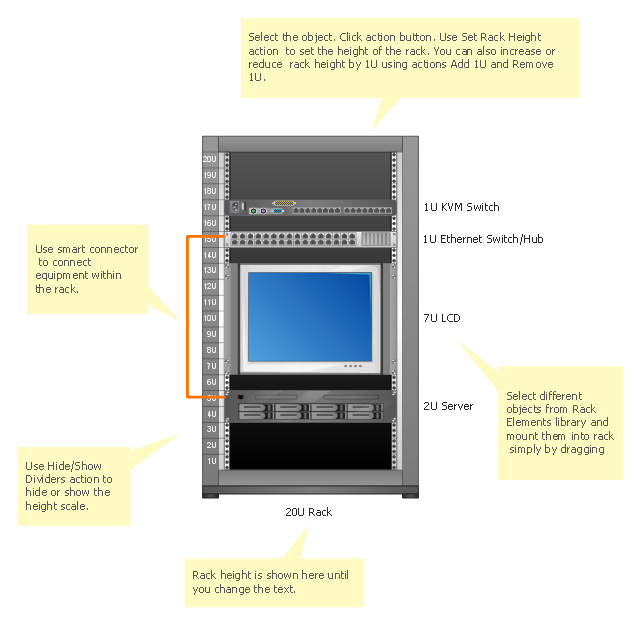
Rack Diagrams
Rack Diagrams visualize the rack mounting of computer and network equipment as the drawing of frontal view of the rack with equipment installed. They are used for choosing the equipment or racks to buy, and help to organize equipment on the racks virtually, without the real installation.
Network Diagramming Software for Design Rack Diagrams
Rack Diagrams visualize the rack mounting of computer and network equipment as the drawing of frontal view of the rack with equipment installed. They are used for choosing the equipment or racks to buy, and help to organize equipment on the racks virtually, without the real installation. Network Diagramming Software - ConceptDraw PRO is perfect for software designers and software developers who need to draw Rack Diagrams.
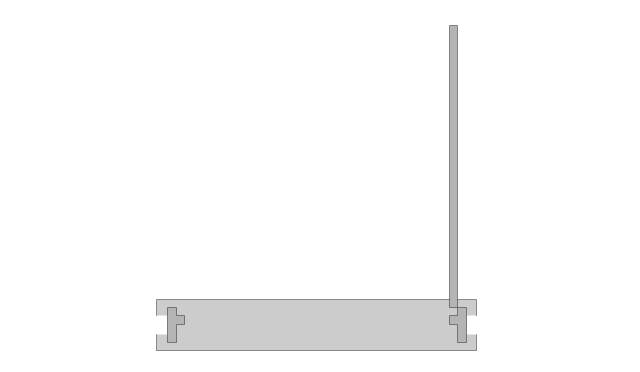
This rack diagram example was redesigned from the Wikimedia Commons file: Rackunit.svg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Rackunit.svg]
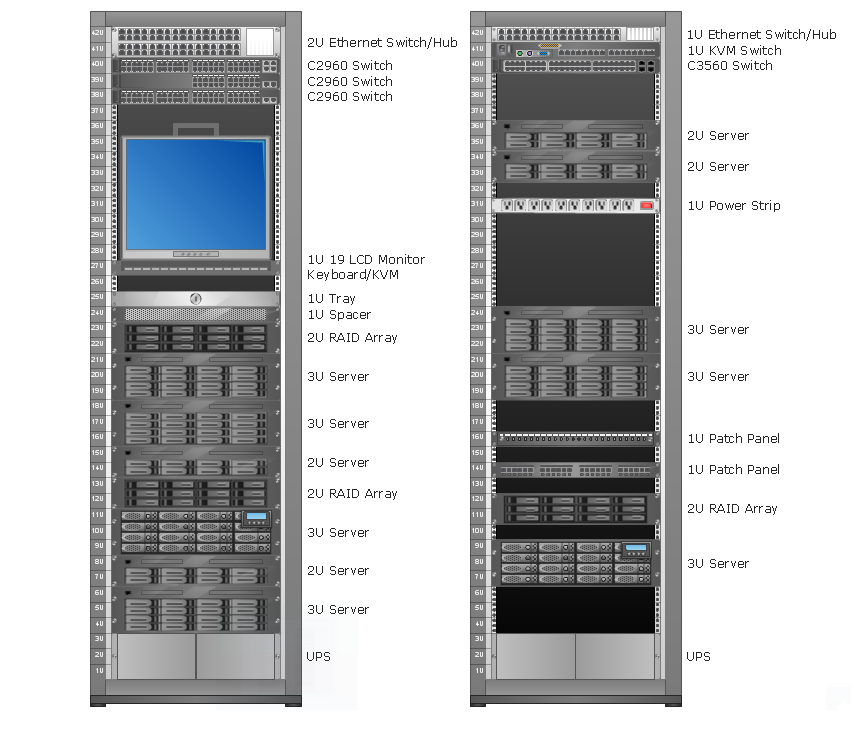
Rack with sample component sizes including an A/ V half-rack unit.
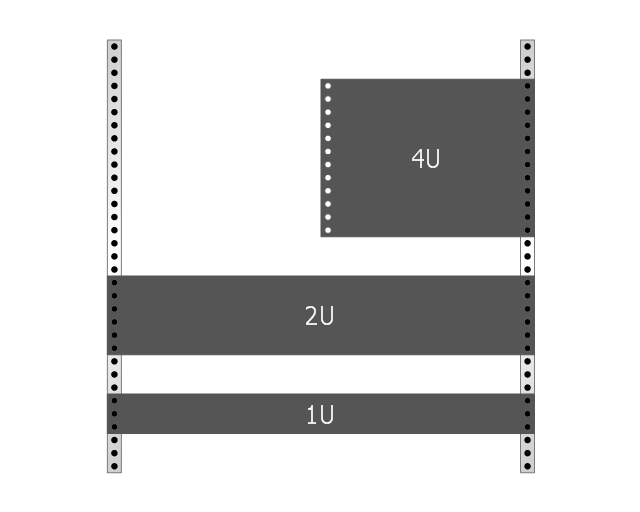
"A rack unit, U or RU as a unit of measure describes the height of equipment[which?] designed to mount in a 19-inch rack or a 23-inch rack. The 19-inch (482.6 mm) or 23-inch (584.2 mm) dimension reflects the width of the equipment mounting-frame in the rack including the frame; the width of the equipment that can be mounted inside the rack is less. One rack unit is 1.75 inches (4.445 cm) high. (This equates to one vershok, an obsolete unit of measurement used officially in Russia until 1924.)
The size of a piece of rack-mounted equipment is frequently described as a number in "U". For example, one rack unit is often referred to as "1U", 2 rack units as "2U" and so on." [Rack unit. Wikipedia]
The example "Rack with sample component sizes including an A/ V half-rack unit" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rack Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Rack with sample component sizes including an A/ V half-rack unit.
"A rack unit, U or RU as a unit of measure describes the height of equipment[which?] designed to mount in a 19-inch rack or a 23-inch rack. The 19-inch (482.6 mm) or 23-inch (584.2 mm) dimension reflects the width of the equipment mounting-frame in the rack including the frame; the width of the equipment that can be mounted inside the rack is less. One rack unit is 1.75 inches (4.445 cm) high. (This equates to one vershok, an obsolete unit of measurement used officially in Russia until 1924.)
The size of a piece of rack-mounted equipment is frequently described as a number in "U". For example, one rack unit is often referred to as "1U", 2 rack units as "2U" and so on." [Rack unit. Wikipedia]
The example "Rack with sample component sizes including an A/ V half-rack unit" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rack Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
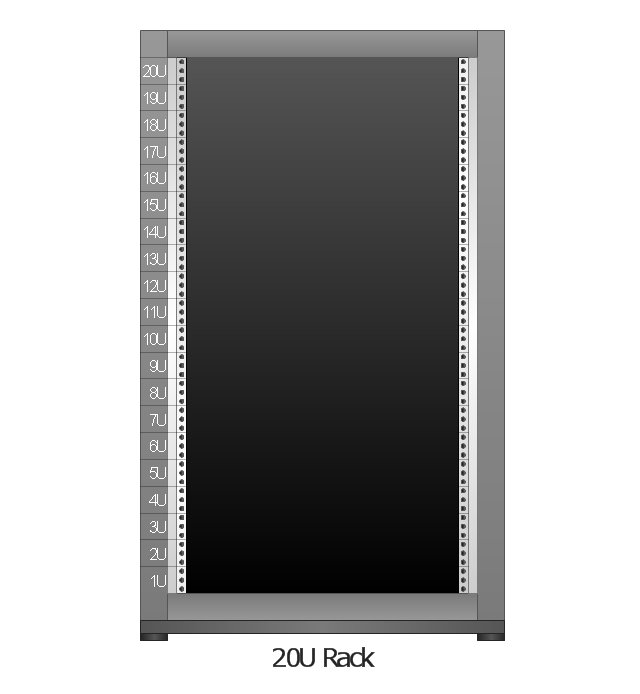
Server rack diagrams visualize the the rack mounting of computer and network equipment as the drawing of frontal view of the rack with equipment installed. They are used for choosing the equipment or racks to buy, and help to organize equipment on the racks virtually, without the real installation.
"A 19-inch rack is a standardized frame or enclosure for mounting multiple equipment modules. Each module has a front panel that is 19 inches (482.6 mm) wide, including edges or ears that protrude on each side which allow the module to be fastened to the rack frame with screws." [19-inch rack. Wikipedia]
"A rack unit, U or RU is a unit of measure that describes the height of equipment designed to mount in a 19-inch rack or a 23-inch rack. The 19-inch (482.6 mm) or 23-inch (584.2 mm) dimension refers to the width of the equipment mounting frame in the rack including the frame; the width of the equipment that can be mounted inside the rack is less. One rack unit is 1.75 inches (4.445 cm) high.
The size of a piece of rack-mounted equipment is frequently described as a number in "U". For example, one rack unit is often referred to as "1U", 2 rack units as "2U" and so on.
A typical full size rack is 42U, which means it holds just over 6 feet of equipment, and a typical "half-height" rack would be 18-22U, or around 3 feet high." [Rack unit. Wikipedia]
The rack diagram template is included in the Rack Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A 19-inch rack is a standardized frame or enclosure for mounting multiple equipment modules. Each module has a front panel that is 19 inches (482.6 mm) wide, including edges or ears that protrude on each side which allow the module to be fastened to the rack frame with screws." [19-inch rack. Wikipedia]
"A rack unit, U or RU is a unit of measure that describes the height of equipment designed to mount in a 19-inch rack or a 23-inch rack. The 19-inch (482.6 mm) or 23-inch (584.2 mm) dimension refers to the width of the equipment mounting frame in the rack including the frame; the width of the equipment that can be mounted inside the rack is less. One rack unit is 1.75 inches (4.445 cm) high.
The size of a piece of rack-mounted equipment is frequently described as a number in "U". For example, one rack unit is often referred to as "1U", 2 rack units as "2U" and so on.
A typical full size rack is 42U, which means it holds just over 6 feet of equipment, and a typical "half-height" rack would be 18-22U, or around 3 feet high." [Rack unit. Wikipedia]
The rack diagram template is included in the Rack Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
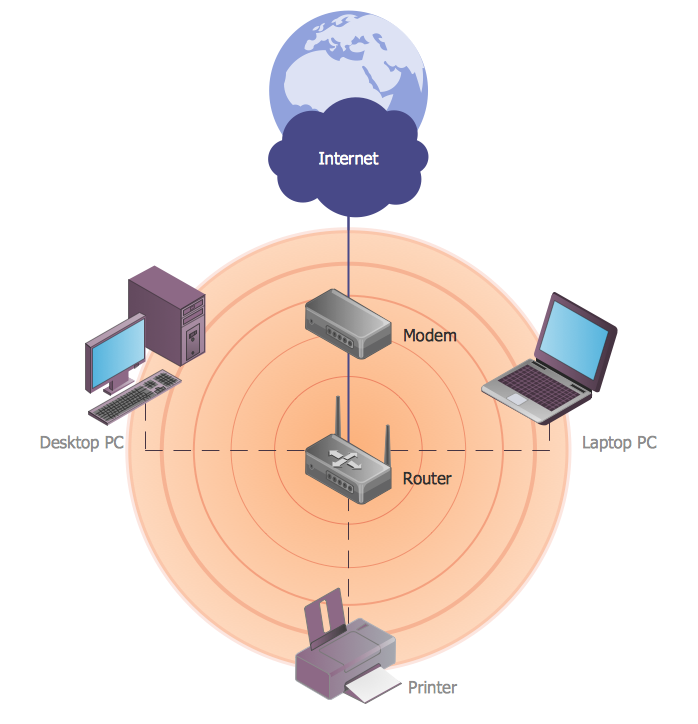
WLAN
ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Wireless Networks Solution gives the ability to its users to create professional looking WLAN schemes and diagrams quick and easy.The vector stencils library "Rack diagrams" contains 33 rack design elements for drawing the computer network server rack diagrams.
"A 19-inch rack is a standardized frame or enclosure for mounting multiple equipment modules. Each module has a front panel that is 19 inches (482.6 mm) wide, including edges or ears that protrude on each side which allow the module to be fastened to the rack frame with screws. ...
Equipment designed to be placed in a rack is typically described as rack-mount, rack-mount instrument, a rack mounted system, a rack mount chassis, subrack, rack mountable, or occasionally simply shelf. The height of the electronic modules is also standardized as multiples of 1.75 inches (44.45 mm) or one rack unit or U (less commonly RU). The industry standard rack cabinet is 42U tall. ...
19-inch racks in 2-post or 4-post form hold most equipment in modern data centers, ISP facilities and professionally designed corporate server rooms. They allow for dense hardware configurations without occupying excessive floorspace or requiring shelving." [19-inch rack. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Rack diagrams - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rack Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"A 19-inch rack is a standardized frame or enclosure for mounting multiple equipment modules. Each module has a front panel that is 19 inches (482.6 mm) wide, including edges or ears that protrude on each side which allow the module to be fastened to the rack frame with screws. ...
Equipment designed to be placed in a rack is typically described as rack-mount, rack-mount instrument, a rack mounted system, a rack mount chassis, subrack, rack mountable, or occasionally simply shelf. The height of the electronic modules is also standardized as multiples of 1.75 inches (44.45 mm) or one rack unit or U (less commonly RU). The industry standard rack cabinet is 42U tall. ...
19-inch racks in 2-post or 4-post form hold most equipment in modern data centers, ISP facilities and professionally designed corporate server rooms. They allow for dense hardware configurations without occupying excessive floorspace or requiring shelving." [19-inch rack. Wikipedia]
The clip art example "Rack diagrams - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rack Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
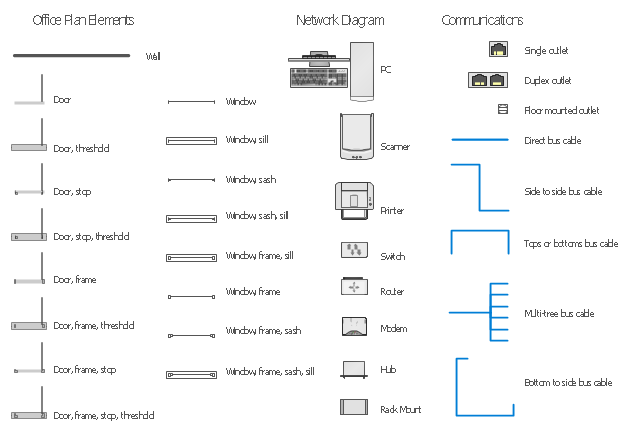
The vector stencils library "Network layout floorplan" contain 34 symbol icons for drawing computer network floor plans, communication equipment layouts, and structured cabling diagrams.
"Structured cabling is building or campus telecommunications cabling infrastructure that consists of a number of standardized smaller elements (hence structured) called subsystems. ...
Structured cabling design and installation is governed by a set of standards that specify wiring data centers, offices, and apartment buildings for data or voice communications using various kinds of cable, most commonly category 5e (CAT-5e), category 6 (CAT-6), and fibre optic cabling and modular connectors. These standards define how to lay the cabling in various topologies in order to meet the needs of the customer, typically using a central patch panel (which is normally 19 inch rack-mounted), from where each modular connection can be used as needed. Each outlet is then patched into a network switch (normally also rack-mounted) for network use or into an IP or PBX (private branch exchange) telephone system patch panel." [Structured cabling. Wikipedia]
The design elements example "Network layout floorplan - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Network Layout Floor Plans solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Structured cabling is building or campus telecommunications cabling infrastructure that consists of a number of standardized smaller elements (hence structured) called subsystems. ...
Structured cabling design and installation is governed by a set of standards that specify wiring data centers, offices, and apartment buildings for data or voice communications using various kinds of cable, most commonly category 5e (CAT-5e), category 6 (CAT-6), and fibre optic cabling and modular connectors. These standards define how to lay the cabling in various topologies in order to meet the needs of the customer, typically using a central patch panel (which is normally 19 inch rack-mounted), from where each modular connection can be used as needed. Each outlet is then patched into a network switch (normally also rack-mounted) for network use or into an IP or PBX (private branch exchange) telephone system patch panel." [Structured cabling. Wikipedia]
The design elements example "Network layout floorplan - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Network Layout Floor Plans solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
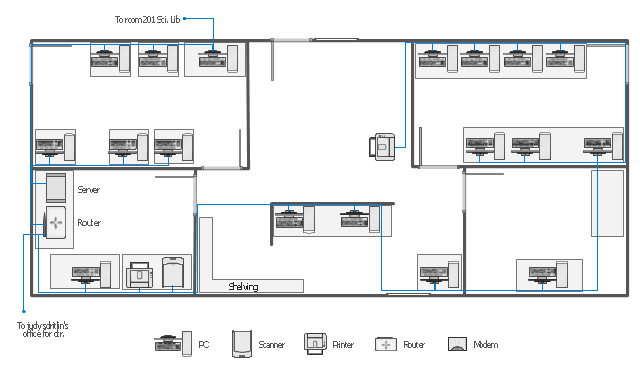
This network layout floorplan example was drawn on the base of the picture "Ethernet cable layout" illustrating "UGA Technical Network Liaison Handbook" from the website of the University of Georgia.
[netinfo.uga.edu/ tnlhand/ landiag.gif]
"The Ethernet physical layer is the physical layer component of the Ethernet family of computer network standards.
The Ethernet physical layer evolved over a considerable time span and encompasses quite a few physical media interfaces and several magnitudes of speed. The speed ranges from 1 Mbit/ s to 100 Gbit/ s, while the physical medium can range from bulky coaxial cable to twisted pair and optical fiber. In general, network protocol stack software will work similarly on all physical layers.
10-gigabit Ethernet was already used in both enterprise and carrier networks by 2007, with 40 Gbit/ s and 100 Gbit/ s Ethernet ratified." [Ethernet physical layer. Wikipedia]
The network layout floorplan example "Ethernet cable layout" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Network Layout Floor Plans solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
[netinfo.uga.edu/ tnlhand/ landiag.gif]
"The Ethernet physical layer is the physical layer component of the Ethernet family of computer network standards.
The Ethernet physical layer evolved over a considerable time span and encompasses quite a few physical media interfaces and several magnitudes of speed. The speed ranges from 1 Mbit/ s to 100 Gbit/ s, while the physical medium can range from bulky coaxial cable to twisted pair and optical fiber. In general, network protocol stack software will work similarly on all physical layers.
10-gigabit Ethernet was already used in both enterprise and carrier networks by 2007, with 40 Gbit/ s and 100 Gbit/ s Ethernet ratified." [Ethernet physical layer. Wikipedia]
The network layout floorplan example "Ethernet cable layout" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Network Layout Floor Plans solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Cisco Network Diagram Software
ConceptDraw PRO is the best network diagram software. To design the Cisco Network Diagrams and visualize the computer networks topology use ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Cisco Network Diagrams solution for ConceptDraw PRO Solution Park.Cisco Network Examples and Templates
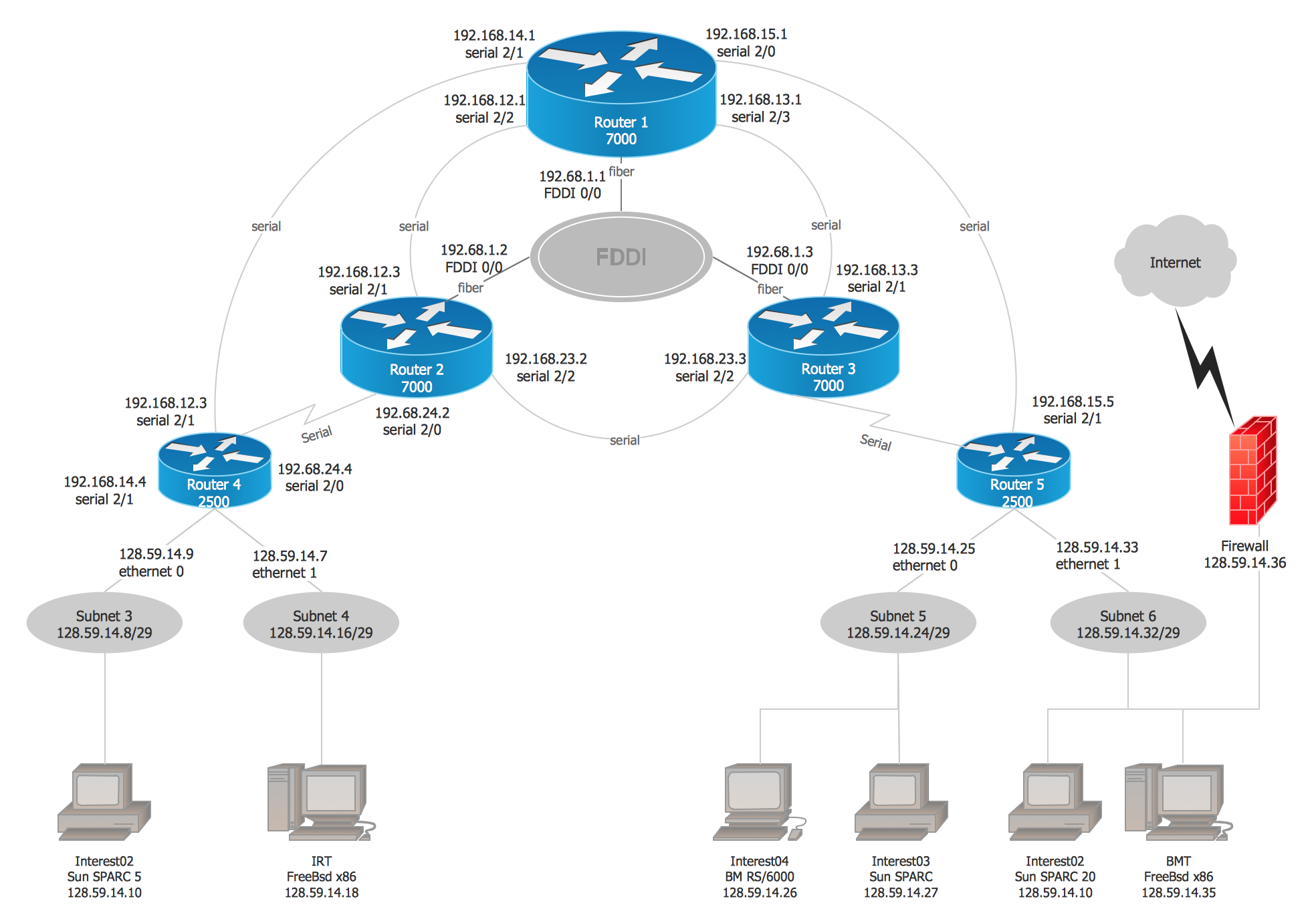
The Cisco Network Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park provides a wide collection of predesigned templates and samples that help you to create the Cisco Network Diagrams in one moment.This IVR diagram sample illustrates how ENUM works by giving an example: Subscriber A sets out to call Subscriber B:
1. The User Agent of an ENUM-enabled subscriber terminal device, or a PBX, or a Gateway, translates the request for the number +34 98 765 4321 in accordance with the rule described in RFC 3761 into the ENUM domain 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.4.3.e164.arpa.
2. A request is sent to the Domain Name System (DNS) asking it to look up the ENUM domain 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.4.3.e164.arpa.
3. The query returns a result in the form of so called Naming Authority Pointer Resource NAPTR records, as per RFC 3403. In the example above, the response is an address that can be reached in the Internet using the VoIP protocol, SIP per RFC 3261.
4. The terminal application now sets up a communication link, and the call is routed via the Internet.
This IVR diagram sample was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Ejemplo ENUM.jpg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Ejemplo_ ENUM.jpg]
"Being able to dial telephone numbers the way customers have come to expect is considered crucial for the convergence of classic telephone service (PSTN) and Internet telephony (Voice over IP, VoIP), and for the development of new IP multimedia services. The problem of a single universal personal identifier for multiple communication services can be solved with different approaches. One simple approach is the Electronic Number Mapping System (ENUM), developed by the IETF, using existing E.164 telephone numbers, protocols and infrastructure to indirectly access different services available under a single personal identifier. ENUM also permits connecting the IP world to the telephone system in a seamless manner." [Telephone number mapping. Wikipedia]
The IVR diagram example "Example ENUM" was designed using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Interactive Voice Response Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
1. The User Agent of an ENUM-enabled subscriber terminal device, or a PBX, or a Gateway, translates the request for the number +34 98 765 4321 in accordance with the rule described in RFC 3761 into the ENUM domain 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.4.3.e164.arpa.
2. A request is sent to the Domain Name System (DNS) asking it to look up the ENUM domain 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.4.3.e164.arpa.
3. The query returns a result in the form of so called Naming Authority Pointer Resource NAPTR records, as per RFC 3403. In the example above, the response is an address that can be reached in the Internet using the VoIP protocol, SIP per RFC 3261.
4. The terminal application now sets up a communication link, and the call is routed via the Internet.
This IVR diagram sample was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Ejemplo ENUM.jpg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Ejemplo_ ENUM.jpg]
"Being able to dial telephone numbers the way customers have come to expect is considered crucial for the convergence of classic telephone service (PSTN) and Internet telephony (Voice over IP, VoIP), and for the development of new IP multimedia services. The problem of a single universal personal identifier for multiple communication services can be solved with different approaches. One simple approach is the Electronic Number Mapping System (ENUM), developed by the IETF, using existing E.164 telephone numbers, protocols and infrastructure to indirectly access different services available under a single personal identifier. ENUM also permits connecting the IP world to the telephone system in a seamless manner." [Telephone number mapping. Wikipedia]
The IVR diagram example "Example ENUM" was designed using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Interactive Voice Response Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"The Ethernet physical layer is the physical layer component of the Ethernet family of computer network standards.
The Ethernet physical layer evolved over a considerable time span and encompasses quite a few physical media interfaces and several magnitudes of speed. The speed ranges from 1 Mbit/ s to 100 Gbit/ s, while the physical medium can range from bulky coaxial cable to twisted pair and optical fiber. In general, network protocol stack software will work similarly on all physical layers.
10-gigabit Ethernet was already used in both enterprise and carrier networks by 2007, with 40 Gbit/ s and 100 Gbit/ s Ethernet ratified. ...
Many Ethernet adapters and switch ports support multiple speeds, using autonegotiation to set the speed and duplex for the best values supported by both connected devices. If auto-negotiation fails, a multiple-speed device will sense the speed used by its partner, but will assume half-duplex. A 10/ 100 Ethernet port supports 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX. A 10/ 100/ 1000 Ethernet port supports 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and 1000BASE-T." [Ethernet physical layer. Wikipedia]
The LAN equipment and cabling layout floorplan example "Ethernet local area network layout floor plan" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Network Layout Floor Plans solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ computer-networks-layout-floor-plans
The Ethernet physical layer evolved over a considerable time span and encompasses quite a few physical media interfaces and several magnitudes of speed. The speed ranges from 1 Mbit/ s to 100 Gbit/ s, while the physical medium can range from bulky coaxial cable to twisted pair and optical fiber. In general, network protocol stack software will work similarly on all physical layers.
10-gigabit Ethernet was already used in both enterprise and carrier networks by 2007, with 40 Gbit/ s and 100 Gbit/ s Ethernet ratified. ...
Many Ethernet adapters and switch ports support multiple speeds, using autonegotiation to set the speed and duplex for the best values supported by both connected devices. If auto-negotiation fails, a multiple-speed device will sense the speed used by its partner, but will assume half-duplex. A 10/ 100 Ethernet port supports 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX. A 10/ 100/ 1000 Ethernet port supports 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and 1000BASE-T." [Ethernet physical layer. Wikipedia]
The LAN equipment and cabling layout floorplan example "Ethernet local area network layout floor plan" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Network Layout Floor Plans solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ computer-networks-layout-floor-plans
This interactive voice response (IVR) diagram sample illustrates how ENUM call forwarding can be achieved. It was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file: Call Forwarding with ENUM.jpg. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Call_ Forwarding_ with_ ENUM.jpg]
"Telephone number mapping is a system of unifying the international telephone number system of the public switched telephone network with the Internet addressing and identification name spaces. Internationally, telephone numbers are systematically organized by the E.164 standard, while the Internet uses the Domain Name System (DNS) for linking domain names to IP addresses and other resource information. Telephone number mapping systems provide facilities to determine applicable Internet communications servers responsible for servicing a given telephone number using DNS queries.
The most prominent facility for telephone number mapping is the E.164 Number Mapping (ENUM) standard. It uses special DNS record types to translate a telephone number into a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) or IP address that can be used in Internet communications." [Telephone number mapping. Wikipedia]
The IVR diagram example "Call Forwarding with ENUM" was designed using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Interactive Voice Response Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Telephone number mapping is a system of unifying the international telephone number system of the public switched telephone network with the Internet addressing and identification name spaces. Internationally, telephone numbers are systematically organized by the E.164 standard, while the Internet uses the Domain Name System (DNS) for linking domain names to IP addresses and other resource information. Telephone number mapping systems provide facilities to determine applicable Internet communications servers responsible for servicing a given telephone number using DNS queries.
The most prominent facility for telephone number mapping is the E.164 Number Mapping (ENUM) standard. It uses special DNS record types to translate a telephone number into a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) or IP address that can be used in Internet communications." [Telephone number mapping. Wikipedia]
The IVR diagram example "Call Forwarding with ENUM" was designed using ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Interactive Voice Response Diagrams solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Network layout floorplan" contain 34 symbol icons for drawing computer network floor plans and communication equipment and cabling layouts.
"Networking hardware may also be known as network equipment or computer networking devices. Units which are the last receiver or generate data are called hosts or data terminal equipment.
All these terms refer to devices facilitating the use of a computer network. Specifically, they mediate data in a computer network. ...
Typically, networking hardware includes gateways, routers, network bridges, switches, hubs, and repeaters. But it also includes hybrid network devices such as multilayer switches, protocol converters, bridge routers, proxy servers, firewalls, network address translators, multiplexers, network interface controllers, wireless network interface controllers, modems, ISDN terminal adapters, line drivers, wireless access points, networking cables and other related hardware.
The most common kind of networking hardware today is a copper-based Ethernet adapter because of its standard inclusion on most modern computer systems. Wireless networking has, however, become increasingly popular, especially for portable and handheld devices.
Other hardware prevalent in computer networking includes data center equipment (such as file servers, database servers and storage areas), network services (such as DNS, DHCP, email, etc.) as well as devices which assure content delivery." [Networking hardware. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Network layout floorplan" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Network Layout Floor Plans solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Networking hardware may also be known as network equipment or computer networking devices. Units which are the last receiver or generate data are called hosts or data terminal equipment.
All these terms refer to devices facilitating the use of a computer network. Specifically, they mediate data in a computer network. ...
Typically, networking hardware includes gateways, routers, network bridges, switches, hubs, and repeaters. But it also includes hybrid network devices such as multilayer switches, protocol converters, bridge routers, proxy servers, firewalls, network address translators, multiplexers, network interface controllers, wireless network interface controllers, modems, ISDN terminal adapters, line drivers, wireless access points, networking cables and other related hardware.
The most common kind of networking hardware today is a copper-based Ethernet adapter because of its standard inclusion on most modern computer systems. Wireless networking has, however, become increasingly popular, especially for portable and handheld devices.
Other hardware prevalent in computer networking includes data center equipment (such as file servers, database servers and storage areas), network services (such as DNS, DHCP, email, etc.) as well as devices which assure content delivery." [Networking hardware. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Network layout floorplan" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Network Layout Floor Plans solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Rack Diagrams | Server | Rack Rate | Rack Server Example Solutions
- Rack units | Rack diagrams - Vector stencils library | Rack units ...
- Server In Rack
- Rack Diagrams | Rack Rate | The Rack | Examples Of Racks
- Rack Diagrams | How to Add a Rack Diagram to a MS Word ...
- Server | Network Diagramming Software for Design Rack Diagrams ...
- Rack diagram - Template | Rack Mount Spacing
- Rack Mount Patch Panel Visio Stencil
- Virtual networks. Computer and Network Examples | Rack Diagrams ...
- Rack Diagrams | Server | Server hardware - Rack diagram ...
- Rack diagram - Template | How To use Switches in Network ...
- Rack diagrams - Vector stencils library | Rack Diagrams | Design ...
- Design elements - Rack diagram | Rack diagrams - Vector stencils ...
- Rack diagram - Template | Cisco Products Additional. Cisco icons ...
- Half Pipe Plans | Soccer (Football) Formation | Rack units | One Half ...
- Design elements - Rack diagram | Rack diagram - Template | 42u ...
- Rack Diagrams | Network Diagramming Software for Design Rack ...
- Rack Diagrams | Rack Diagrams | Design Element: Rack Diagram ...
- Design Element: Rack Diagram for Network Diagrams | Network ...
- Rack diagrams - Vector stencils library
_Win_Mac.png)

-rack-diagrams---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)











-rack-diagrams---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-rack-diagrams---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-rack-diagrams---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-rack-diagrams---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-rack-diagrams---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-rack-diagrams---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)


-rack-diagrams---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-rack-diagrams---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-rack-diagrams---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
























-ethernet-local-area-network-layout-floor-plan.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-ethernet-local-area-network-layout-floor-plan.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)