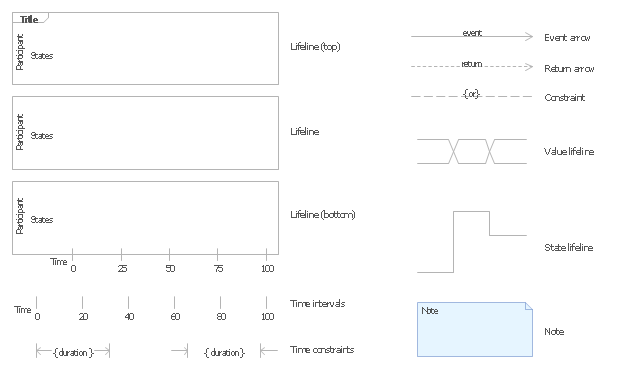
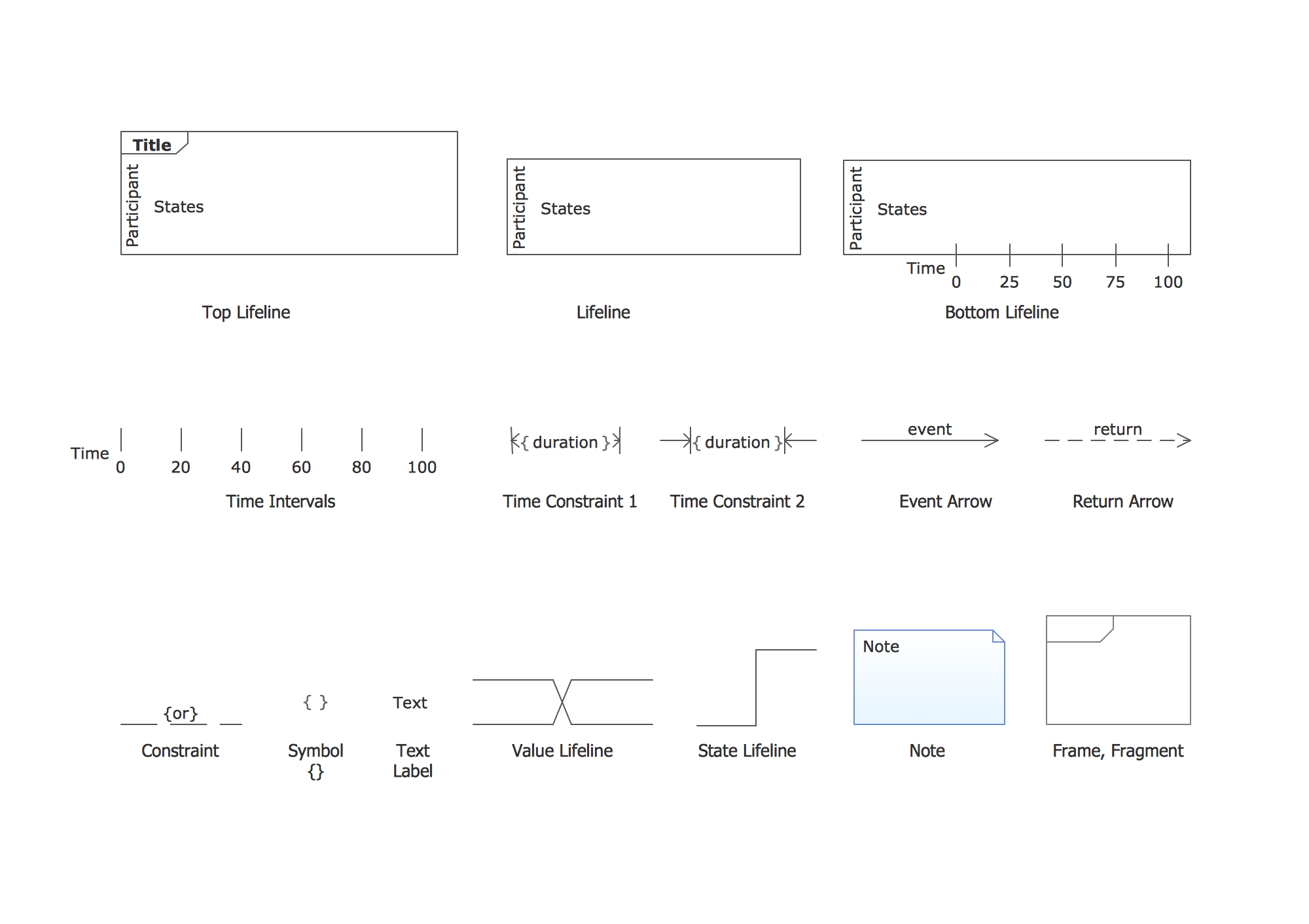
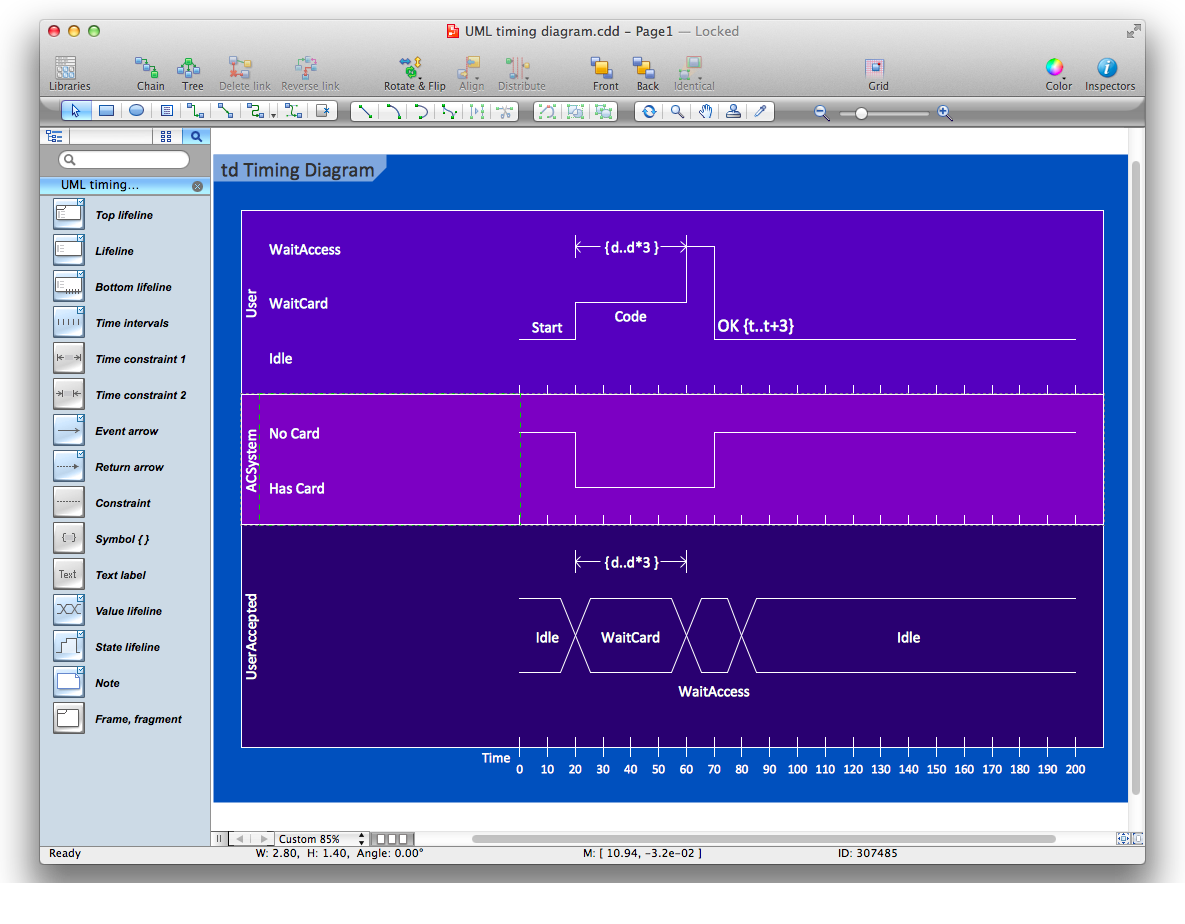
The vector stencils library "UML timing diagrams" contains 15 symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"The following nodes and edges are typically drawn in a UML timing diagram: lifeline, state or condition timeline, destruction event, duration constraint, time constraint. ...
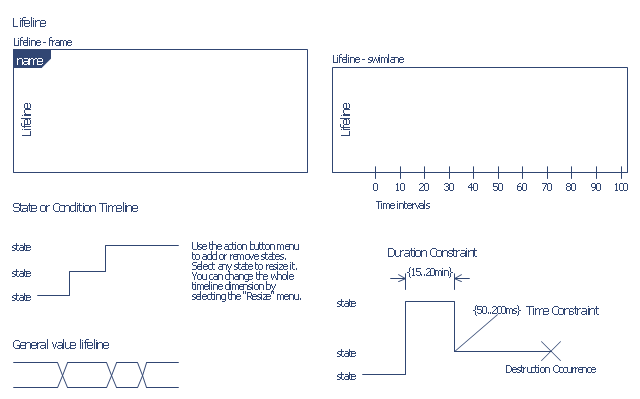
Lifeline is a named element which represents an individual participant in the interaction. ... lifelines represent only one interacting entity. ...
Lifeline on the timing diagrams is represented by the name of classifier or the instance it represents. It could be placed inside diagram frame or a "swimlane". ...
Timing diagram could show states of the participating classifier or attribute, or some testable conditions, such as a discrete or enumerable value of an attribute. ...
UML also allows the state/ condition dimension be continuous. It could be used in scenarios where entities undergo continuous state changes, such as temperature or density. ...
Destruction occurrence is a message occurrence which represents the destruction of the instance described by the lifeline. It may result in the subsequent destruction of other objects that this object owns by composition. No other occurrence may appear after the destruction event on a given lifeline.
Complete UML name of the occurrence is destruction occurrence specification. Until UML 2.4 it was called destruction event, and earlier - stop.
The destruction event is depicted by a cross in the form of an X at the end of a timeline. ...
Duration constraint is an interval constraint that refers to a duration interval. The duration interval is duration used to determine whether the constraint is satisfied.
The semantics of a duration constraint is inherited from constraints. If constraints are violated, traces become negative which means that system is considered as failed.
Duration constraint is shown as some graphical association between a duration interval and the constructs that it constrains. ...
Time constraint is an interval constraint that refers to a time interval. The time interval is time expression used to determine whether the constraint is satisfied.
The semantics of a time constraint is inherited from constraints. All traces where the constraints are violated are negative traces, i.e., if they occur, the system is considered as failed.
Time constraint is shown as graphical association between a time interval and the construct that it constrains. Typically this graphical association is a small line, e.g., between an occurrence specification and a time interval." [uml-diagrams.org/ timing-diagrams.html]
The example "Design elements - UML timing diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"The following nodes and edges are typically drawn in a UML timing diagram: lifeline, state or condition timeline, destruction event, duration constraint, time constraint. ...
Lifeline is a named element which represents an individual participant in the interaction. ... lifelines represent only one interacting entity. ...
Lifeline on the timing diagrams is represented by the name of classifier or the instance it represents. It could be placed inside diagram frame or a "swimlane". ...
Timing diagram could show states of the participating classifier or attribute, or some testable conditions, such as a discrete or enumerable value of an attribute. ...
UML also allows the state/ condition dimension be continuous. It could be used in scenarios where entities undergo continuous state changes, such as temperature or density. ...
Destruction occurrence is a message occurrence which represents the destruction of the instance described by the lifeline. It may result in the subsequent destruction of other objects that this object owns by composition. No other occurrence may appear after the destruction event on a given lifeline.
Complete UML name of the occurrence is destruction occurrence specification. Until UML 2.4 it was called destruction event, and earlier - stop.
The destruction event is depicted by a cross in the form of an X at the end of a timeline. ...
Duration constraint is an interval constraint that refers to a duration interval. The duration interval is duration used to determine whether the constraint is satisfied.
The semantics of a duration constraint is inherited from constraints. If constraints are violated, traces become negative which means that system is considered as failed.
Duration constraint is shown as some graphical association between a duration interval and the constructs that it constrains. ...
Time constraint is an interval constraint that refers to a time interval. The time interval is time expression used to determine whether the constraint is satisfied.
The semantics of a time constraint is inherited from constraints. All traces where the constraints are violated are negative traces, i.e., if they occur, the system is considered as failed.
Time constraint is shown as graphical association between a time interval and the construct that it constrains. Typically this graphical association is a small line, e.g., between an occurrence specification and a time interval." [uml-diagrams.org/ timing-diagrams.html]
The example "Design elements - UML timing diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
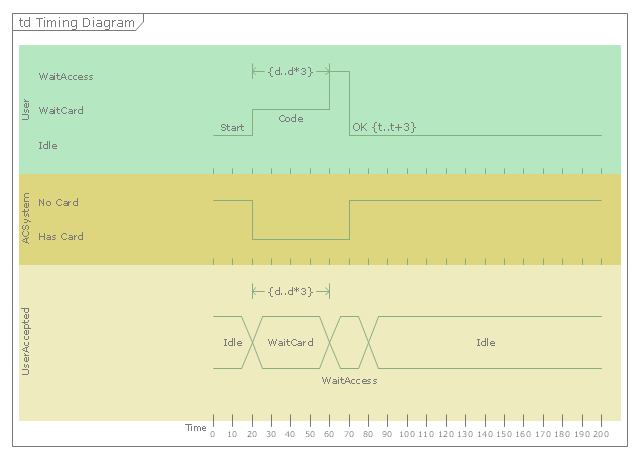
"A timing diagram in the Unified Modeling Language 2.0 is a specific type of interaction diagram, where the focus is on timing constraints.
Timing diagrams are used to explore the behaviors of objects throughout a given period of time. A timing diagram is a special form of a sequence diagram. The differences between timing diagram and sequence diagram are the axes are reversed so that the time is increased from left to right and the lifelines are shown in separate compartments arranged vertically.
There are two basic flavors of timing diagram: the concise notation, and the robust notation." [Timing diagram (Unified Modeling Language). Wikipedia]
This UML timing diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Timing diagrams are used to explore the behaviors of objects throughout a given period of time. A timing diagram is a special form of a sequence diagram. The differences between timing diagram and sequence diagram are the axes are reversed so that the time is increased from left to right and the lifelines are shown in separate compartments arranged vertically.
There are two basic flavors of timing diagram: the concise notation, and the robust notation." [Timing diagram (Unified Modeling Language). Wikipedia]
This UML timing diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
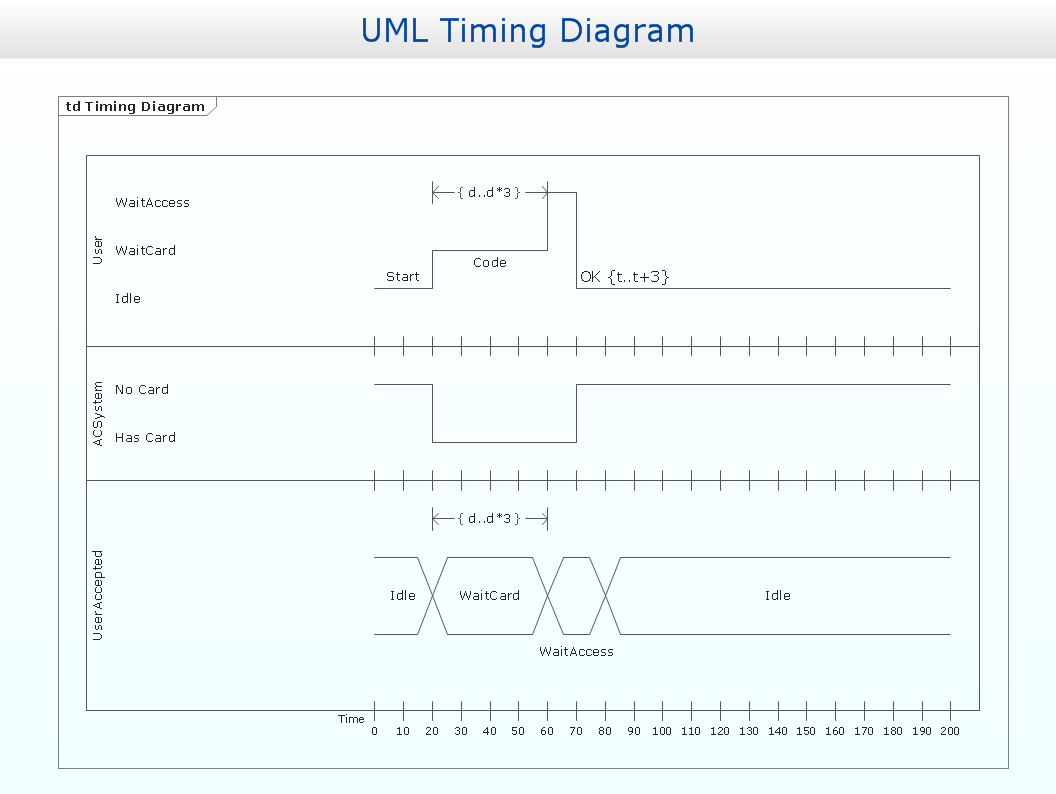
UML Timing Diagram, Design Elements
UML Timing Diagram as special form of a sequence diagram are used to explore the behaviors of objects throughout a given period of time. ConceptDraw has 393 vector stencils in the 13 libraries that helps you to start using software for designing your own UML Diagrams. You can use the appropriate stencils of UML notation from UML Timing library."A timing diagram in the Unified Modeling Language 2.0 is a specific type of interaction diagram, where the focus is on timing constraints.
Timing diagrams are used to explore the behaviors of objects throughout a given period of time. A timing diagram is a special form of a sequence diagram. The differences between timing diagram and sequence diagram are the axes are reversed so that the time is increased from left to right and the lifelines are shown in separate compartments arranged vertically.
There are two basic flavors of timing diagram: the concise notation, and the robust notation." [Timing diagram (Unified Modeling Language). Wikipedia]
This UML timing diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Timing diagrams are used to explore the behaviors of objects throughout a given period of time. A timing diagram is a special form of a sequence diagram. The differences between timing diagram and sequence diagram are the axes are reversed so that the time is increased from left to right and the lifelines are shown in separate compartments arranged vertically.
There are two basic flavors of timing diagram: the concise notation, and the robust notation." [Timing diagram (Unified Modeling Language). Wikipedia]
This UML timing diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
The vector stencils library "UML timing diagrams" contains 15 symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software.
"The following nodes and edges are typically drawn in a UML timing diagram: lifeline, state or condition timeline, destruction event, duration constraint, time constraint. ...
Lifeline is a named element which represents an individual participant in the interaction. ... lifelines represent only one interacting entity. ...
Lifeline on the timing diagrams is represented by the name of classifier or the instance it represents. It could be placed inside diagram frame or a "swimlane". ...
Timing diagram could show states of the participating classifier or attribute, or some testable conditions, such as a discrete or enumerable value of an attribute. ...
UML also allows the state/ condition dimension be continuous. It could be used in scenarios where entities undergo continuous state changes, such as temperature or density. ...
Destruction occurrence is a message occurrence which represents the destruction of the instance described by the lifeline. It may result in the subsequent destruction of other objects that this object owns by composition. No other occurrence may appear after the destruction event on a given lifeline.
Complete UML name of the occurrence is destruction occurrence specification. Until UML 2.4 it was called destruction event, and earlier - stop.
The destruction event is depicted by a cross in the form of an X at the end of a timeline. ...
Duration constraint is an interval constraint that refers to a duration interval. The duration interval is duration used to determine whether the constraint is satisfied.
The semantics of a duration constraint is inherited from constraints. If constraints are violated, traces become negative which means that system is considered as failed.
Duration constraint is shown as some graphical association between a duration interval and the constructs that it constrains. ...
Time constraint is an interval constraint that refers to a time interval. The time interval is time expression used to determine whether the constraint is satisfied.
The semantics of a time constraint is inherited from constraints. All traces where the constraints are violated are negative traces, i.e., if they occur, the system is considered as failed.
Time constraint is shown as graphical association between a time interval and the construct that it constrains. Typically this graphical association is a small line, e.g., between an occurrence specification and a time interval." [uml-diagrams.org/ timing-diagrams.html]
The example "Design elements - UML timing diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
"The following nodes and edges are typically drawn in a UML timing diagram: lifeline, state or condition timeline, destruction event, duration constraint, time constraint. ...
Lifeline is a named element which represents an individual participant in the interaction. ... lifelines represent only one interacting entity. ...
Lifeline on the timing diagrams is represented by the name of classifier or the instance it represents. It could be placed inside diagram frame or a "swimlane". ...
Timing diagram could show states of the participating classifier or attribute, or some testable conditions, such as a discrete or enumerable value of an attribute. ...
UML also allows the state/ condition dimension be continuous. It could be used in scenarios where entities undergo continuous state changes, such as temperature or density. ...
Destruction occurrence is a message occurrence which represents the destruction of the instance described by the lifeline. It may result in the subsequent destruction of other objects that this object owns by composition. No other occurrence may appear after the destruction event on a given lifeline.
Complete UML name of the occurrence is destruction occurrence specification. Until UML 2.4 it was called destruction event, and earlier - stop.
The destruction event is depicted by a cross in the form of an X at the end of a timeline. ...
Duration constraint is an interval constraint that refers to a duration interval. The duration interval is duration used to determine whether the constraint is satisfied.
The semantics of a duration constraint is inherited from constraints. If constraints are violated, traces become negative which means that system is considered as failed.
Duration constraint is shown as some graphical association between a duration interval and the constructs that it constrains. ...
Time constraint is an interval constraint that refers to a time interval. The time interval is time expression used to determine whether the constraint is satisfied.
The semantics of a time constraint is inherited from constraints. All traces where the constraints are violated are negative traces, i.e., if they occur, the system is considered as failed.
Time constraint is shown as graphical association between a time interval and the construct that it constrains. Typically this graphical association is a small line, e.g., between an occurrence specification and a time interval." [uml-diagrams.org/ timing-diagrams.html]
The example "Design elements - UML timing diagrams" is included in the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Timing diagram
UML Timing Diagram as special form of a sequence diagram is used to explore the behaviours of objects throughout a given period of time.
Diagramming Software for Design UML Timing Diagrams
UML Timing Diagram as special form of a sequence diagram are used to explore the behaviors of objects throughout a given period of time.
The vector stencils library "Bank UML timing diagram" contains 8 shapes for drawing UML timing diagrams.
Use it for object-oriented modeling of your bank information system.
"A timing diagram in the Unified Modeling Language 2.0 is a specific type of interaction diagram, where the focus is on timing constraints.
Timing diagrams are used to explore the behaviors of objects throughout a given period of time. A timing diagram is a special form of a sequence diagram. The differences between timing diagram and sequence diagram are the axes are reversed so that the time is increased from left to right and the lifelines are shown in separate compartments arranged vertically.
There are two basic flavors of timing diagram: the concise notation, and the robust notation." [Timing diagram. Wikipedia]
This example of UML timing diagram symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Use it for object-oriented modeling of your bank information system.
"A timing diagram in the Unified Modeling Language 2.0 is a specific type of interaction diagram, where the focus is on timing constraints.
Timing diagrams are used to explore the behaviors of objects throughout a given period of time. A timing diagram is a special form of a sequence diagram. The differences between timing diagram and sequence diagram are the axes are reversed so that the time is increased from left to right and the lifelines are shown in separate compartments arranged vertically.
There are two basic flavors of timing diagram: the concise notation, and the robust notation." [Timing diagram. Wikipedia]
This example of UML timing diagram symbols for the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software is included in the ATM UML Diagrams solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
Sequence Diagram for Cloud Computing
One of the ways effectively visualize what is a Cloud computing or Cloud computing architecture, is to create the Sequence diagram for Cloud computing. The ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software enhanced with Cloud Computing Diagrams solution from the Computers and Network area of ConceptDraw Solution Park will help you design all desired types of diagrams related with cloud computing.- Robust Notation Value Lifeline In Uml
- Whats A Value Lifeline In Uml
- Timing diagram | Diagramming Software for Design UML Timing ...
- Design elements - UML timing diagrams
- Design elements - UML timing diagrams | Vector stencils library ...
- UML timing diagram example
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Timing Diagrams | Timing ...
- Design elements - UML timing diagrams | UML sequence diagram ...
- Difference Between Lifeline Entity And Lifeline In Sequence Diagram
- UML Class Diagram Generalization Example UML Diagrams ...
- Lifeline Diagram
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Timing Diagrams | UML ...
- UML Sequence Diagram. Design Elements | Design Data Flow. DFD ...
- Diagramming Software for Design UML Timing Diagrams | Timing ...
- Business Process Elements: Events | BPMN 2.0 | Business Process ...
- UML timing diagram example | Diagramming Software for Design ...
- State Diagram Example - Online Store | FSM — Finite-state Machine ...
- UML Object Diagram. Design Elements | UML Deployment Diagram ...
- UML Diagram | UML Activity Diagram. Design Elements | UML ...