HelpDesk
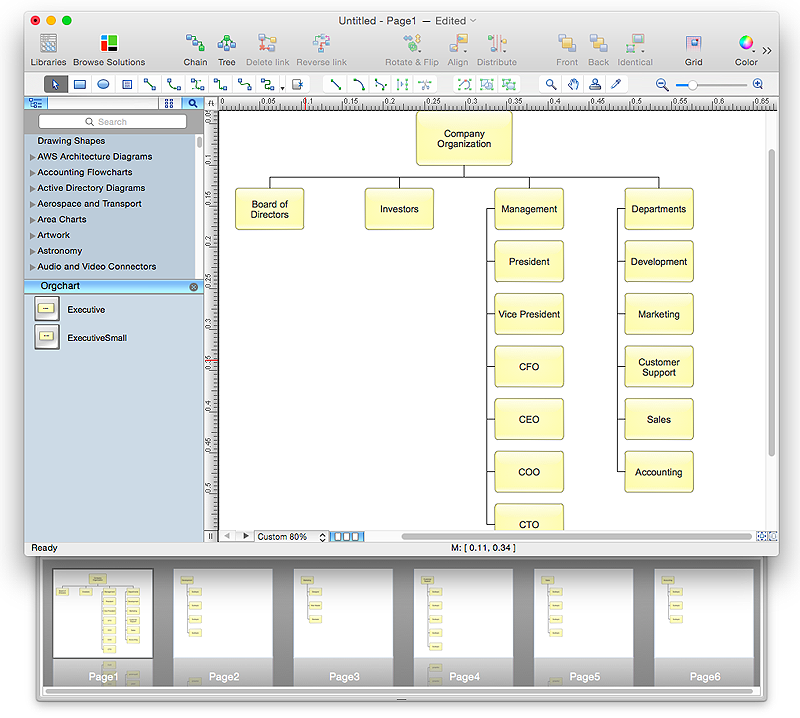
How to Create Organizational Chart Quickly
Use ConceptDraw MINDMAP for generating structured data on organization structure and then ConceptDraw PRO for presenting the results as chart.HelpDesk
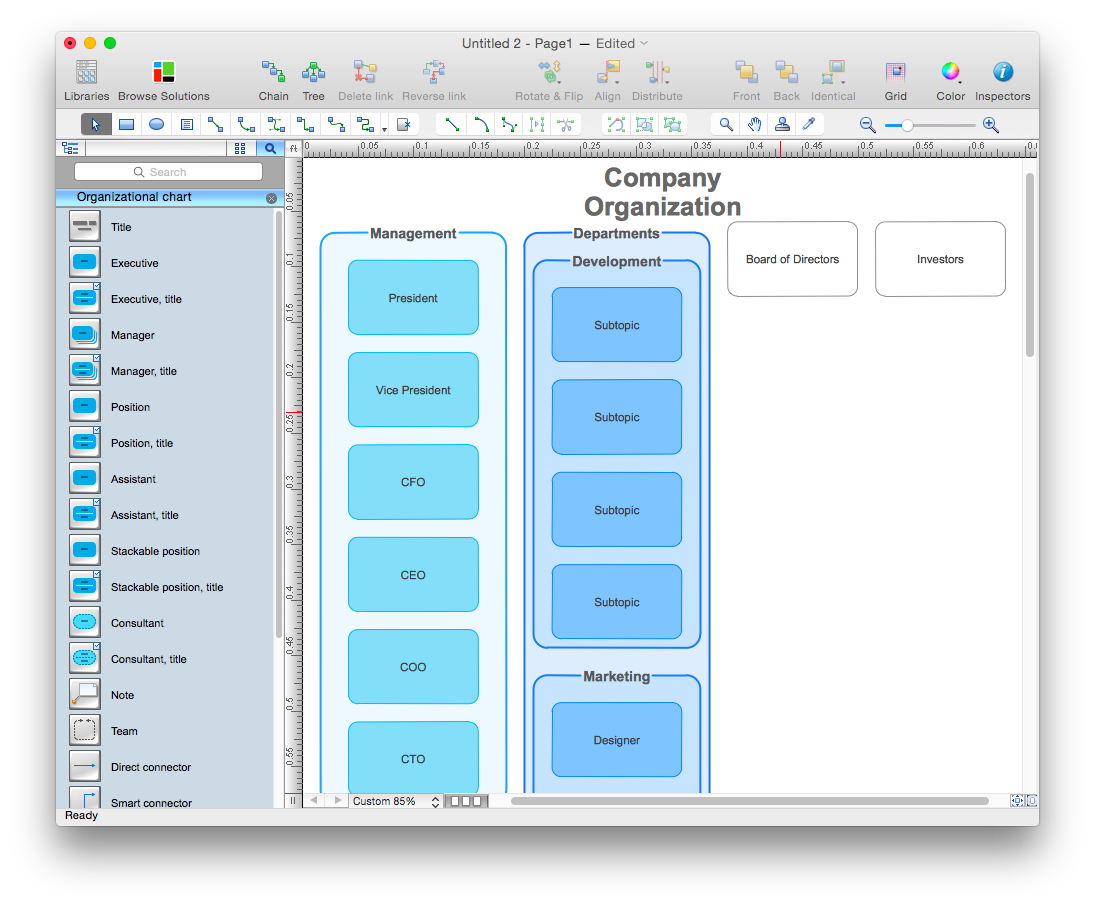
How to Create Organizational Chart Using Management Solution
Use ConceptDraw MINDMAP for generating structured data on organization structure and then ConceptDraw PRO for presenting the results as chart.HelpDesk
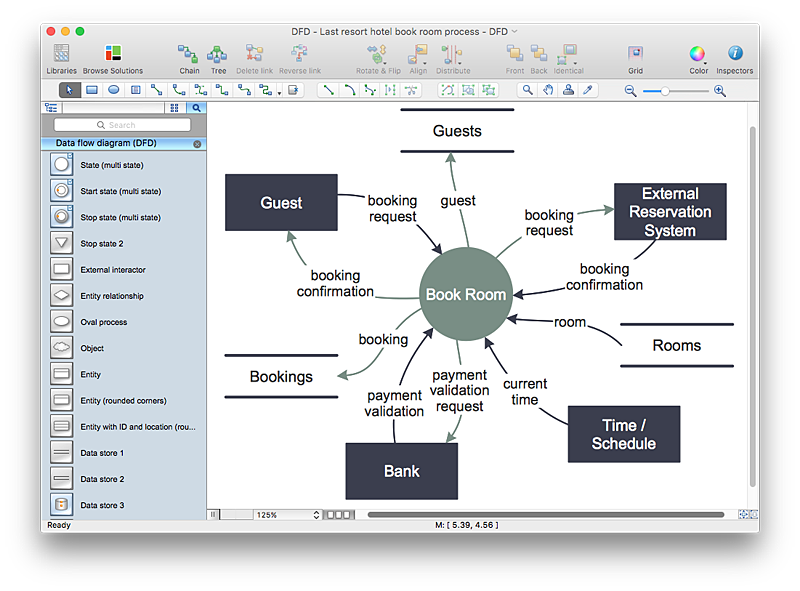
How to Create a Data Flow Diagram using ConceptDraw PRO
Data flow diagramming is a highly effective technique for showing the flow of information through a system. Data flow diagrams reveal relationships among and between the various components in a program or system. DFD is an important technique for modeling a system’s high-level detail by showing how input data is transformed to output results through a sequence of functional transformations. The set of standard symbols is used to depict how these components interact in a system. ConceptDraw PRO allows you to draw a simple and clear Data Flow Diagram using special libraries.HelpDesk
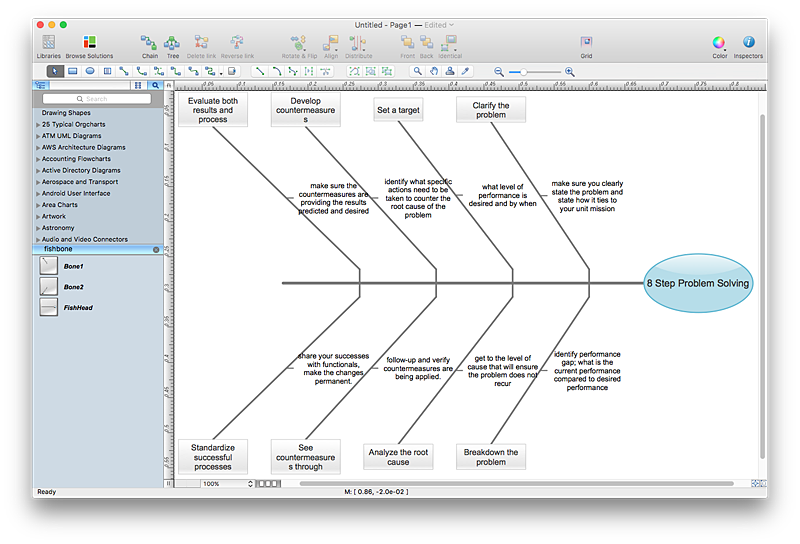
How to Create a Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram Quickly
A Fishbone (Ishikawa) diagram is also called cause-and-effect diagram. Fishbone diagram is often used in business to determine the cause of some problem. The diagram illustrates the main causes and sub-causes leading to an event. The main goal of the Fishbone diagram is to illustrate in a graphical way the relationship between a given outcome and all the factors that influence this outcome. The complete diagram resembles a fish skeleton as its name implies. The ability to create a Fishbone Diagram is supported by the Fishbone Diagram solution. Use ConceptDraw MINDMAP for structuring data and then ConceptDraw PRO for generating a Fishbone Diagram from mind map structure."In mathematics, the Euclidean algorithm, or Euclid's algorithm, is a method for computing the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two (usually positive) integers, also known as the greatest common factor (GCF) or highest common factor (HCF). ...
The GCD of two positive integers is the largest integer that divides both of them without leaving a remainder (the GCD of two integers in general is defined in a more subtle way).
In its simplest form, Euclid's algorithm starts with a pair of positive integers, and forms a new pair that consists of the smaller number and the difference between the larger and smaller numbers. The process repeats until the numbers in the pair are equal. That number then is the greatest common divisor of the original pair of integers.
The main principle is that the GCD does not change if the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number. ... Since the larger of the two numbers is reduced, repeating this process gives successively smaller numbers, so this repetition will necessarily stop sooner or later - when the numbers are equal (if the process is attempted once more, one of the numbers will become 0)." [Euclidean algorithm. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Euclidean algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The GCD of two positive integers is the largest integer that divides both of them without leaving a remainder (the GCD of two integers in general is defined in a more subtle way).
In its simplest form, Euclid's algorithm starts with a pair of positive integers, and forms a new pair that consists of the smaller number and the difference between the larger and smaller numbers. The process repeats until the numbers in the pair are equal. That number then is the greatest common divisor of the original pair of integers.
The main principle is that the GCD does not change if the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number. ... Since the larger of the two numbers is reduced, repeating this process gives successively smaller numbers, so this repetition will necessarily stop sooner or later - when the numbers are equal (if the process is attempted once more, one of the numbers will become 0)." [Euclidean algorithm. Wikipedia]
The flowchart example "Euclidean algorithm" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Mathematics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
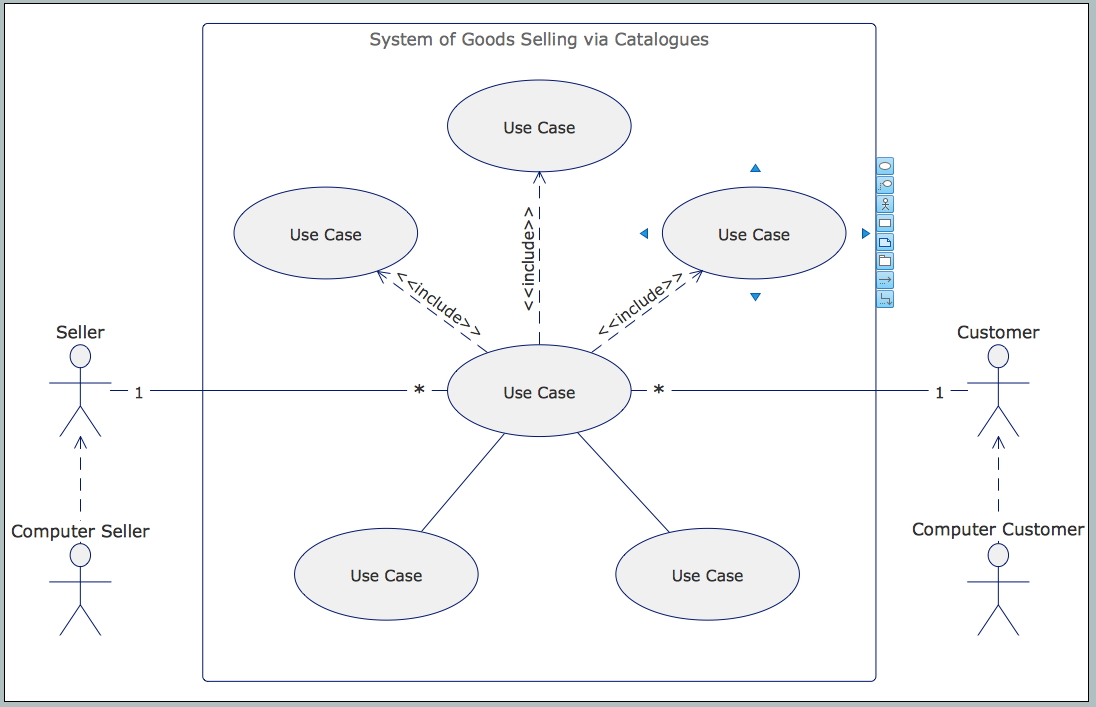
HelpDesk
How to Create a UML Diagram Quickly
UML diagramming software with rich examples and template. ConceptDraw is ideal for software designers and software developers who need to draw UML Diagrams- Simple Flow Chart | Creating a Simple Flowchart | Flowchart ...
- Simple Diagramming | Simple Drawing Applications for Mac ...
- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Solving quadratic equation ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Simple Flow Chart ...
- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Solving quadratic equation ...
- Simple Flow Chart | Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning ...
- Flowchart Definition | Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Cross ...
- Simple Flow Chart | Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Flow ...
- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Basic Audit Flowchart . Flowchart ...
- Account Flow Chart Sample
- Basic Diagramming | Types of Flowchart - Overview | Euclidean ...
- Process Flowchart | Process Flow Diagram | How to Draw a Process ...
- Solving quadratic equation algorithm - Flowchart | Euclidean ...
- Solving quadratic equation algorithm - Flowchart | Contoh Flowchart ...
- Euclidean algorithm - Flowchart | Flow Chart For Greatest Common ...
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning | Flowchart design ...
- Cross-Functional Flowchart (Swim Lanes) | Swim Lane Diagrams ...
- Basic Diagramming | Types of Flowchart - Overview | Mathematics ...
- Business Process Elements: Swimlanes | Swim Lane Diagrams ...
- Flowchart design. Flowchart symbols, shapes, stencils and icons ...