HelpDesk
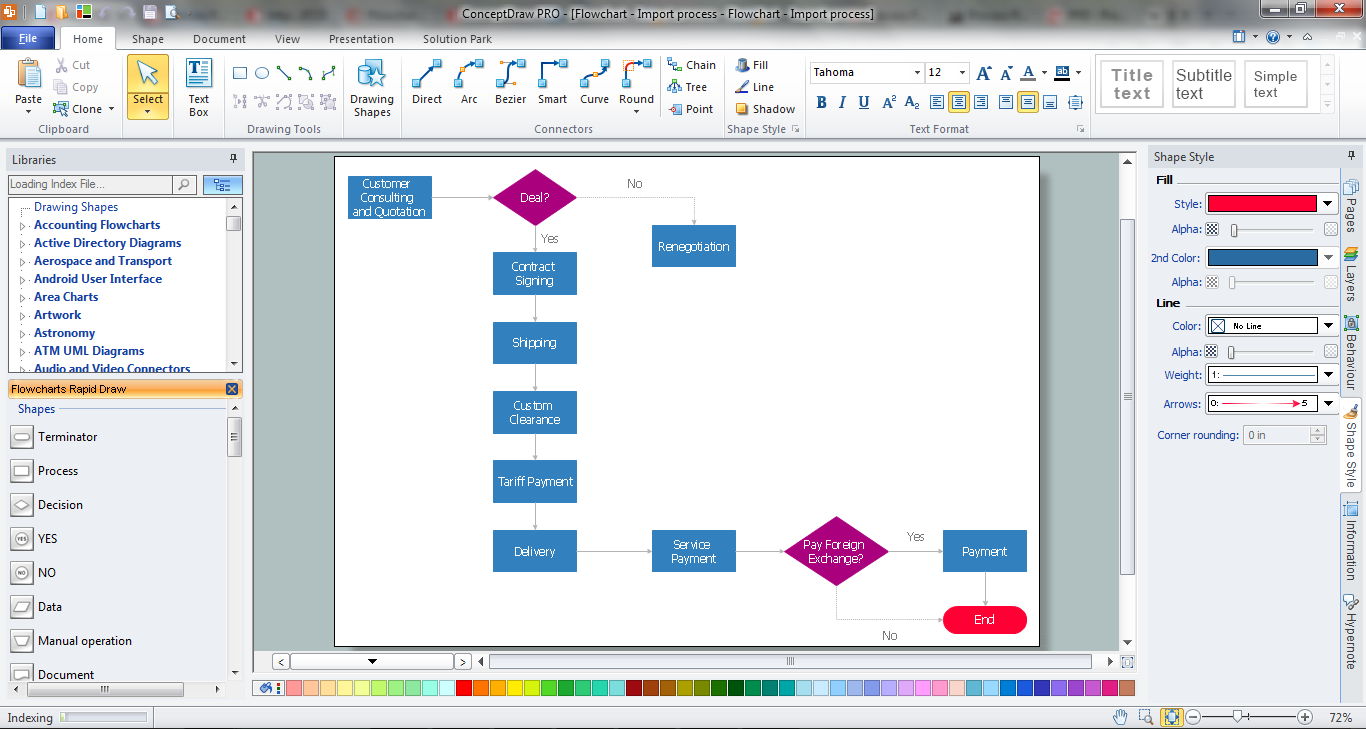
How to Draw a Process Flow Diagram
Process Flow diagrams are used in chemical and process engineering to show the flow of chemicals and the equipment involved in the process. When it comes to creating a process flow diagram, it's important to use software that is capable of describing a wide range of processes, using techniques and graphical notation that are easily recognized by engineering workers. An ideal drawing platform will utilize functions that can cope with the output of a high volume of engineering processes, that may change rapidly from development to implementation stages. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM , with the extended functionality of the Chemical and Process Engineering Diagrams solution, is the ideal medium for creating designs of this type. The Chemical and Process Engineering Diagrams solution complements this feature with a library of selected icons to represent various steps — all instantly recognizable and applicable to a wide user base. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM allows you to draw the Process Flow diagram easily using the set of special libraries."A process flow diagram (PFD) is a diagram commonly used in chemical and process engineering to indicate the general flow of plant processes and equipment. The PFD displays the relationship between major equipment of a plant facility and does not show minor details such as piping details and designations. Another commonly used term for a PFD is a flowsheet. ...
Process flow diagrams of multiple process units within a large industrial plant will usually contain less detail and may be called block flow diagrams or schematic flow diagrams." [Process flow diagram. Wikipedia]
The process flow diagram (PFD) template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Process flow diagrams of multiple process units within a large industrial plant will usually contain less detail and may be called block flow diagrams or schematic flow diagrams." [Process flow diagram. Wikipedia]
The process flow diagram (PFD) template for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This is a schematic process flow diagram of the processes used in a typical oil refinery.
This process flow diagram (PFD) example was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: RefineryFlow.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:RefineryFlow.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units. In many ways, oil refineries use much of the technology of, and can be thought of, as types of chemical plants. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot (tank farm) at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.
An oil refinery is considered an essential part of the downstream side of the petroleum industry." [Oil refinery. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This process flow diagram (PFD) example was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: RefineryFlow.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:RefineryFlow.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units. In many ways, oil refineries use much of the technology of, and can be thought of, as types of chemical plants. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot (tank farm) at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products.
An oil refinery is considered an essential part of the downstream side of the petroleum industry." [Oil refinery. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Process Flow Chart Symbols
Process Flow Chart is a visual diagram which shows the processes and relationships between the major components in a system, and uses for this the special process flow chart symbols: special shapes to represent different types of actions and process steps, lines and arrows to represent relationships and sequence of steps. It often named process flow diagram, it use colored flowchart symbols. It is incredibly convenient to use the ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software extended with Flowcharts Solution from the "Diagrams" Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park for designing professional looking Process Flow Charts.Process Flow Diagram Symbols
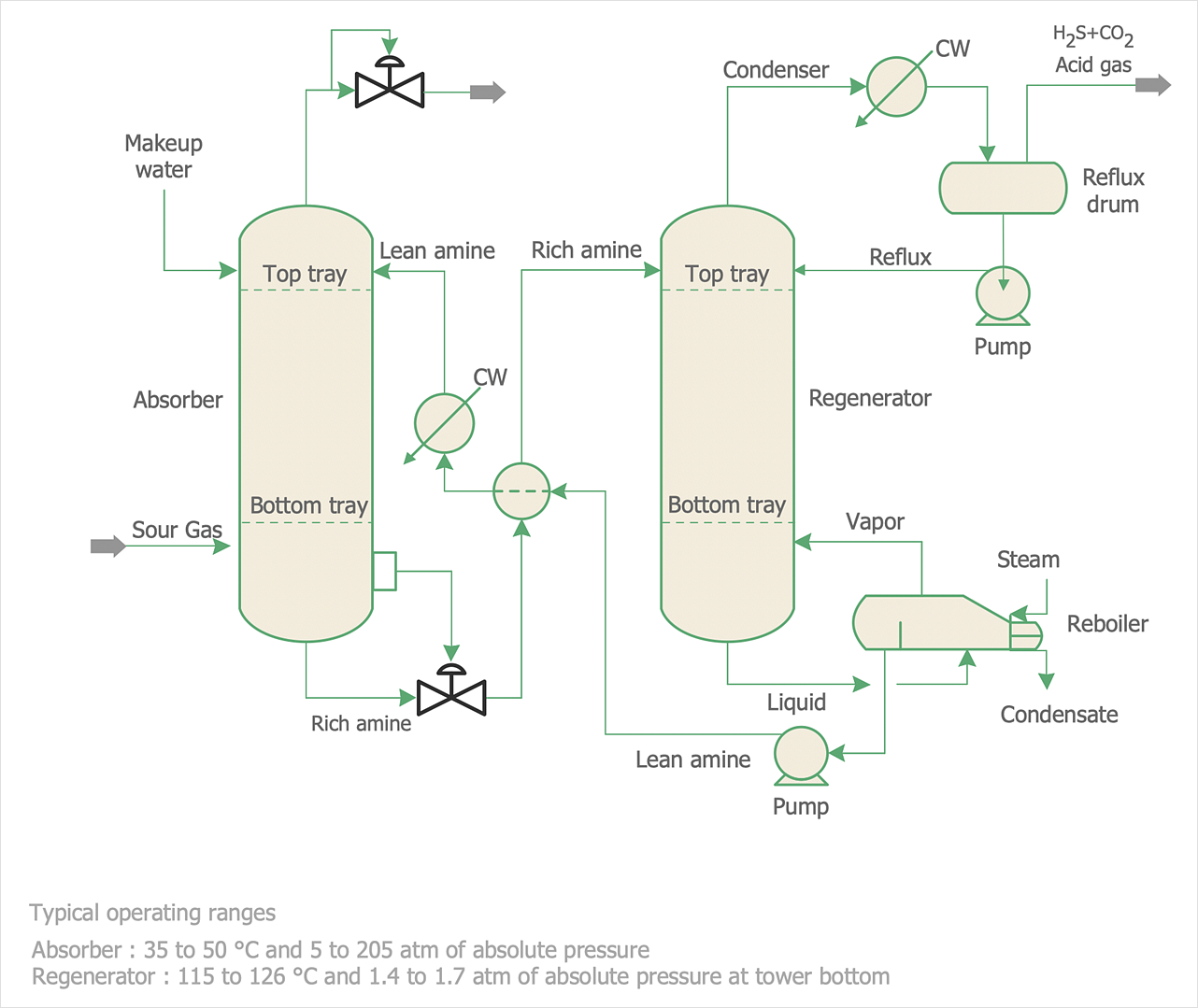
Chemical and Process Engineering Solution from the Industrial Engineering Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is a unique tool which contains variety of predesigned process flow diagram symbols for easy creating various Chemical and Process Flow Diagrams in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM.This process flow diagram (PFD) example shows an amine treating system for the removal of gaseous hydrogen sulfide from gas streams. It is used in oil refineries and chemical plants. This PFD sample was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: AmineTreating.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:AmineTreating.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Amine gas treating, also known as gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from gases. It is a common unit process used in refineries, and is also used in petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries.
Processes within oil refineries or chemical processing plants that remove hydrogen sulfide are referred to as "sweetening" processes because the odor of the processed products is improved by the absence of hydrogen sulfide. An alternative to the use of amines involves membrane technology. Membranes are attractive since no reagents are consumed.
Many different amines are used in gas treating:
Diethanolamine (DEA),
Monoethanolamine (MEA),
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA),
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA),
Aminoethoxyethanol (Diglycolamine) (DGA).
The most commonly used amines in industrial plants are the alkanolamines DEA, MEA, and MDEA. These amines are also used in many oil refineries to remove sour gases from liquid hydrocarbons such as liquified petroleum gas (LPG)." [Amine gas treating. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Amine treating unit schematic diagram" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Amine gas treating, also known as gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from gases. It is a common unit process used in refineries, and is also used in petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industries.
Processes within oil refineries or chemical processing plants that remove hydrogen sulfide are referred to as "sweetening" processes because the odor of the processed products is improved by the absence of hydrogen sulfide. An alternative to the use of amines involves membrane technology. Membranes are attractive since no reagents are consumed.
Many different amines are used in gas treating:
Diethanolamine (DEA),
Monoethanolamine (MEA),
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA),
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA),
Aminoethoxyethanol (Diglycolamine) (DGA).
The most commonly used amines in industrial plants are the alkanolamines DEA, MEA, and MDEA. These amines are also used in many oil refineries to remove sour gases from liquid hydrocarbons such as liquified petroleum gas (LPG)." [Amine gas treating. Wikipedia]
The PFD example "Amine treating unit schematic diagram" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This PFD of jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating was redrawn from Wikipedia file: ConvLPGMerox.png. [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:ConvKeroMerox.png]
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported icense. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Merox is an acronym for mercaptan oxidation. It is a proprietary catalytic chemical process developed by UOP used in oil refineries and natural gas processing plants to remove mercaptans from LPG, propane, butanes, light naphthas, kerosene and jet fuel by converting them to liquid hydrocarbon disulfides.
The Merox process requires an alkaline environment which, in some of the process versions, is provided by an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a strong base, commonly referred to as caustic. In other versions of the process, the alkalinity is provided by ammonia, which is a weak base.
The catalyst in some versions of the process is a water-soluble liquid. In other versions, the catalyst is impregnated onto charcoal granules.
Processes within oil refineries or natural gas processing plants that remove mercaptans and/ or hydrogen sulfide (H2S) are commonly referred to as sweetening processes because they results in products which no longer have the sour, foul odors of mercaptans and hydrogen sulfide. The liquid hydrocarbon disulfides may remain in the sweetened products, they may be used as part of the refinery or natural gas processing plant fuel, or they may be processed further.
The Merox process is usually more economical than using a catalytic hydrodesulfurization process for much the same purpose." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ Merox]
The process flow diagram (PFD) example "Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported icense. [creativecommons.org/ licenses/ by-sa/ 3.0/ deed.en]
"Merox is an acronym for mercaptan oxidation. It is a proprietary catalytic chemical process developed by UOP used in oil refineries and natural gas processing plants to remove mercaptans from LPG, propane, butanes, light naphthas, kerosene and jet fuel by converting them to liquid hydrocarbon disulfides.
The Merox process requires an alkaline environment which, in some of the process versions, is provided by an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a strong base, commonly referred to as caustic. In other versions of the process, the alkalinity is provided by ammonia, which is a weak base.
The catalyst in some versions of the process is a water-soluble liquid. In other versions, the catalyst is impregnated onto charcoal granules.
Processes within oil refineries or natural gas processing plants that remove mercaptans and/ or hydrogen sulfide (H2S) are commonly referred to as sweetening processes because they results in products which no longer have the sour, foul odors of mercaptans and hydrogen sulfide. The liquid hydrocarbon disulfides may remain in the sweetened products, they may be used as part of the refinery or natural gas processing plant fuel, or they may be processed further.
The Merox process is usually more economical than using a catalytic hydrodesulfurization process for much the same purpose." [en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ Merox]
The process flow diagram (PFD) example "Jet fuel mercaptan oxidation treating" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
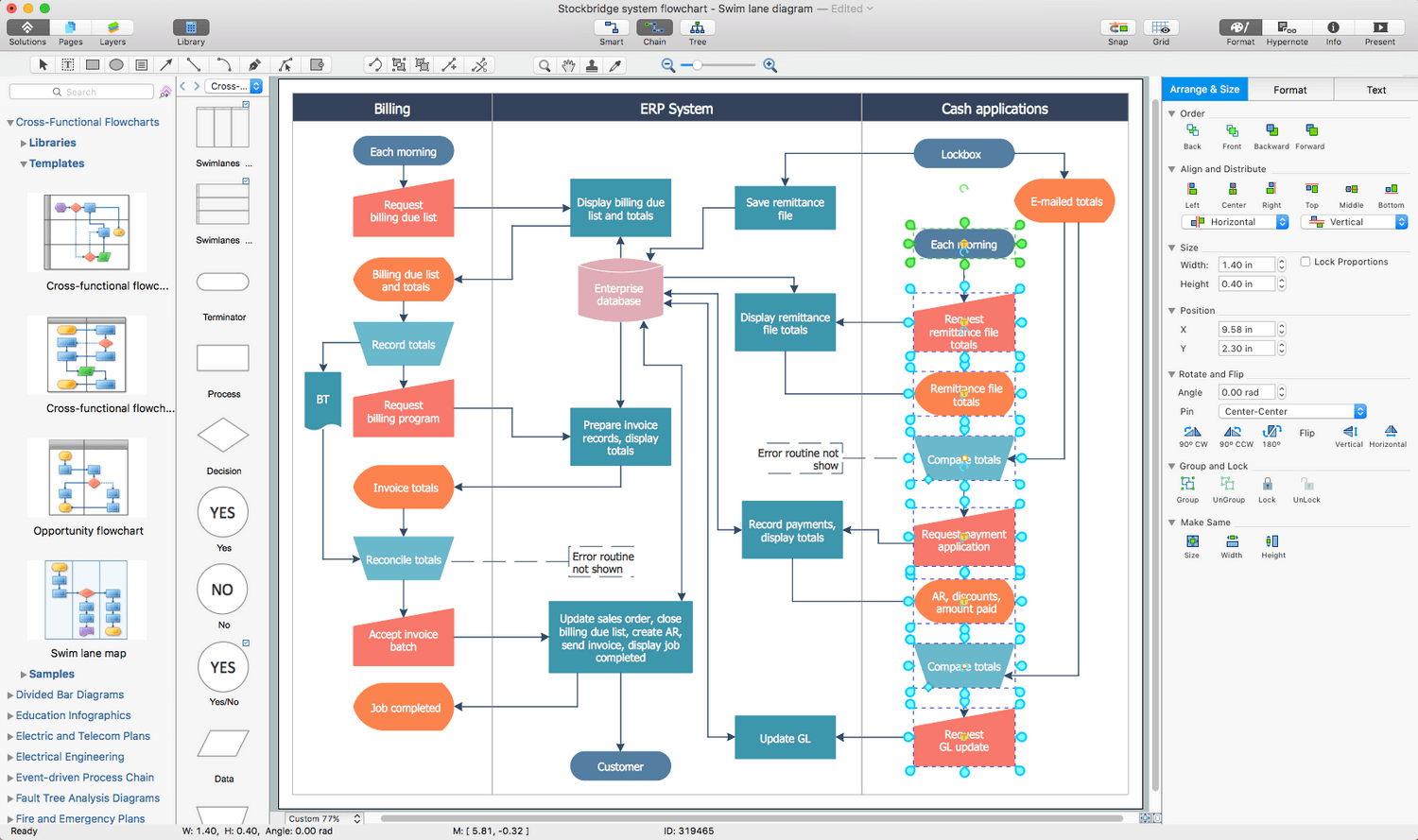
Process Flowchart
The main reason of using Process Flowchart or PFD is to show relations between major parts of the system. Process Flowcharts are used in process engineering and chemical industry where there is a requirement of depicting relationships between major components only and not include minor parts. Process Flowcharts for single unit or multiple units differ in their structure and implementation. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is Professional business process mapping software for making Process flowcharts, Process flow diagram, Workflow diagram, flowcharts and technical illustrations for business documents and also comprehensive visio for mac application. Easier define and document basic work and data flows, financial, production and quality management processes to increase efficiency of your business with ConcepDraw DIAGRAM. Business process mapping software with Flowchart Maker ConceptDraw DIAGRAM includes extensive drawing tools, rich examples and templates, process flowchart symbols and shape libraries, smart connectors that allow you create the flowcharts of complex processes, process flow diagrams, procedures and information exchange. Process Flowchart Solution is project management workflow tools which is part ConceptDraw Project marketing project management software. Drawing charts, diagrams, and network layouts has long been the monopoly of Microsoft Visio, making Mac users to struggle when needing such visio alternative like visio for mac, it requires only to view features, make a minor edit to, or print a diagram or chart. Thankfully to MS Visio alternative like ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software, this is cross-platform charting and business process management tool, now visio alternative for making sort of visio diagram is not a problem anymore however many people still name it business process visio tools.
Process Flow Diagram
A Process Flow Diagram (PFD) is a diagram which shows the relationships between the main components in a system. Process Flow Diagrams are widely used by engineers in chemical and process engineering, they allows to indicate the general flow of plant process streams and equipment, helps to design the petroleum refineries, petrochemical and chemical plants, natural gas processing plants, and many other industrial facilities. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with powerful tools of Flowcharts Solution from the "Diagrams" Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is effective for drawing: Process Flow Diagram, Flow Process Diagram, Business Process Flow Diagrams.Business Process Flow Diagram
Business Process Flow Diagram is a graphical presentation of business processes and process flows. It is one of the main tool of business analysis and business process re-engineering that lets identify and easy understand process flows within organization. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM extended with Business Process Workflow Diagrams solution from the Business Processes area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is a powerful software which lets easy design Business Process Flow Diagram of any complexity.This PFD sample was redesigned from the Wikipedia file: NaturalGasCondensate.png.
"This is a schematic flow diagram of a typical facility for separating and recovering liquid condensate from raw natural gas."
[en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:NaturalGasCondensate.png]
"Natural-gas condensate is a low-density mixture of hydrocarbon liquids that are present as gaseous components in the raw natural gas produced from many natural gas fields. It condenses out of the raw gas if the temperature is reduced to below the hydrocarbon dew point temperature of the raw gas.
The natural gas condensate is also referred to as simply condensate, or gas condensate, or sometimes natural gasoline because it contains hydrocarbons within the gasoline boiling range. Raw natural gas may come from any one of three types of gas wells:
(1) Crude oil wells - Raw natural gas that comes from crude oil wells is called associated gas. This gas can exist separate from the crude oil in the underground formation, or dissolved in the crude oil.
(2) Dry gas wells - These wells typically produce only raw natural gas that does not contain any hydrocarbon liquids. Such gas is called non-associated gas.
(3) Condensate wells - These wells produce raw natural gas along with natural gas liquid. Such gas is also non-associated gas and often referred to as wet gas." [Natural-gas condensate. Wikipedia]
The process flow diagram example "Natural gas condensate - PFD" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"This is a schematic flow diagram of a typical facility for separating and recovering liquid condensate from raw natural gas."
[en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/ File:NaturalGasCondensate.png]
"Natural-gas condensate is a low-density mixture of hydrocarbon liquids that are present as gaseous components in the raw natural gas produced from many natural gas fields. It condenses out of the raw gas if the temperature is reduced to below the hydrocarbon dew point temperature of the raw gas.
The natural gas condensate is also referred to as simply condensate, or gas condensate, or sometimes natural gasoline because it contains hydrocarbons within the gasoline boiling range. Raw natural gas may come from any one of three types of gas wells:
(1) Crude oil wells - Raw natural gas that comes from crude oil wells is called associated gas. This gas can exist separate from the crude oil in the underground formation, or dissolved in the crude oil.
(2) Dry gas wells - These wells typically produce only raw natural gas that does not contain any hydrocarbon liquids. Such gas is called non-associated gas.
(3) Condensate wells - These wells produce raw natural gas along with natural gas liquid. Such gas is also non-associated gas and often referred to as wet gas." [Natural-gas condensate. Wikipedia]
The process flow diagram example "Natural gas condensate - PFD" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemical and Process Engineering solution from the Chemical and Process Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Chemical and Process Engineering
Chemical and Process Engineering
This chemical engineering solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM.9.5 (or later) with process flow diagram symbols, samples, process diagrams templates and libraries of design elements for creating process and instrumentation diagrams, block flow diagrams (BFD
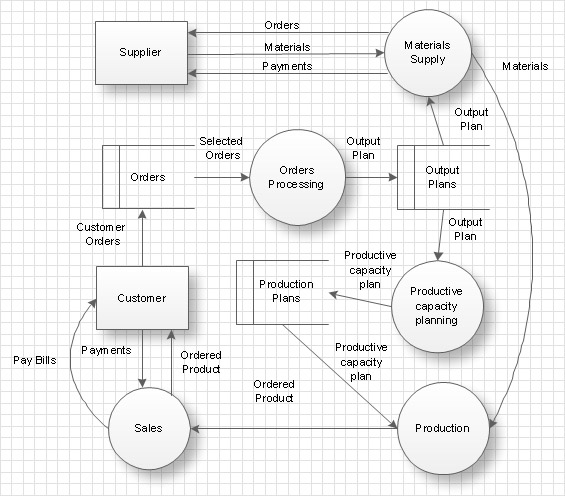
Data Flow Diagram
Data Flow Diagram (DFD) is the part of the Structured Systems Analysis and Design Methodology (SSADM), which is intended for information systems projection and analysis. Data Flow Diagrams allow graphically represent the data flows in information system and analyze the data processing during the structural projection. This type of diagrams lets visually show a work of information system and results of this work, it is often used in connection with human processes and can be displayed as Workflow diagram. Data Flow Diagram visualizes processes and functions, external entities, data depositories, and data flows connecting these elements and indicating direction and data character. Each of these elements used for DFD has its own graphical notation. There are two notations to draw DFDs - Yourdon & Coad and Gane & Sarson. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM extended with Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) solution from Software Developmant area is ideal for designing professional looking DFDs, which can be then easily exported in various formats.ConceptDraw DIAGRAM
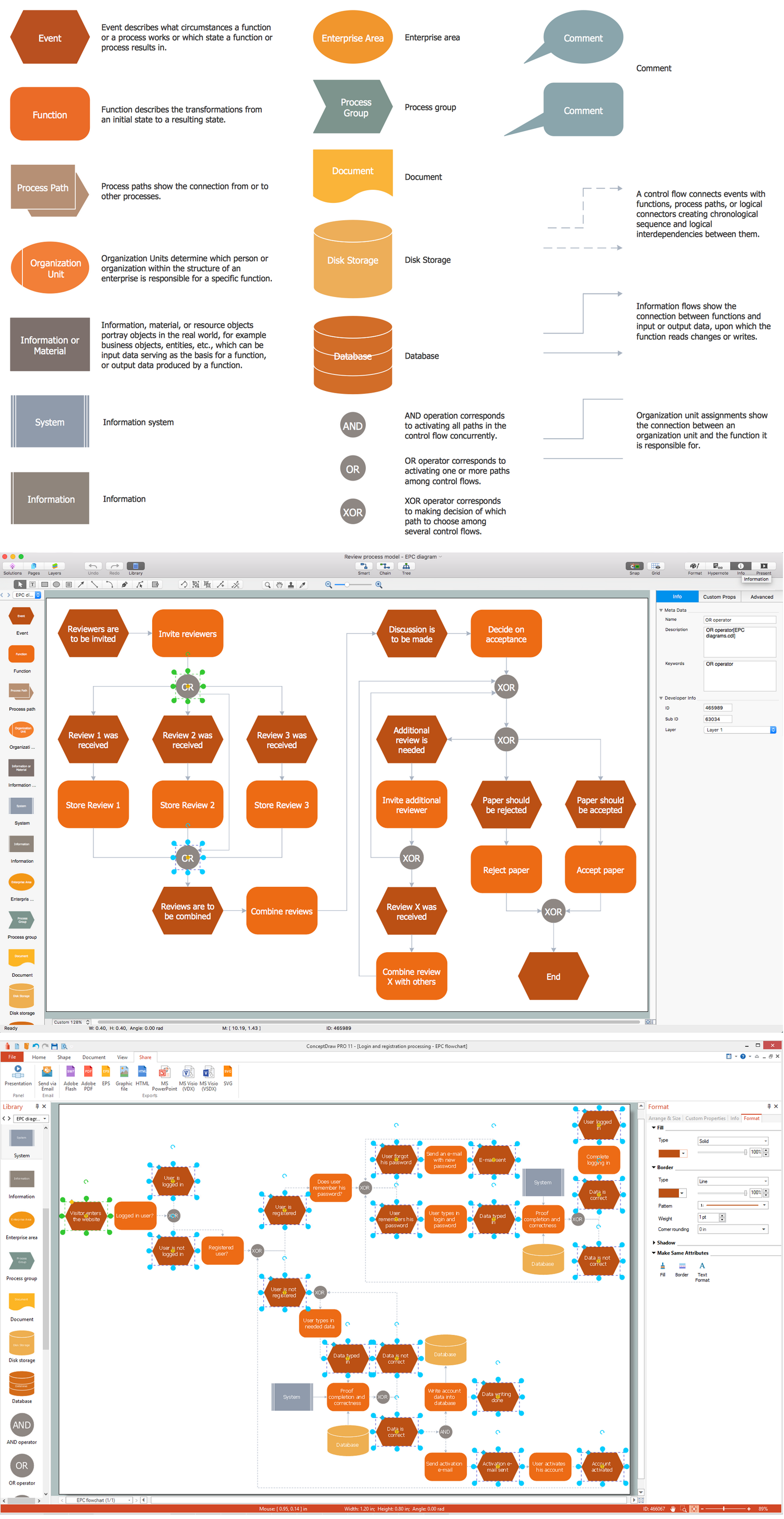
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is a powerful business and technical diagramming software tool that enables you to design professional-looking graphics, diagrams, flowcharts, floor plans and much more in just minutes. Maintain business processes performance with clear visual documentation. Effectively present and communicate information in a clear and concise manner with ConceptDraw DIAGRAM.Business process Flow Chart — Event-Driven Process chain (EPC) diagrams
Event-Driven Process chain Diagrams for improvement throughout an organisation. Best software for Process Flow Diagram. The Event-driven Process Chain (EPC) Diagrams allows managers to plan processes and resources.Simple Flow Chart
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Flowcharts Solution from the 'Diagrams' area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is a powerful tool for drawing Flow Charts of any complexity you need. Irrespective of whether you want to draw a Simple Flow Chart or large complex Flow Diagram, you estimate to do it without efforts thanks to the extensive drawing tools of Flowcharts solution, there are professional flowchart symbols and basic flowchart symbols. This sample shows the Gravitational Search Algorithm (GSA) that is the optimization algorithm.Process Flow Chart
A Process Flow Chart is a type of flowchart which is mostly used in industrial, chemical and process engineering for illustrating high-level processes, major plant processes and not shows minor details. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Flowcharts Solution from the "Diagrams" Area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is the best way to create Process Flow Chart and other types of flowcharts.UML 2 4 Process Flow Diagram
This sample was created in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software using the UML Activity Diagram library of the Rapid UML Solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.Swim Lane Diagrams
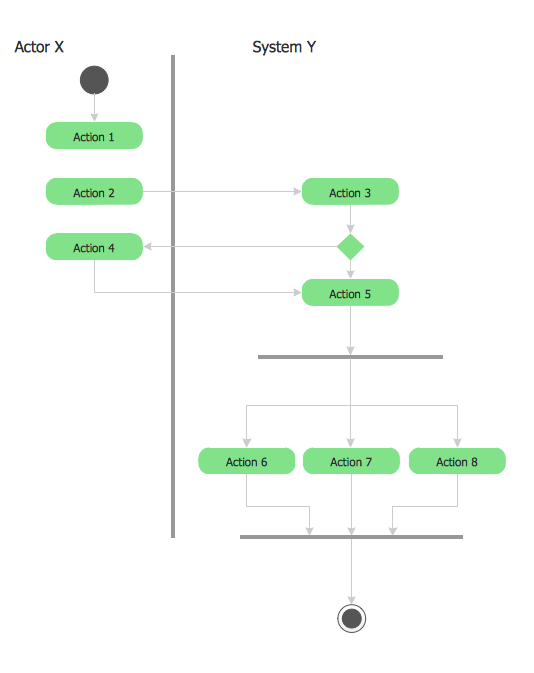
Swim Lane Diagrams are the kind of process flow diagrams and effective tool for documenting the business processes required for any business company for its productive work, for easy defining the weak points, reasons of defects, or delays during the process. Swim Lane Diagram is based on the IDEF3 standard and was developed primarily for using in projecting. Its name derives from the use of horizontal or vertical lanes. The blocks that denote the parts of the processes are arranged within definite lanes according to the belonging to responsible worker. So the process of any complexity is visually divided into the parts and represented with indication the responsibility for execution of each part. This significantly facilitates the comprehension of its work. Use the ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software and predesigned vector objects from the Swim Lanes library of Business Process Mapping Solution included to ConceptDraw Solution Park to easy develop Swim Lanes Flowcharts and Diagrams, for modeling and documenting the business processes in a simple and visual graphic form.Wiring Diagrams with ConceptDraw DIAGRAM
A Wiring Diagram is a comprehensive schematic that depicts the electrical circuit system, shows all the connectors, wiring, signal connections (buses), terminal boards between electrical or electronic components and devices of the circuit. Wiring Diagram illustrates how the components are connected electrically and identifies the wires by colour coding or wire numbers. These diagrams are necessary and obligatory for identifying and fixing faults of electrical or electronic circuits, and their elimination. For designing Wiring Diagrams are used the standardized symbols representing electrical components and devices. ConceptDraw Solution Park offers the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area with 26 libraries of graphics design elements and electrical schematic symbols for easy drawing various Wiring Diagrams, Electrical Circuit and Wiring Blueprints, Electrical and Telecom schematics of any complexity, Electrical Engineering Diagrams, Power Systems Diagrams, Repair Diagrams, Maintenance Schemes, etc. in ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software.- Process Flow Diagram Symbols | How to Create a Mechanical ...
- Oil And Gas Process Flow Diagram
- Data Flow Diagram | Process Flowchart | Swim Lane Diagrams ...
- Process Flow Diagram Symbols | Design elements - Heating ...
- Process Flowchart | Process Engineering | Process Flow Diagram ...
- Process Flow Diagram
- Process Flow Diagram Symbols | Mechanical Drawing Symbols ...
- Process flow diagram - Typical oil refinery | Natural gas condensate ...
- Process Flow Diagram Symbols | Chemical Engineering | Chemical ...
- Process Flow Diagram Symbols | Process Flow Diagram | Technical ...
- Process Flowchart | How to Draw a Process Flow Diagram in ...
- Process Flowchart | Process Flow Diagram Symbols | Engineering ...
- Process Flow Diagram Symbols | Chemical Engineering | Process ...
- Process Flow Template
- Process Flowchart | Flowchart Components | Process Flow Diagram ...
- Process Flow Diagram Symbols
- How to Draw a Chemical Process Flow Diagram | How to Draw a ...
- Process Flow Diagram Symbols | How to Draw a Chemical Process ...
- Chemical and Process Engineering | Technical Drawing Software ...
-template-process-flow-diagram-(pfd)-template.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-process-flow-diagram---typical-oil-refinery.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-amine-treating-unit-schematic-diagram.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-jet-fuel-mercaptan-oxidation-treating---pfd.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)

-natural-gas-condensate---pfd.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)