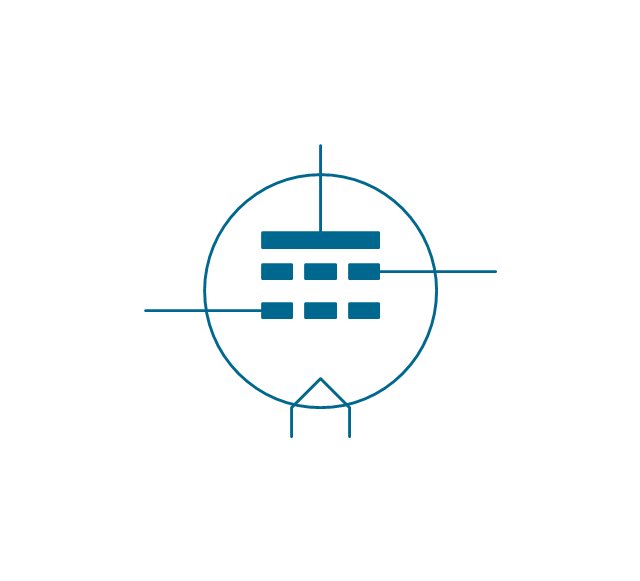
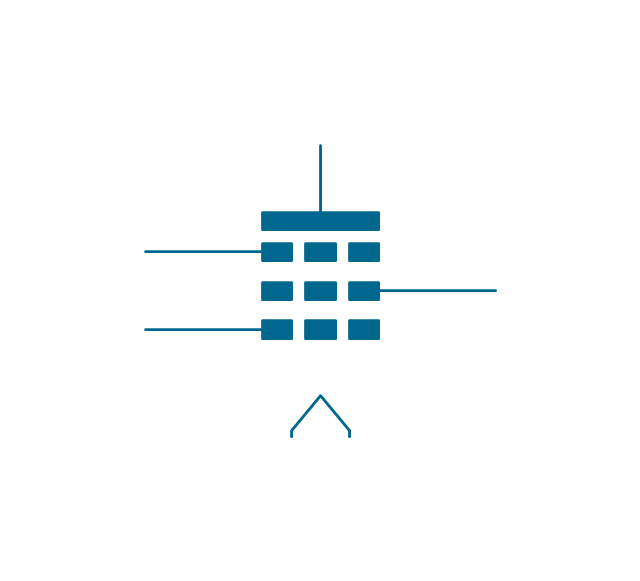
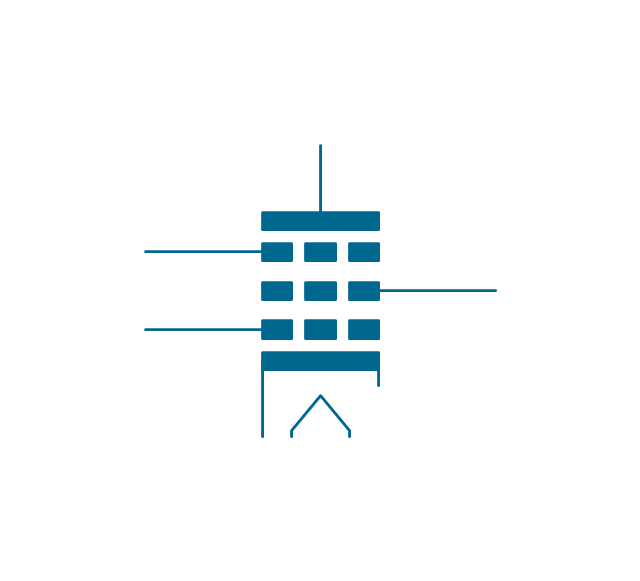
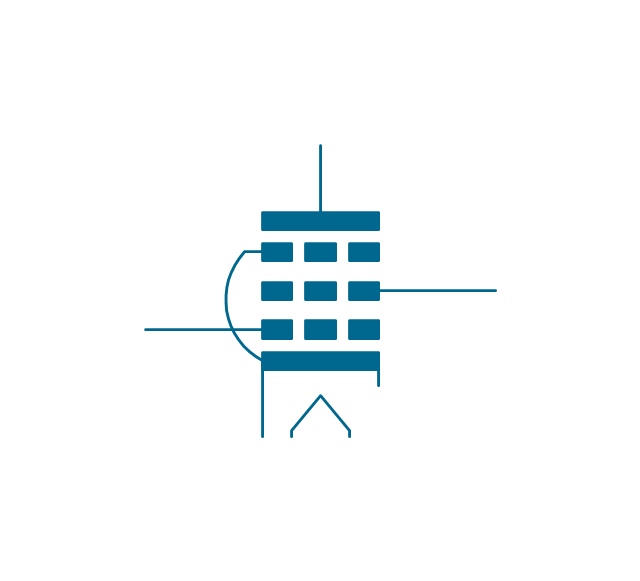
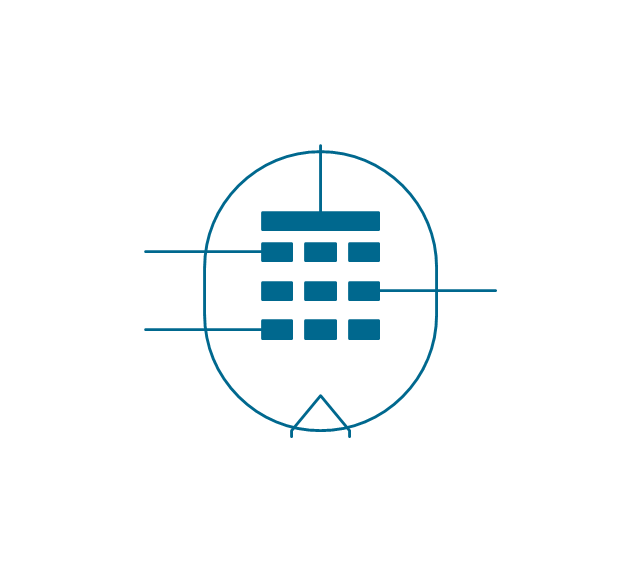
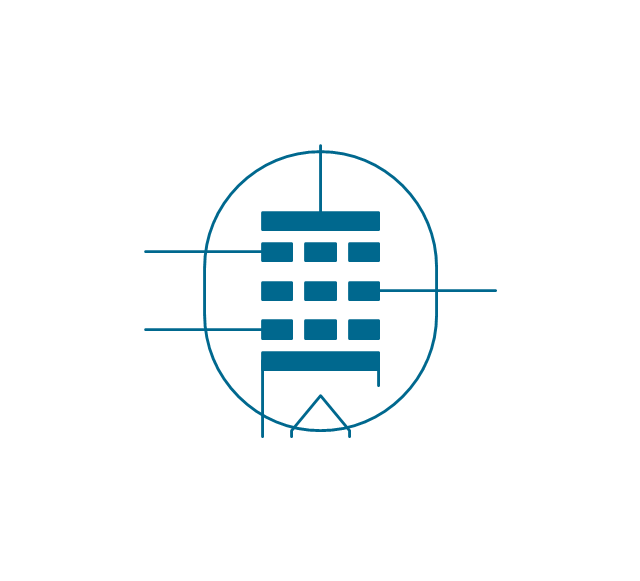
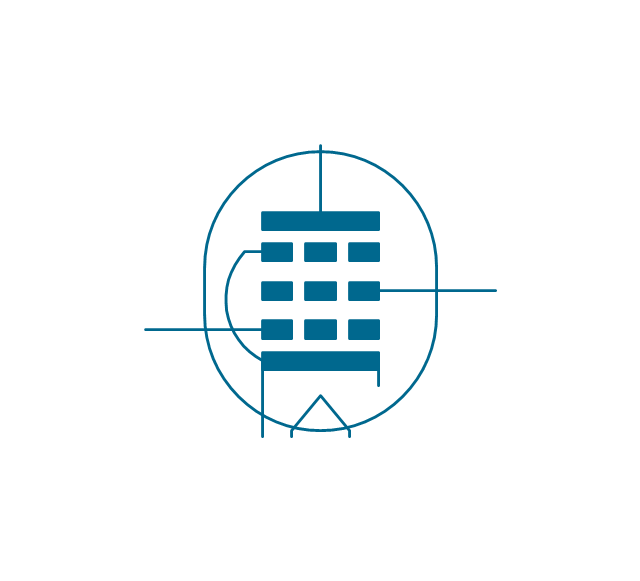
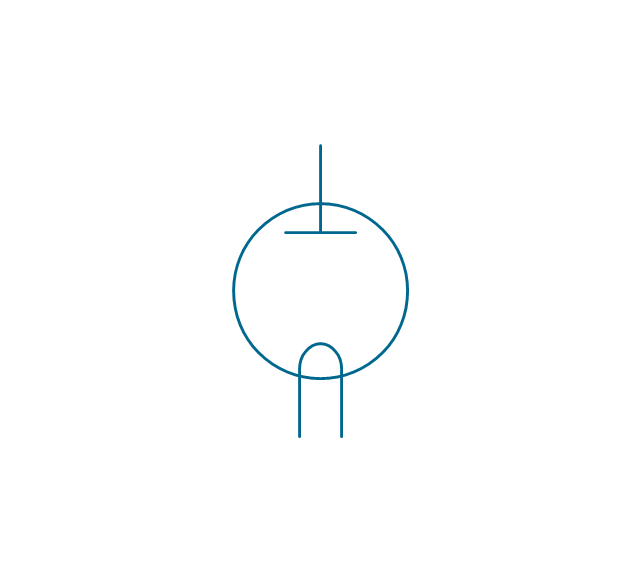
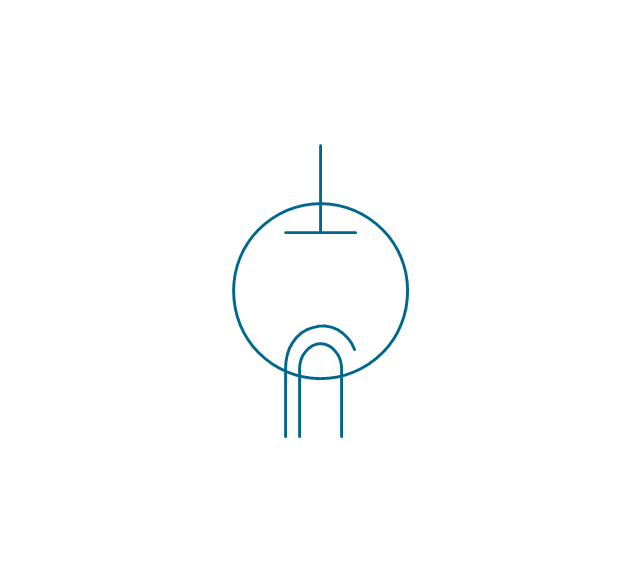
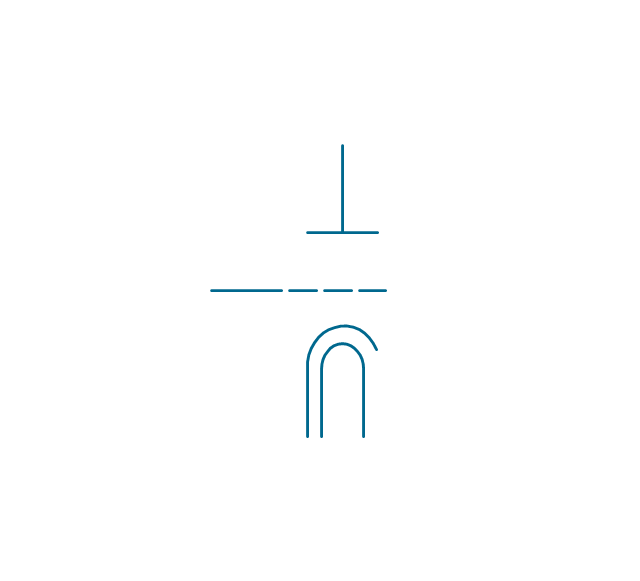
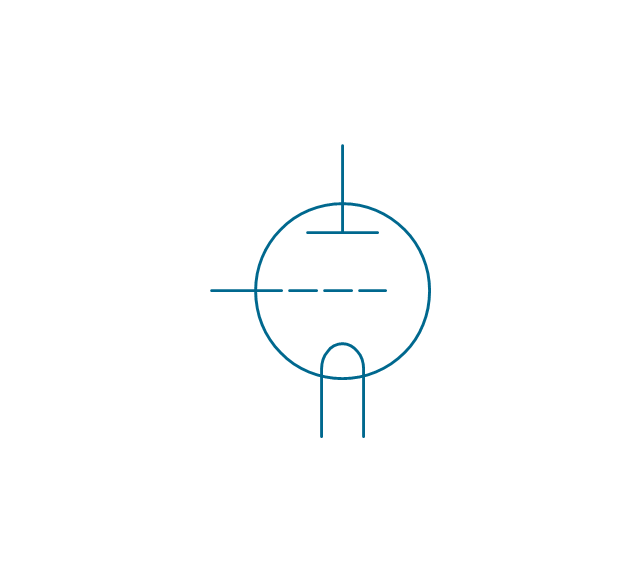
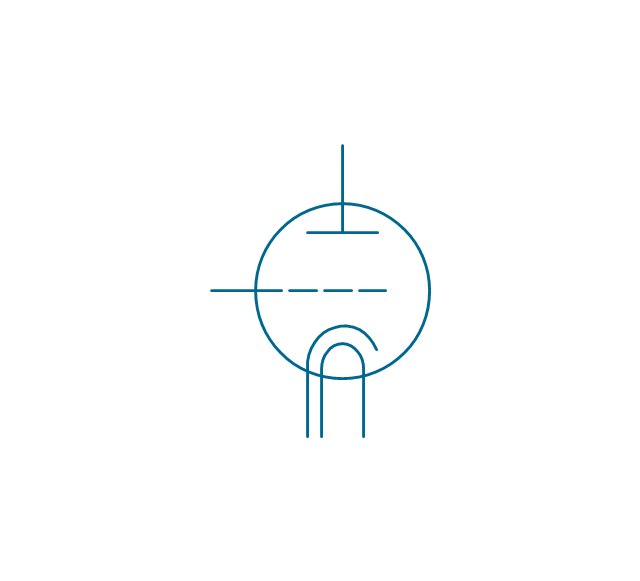
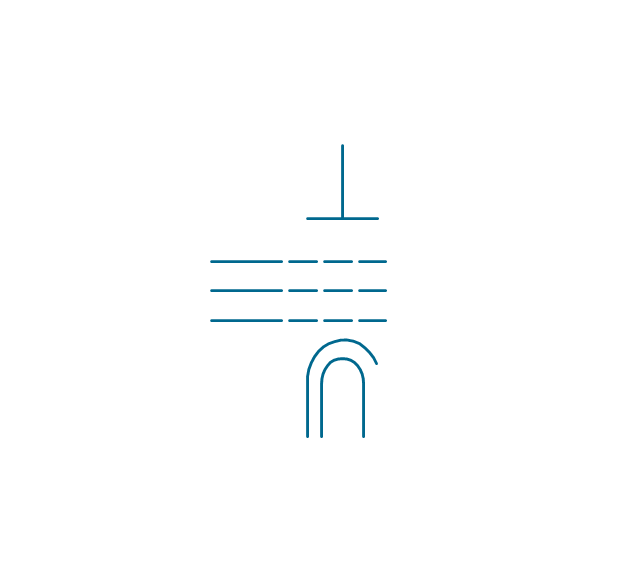
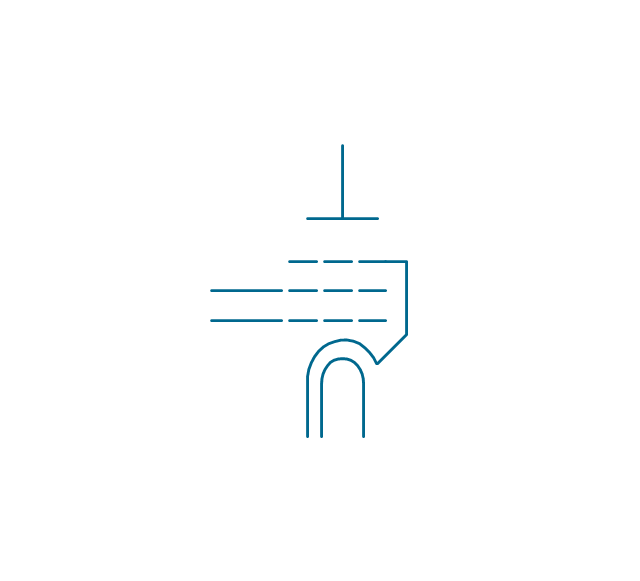
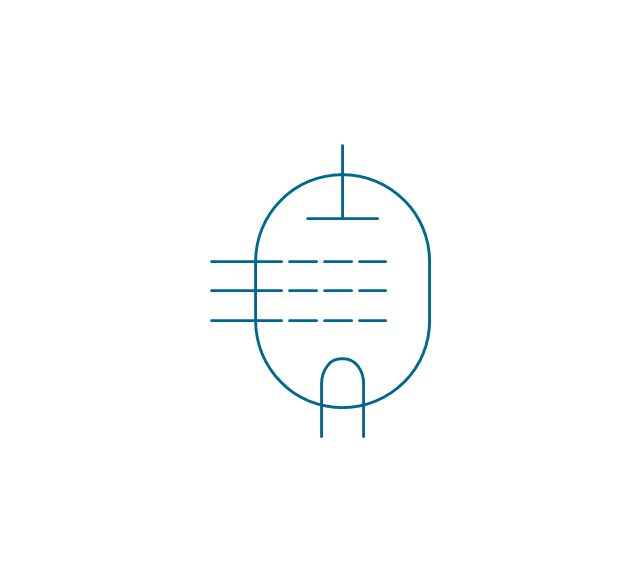
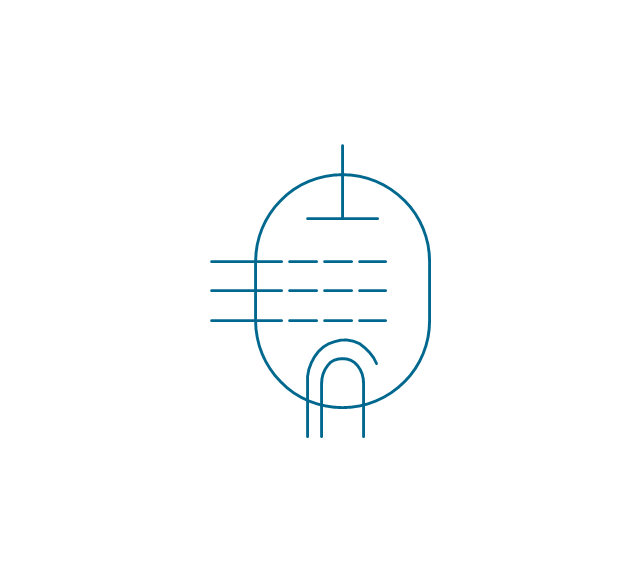
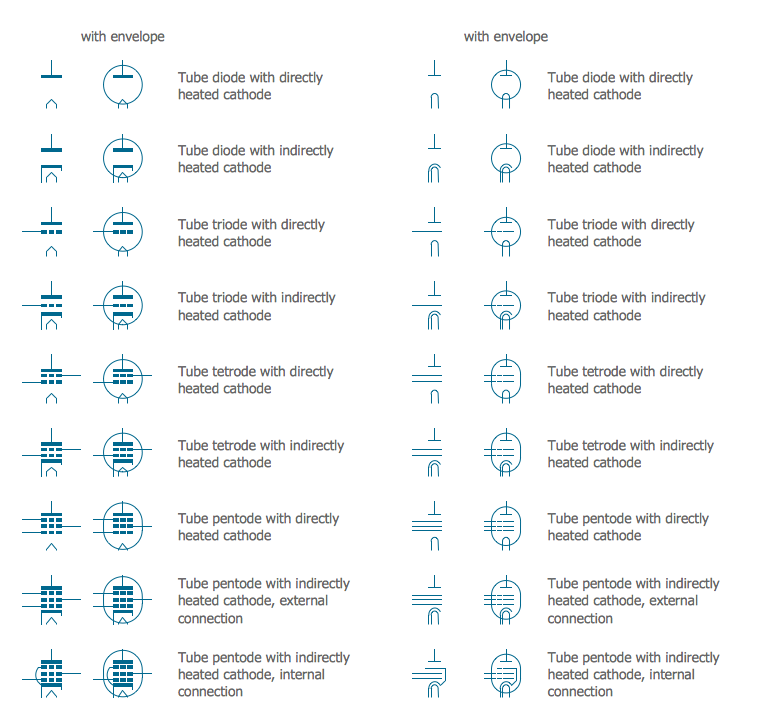
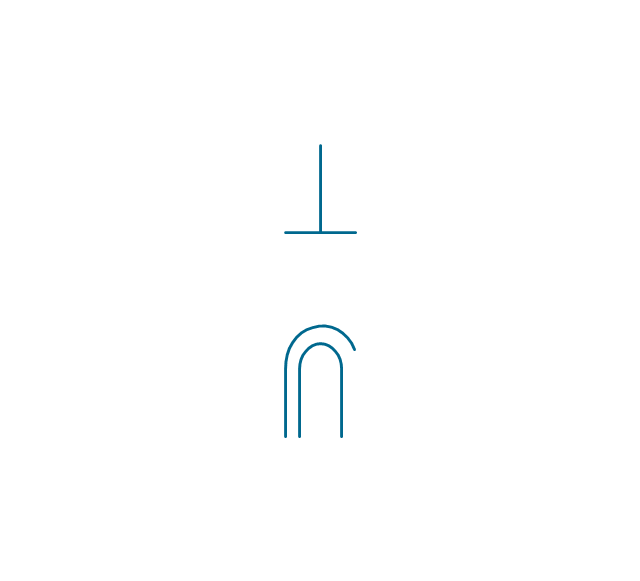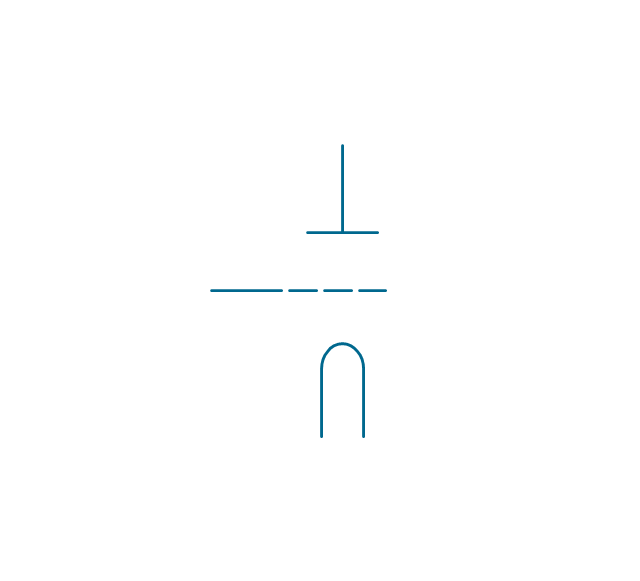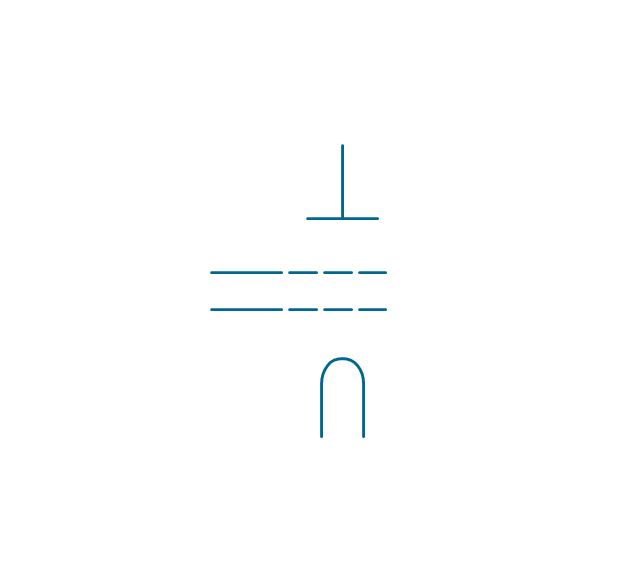The vector stencils library "Electron tubes" contains 36 element symbols of electron tubes.
Use it for drawing electrical schematics and electronic circuit diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use it for drawing electrical schematics and electronic circuit diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
The vector stencils library "Electron tubes" contains 36 element symbols of electron tubes.
Use it for drawing electrical schematics and electronic circuit diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use it for drawing electrical schematics and electronic circuit diagrams in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
The vector stencils library "Semiconductors" contains 22 symbols of rectifiers, diodes, charge transfer and electronic conduction devices, switches, cathodes, transistors, thyristors, and transceivers.
Use these shapes for semiconductor (SIS) design in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use these shapes for semiconductor (SIS) design in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
The vector stencils library "Semiconductors" contains 22 symbols of rectifiers, diodes, charge transfer and electronic conduction devices, switches, cathodes, transistors, thyristors, and transceivers.
Use these shapes for semiconductor (SIS) design in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Use these shapes for semiconductor (SIS) design in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
www.conceptdraw.com/ solution-park/ engineering-electrical
Electrical Symbols — Electron Tubes
Invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, vacuum tubes were a basic component for electronics throughout the first half of the twentieth century, which saw the diffusion of radio, television, radar, sound reinforcement, sound recording and reproduction, large telephone networks, analog and digital computers, and industrial process control. From the mid-1950s solid-state devices such as transistors gradually replaced tubes. However, there are still a few applications for which tubes are preferred to semiconductors; for example, the magnetron used in microwave ovens, and certain high-frequency amplifiers. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw PRO make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.Electrical Symbols — Semiconductor
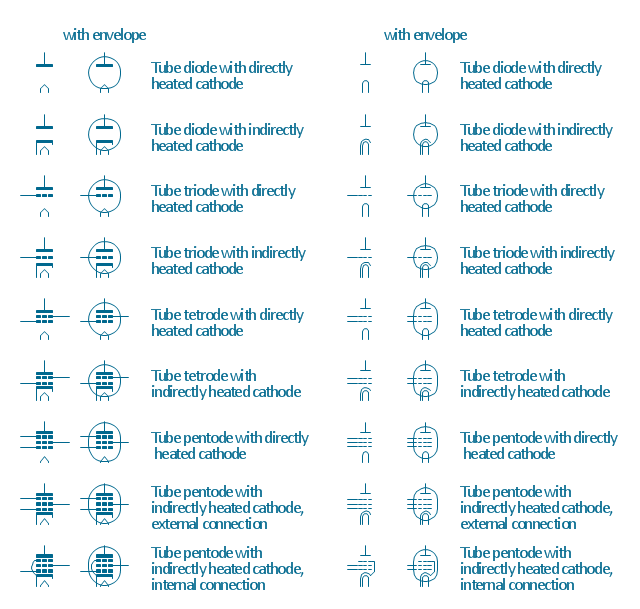
Semiconductors are crystalline or amorphous solids with distinct electrical characteristics. They are of high resistance — higher than typical resistance materials, but still of much lower resistance than insulators. Their resistance decreases as their temperature increases, which is behavior opposite to that of a metal. Finally, their conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by the deliberate, controlled introduction of impurities into the crystal structure, which lowers its resistance but also permits the creation of semiconductor junctions between differently-doped regions of the extrinsic semiconductor crystal. The behavior of charge carriers which include electrons, ions and electron holes at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors and all modern electronics. 26 libraries of the Electrical Engineering Solution of ConceptDraw PRO make your electrical diagramming simple, efficient, and effective. You can simply and quickly drop the ready-to-use objects from libraries into your document to create the electrical diagram.The vector stencils library "Design elements - Electron tubes" contains 36 element symbols of electron tubes.
Use it for drawing electrical schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"One classification of vacuum tubes is by the number of active electrodes, (neglecting the filament or heater). A device with two active elements is a diode, usually used for rectification. Devices with three elements are triodes used for amplification and switching. Additional electrodes create tetrodes, pentodes, and so forth, which have multiple additional functions made possible by the additional controllable electrodes.
Other classifications are:
(1) by frequency range (audio, radio, VHF, UHF, microwave),
(2) by power rating (small-signal, audio power, high-power radio transmitting),
(3) by design (e.g., sharp- versus remote-cutoff in some pentodes),
(4) by application (receiving tubes, transmitting tubes, amplifying or switching, rectification, mixing),
(5) special qualities (long life, very low microphonic and low noise audio amplification, and so on).
Multiple classifications may apply to a device; for example similar dual triodes can be used for audio preamplification and as flip-flops in computers, although linearity is important in the former case and long life in the latter.
Tubes have different functions, such as cathode ray tubes which create a beam of electrons for display purposes (such as the television picture tube) in addition to more specialized functions such as electron microscopy and electron beam lithography. X-ray tubes are also vacuum tubes. Phototubes and photomultipliers rely on electron flow through a vacuum, though in those cases electron emission from the cathode depends on energy from photons rather than thermionic emission." [Vacuum tube. Wikipedia]
The symbols example "Design elements - Electron tubes" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for drawing electrical schematics and electronic circuit diagrams.
"One classification of vacuum tubes is by the number of active electrodes, (neglecting the filament or heater). A device with two active elements is a diode, usually used for rectification. Devices with three elements are triodes used for amplification and switching. Additional electrodes create tetrodes, pentodes, and so forth, which have multiple additional functions made possible by the additional controllable electrodes.
Other classifications are:
(1) by frequency range (audio, radio, VHF, UHF, microwave),
(2) by power rating (small-signal, audio power, high-power radio transmitting),
(3) by design (e.g., sharp- versus remote-cutoff in some pentodes),
(4) by application (receiving tubes, transmitting tubes, amplifying or switching, rectification, mixing),
(5) special qualities (long life, very low microphonic and low noise audio amplification, and so on).
Multiple classifications may apply to a device; for example similar dual triodes can be used for audio preamplification and as flip-flops in computers, although linearity is important in the former case and long life in the latter.
Tubes have different functions, such as cathode ray tubes which create a beam of electrons for display purposes (such as the television picture tube) in addition to more specialized functions such as electron microscopy and electron beam lithography. X-ray tubes are also vacuum tubes. Phototubes and photomultipliers rely on electron flow through a vacuum, though in those cases electron emission from the cathode depends on energy from photons rather than thermionic emission." [Vacuum tube. Wikipedia]
The symbols example "Design elements - Electron tubes" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube (in North America), tube, or thermionic valve or valve (in British English) is a device controlling electric current through a vacuum in a sealed container. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode, contains only two elements; current can only flow in one direction through the device between the two electrodes, as electrons emitted by the hot cathode travel through the tube and are collected by the anode. Addition of a third and additional electrodes allows the current flowing between cathode and anode to be controlled in various ways. The device can be used as an electronic amplifier, a rectifier, an electronically controlled switch, an oscillator, and for other purposes.
Vacuum tubes mostly rely on thermionic emission of electrons from a hot filament or a cathode heated by the filament. Some electron tube devices rely on the properties of a discharge through an ionized gas." [Vacuum tube. Wikipedia]
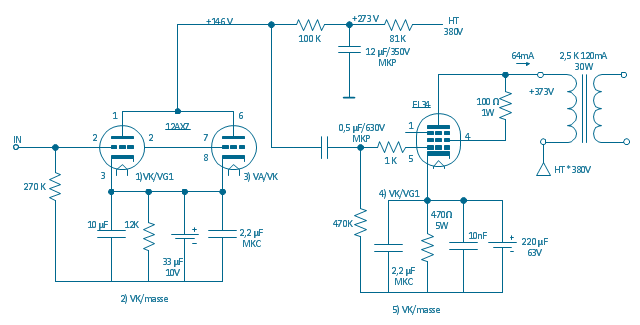
"The EL34 is a thermionic valve or vacuum tube of the power pentode type. It has an international octal base (indicated by the '3' in the part number) and is found mainly in the final output stages of audio amplification circuits and was designed to be suitable as a series regulator by virtue of its high permissible voltage between heater and cathode and other parameters. The American RETMA tube designation number for this tube is 6CA7. Russian analog is 6P27S (Cyrillic: 6П27C )" [EL34. Wikipedia]
This circuit diagram sample was redrawn from the Wikipedia Commons file: EL34 schematics (circuit diagram).gif. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:EL34_ schematics_ %28circuit_ diagram%29.gif]
The example "Circuit diagram - EL 34 schematics" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Vacuum tubes mostly rely on thermionic emission of electrons from a hot filament or a cathode heated by the filament. Some electron tube devices rely on the properties of a discharge through an ionized gas." [Vacuum tube. Wikipedia]
"The EL34 is a thermionic valve or vacuum tube of the power pentode type. It has an international octal base (indicated by the '3' in the part number) and is found mainly in the final output stages of audio amplification circuits and was designed to be suitable as a series regulator by virtue of its high permissible voltage between heater and cathode and other parameters. The American RETMA tube designation number for this tube is 6CA7. Russian analog is 6P27S (Cyrillic: 6П27C )" [EL34. Wikipedia]
This circuit diagram sample was redrawn from the Wikipedia Commons file: EL34 schematics (circuit diagram).gif. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:EL34_ schematics_ %28circuit_ diagram%29.gif]
The example "Circuit diagram - EL 34 schematics" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "Semiconductors" contains 22 symbols of rectifiers, diodes, charge transfer and electronic conduction devices, switches, cathodes, transistors, thyristors, and transceivers for semiconductor (SIS) design.
"Semiconductor devices are electronic components that exploit the electronic properties of semiconductor materials, principally silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, as well as organic semiconductors. Semiconductor devices have replaced thermionic devices (vacuum tubes) in most applications. They use electronic conduction in the solid state as opposed to the gaseous state or thermionic emission in a high vacuum.
Semiconductor devices are manufactured both as single discrete devices and as integrated circuits (ICs), which consist of a number - from a few (as low as two) to billions - of devices manufactured and interconnected on a single semiconductor substrate, or wafer. ...
All transistor types can be used as the building blocks of logic gates, which are fundamental in the design of digital circuits. In digital circuits like microprocessors, transistors act as on-off switches; in the MOSFET, for instance, the voltage applied to the gate determines whether the switch is on or off.
Transistors used for analog circuits do not act as on-off switches; rather, they respond to a continuous range of inputs with a continuous range of outputs. Common analog circuits include amplifiers and oscillators.
Circuits that interface or translate between digital circuits and analog circuits are known as mixed-signal circuits.
Power semiconductor devices are discrete devices or integrated circuits intended for high current or high voltage applications. Power integrated circuits combine IC technology with power semiconductor technology, these are sometimes referred to as "smart" power devices. Several companies specialize in manufacturing power semiconductors." [Semiconductor device. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Semiconductors" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"Semiconductor devices are electronic components that exploit the electronic properties of semiconductor materials, principally silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, as well as organic semiconductors. Semiconductor devices have replaced thermionic devices (vacuum tubes) in most applications. They use electronic conduction in the solid state as opposed to the gaseous state or thermionic emission in a high vacuum.
Semiconductor devices are manufactured both as single discrete devices and as integrated circuits (ICs), which consist of a number - from a few (as low as two) to billions - of devices manufactured and interconnected on a single semiconductor substrate, or wafer. ...
All transistor types can be used as the building blocks of logic gates, which are fundamental in the design of digital circuits. In digital circuits like microprocessors, transistors act as on-off switches; in the MOSFET, for instance, the voltage applied to the gate determines whether the switch is on or off.
Transistors used for analog circuits do not act as on-off switches; rather, they respond to a continuous range of inputs with a continuous range of outputs. Common analog circuits include amplifiers and oscillators.
Circuits that interface or translate between digital circuits and analog circuits are known as mixed-signal circuits.
Power semiconductor devices are discrete devices or integrated circuits intended for high current or high voltage applications. Power integrated circuits combine IC technology with power semiconductor technology, these are sometimes referred to as "smart" power devices. Several companies specialize in manufacturing power semiconductors." [Semiconductor device. Wikipedia]
The shapes example "Design elements - Semiconductors" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube (in North America), tube, or thermionic valve or valve (in British English) is a device controlling electric current through a vacuum in a sealed container. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode, contains only two elements; current can only flow in one direction through the device between the two electrodes, as electrons emitted by the hot cathode travel through the tube and are collected by the anode. Addition of a third and additional electrodes allows the current flowing between cathode and anode to be controlled in various ways. The device can be used as an electronic amplifier, a rectifier, an electronically controlled switch, an oscillator, and for other purposes.
Vacuum tubes mostly rely on thermionic emission of electrons from a hot filament or a cathode heated by the filament. Some electron tube devices rely on the properties of a discharge through an ionized gas." [Vacuum tube. Wikipedia]
"The EL34 is a thermionic valve or vacuum tube of the power pentode type. It has an international octal base (indicated by the '3' in the part number) and is found mainly in the final output stages of audio amplification circuits and was designed to be suitable as a series regulator by virtue of its high permissible voltage between heater and cathode and other parameters. The American RETMA tube designation number for this tube is 6CA7. Russian analog is 6P27S (Cyrillic: 6П27C )" [EL34. Wikipedia]
This circuit diagram sample was redrawn from the Wikipedia Commons file: EL34 schematics (circuit diagram).gif. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:EL34_ schematics_ %28circuit_ diagram%29.gif]
The example "Circuit diagram - EL 34 schematics" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Vacuum tubes mostly rely on thermionic emission of electrons from a hot filament or a cathode heated by the filament. Some electron tube devices rely on the properties of a discharge through an ionized gas." [Vacuum tube. Wikipedia]
"The EL34 is a thermionic valve or vacuum tube of the power pentode type. It has an international octal base (indicated by the '3' in the part number) and is found mainly in the final output stages of audio amplification circuits and was designed to be suitable as a series regulator by virtue of its high permissible voltage between heater and cathode and other parameters. The American RETMA tube designation number for this tube is 6CA7. Russian analog is 6P27S (Cyrillic: 6П27C )" [EL34. Wikipedia]
This circuit diagram sample was redrawn from the Wikipedia Commons file: EL34 schematics (circuit diagram).gif. [commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:EL34_ schematics_ %28circuit_ diagram%29.gif]
The example "Circuit diagram - EL 34 schematics" was drawn using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Electrical Engineering solution from the Engineering area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
- Sketch Of Direct And Indirectly Heated Triode
- Electron tubes - Vector stencils library | Direct Heating Triode Symbol
- Electrical Symbols Of Triode Transformer
- Electrical Symbol Of Triode
- Triode , envelope, direct. heated 2
- Turn-off triode , env
- Turn-off triode
- Semiconductors - Vector stencils library | Design elements ...
- Vacuum Tube Diode Triode Pentode
- Semiconductors - Vector stencils library | Electrical Drawing ...
- Internal Connection
- Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols | Electron tubes ...
- Electrical Symbols — Semiconductor | Semiconductors - Vector ...
- Pentode As Triode Schematic
- Circuit Diagram Of Triode As Switcher
- Electrical Symbols, Electrical Diagram Symbols | Electrical Drawing ...
- Electrical Drawing Software and Electrical Symbols | Electrical ...
- Design elements - Electron tubes | Electrical Symbols, Electrical ...
- Circuit diagram - EL 34 schematics
- Design elements