wikipedia]
The iPhone interface template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Graphic User Interface solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - Activity indicator view ...
- graphic user interface (GUI)
- Graphic User Interface
- iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface (GUI) - Standby mode ...
- GUI Prototyping with ConceptDraw PRO | Windows Vista graphic ...
- Mac OS X Lion user graphic interface (GUI) template | Software ...
- Software Development | Mac OS X Lion user graphic interface (GUI ...
- Graphic User Interface | Software Development | - Conceptdraw.com
- Graphic User Interface | GUI Prototyping with ConceptDraw PRO ...
- Fishbone Diagram | Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) | Graphic ...
- What is a Dashboard Area | iPhone OS (iOS) graphic user interface ...
- Best Vector Drawing Application for Mac OS X | ConceptDraw PRO ...
- Program to Make Flow Chart | Software Development | Good Flow ...
- ConceptDraw PRO The best Business Drawing Software | UML ...
- Entity Relationship Diagram Software for Mac | Best Diagramming ...
- Design elements - Composition charts and indicators | Constant ...
- Value Stream Mapping | Quality | Value stream with ConceptDraw ...
- Project Exchange | ConceptDraw PRO The best Business Drawing ...
- ConceptDraw PRO The best Business Drawing Software ...
- IDEF0 diagram - Application development | Applications | Software ...
-graphic-user-interface-(gui)---activity-indicator-view.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-graphic-user-interface-(gui)---alarm-setting.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-graphic-user-interface-(gui)---more-function-view.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-graphic-user-interface-(gui)---clock-application.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-graphic-user-interface-(gui)---standby-mode.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-graphic-user-interface-(gui)---horizontal-mode.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)