Organic Chemistry Symbols
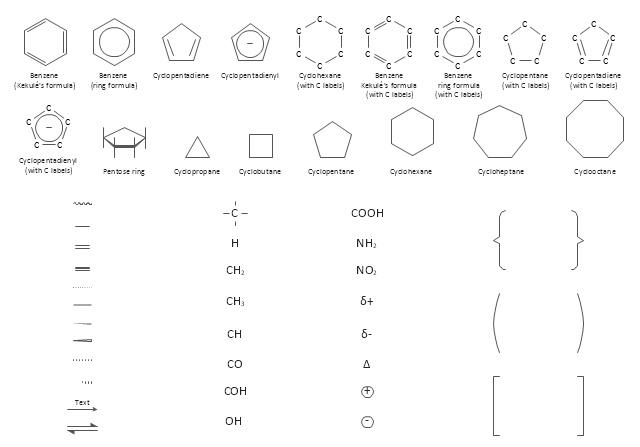
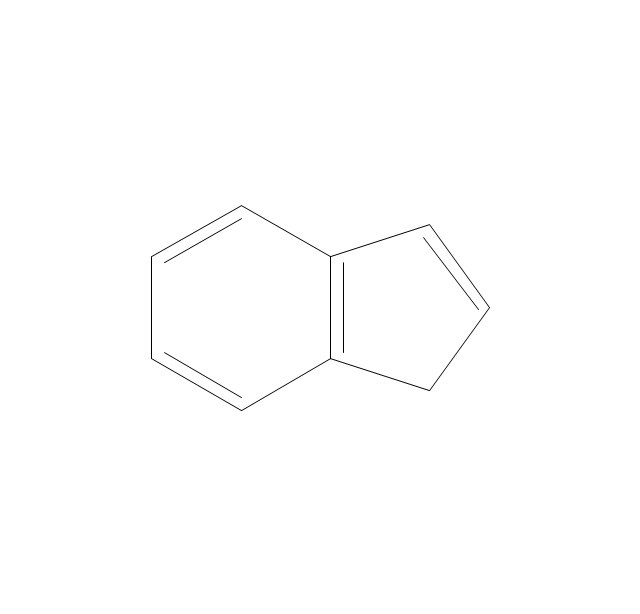
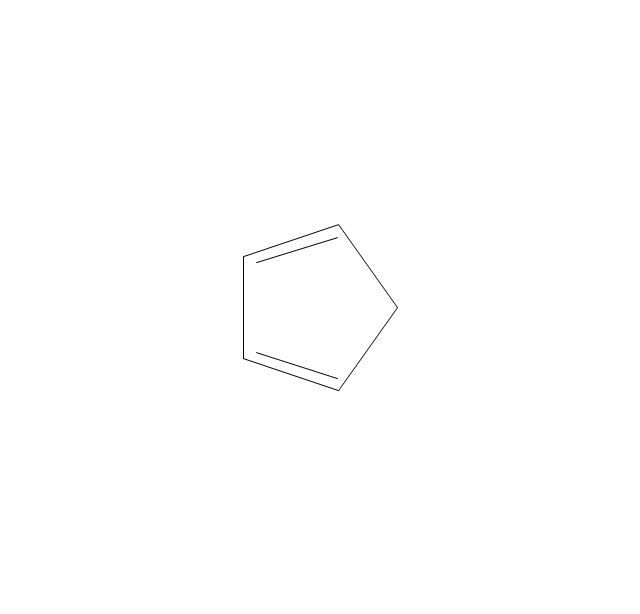
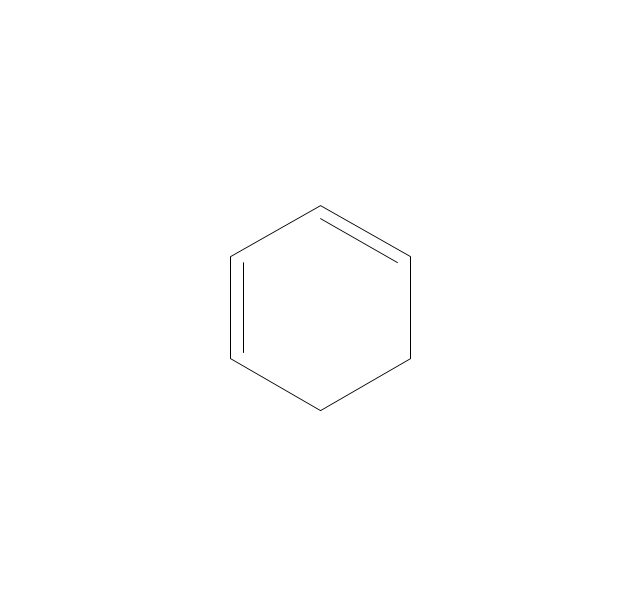
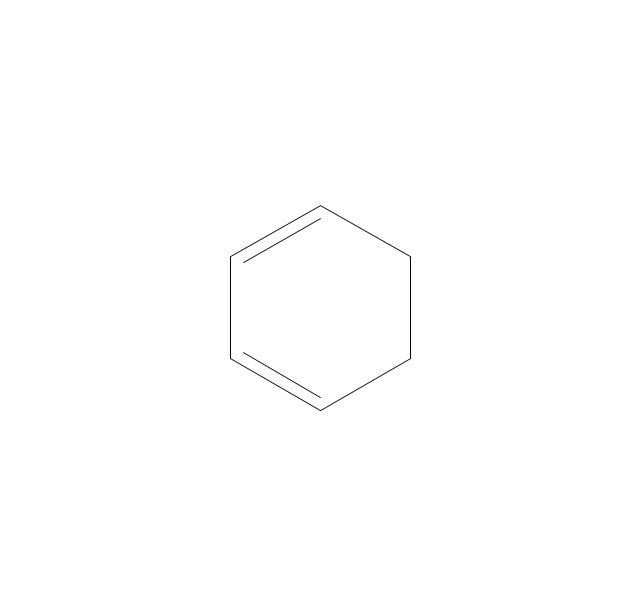
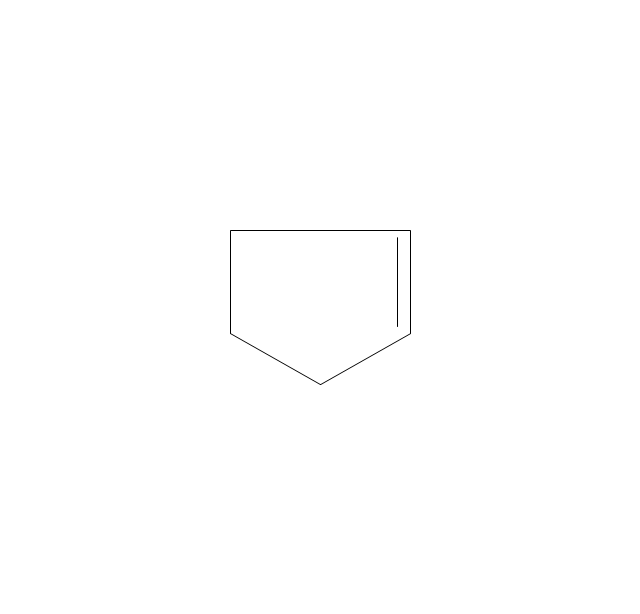
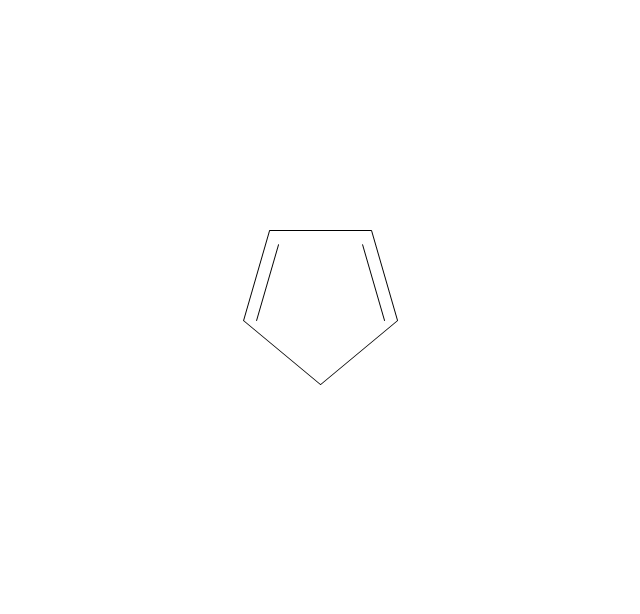
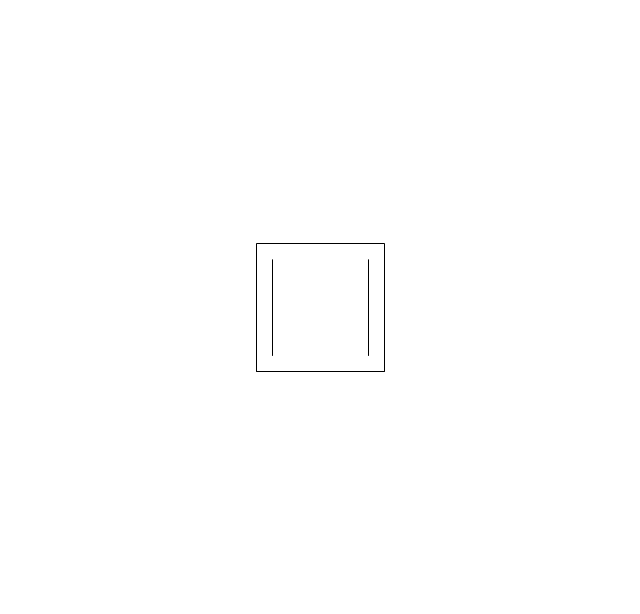
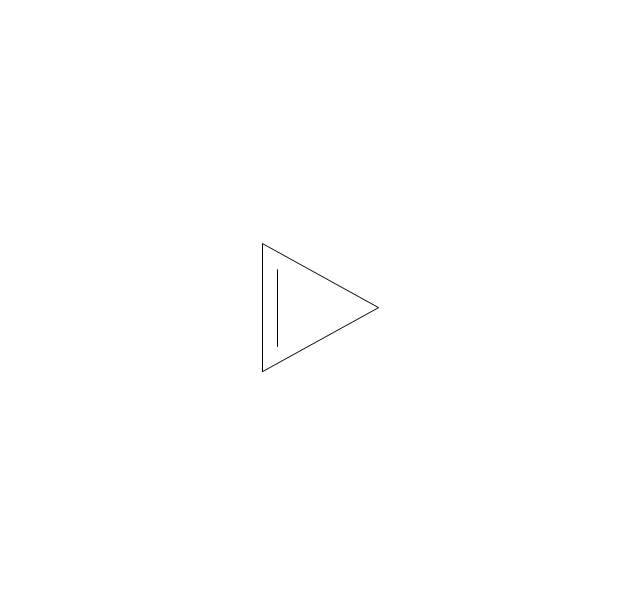
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is effective for drawing various organic chemistry schemes, diagrams, illustrations thanks to the included collection of predesigned organic chemistry symbols.The vector stencils library "Chemical drawings" contains 81 symbols of organic compounds and functional groups for chemical drawing.
Use it to draw structural formulas of organic molecules, schemes of chemical reactions and organic chemistry diagrams.
"Structural drawings.
Organic molecules are described more commonly by drawings or structural formulas, combinations of drawings and chemical symbols. The line-angle formula is simple and unambiguous. In this system, the endpoints and intersections of each line represent one carbon, and hydrogen atoms can either be notated explicitly or assumed to be present as implied by tetravalent carbon. The depiction of organic compounds with drawings is greatly simplified by the fact that carbon in almost all organic compounds has four bonds, nitrogen three, oxygen two, and hydrogen one. ...
Organic reactions.
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. While pure hydrocarbons undergo certain limited classes of reactions, many more reactions which organic compounds undergo are largely determined by functional groups. The general theory of these reactions involves careful analysis of such properties as the electron affinity of key atoms, bond strengths and steric hindrance. These issues can determine the relative stability of short-lived reactive intermediates, which usually directly determine the path of the reaction.
The basic reaction types are: addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions and redox reactions. ...
Each reaction has a stepwise reaction mechanism that explains how it happens in sequence - although the detailed description of steps is not always clear from a list of reactants alone.
The stepwise course of any given reaction mechanism can be represented using arrow pushing techniques in which curved arrows are used to track the movement of electrons as starting materials transition through intermediates to final products." [Organic chemistry. Wikipedia]
The chemical symbols example "Design elements - Chemical drawings" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to draw structural formulas of organic molecules, schemes of chemical reactions and organic chemistry diagrams.
"Structural drawings.
Organic molecules are described more commonly by drawings or structural formulas, combinations of drawings and chemical symbols. The line-angle formula is simple and unambiguous. In this system, the endpoints and intersections of each line represent one carbon, and hydrogen atoms can either be notated explicitly or assumed to be present as implied by tetravalent carbon. The depiction of organic compounds with drawings is greatly simplified by the fact that carbon in almost all organic compounds has four bonds, nitrogen three, oxygen two, and hydrogen one. ...
Organic reactions.
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. While pure hydrocarbons undergo certain limited classes of reactions, many more reactions which organic compounds undergo are largely determined by functional groups. The general theory of these reactions involves careful analysis of such properties as the electron affinity of key atoms, bond strengths and steric hindrance. These issues can determine the relative stability of short-lived reactive intermediates, which usually directly determine the path of the reaction.
The basic reaction types are: addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions and redox reactions. ...
Each reaction has a stepwise reaction mechanism that explains how it happens in sequence - although the detailed description of steps is not always clear from a list of reactants alone.
The stepwise course of any given reaction mechanism can be represented using arrow pushing techniques in which curved arrows are used to track the movement of electrons as starting materials transition through intermediates to final products." [Organic chemistry. Wikipedia]
The chemical symbols example "Design elements - Chemical drawings" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Chemistry Drawings
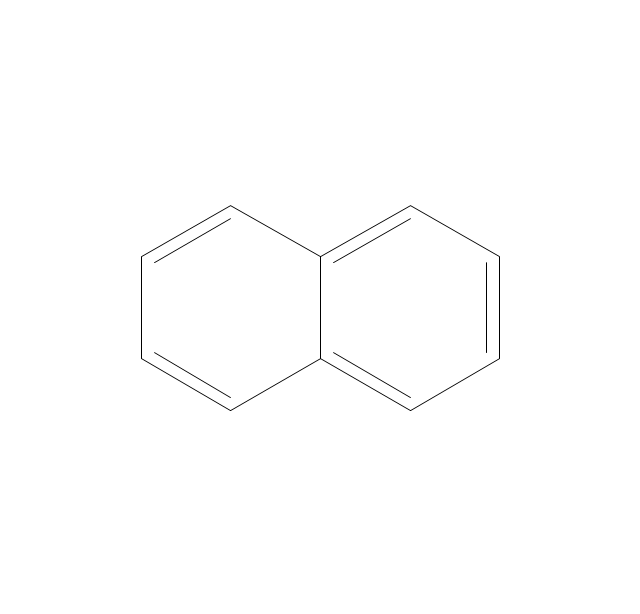
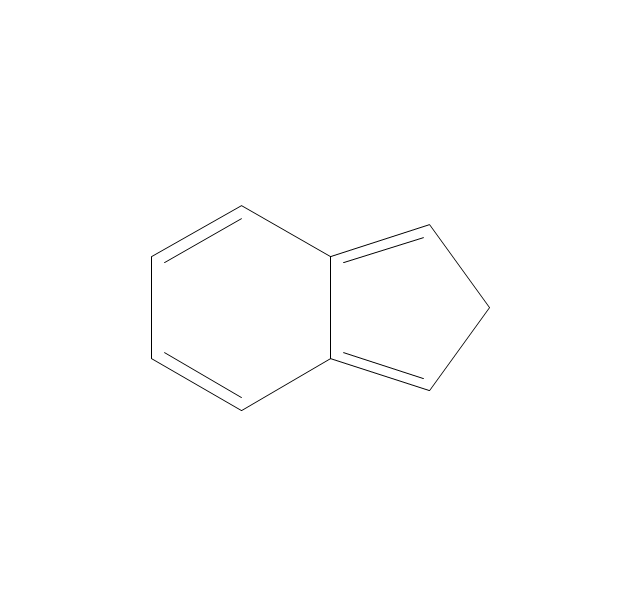
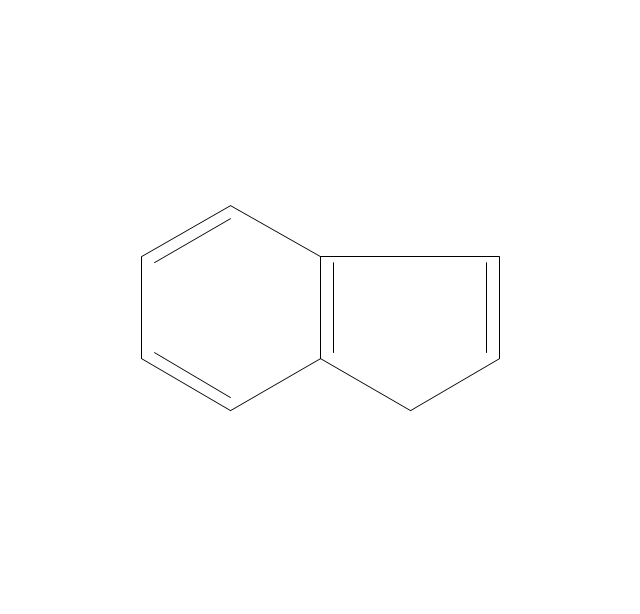
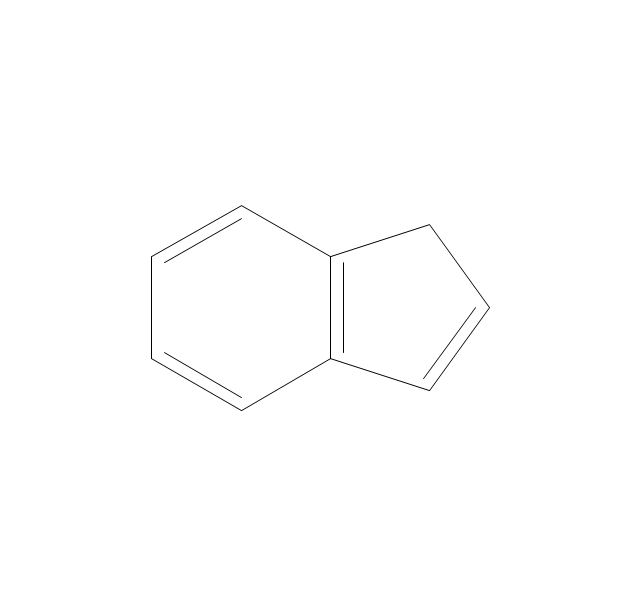
ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software extended with Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area is a powerful chemistry drawing software that is ideal for quick and easy designing of various: chemistry drawings, scientific and educational chemistry illustrations, schemes and diagrams of chemical and biological lab set-ups, images with chemical formulas, molecular structures, chemical reaction schemes, schemes of labware, that can be then successfully used in the field of science and education, on various conferences, and so on.The vector stencils library "Aromatics" contains 23 symbols of aromatic rings for chemical drawing of molecular structural formulas and reaction mechanism schemes in organic chemistry.
"In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. ... Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double-bonded to one another. These bonds may be seen as a hybrid of a single bond and a double bond, each bond in the ring identical to every other. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Kekulé (see History section below). The model for benzene consists of two resonance forms, which corresponds to the double and single bonds superimposing to give rise to six one-and-a-half bonds. Benzene is a more stable molecule than would be expected without accounting for charge delocalization. ... Types of aromatic compounds. The overwhelming majority of aromatic compounds are compounds of carbon, but they need not be hydrocarbons. 1. Neutral homocyclics. Benzene, as well as most other annulenes (cyclodecapentaene excepted) with the formula CnHn where n is an even number, such as cyclotetradecaheptaene. 2. Heterocyclics. In heterocyclic aromatics (heteroaromats), one or more of the atoms in the aromatic ring is of an element other than carbon. This can lessen the ring's aromaticity, and thus (as in the case of furan) increase its reactivity. Other examples include pyridine, pyrazine, imidazole, pyrazole, oxazole, thiophene, and their benzannulated analogs (benzimidazole, for example). 3. Polycyclics. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are molecules containing two or more simple aromatic rings fused together by sharing two neighboring carbon atoms (see also simple aromatic rings). Examples are naphthalene, anthracene, and phenanthrene. 4. Substituted aromatics. Many chemical compounds are aromatic rings with other functional groups attached. Examples include trinitrotoluene (TNT), acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), paracetamol, and the nucleotides of DNA. 5. Atypical aromatic compounds. Aromaticity is found in ions as well: the cyclopropenyl cation (2e system), the cyclopentadienyl anion (6e system), the tropylium ion (6e), and the cyclooctatetraene dianion (10e). Aromatic properties have been attributed to non-benzenoid compounds such as tropone. Aromatic properties are tested to the limit in a class of compounds called cyclophanes. A special case of aromaticity is found in homoaromaticity where conjugation is interrupted by a single sp³ hybridized carbon atom. When carbon in benzene is replaced by other elements in borabenzene, silabenzene, germanabenzene, stannabenzene, phosphorine or pyrylium salts the aromaticity is still retained. Aromaticity also occurs in compounds that are not carbon-based at all. Inorganic 6-membered-ring compounds analogous to benzene have been synthesized. Hexasilabenzene (Si6H6) and borazine (B3N3H6) are structurally analogous to benzene, with the carbon atoms replaced by another element or elements. In borazine, the boron and nitrogen atoms alternate around the ring." [Aromaticity. Wikipedia]
The organic compound structural formulas example "Aromatics - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. ... Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double-bonded to one another. These bonds may be seen as a hybrid of a single bond and a double bond, each bond in the ring identical to every other. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Kekulé (see History section below). The model for benzene consists of two resonance forms, which corresponds to the double and single bonds superimposing to give rise to six one-and-a-half bonds. Benzene is a more stable molecule than would be expected without accounting for charge delocalization. ... Types of aromatic compounds. The overwhelming majority of aromatic compounds are compounds of carbon, but they need not be hydrocarbons. 1. Neutral homocyclics. Benzene, as well as most other annulenes (cyclodecapentaene excepted) with the formula CnHn where n is an even number, such as cyclotetradecaheptaene. 2. Heterocyclics. In heterocyclic aromatics (heteroaromats), one or more of the atoms in the aromatic ring is of an element other than carbon. This can lessen the ring's aromaticity, and thus (as in the case of furan) increase its reactivity. Other examples include pyridine, pyrazine, imidazole, pyrazole, oxazole, thiophene, and their benzannulated analogs (benzimidazole, for example). 3. Polycyclics. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are molecules containing two or more simple aromatic rings fused together by sharing two neighboring carbon atoms (see also simple aromatic rings). Examples are naphthalene, anthracene, and phenanthrene. 4. Substituted aromatics. Many chemical compounds are aromatic rings with other functional groups attached. Examples include trinitrotoluene (TNT), acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), paracetamol, and the nucleotides of DNA. 5. Atypical aromatic compounds. Aromaticity is found in ions as well: the cyclopropenyl cation (2e system), the cyclopentadienyl anion (6e system), the tropylium ion (6e), and the cyclooctatetraene dianion (10e). Aromatic properties have been attributed to non-benzenoid compounds such as tropone. Aromatic properties are tested to the limit in a class of compounds called cyclophanes. A special case of aromaticity is found in homoaromaticity where conjugation is interrupted by a single sp³ hybridized carbon atom. When carbon in benzene is replaced by other elements in borabenzene, silabenzene, germanabenzene, stannabenzene, phosphorine or pyrylium salts the aromaticity is still retained. Aromaticity also occurs in compounds that are not carbon-based at all. Inorganic 6-membered-ring compounds analogous to benzene have been synthesized. Hexasilabenzene (Si6H6) and borazine (B3N3H6) are structurally analogous to benzene, with the carbon atoms replaced by another element or elements. In borazine, the boron and nitrogen atoms alternate around the ring." [Aromaticity. Wikipedia]
The organic compound structural formulas example "Aromatics - Vector stencils library" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Chemistry
Chemistry
This solution extends ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software with samples, template and libraries of vector stencils for drawing the Chemistry Illustrations for science and education.
The vector stencils library "Aromatics" contains 23 symbols of aromatic rings for chemical drawing of molecular structural formulas and reaction mechanism schemes in organic chemistry.
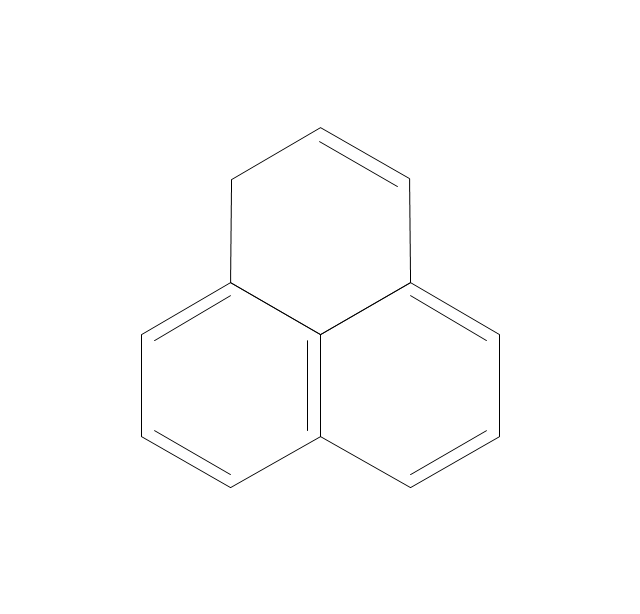
"An aromatic hydrocarbon or arene (or sometimes aryl hydrocarbon) is a hydrocarbon with alternating double and single bonds between carbon atoms forming rings. The term 'aromatic' was assigned before the physical mechanism determining aromaticity was discovered, and was derived from the fact that many of the compounds have a sweet scent. The configuration of six carbon atoms in aromatic compounds is known as a benzene ring, after the simplest possible such hydrocarbon, benzene. Aromatic hydrocarbons can be monocyclic (MAH) or polycyclic (PAH)." [Aromatic hydrocarbon. Wikipedia]
The chemical symbols example "Design elements - Aromatic hydrocarbons (arenes)" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"An aromatic hydrocarbon or arene (or sometimes aryl hydrocarbon) is a hydrocarbon with alternating double and single bonds between carbon atoms forming rings. The term 'aromatic' was assigned before the physical mechanism determining aromaticity was discovered, and was derived from the fact that many of the compounds have a sweet scent. The configuration of six carbon atoms in aromatic compounds is known as a benzene ring, after the simplest possible such hydrocarbon, benzene. Aromatic hydrocarbons can be monocyclic (MAH) or polycyclic (PAH)." [Aromatic hydrocarbon. Wikipedia]
The chemical symbols example "Design elements - Aromatic hydrocarbons (arenes)" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
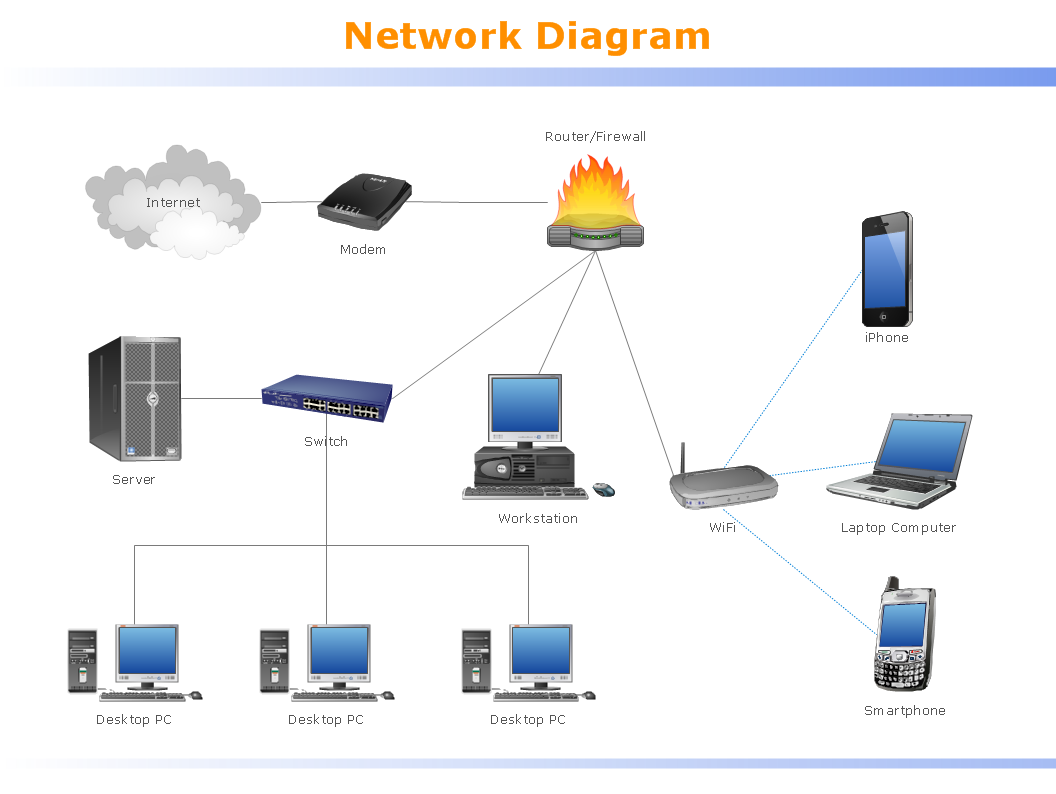
Local area network (LAN). Computer and Network Examples
Local Area Network (LAN) is a network which consists of computers and peripheral devices connected each other and to the local domain server, and covers a little territory or small number of buildings, such as home, school, laboratory, office, etc. LAN serves for few hundreds of users. It includes many cables and wires, and demands to design previously a Network diagram. All local area network devices can use the shared printers and disk storage. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is a perfect network diagramming software with examples of LAN Diagrams, templates and predesigned vector objects. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM is the ideal choice for network engineers and network designers who need to draw fast and easy Local Area Network Diagrams, for IT specialists, developers and other IT professionals which need to visualize the communication schemes of LAN and visually document the LAN's physical structure and arrangement in houses, offices and other buildings. Ready-to-use vector objects from Computer Network Diagrams solution will help you design LAN diagrams in minutes.
Chemistry Equation Symbols
If you are related with chemistry in you work or education activity, you need often draw various illustrations with chemistry equations. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software offers you the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area. Chemistry solution provides the Chemical Drawings Library with large quantity of vector chemistry equation symbols to help you create professional looking chemistry diagrams quick and easy.Pyramid Diagram
Pyramid diagram is a chart used to visualize the data in a hierarchical (pyramid-like) structure and depict the foundation-based relationships. Pyramid diagram looks like a triangle divided by lines into several sections (layers) and can be oriented up or down, and represented in 2D or 3D view. 2D Pyramid diagrams are a great way to illustrate the hierarchical structure, 3D Pyramids are equally good to represent the class stratification and hierarchy. ConceptDraw DIAGRAM diagramming and vector drawing software with included Pyramid Diagrams solution from Marketing area of ConceptDraw Solution Park is a powerful application which contains templates and library of vector design elements for instantly drawing three level Pyramid model, four level and five level Triangle charts. All predesigned objects are easy for changing color style and resizing according to your needs, and ConceptDraw documents with Pyramid diagrams can be easy exported in various formats for further using in marketing presentations, for effective analyzing hierarchy levels and illustration your data and ideas.The vector stencils library "Chemical elements" contains 118 icon symbols of chemical elements.
Use these shapes for drawing atoms, structural formulas of inorganic and organic molecules and ions, and schemes of chemical reaction mechanisms in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-chemistry
Use these shapes for drawing atoms, structural formulas of inorganic and organic molecules and ions, and schemes of chemical reaction mechanisms in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ science-education-chemistry
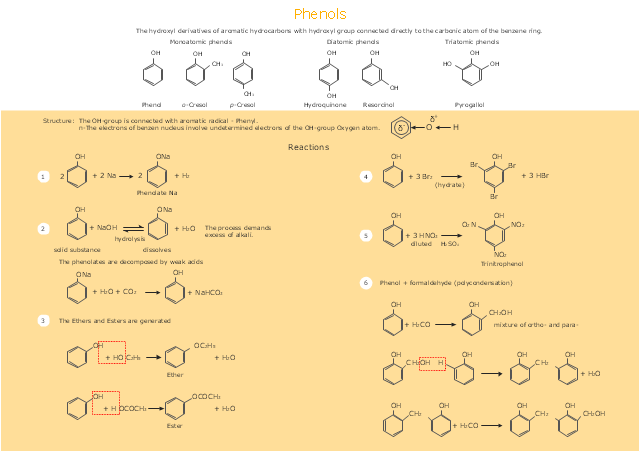
This drawing illustrates examples o f phenolic compounds molecular structures, and chemical reactions of phenols.
"In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule. ...
Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).
Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring." [Phenols. Wikipedia]
The chemical drawing example "Phenols" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule. ...
Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).
Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring." [Phenols. Wikipedia]
The chemical drawing example "Phenols" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Chemical drawings" contains 81 symbols of organic compounds and functional groups for chemical drawing.
Use it to draw structural formulas of organic molecules, schemes of chemical reactions and organic chemistry diagrams.
"Structural drawings.
Organic molecules are described more commonly by drawings or structural formulas, combinations of drawings and chemical symbols. The line-angle formula is simple and unambiguous. In this system, the endpoints and intersections of each line represent one carbon, and hydrogen atoms can either be notated explicitly or assumed to be present as implied by tetravalent carbon. The depiction of organic compounds with drawings is greatly simplified by the fact that carbon in almost all organic compounds has four bonds, nitrogen three, oxygen two, and hydrogen one. ...
Organic reactions.
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. While pure hydrocarbons undergo certain limited classes of reactions, many more reactions which organic compounds undergo are largely determined by functional groups. The general theory of these reactions involves careful analysis of such properties as the electron affinity of key atoms, bond strengths and steric hindrance. These issues can determine the relative stability of short-lived reactive intermediates, which usually directly determine the path of the reaction.
The basic reaction types are: addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions and redox reactions. ...
Each reaction has a stepwise reaction mechanism that explains how it happens in sequence - although the detailed description of steps is not always clear from a list of reactants alone.
The stepwise course of any given reaction mechanism can be represented using arrow pushing techniques in which curved arrows are used to track the movement of electrons as starting materials transition through intermediates to final products." [Organic chemistry. Wikipedia]
The chemical symbols example "Design elements - Chemical drawings" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it to draw structural formulas of organic molecules, schemes of chemical reactions and organic chemistry diagrams.
"Structural drawings.
Organic molecules are described more commonly by drawings or structural formulas, combinations of drawings and chemical symbols. The line-angle formula is simple and unambiguous. In this system, the endpoints and intersections of each line represent one carbon, and hydrogen atoms can either be notated explicitly or assumed to be present as implied by tetravalent carbon. The depiction of organic compounds with drawings is greatly simplified by the fact that carbon in almost all organic compounds has four bonds, nitrogen three, oxygen two, and hydrogen one. ...
Organic reactions.
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. While pure hydrocarbons undergo certain limited classes of reactions, many more reactions which organic compounds undergo are largely determined by functional groups. The general theory of these reactions involves careful analysis of such properties as the electron affinity of key atoms, bond strengths and steric hindrance. These issues can determine the relative stability of short-lived reactive intermediates, which usually directly determine the path of the reaction.
The basic reaction types are: addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions and redox reactions. ...
Each reaction has a stepwise reaction mechanism that explains how it happens in sequence - although the detailed description of steps is not always clear from a list of reactants alone.
The stepwise course of any given reaction mechanism can be represented using arrow pushing techniques in which curved arrows are used to track the movement of electrons as starting materials transition through intermediates to final products." [Organic chemistry. Wikipedia]
The chemical symbols example "Design elements - Chemical drawings" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Laboratory equipment" contains 31 clipart icons of chemical laboratory equipment and labware.
Use these shapes for drawing part assembly and mounting schemes of glassware apparatus in chemical experiment diagrams and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these shapes for drawing part assembly and mounting schemes of glassware apparatus in chemical experiment diagrams and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
This italian chemical safety infographic example shows the ethyl acetate infobox including 3 sections: GHS hazard pictograms, Hazard statements and Precautionary statements.
It was designed on the base of the table from the Wikimedia Commons file: Consigli P.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Consigli_ P.png]
"Ethyl acetate is the organic compound with the formula CH3–COO–CH2–CH3. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell (similar to pear drops) and is used in glues, nail polish removers, decaffeinating tea and coffee, and cigarettes (see list of additives in cigarettes). Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent." [Ethyl acetate. Wikipedia]
The chemical safety infographic sample "Acetato di etile" was created using ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the GHS Hazard Pictograms solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
It was designed on the base of the table from the Wikimedia Commons file: Consigli P.png. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Consigli_ P.png]
"Ethyl acetate is the organic compound with the formula CH3–COO–CH2–CH3. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell (similar to pear drops) and is used in glues, nail polish removers, decaffeinating tea and coffee, and cigarettes (see list of additives in cigarettes). Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent." [Ethyl acetate. Wikipedia]
The chemical safety infographic sample "Acetato di etile" was created using ConceptDraw PRO software extended with the GHS Hazard Pictograms solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
 Healthcare Management Workflow Diagrams
Healthcare Management Workflow Diagrams
Healthcare Management Workflow Diagrams solution contains large set of colorful samples and libraries with predesigned vector pictograms and symbols of health, healthcare equipment, medical instruments, pharmaceutical tools, transport, medication, departments of healthcare organizations, the medical icons of people and human anatomy, as well as the predesigned flowchart objects, connectors and arrows, which make it the best for designing clear and comprehensive Medi?al Workflow Diagrams and Block Diagrams, Healthcare Management Flowcharts and Infographics, Healthcare Workflow Diagram, for depicting the healthcare workflow and clinical workflows in healthcare, for making the workflow analysis healthcare and healthcare workflow management.
The vector stencils library "Laboratory equipment" contains 31 clipart icons of chemical laboratory equipment and labware.
Use these shapes for drawing part assembly and mounting schemes of glassware apparatus in chemical experiment diagrams and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use these shapes for drawing part assembly and mounting schemes of glassware apparatus in chemical experiment diagrams and illustrations in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Chemistry solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Chemistry Symbols and Meanings | Organic Chemistry Symbols ...
- Organic Chemistry Symbols | Chemical Engineering | Chemistry ...
- Process Flow Diagram Symbols | Chemistry Symbols and Meanings ...
- Organic Chemistry Symbols | Chemistry Symbols and Meanings ...
- Organic Chemistry Symbols | Design elements - Chemical drawings ...
- Design elements - Chemical drawings | Chemistry | Carbonyl ...
- Design elements - Periodic table of chemical elements | Organic ...
- Electrical Symbols — Rotating Equipment | Organic Chemistry ...
- Chemistry Drawings | How to Draw Chemistry Structures | Design ...
- Organic Chemistry Symbols
- Organic Chemistry Symbols | Chemistry Equation Symbols | Design ...
- Chemistry Symbols and Meanings | Design elements - Chemical ...
- Design elements - Periodic table of chemical elements | Chemistry ...
- Chemistry Symbols and Meanings | Chemistry Equation Symbols ...
- Design elements - Chemical drawings | Design elements - TCA ...
- Chemistry Equation Symbols | Organic Chemistry Symbols ...
- Chemistry Symbols and Meanings | Chemistry Drawing Software ...
- Phenols | Chemistry | Organic Chemistry Symbols | Examples Of ...
- Symbol Of All Aromatic Compounds
- Organic Chemistry Symbols | Chemistry | Chemistry Drawing ...

.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)


-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-chemical-elements---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)

--laboratory-equipment---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-laboratory-equipment---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)
-laboratory-equipment---vector-stencils-library.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)