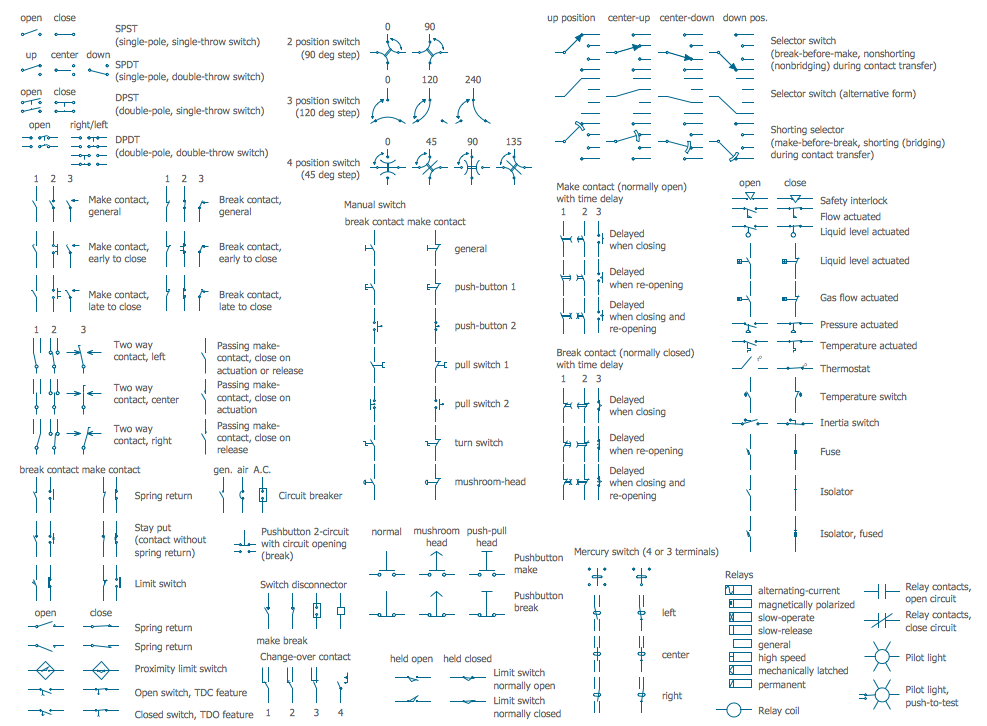
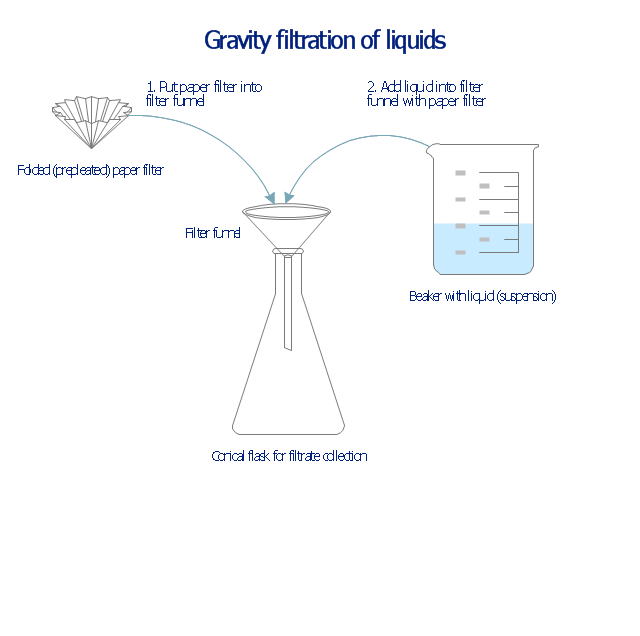
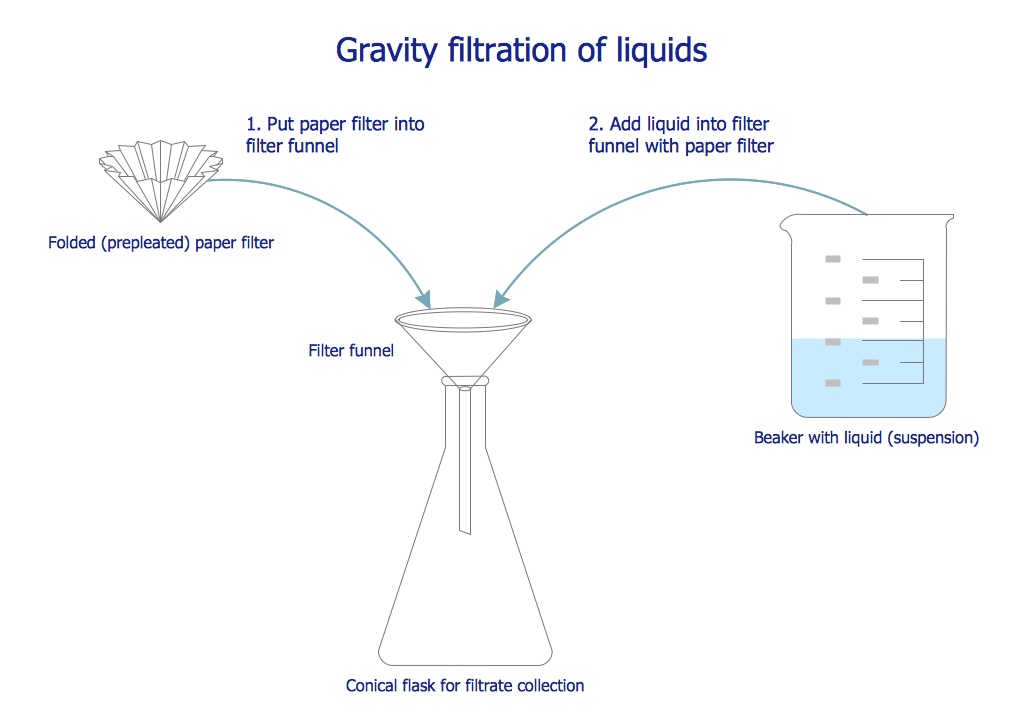
This chemical laboratory technique drawing depict gravity filtration of liquid through prepleated paper filter step-by-step.
1. Put folded filter paper cone into glass filter funnel inserted into neck of conical (Erlenmeyer) flask.
2. Add liquid suspension from the glass beaker with a spout into the funnel with paper filter.
3. Collect filtrate in the conical flask and solid on the paper filter in the funnel.
"Filtration is commonly the mechanical or physical operation which is used for the separation of solids from fluids (liquids or gases) by interposing a medium through which only the fluid can pass. The fluid that pass through is called a filtrate. Oversize solids in the fluid are retained, but the separation is not complete; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles (depending on the pore size and filter thickness)." [Filtration. Wikipedia]
"Filter paper is a semi-permeable paper barrier placed perpendicular to a liquid or air flow. It is used to separate fine solids from liquids or air." [Filter paper. Wikipedia]
The chemical lab drawing example "Gravity filtration of liquids" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
1. Put folded filter paper cone into glass filter funnel inserted into neck of conical (Erlenmeyer) flask.
2. Add liquid suspension from the glass beaker with a spout into the funnel with paper filter.
3. Collect filtrate in the conical flask and solid on the paper filter in the funnel.
"Filtration is commonly the mechanical or physical operation which is used for the separation of solids from fluids (liquids or gases) by interposing a medium through which only the fluid can pass. The fluid that pass through is called a filtrate. Oversize solids in the fluid are retained, but the separation is not complete; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles (depending on the pore size and filter thickness)." [Filtration. Wikipedia]
"Filter paper is a semi-permeable paper barrier placed perpendicular to a liquid or air flow. It is used to separate fine solids from liquids or air." [Filter paper. Wikipedia]
The chemical lab drawing example "Gravity filtration of liquids" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
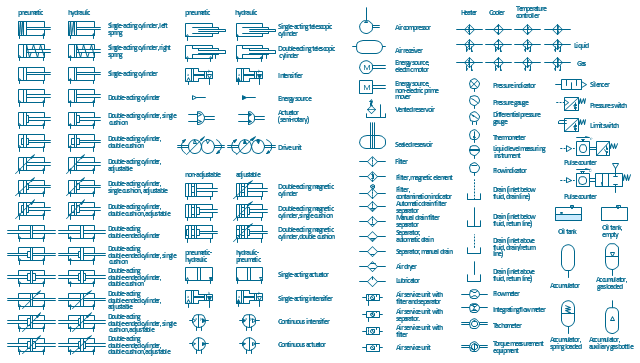
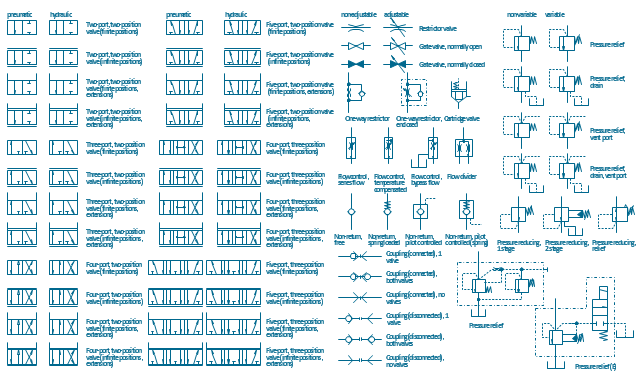
The vector stencils library "Fluid power equipment" contains 113 symbols of hydraulic and pneumatic equipment including pumps, motors, air compressors, cylinders, meters, gauges, and actuators. Use it to design fluid power and hydraulic control systems.
"Fluid power is the use of fluids under pressure to generate, control, and transmit power. Fluid power is subdivided into hydraulics using a liquid such as mineral oil or water, and pneumatics using a gas such as air or other gases. Compressed-air and water-pressure systems were once used to transmit power from a central source to industrial users over extended geographic areas; fluid power systems today are usually within a single building or mobile machine." [Fluid power. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Fluid power equipment" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mechanical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Fluid power is the use of fluids under pressure to generate, control, and transmit power. Fluid power is subdivided into hydraulics using a liquid such as mineral oil or water, and pneumatics using a gas such as air or other gases. Compressed-air and water-pressure systems were once used to transmit power from a central source to industrial users over extended geographic areas; fluid power systems today are usually within a single building or mobile machine." [Fluid power. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Fluid power equipment" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mechanical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
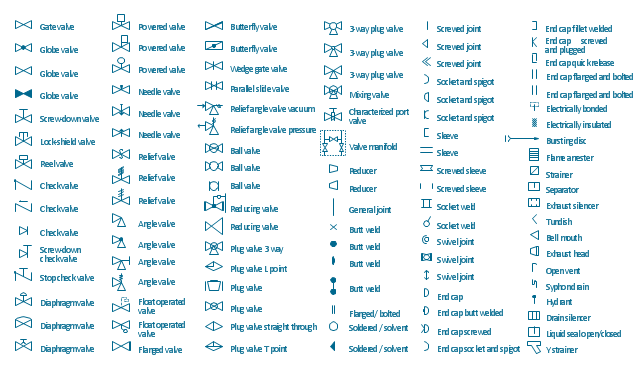
The vector stencils library "Valves and fittings" contains 104 symbols of valve components.
Use these icons for drawing industrial piping systems; process, vacuum, and fluids piping; hydraulics piping; air and gas piping; materials distribution; and liquid transfer systems.
"A valve is a device that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically valves fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure.
The simplest, and very ancient, valve is simply a freely hinged flap which drops to obstruct fluid (gas or liquid) flow in one direction, but is pushed open by flow in the opposite direction. This is called a check valve, as it prevents or "checks" the flow in one direction. ...
Valves are found in virtually every industrial process, including water & sewage processing, mining, power generation, processing of oil, gas & petroleum, food manufacturing, chemical & plastic manufacturing and many other fields. ...
Valves may be operated manually, either by a handle, lever, pedal or wheel. Valves may also be automatic, driven by changes in pressure, temperature, or flow. These changes may act upon a diaphragm or a piston which in turn activates the valve, examples of this type of valve found commonly are safety valves fitted to hot water systems or boilers.
More complex control systems using valves requiring automatic control based on an external input (i.e., regulating flow through a pipe to a changing set point) require an actuator. An actuator will stroke the valve depending on its input and set-up, allowing the valve to be positioned accurately, and allowing control over a variety of requirements." [Valve. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Valves and fittings" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these icons for drawing industrial piping systems; process, vacuum, and fluids piping; hydraulics piping; air and gas piping; materials distribution; and liquid transfer systems.
"A valve is a device that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically valves fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure.
The simplest, and very ancient, valve is simply a freely hinged flap which drops to obstruct fluid (gas or liquid) flow in one direction, but is pushed open by flow in the opposite direction. This is called a check valve, as it prevents or "checks" the flow in one direction. ...
Valves are found in virtually every industrial process, including water & sewage processing, mining, power generation, processing of oil, gas & petroleum, food manufacturing, chemical & plastic manufacturing and many other fields. ...
Valves may be operated manually, either by a handle, lever, pedal or wheel. Valves may also be automatic, driven by changes in pressure, temperature, or flow. These changes may act upon a diaphragm or a piston which in turn activates the valve, examples of this type of valve found commonly are safety valves fitted to hot water systems or boilers.
More complex control systems using valves requiring automatic control based on an external input (i.e., regulating flow through a pipe to a changing set point) require an actuator. An actuator will stroke the valve depending on its input and set-up, allowing the valve to be positioned accurately, and allowing control over a variety of requirements." [Valve. Wikipedia]
The example "Design elements - Valves and fittings" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Fluid power valves" contains 93 symbols of pre-made hydraulic and pneumatic valves, including directional control valves, flow control valves, pressure control valves, and electrohydraulic and electropneumatic valves.
"Control valves are valves used to control conditions such as flow, pressure, temperature, and liquid level by fully or partially opening or closing in response to signals received from controllers that compare a "setpoint" to a "process variable" whose value is provided by sensors that monitor changes in such conditions.
The opening or closing of control valves is usually done automatically by electrical, hydraulic or pneumatic actuators. Positioners are used to control the opening or closing of the actuator based on electric, or pneumatic signals.
A control valve consists of three main parts in which each part exist in several types and designs: Valve's actuator, Valve's positioner, Valve's body.
" [Control valves. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Fluid power valves" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mechanical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Control valves are valves used to control conditions such as flow, pressure, temperature, and liquid level by fully or partially opening or closing in response to signals received from controllers that compare a "setpoint" to a "process variable" whose value is provided by sensors that monitor changes in such conditions.
The opening or closing of control valves is usually done automatically by electrical, hydraulic or pneumatic actuators. Positioners are used to control the opening or closing of the actuator based on electric, or pneumatic signals.
A control valve consists of three main parts in which each part exist in several types and designs: Valve's actuator, Valve's positioner, Valve's body.
" [Control valves. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Fluid power valves" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mechanical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Chemistry
Chemistry
This solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with samples, template and libraries of vector stencils for drawing the Chemistry Illustrations for science and education.
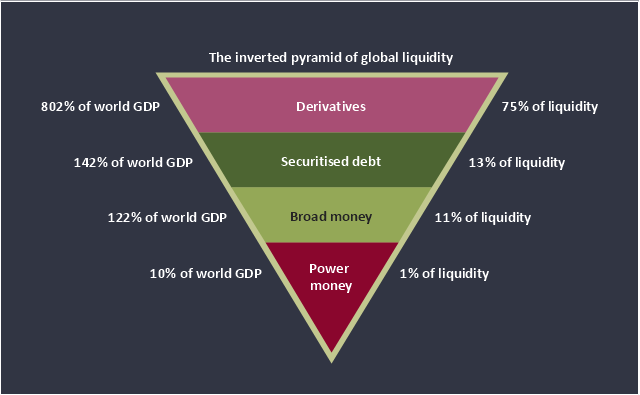
This inverted pyramid diagram of global liquidity shows world GDP and liquidity for 4 levels: derivatives, securitised debt, broad money, and power money.
"In business, economics or investment, market liquidity is a market's ability to facilitate an asset being sold quickly without having to reduce its price very much (or even at all). Equivalently, an asset's market liquidity (or simply "an asset's liquidity") is the asset's ability to sell quickly without having to reduce its price very much. Liquidity is about how big the trade-off is between the speed of the sale and the price it can be sold for. In a liquid market, the trade-off is mild: selling quickly will not reduce the price much. In a relatively illiquid market, selling it quickly will require cutting its price by some amount.
Money, or cash, is the most liquid asset, because it can be "sold" for goods and services instantly with no loss of value. There is no wait for a suitable buyer of the cash. There is no trade-off between speed and value. It can be used immediately to perform economic actions like buying, selling, or paying debt, meeting immediate wants and needs.
If an asset is moderately (or very) liquid, it has moderate (or high) liquidity. In an alternative definition, liquidity can mean the amount of highly liquid assets. If a business has moderate liquidity, it has a moderate amount of very liquid assets. If a business has sufficient liquidity, it has a sufficient amount of very liquid assets and the ability to meet its payment obligations." [Market liquidity. Wikipedia]
This inverted triangle diagram was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file The inverted pyramid of global liquidity.gif. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:The_ inverted_ pyramid_ of_ global_ liquidity.gif]
This triangular chart example is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In business, economics or investment, market liquidity is a market's ability to facilitate an asset being sold quickly without having to reduce its price very much (or even at all). Equivalently, an asset's market liquidity (or simply "an asset's liquidity") is the asset's ability to sell quickly without having to reduce its price very much. Liquidity is about how big the trade-off is between the speed of the sale and the price it can be sold for. In a liquid market, the trade-off is mild: selling quickly will not reduce the price much. In a relatively illiquid market, selling it quickly will require cutting its price by some amount.
Money, or cash, is the most liquid asset, because it can be "sold" for goods and services instantly with no loss of value. There is no wait for a suitable buyer of the cash. There is no trade-off between speed and value. It can be used immediately to perform economic actions like buying, selling, or paying debt, meeting immediate wants and needs.
If an asset is moderately (or very) liquid, it has moderate (or high) liquidity. In an alternative definition, liquidity can mean the amount of highly liquid assets. If a business has moderate liquidity, it has a moderate amount of very liquid assets. If a business has sufficient liquidity, it has a sufficient amount of very liquid assets and the ability to meet its payment obligations." [Market liquidity. Wikipedia]
This inverted triangle diagram was redesigned using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from Wikimedia Commons file The inverted pyramid of global liquidity.gif. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:The_ inverted_ pyramid_ of_ global_ liquidity.gif]
This triangular chart example is included in the Pyramid Diagrams solution from the Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Chemistry Symbols and Meanings
Chemistry solution offers 5 libraries with large collection of vector chemistry symbols and meanings, chemistry equation symbols, organic chemistry symbols, and chemical clipart: Chemical Elements Library, Chemical Drawings Library, Conformations Library, Laboratory Equipment Library, Periodic Table of Chemical Elements Library.This PFD sample was redesigned from the Wikipedia file: NaturalGasCondensate.png.
"This is a schematic flow diagram of a typical facility for separating and recovering liquid condensate from raw natural gas."
[en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:NaturalGasCondensate.png]
"Natural-gas condensate is a low-density mixture of hydrocarbon liquids that are present as gaseous components in the raw natural gas produced from many natural gas fields. It condenses out of the raw gas if the temperature is reduced to below the hydrocarbon dew point temperature of the raw gas.
The natural gas condensate is also referred to as simply condensate, or gas condensate, or sometimes natural gasoline because it contains hydrocarbons within the gasoline boiling range. Raw natural gas may come from any one of three types of gas wells:
(1) Crude oil wells - Raw natural gas that comes from crude oil wells is called associated gas. This gas can exist separate from the crude oil in the underground formation, or dissolved in the crude oil.
(2) Dry gas wells - These wells typically produce only raw natural gas that does not contain any hydrocarbon liquids. Such gas is called non-associated gas.
(3) Condensate wells - These wells produce raw natural gas along with natural gas liquid. Such gas is also non-associated gas and often referred to as wet gas." [Natural-gas condensate. Wikipedia]
The process flow diagram example "Natural gas condensate - PFD" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"This is a schematic flow diagram of a typical facility for separating and recovering liquid condensate from raw natural gas."
[en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:NaturalGasCondensate.png]
"Natural-gas condensate is a low-density mixture of hydrocarbon liquids that are present as gaseous components in the raw natural gas produced from many natural gas fields. It condenses out of the raw gas if the temperature is reduced to below the hydrocarbon dew point temperature of the raw gas.
The natural gas condensate is also referred to as simply condensate, or gas condensate, or sometimes natural gasoline because it contains hydrocarbons within the gasoline boiling range. Raw natural gas may come from any one of three types of gas wells:
(1) Crude oil wells - Raw natural gas that comes from crude oil wells is called associated gas. This gas can exist separate from the crude oil in the underground formation, or dissolved in the crude oil.
(2) Dry gas wells - These wells typically produce only raw natural gas that does not contain any hydrocarbon liquids. Such gas is called non-associated gas.
(3) Condensate wells - These wells produce raw natural gas along with natural gas liquid. Such gas is also non-associated gas and often referred to as wet gas." [Natural-gas condensate. Wikipedia]
The process flow diagram example "Natural gas condensate - PFD" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
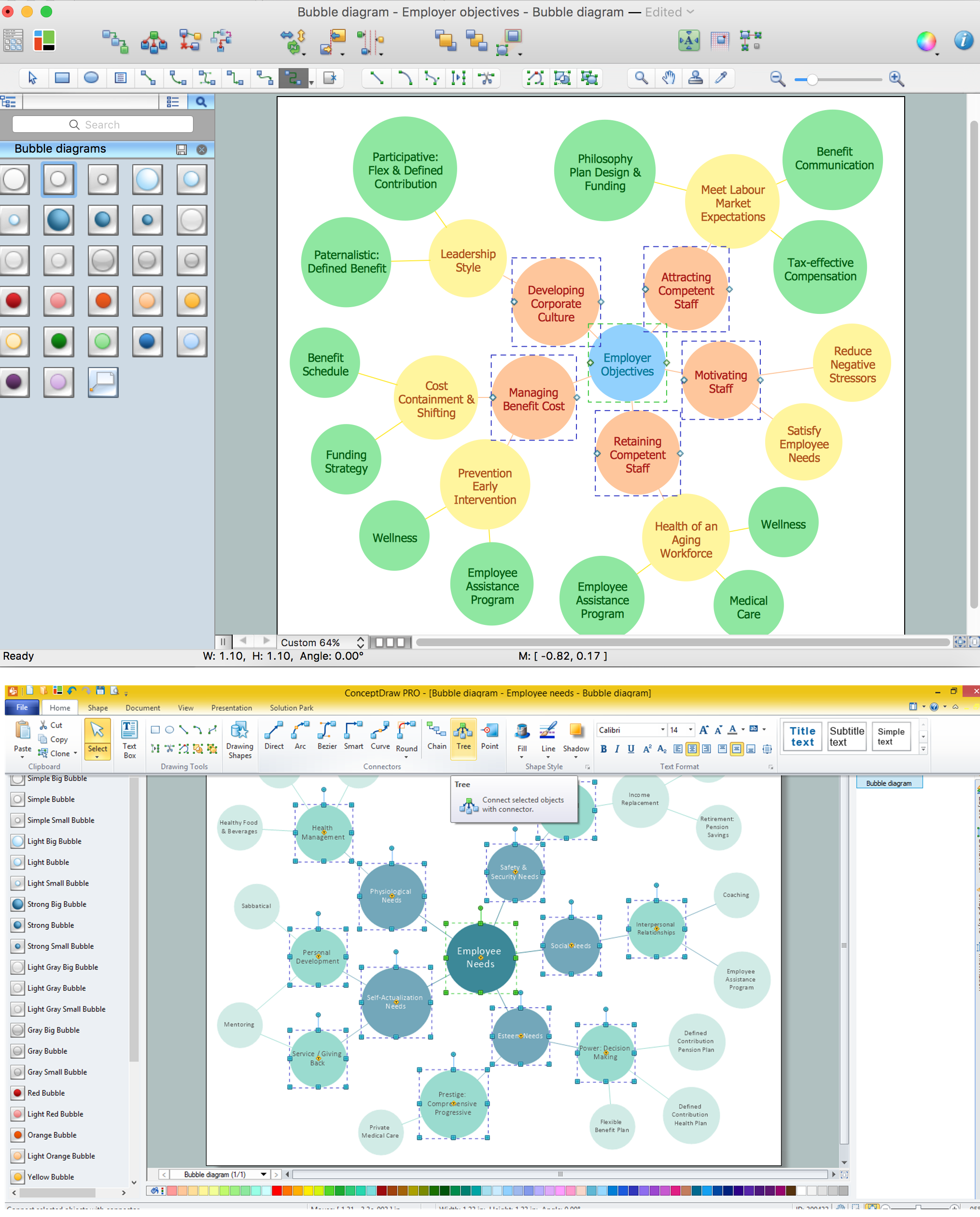
How To Make a Bubble Chart
Bubble diagrams solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software with templates, Using ConceptDraw Connectors, you can make a bubble chart in moments. Using ConceptDraw you will be able to make a bubble chart from the ready ConceptDraw library objects or make your own objects. The created diagram can represent ideas organization, in brainstorming processes, by teachers for explaining difficult ideas or for presentations.Retract resistor check valve application: pneumatic cylinder, piston driven by Compressed air through 2 Retract resistor check valves.
"A check valve, clack valve, non-return valve or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid (liquid or gas) to flow through it in only one direction.
Check valves are two-port valves, meaning they have two openings in the body, one for fluid to enter and the other for fluid to leave. There are various types of check valves used in a wide variety of applications. Check valves are often part of common household items. Although they are available in a wide range of sizes and costs, check valves generally are very small, simple, or inexpensive. Check valves work automatically and most are not controlled by a person or any external control; accordingly, most do not have any valve handle or stem. The bodies (external shells) of most check valves are made of plastic or metal.
An important concept in check valves is the cracking pressure which is the minimum upstream pressure at which the valve will operate. Typically the check valve is designed for and can therefore be specified for a specific cracking pressure.
Heart valves are essentially inlet and outlet check valves for the heart ventricles, since the ventricles act as pumps." [Check valve. Wikipedia]
This hydraulic schematic example was redrawn using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from the Wikimedia Commons file: Retract resistor check valve application.png.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Retract_ resistor_ check_ valve_ application.png]
The hydraulic engineering drawing example "Retract resistor check valve application" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mechanical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A check valve, clack valve, non-return valve or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid (liquid or gas) to flow through it in only one direction.
Check valves are two-port valves, meaning they have two openings in the body, one for fluid to enter and the other for fluid to leave. There are various types of check valves used in a wide variety of applications. Check valves are often part of common household items. Although they are available in a wide range of sizes and costs, check valves generally are very small, simple, or inexpensive. Check valves work automatically and most are not controlled by a person or any external control; accordingly, most do not have any valve handle or stem. The bodies (external shells) of most check valves are made of plastic or metal.
An important concept in check valves is the cracking pressure which is the minimum upstream pressure at which the valve will operate. Typically the check valve is designed for and can therefore be specified for a specific cracking pressure.
Heart valves are essentially inlet and outlet check valves for the heart ventricles, since the ventricles act as pumps." [Check valve. Wikipedia]
This hydraulic schematic example was redrawn using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software from the Wikimedia Commons file: Retract resistor check valve application.png.
[commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Retract_ resistor_ check_ valve_ application.png]
The hydraulic engineering drawing example "Retract resistor check valve application" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mechanical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
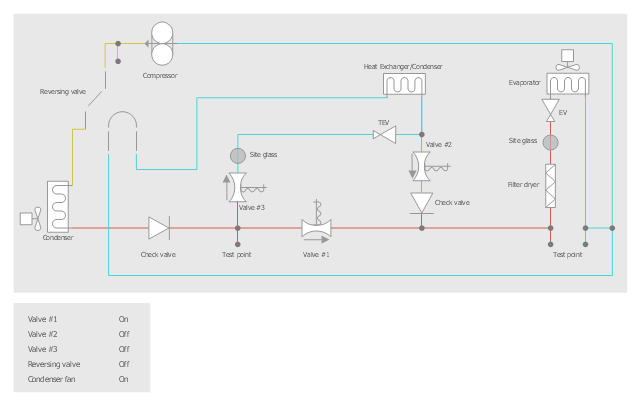
This HVAC schematics sample depicts the house cool mode of central air pool heater. It was drawn on the base of the HVAC schematics in the post "Central Air Pool Heater" from the Nathan Stratton's blog.
"With House Cool Mode, hot gas leaves the compressor runs through the reversing value into the condenser where it condenses into a liquid. Valve #1 is ON so liquid is able to leave the outside unit and run through the filter dryer and site glass into the evaporator upstairs in the house where the liquid flashes into a gas as it passes through the expansion valve and absorbs heat from the air passing through the evaporator. The cold gas travels downstairs and outside to the compressor and the cycle starts all over again." [robotics.net/ projects/ central-air-pool-heater/ ]
The HVAC schematics example "Central air pool heater" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the HVAC Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"With House Cool Mode, hot gas leaves the compressor runs through the reversing value into the condenser where it condenses into a liquid. Valve #1 is ON so liquid is able to leave the outside unit and run through the filter dryer and site glass into the evaporator upstairs in the house where the liquid flashes into a gas as it passes through the expansion valve and absorbs heat from the air passing through the evaporator. The cold gas travels downstairs and outside to the compressor and the cycle starts all over again." [robotics.net/ projects/ central-air-pool-heater/ ]
The HVAC schematics example "Central air pool heater" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the HVAC Plans solution from the Building Plans area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This PFD of jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating was redrawn from Wikipedia file: ConvLPGMerox.png. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:ConvKeroMerox.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported icense. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Merox is an acronym for mercaptan oxidation. It is a proprietary catalytic chemical process developed by UOP used in oil refineries and natural gas processing plants to remove mercaptans from LPG, propane, butanes, light naphthas, kerosene and jet fuel by converting them to liquid hydrocarbon disulfides.
The Merox process requires an alkaline environment which, in some of the process versions, is provided by an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a strong base, commonly referred to as caustic. In other versions of the process, the alkalinity is provided by ammonia, which is a weak base.
The catalyst in some versions of the process is a water-soluble liquid. In other versions, the catalyst is impregnated onto charcoal granules.
Processes within oil refineries or natural gas processing plants that remove mercaptans and/ or hydrogen sulfide (H2S) are commonly referred to as sweetening processes because they results in products which no longer have the sour, foul odors of mercaptans and hydrogen sulfide. The liquid hydrocarbon disulfides may remain in the sweetened products, they may be used as part of the refinery or natural gas processing plant fuel, or they may be processed further.
The Merox process is usually more economical than using a catalytic hydrodesulfurization process for much the same purpose." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ Merox]
The process flow diagram (PFD) example "Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported icense. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Merox is an acronym for mercaptan oxidation. It is a proprietary catalytic chemical process developed by UOP used in oil refineries and natural gas processing plants to remove mercaptans from LPG, propane, butanes, light naphthas, kerosene and jet fuel by converting them to liquid hydrocarbon disulfides.
The Merox process requires an alkaline environment which, in some of the process versions, is provided by an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a strong base, commonly referred to as caustic. In other versions of the process, the alkalinity is provided by ammonia, which is a weak base.
The catalyst in some versions of the process is a water-soluble liquid. In other versions, the catalyst is impregnated onto charcoal granules.
Processes within oil refineries or natural gas processing plants that remove mercaptans and/ or hydrogen sulfide (H2S) are commonly referred to as sweetening processes because they results in products which no longer have the sour, foul odors of mercaptans and hydrogen sulfide. The liquid hydrocarbon disulfides may remain in the sweetened products, they may be used as part of the refinery or natural gas processing plant fuel, or they may be processed further.
The Merox process is usually more economical than using a catalytic hydrodesulfurization process for much the same purpose." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ Merox]
The process flow diagram (PFD) example "Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This process flow diagram (PFD) example shows an amine treating system for the removal of gaseous hydrogen sulfide from gas streams. It is used in oil refineries and chemical plants. This PFD sample was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: AmineTreating.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:AmineTreating.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Amine gas treating, also known as gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from gases. It is a common unit process used in refineries, and is also used in petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries.
Processes within oil refineries or chemical processing plants that remove hydrogen sulfide are referred to as "sweetening" processes because the odor of the processed products is improved by the absence of hydrogen sulfide. An alternative to the use of amines involves membrane technology. Membranes are attractive since no reagents are consumed.
Many different amines are used in gas treating:
Diethanolamine (DEA),
Monoethanolamine (MEA),
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA),
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA),
Aminoethoxyethanol (Diglycolamine) (DGA).
The most commonly used amines in industrial plants are the alkanolamines DEA, MEA, and MDEA. These amines are also used in many oil refineries to remove sour gases from liquid hydrocarbons such as liquified petroleum gas (LPG)." [Amine gas treating. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Amine treating unit schematic diagram" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Amine gas treating, also known as gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from gases. It is a common unit process used in refineries, and is also used in petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries.
Processes within oil refineries or chemical processing plants that remove hydrogen sulfide are referred to as "sweetening" processes because the odor of the processed products is improved by the absence of hydrogen sulfide. An alternative to the use of amines involves membrane technology. Membranes are attractive since no reagents are consumed.
Many different amines are used in gas treating:
Diethanolamine (DEA),
Monoethanolamine (MEA),
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA),
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA),
Aminoethoxyethanol (Diglycolamine) (DGA).
The most commonly used amines in industrial plants are the alkanolamines DEA, MEA, and MDEA. These amines are also used in many oil refineries to remove sour gases from liquid hydrocarbons such as liquified petroleum gas (LPG)." [Amine gas treating. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Amine treating unit schematic diagram" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This is a schematic process flow diagram of the processes used in a typical oil refinery.
This process flow diagram (PFD) example was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: RefineryFlow.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:RefineryFlow.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units. In many ways, oil refineries use much of the technology of, and can be thought of, as types of chemical plants. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot (tank farm) at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.
An oil refinery is considered an essential part of the downstream side of the petroleum industry." [Oil refinery. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This process flow diagram (PFD) example was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: RefineryFlow.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:RefineryFlow.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units. In many ways, oil refineries use much of the technology of, and can be thought of, as types of chemical plants. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot (tank farm) at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.
An oil refinery is considered an essential part of the downstream side of the petroleum industry." [Oil refinery. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Electrical Symbols — Switches and Relays
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The mechanism of a switch may be operated directly by a human operator to control a circuit (for example, a light switch or a keyboard button), may be operated by a moving object such as a door-operated switch, or may be operated by some sensing element for pressure, temperature or flow. A relay is a switch that is operated by electricity. Switches are made to handle a wide range of voltages and currents; very large switches may be used to isolate high-voltage circuits in electrical substations. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw PRO make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.- Liquid Examples Clipart
- Gravity filtration of liquids | Chemistry Symbols and Meanings ...
- Example Of Liquid With Symbols
- Solid Liquid And Gas Examples
- Gravity filtration of liquids | Chemistry | Chemistry Symbols and ...
- Water cycle diagram | Solid Liquid Gas Clipart
- Hydraulic schematic | Hydraulic 4-ported 3-position valve template ...
- Gravity filtration of liquids | Water cycle diagram | Design elements ...
- Examples Of Solid Liquid And Gas
- Gravity filtration of liquids | Diagram Of Gravity Filtration Techniques
- Design elements - Laboratory equipment | Gravity filtration of liquids ...
- Solid Liquid Gas Chart
- Mechanical Drawing Symbols | Design elements - Fluid power ...
- Pumps - Vector stencils library | Liquid Container Symbol For ...
- Chemistry Symbols and Meanings | Design elements - Fluid power ...
- Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery | Gas To Liquid ...
- Gravity filtration of liquids | ConceptDraw PROJECT: Filter Tasks and ...
- Amine treating unit schematic diagram | Amine Liquid Treating Still ...
- Hydraulic schematic | Directional control valve | Directional control ...
- Mechanical Drawing Symbols | Design elements - Fluid power ...
-natural-gas-condensate---pfd.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-jet-fuel-mercaptan-oxidation-treating---pfd.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-amine-treating-unit-schematic-diagram.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-process-flow-diagram---typical-oil-refinery.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)